Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Загружено:
rohithvijayakumarrОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Загружено:
rohithvijayakumarrАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6/3/2016
HighstrengthlowalloysteelWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
Highstrengthlowalloysteel
FromWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
Highstrengthlowalloysteel(HSLA)isatypeofalloysteelthatprovidesbettermechanicalpropertiesor
greaterresistancetocorrosionthancarbonsteel.HSLAsteelsvaryfromothersteelsinthattheyarenot
madetomeetaspecificchemicalcompositionbutrathertospecificmechanicalproperties.Theyhavea
carboncontentbetween0.050.25%toretainformabilityandweldability.Otheralloyingelementsinclude
upto2.0%manganeseandsmallquantitiesofcopper,nickel,niobium,nitrogen,vanadium,chromium,
molybdenum,titanium,calcium,rareearthelements,orzirconium.[1][2]Copper,titanium,vanadium,and
niobiumareaddedforstrengtheningpurposes.[2]Theseelementsareintendedtoalterthemicrostructureof
carbonsteels,whichisusuallyaferritepearliteaggregate,toproduceaveryfinedispersionofalloy
carbidesinanalmostpureferritematrix.Thiseliminatesthetoughnessreducingeffectofapearliticvolume
fractionyetmaintainsandincreasesthematerial'sstrengthbyrefiningthegrainsize,whichinthecaseof
ferriteincreasesyieldstrengthby50%foreveryhalvingofthemeangraindiameter.Precipitation
strengtheningplaysaminorrole,too.Theiryieldstrengthscanbeanywherebetween250590megapascals
(36,00086,000psi).BecauseoftheirhigherstrengthandtoughnessHSLAsteelsusuallyrequire25to30%
morepowertoform,ascomparedtocarbonsteels.[2]
Copper,silicon,nickel,chromium,andphosphorusareaddedtoincreasecorrosionresistance.Zirconium,
calcium,andrareearthelementsareaddedforsulfideinclusionshapecontrolwhichincreasesformability.
TheseareneededbecausemostHSLAsteelshavedirectionallysensitiveproperties.Formabilityandimpact
strengthcanvarysignificantlywhentestedlongitudinallyandtransverselytothegrain.Bendsthatare
paralleltothelongitudinalgrainaremorelikelytocrackaroundtheouteredgebecauseitexperiences
tensileloads.ThisdirectionalcharacteristicissubstantiallyreducedinHSLAsteelsthathavebeentreated
forsulfideshapecontrol.[2]
Theyareusedincars,trucks,cranes,bridges,rollercoastersandotherstructuresthataredesignedtohandle
largeamountsofstressorneedagoodstrengthtoweightratio.[2]HSLAsteelcrosssectionsandstructures
areusually20to30%lighterthanacarbonsteelwiththesamestrength.[3][4]
HSLAsteelsarealsomoreresistanttorustthanmostcarbonsteelsbecauseoftheirlackofpearlitethe
finelayersofferrite(almostpureiron)andcementiteinpearlite.HSLAsteelsusuallyhavedensitiesof
around7800kg/m.[5]
Contents
1
2
3
4
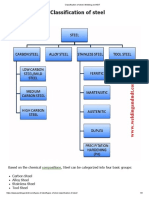
Classifications
SAEgrades
Notes
References
Classifications
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Highstrength_lowalloy_steel
1/5
6/3/2016
HighstrengthlowalloysteelWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
Weatheringsteels:steelswhichhavebettercorrosionresistance.AcommonexampleisCORTEN.
Controlrolledsteels:hotrolledsteelswhichhaveahighlydeformedaustenitestructurethatwill
transformtoaveryfineequiaxedferritestructureuponcooling.
Pearlitereducedsteels:lowcarboncontentsteelswhichleadtolittleornopearlite,butratheravery
finegrainferritematrix.Itisstrengthenedbyprecipitationhardening.
Acicularferritesteels:Thesesteelsarecharacterizedbyaveryfinehighstrengthacicularferrite
structure,averylowcarboncontent,andgoodhardenability.
Dualphasesteels:Thesesteelshaveaferritemicrostruturethatcontainsmall,uniformlydistributed
sectionsofmartensite.Thismicrostructuregivesthesteelsalowyieldstrength,highrateofwork
hardening,andgoodformability.[1]
Microalloyedsteels:steelswhichcontainverysmalladditionsofniobium,vanadium,and/or
titaniumtoobtainarefinedgrainsizeand/orprecipitationhardening.
AcommontypeofmicroalloyedsteelisimprovedformabilityHSLA.Ithasayieldstrengthupto
80,000psi(550MPa)butonlycosts24%morethanA36steel(36,000psi(250MPa)).Oneofthe
disadvantagesofthissteelisthatitis30to40%lessductile.IntheU.S.,thesesteelsaredictatedbythe
ASTMstandardsA1008/A1008MandA1011/A1011MforsheetmetalandA656/A656Mforplates.These
steelsweredevelopedfortheautomotiveindustrytoreduceweightwithoutlosingstrength.Examplesof
usesincludedoorintrusionbeams,chassismembers,reinforcingandmountingbrackets,steeringand
suspensionparts,bumpers,andwheels.[2][6]
SAEgrades
TheSocietyofAutomotiveEngineers(SAE)maintainsstandardsforHSLAsteelgradesbecausetheyare
oftenusedinautomotiveapplications.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Highstrength_lowalloy_steel
2/5
6/3/2016
Grade
HighstrengthlowalloysteelWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
%Carbon
(max)
SAEHSLAsteelgradecompositions[7]
%
%
%Sulfur %Silicon
Manganese
Phosphorus
(max)
(max)
(max)
(max)
Notes
Niobiumorvanadium
treated
942X 0.21
1.35
0.04
0.05
0.90
945A 0.15
1.00
0.04
0.05
0.90
945C
0.23
1.40
0.04
0.05
0.90
945X 0.22
1.35
0.04
0.05
0.90
950A 0.15
1.30
0.04
0.05
0.90
950B
0.22
1.30
0.04
0.05
0.90
950C
0.25
1.60
0.04
0.05
0.90
950D 0.15
1.00
0.15
0.05
0.90
950X 0.23
1.35
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobiumorvanadium
treated
955X 0.25
1.35
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobium,vanadium,or
nitrogentreated
960X 0.26
1.45
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobium,vanadium,or
nitrogentreated
965X 0.26
1.45
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobium,vanadium,or
nitrogentreated
Niobiumorvanadium
treated
970X 0.26
1.65
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobium,vanadium,or
nitrogentreated
980X 0.26
1.65
0.04
0.05
0.90
Niobium,vanadium,or
nitrogentreated
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Highstrength_lowalloy_steel
3/5
6/3/2016
Grade
942X
HighstrengthlowalloysteelWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
SAEHSLAsteelgrademechanicalproperties[8]
Yieldstrength(min)
Ultimatetensilestrength
Form
[psi(MPa)]
(min)[psi(MPa)]
Plates,shapes&barsupto4in. 42,000(290)
60,000(414)
Sheet&strip
45,000(310)
60,000(414)
00.5in. 45,000(310)
65,000(448)
0.51.5in. 42,000(290)
62,000(427)
1.53in. 40,000(276)
62,000(427)
Plates,shapes&bars:
945A,C
945X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto1.5in.
45,000(310)
60,000(414)
Sheet&strip
50,000(345)
70,000(483)
00.5in. 50,000(345)
70,000(483)
0.51.5in. 45,000(310)
67,000(462)
1.53in. 42,000(290)
63,000(434)
Plates,shapes&bars:
950A,B,C,D
950X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto1.5in.
50,000(345)
65,000(448)
955X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto1.5in.
55,000(379)
70,000(483)
960X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto1.5in.
60,000(414)
75,000(517)
965X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto0.75in.
65,000(448)
80,000(552)
970X
Sheet,strip,plates,shapes&
barsupto0.75in.
70,000(483)
85,000(586)
980X
Sheet,strip&platesupto0.375
80,000(552)
in.
95,000(655)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Highstrength_lowalloy_steel
4/5
6/3/2016
HighstrengthlowalloysteelWikipedia,thefreeencyclopedia
RankingofvariouspropertiesforSAEHSLAsteelgrades[9]
Rank
Weldability
Formability
Toughness
Worst 980X
980X
980X
970X
970X
970X
965X
965X
965X
960X
960X
960X
955X,950C,942X 955X
955X
945C
950C
945C,950C,942X
950B,950X
950D
945X,950X
945X
950B,950X,942X 950D
950D
945C,945X
950B
950A
950A
950A
945A
945A
945A
Best
Notes
1.ClassificationofCarbonandLowAlloySteels,retrieved20081006
2.HSLASteel,20021115,archivedfromtheoriginalon20100103,retrieved20081011.
3.Degarmo,p.116.
4.Samedensityascarbonsteel,seenextparagraph
5."Stainlesssteelpropertiesforstructuralautomotiveapplications"(PDF).EuroInox.June2000.Retrieved
20070814.
6.Coldrolledsheetsteel,archivedfromtheoriginalon20080430,retrieved20081011
7.Oberg,pp.440441.
8.Oberg,p.441.
9.Oberg,p.442.
References
Degarmo,E.PaulBlack,JT.Kohser,RonaldA.(2003),MaterialsandProcessesinManufacturing
(9thed.),Wiley,ISBN0471656534.
Oberg,E.etal.(1996),Machinery'sHandbook(25thed.),IndustrialPressInc
Retrievedfrom"https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Highstrength_low
alloy_steel&oldid=710737767"
Categories: Steels
Thispagewaslastmodifiedon18March2016,at19:32.
TextisavailableundertheCreativeCommonsAttributionShareAlikeLicenseadditionaltermsmay
apply.Byusingthissite,youagreetotheTermsofUseandPrivacyPolicy.Wikipediaisa
registeredtrademarkoftheWikimediaFoundation,Inc.,anonprofitorganization.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Highstrength_lowalloy_steel
5/5
Вам также может понравиться
- Alloy SteelДокумент9 страницAlloy Steelamr_scorpion_engОценок пока нет
- M 1.2.8 Carbon, Lowalloyed, Fine Grained, and ThermomechanicalyДокумент17 страницM 1.2.8 Carbon, Lowalloyed, Fine Grained, and Thermomechanicalydokumen qcОценок пока нет
- Classification of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steels: AbstractДокумент23 страницыClassification of Carbon and Low-Alloy Steels: AbstractharieduidОценок пока нет
- Low Carbon SteelДокумент2 страницыLow Carbon SteelDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Alloy SteelДокумент6 страницAlloy SteelSiva BhaskarОценок пока нет
- 10-Low Alloy Steel PDFДокумент32 страницы10-Low Alloy Steel PDFIdes Trian100% (1)
- Interpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsДокумент61 страницаInterpretation of The Microstructure of SteelsCiresica Sanda Cocindau100% (1)
- High Strength Low Alloy SteelsДокумент42 страницыHigh Strength Low Alloy SteelsDeepak PatelОценок пока нет
- Alloy SteelДокумент5 страницAlloy SteelKun Hadipati Kusuma NegaraОценок пока нет
- Structure and PropertiedДокумент43 страницыStructure and PropertiedJalaj GaurОценок пока нет
- AlloysДокумент91 страницаAlloysNiccoloОценок пока нет
- Alloy Steel Wikipedia The Free EncyclopeДокумент4 страницыAlloy Steel Wikipedia The Free Encyclopestephen johnsonОценок пока нет
- Metallurgy of MaterialsДокумент15 страницMetallurgy of Materialscal2_uniОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 MaterialДокумент16 страницAssignment 1 MaterialLuqman Arif0% (1)
- Types of Alloy Steel: Alloy Steel Is A Class of Steel That, in Addition To Carbon, Is Alloyed With Other ElementsДокумент4 страницыTypes of Alloy Steel: Alloy Steel Is A Class of Steel That, in Addition To Carbon, Is Alloyed With Other ElementsSaadОценок пока нет
- Effects of Alloying ElementsДокумент3 страницыEffects of Alloying Elementsdraj1875977Оценок пока нет
- Effect of Elements in SteelДокумент3 страницыEffect of Elements in SteelJayakrishnan Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Chapter 4Документ82 страницыChapter 4api-271354682Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Composition SteelДокумент6 страницChemical Composition SteelSahil JhambОценок пока нет
- Effects of Elements On SteelДокумент4 страницыEffects of Elements On SteelmichaelОценок пока нет
- 4 Ferrous MetalsДокумент26 страниц4 Ferrous MetalsLira AgbonОценок пока нет
- What Is SteelДокумент4 страницыWhat Is SteelViswatej ChoudaryОценок пока нет
- 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical PropertiesДокумент12 страниц21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Propertieshaidv254100% (1)
- Chemical Composition of Structural SteelДокумент2 страницыChemical Composition of Structural SteelSreedhar Patnaik.MОценок пока нет
- To Be EditedДокумент6 страницTo Be EditedSasaleleОценок пока нет
- Classification of Carbon and Low Alloy SteelsДокумент4 страницыClassification of Carbon and Low Alloy SteelsmomoitachiОценок пока нет
- Welding Steel Alloys: Low-Carbon SteelsДокумент3 страницыWelding Steel Alloys: Low-Carbon SteelsRathnakrajaОценок пока нет
- Ferrous and NonДокумент13 страницFerrous and NonIrvansyah RazadinОценок пока нет
- Alloying Elements of Steels and PropertiesДокумент3 страницыAlloying Elements of Steels and PropertiesdaimaheshОценок пока нет
- Elements of SteelДокумент1 страницаElements of Steelashish.mathur1Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Composition of SteelДокумент7 страницChemical Composition of SteelArslan RaoОценок пока нет
- Effect of Chemical Elements in Steel - Steel Tank Institute - Steel Plate Fabricators Association (STI - SPFA)Документ4 страницыEffect of Chemical Elements in Steel - Steel Tank Institute - Steel Plate Fabricators Association (STI - SPFA)Hossein Hosseini RadОценок пока нет
- Unit Iii: V 6Cwodc-3VrkДокумент237 страницUnit Iii: V 6Cwodc-3VrkDinesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Weldability of High Strength Low Alloy SteelДокумент34 страницыWeldability of High Strength Low Alloy SteelGanesan Veerasamy100% (1)
- FC-06-Engineering Material & Metallurgy PDFДокумент431 страницаFC-06-Engineering Material & Metallurgy PDFsomnath ghosh100% (1)
- Effects of MN, P, S, Si & V On The Mechanical Properties of SteelДокумент2 страницыEffects of MN, P, S, Si & V On The Mechanical Properties of SteelMohit SunnyОценок пока нет
- Local - Media FILEДокумент7 страницLocal - Media FILEmacksabado78Оценок пока нет
- SteelДокумент20 страницSteelShashank SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Steel ClassificationДокумент3 страницыSteel Classificationasfarjee100% (1)
- Hsla SteelДокумент22 страницыHsla SteelriteshbarmanОценок пока нет
- SteelДокумент31 страницаSteelumairОценок пока нет
- (Simple) Alloy Steels and Cast IronДокумент30 страниц(Simple) Alloy Steels and Cast IronAbdo siyedОценок пока нет
- Steel Grades What Are The Different TypeДокумент9 страницSteel Grades What Are The Different TypeSyed Shoaib RazaОценок пока нет
- Alloying Elements ExcelДокумент18 страницAlloying Elements ExcelRavindra ErabattiОценок пока нет
- 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Properties - Jeremy HДокумент7 страниц21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Properties - Jeremy HxnitinxОценок пока нет
- Effects of MN, P, S, Si & V On The Mechanical Properties of SteelДокумент2 страницыEffects of MN, P, S, Si & V On The Mechanical Properties of SteelsudhakarОценок пока нет
- Welding Steel AlloysДокумент2 страницыWelding Steel AlloysRathnakrajaОценок пока нет
- Classification of Steel - Welding and NDTДокумент3 страницыClassification of Steel - Welding and NDTAshif Iqubal100% (1)
- Low Alloy Steel - An OverviewДокумент10 страницLow Alloy Steel - An OverviewhaharameshОценок пока нет
- Stainless Steels Heat TreatmentДокумент3 страницыStainless Steels Heat TreatmentBrandon HaleОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Stainless Steel and Special SteelsДокумент38 страницPresentation On Stainless Steel and Special Steelsanon_81731900Оценок пока нет
- MATERIALSДокумент13 страницMATERIALSMadhubalan AlagarОценок пока нет
- Effects of MN, P, S, SiДокумент2 страницыEffects of MN, P, S, SiAdithya ShourieОценок пока нет
- 211 2aДокумент33 страницы211 2aMada ChohОценок пока нет
- MEM MicroprojectДокумент12 страницMEM MicroprojectprathaОценок пока нет
- All DataДокумент121 страницаAll DataShashank SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Chromium:-: 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical PropertiesДокумент8 страницChromium:-: 21 Chemical Elements and Effects On Steel Mechanical Propertiesdhoni03Оценок пока нет
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonОт EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- EPA Method 3305 PDFДокумент3 страницыEPA Method 3305 PDFDave SalgueroОценок пока нет
- 11718-Article Text-42418-1-10-20161220Документ7 страниц11718-Article Text-42418-1-10-20161220BibahОценок пока нет
- ManometerДокумент2 страницыManometerAlexanderSorianoОценок пока нет
- Shell Gadus S2 OG Clear Oil 20000Документ2 страницыShell Gadus S2 OG Clear Oil 20000Xavier DiazОценок пока нет
- Leaf Spring AnalysisДокумент9 страницLeaf Spring AnalysisThilli KaniОценок пока нет
- Eca ChangeoverДокумент61 страницаEca ChangeoverVijai Singh100% (1)
- Efficient Biosorption of Cadmium by Eucalyptus Globulus Fruit Biomass Using ProcessДокумент12 страницEfficient Biosorption of Cadmium by Eucalyptus Globulus Fruit Biomass Using ProcessRabialtu SulihahОценок пока нет
- Florgard Epu SL - TDSДокумент3 страницыFlorgard Epu SL - TDSGabriel GabeОценок пока нет
- 04 Welding SOPДокумент3 страницы04 Welding SOProhan khariwaleОценок пока нет
- Studies in Optimization of Non Aqueous Film Coating Parameters PDFДокумент7 страницStudies in Optimization of Non Aqueous Film Coating Parameters PDFTiara Anindita NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Atoms and Molecules Reviewer 1 15Документ5 страницAtoms and Molecules Reviewer 1 15Vienna GilmoreОценок пока нет
- Bitesize Bio SDS-PAGE Cheat Sheet: Essential Buffer and Gel Recipes For Your LaboratoryДокумент4 страницыBitesize Bio SDS-PAGE Cheat Sheet: Essential Buffer and Gel Recipes For Your LaboratoryCristian RuizОценок пока нет
- MasterEmaco S 466 PDFДокумент145 страницMasterEmaco S 466 PDFSri KanthОценок пока нет
- Eye Drops PreparationДокумент1 страницаEye Drops PreparationJai MurugeshОценок пока нет
- Structure-Property Relationships of Flexible Polyurethane FoamsДокумент10 страницStructure-Property Relationships of Flexible Polyurethane Foamstoiec hocОценок пока нет
- Class 6 Asm 1 Science Chemistry Unit 1: Sorting Separation and ChangesДокумент2 страницыClass 6 Asm 1 Science Chemistry Unit 1: Sorting Separation and Changessipdas 10a100% (1)
- Chem Academy: Enolate ChemistryДокумент13 страницChem Academy: Enolate ChemistryHamit RanaОценок пока нет
- DPP 9Документ3 страницыDPP 9Sarvesh DubeyОценок пока нет
- Pacing Guide: Inspire ChemistryДокумент6 страницPacing Guide: Inspire Chemistryjsencion977Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Dry Rubber Content: 1. ScopeДокумент2 страницыDetermination of Dry Rubber Content: 1. ScopeDevender KumarОценок пока нет
- Crystex HD OT 20 PDFДокумент2 страницыCrystex HD OT 20 PDFmeidyОценок пока нет
- 26252.9.6. Uniformity of Content of Single-Dose PreparationsДокумент1 страница26252.9.6. Uniformity of Content of Single-Dose PreparationsMiyyada Aichaoui100% (1)
- Module 7 LipidsДокумент3 страницыModule 7 Lipidsgarciamigueld23Оценок пока нет
- Emulsion Fuel Technology in Combustion FurnacesДокумент3 страницыEmulsion Fuel Technology in Combustion Furnacesvuongcoi102Оценок пока нет
- Dehydration of AlcoholsДокумент6 страницDehydration of Alcoholsعبدالله هنيةОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Report - Module 2 (Refractometry)Документ37 страницLaboratory Report - Module 2 (Refractometry)Jeremy Kyle Edson AustriaОценок пока нет
- Sample Questions For Anaphy and PhysiologyДокумент90 страницSample Questions For Anaphy and PhysiologyMaria Jeorgia SalinasОценок пока нет
- EVA Resin 2018Документ1 страницаEVA Resin 2018AminulIslamОценок пока нет
- Design of FRP-Profiles & All-FRP-Structures (2009) - Presentation PDFДокумент67 страницDesign of FRP-Profiles & All-FRP-Structures (2009) - Presentation PDFJulio Humberto Díaz RondánОценок пока нет
- Spectrometric Identification of Organic CompoundsДокумент466 страницSpectrometric Identification of Organic CompoundsMarie L100% (5)