Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Periodic Table Hints
Загружено:
Deepa KarthikИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Periodic Table Hints
Загружено:
Deepa KarthikАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Periodic Table Hints
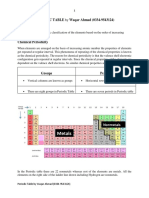
1 What are the horizontal rows and vertical column in a periodic table
known as?
A: The horizontal rows are called period and the vertical column are called group.
2 What information does the group number of an element tells us?
A: It tells us the number of valence electrons that an atom has. For example,
group 1 elements have 1 valence electron and group 7 elements have 7
electrons on the outer shell.
3 What information does the period number of an element tells us?
A: It tells us the number of electrons an atom has. For example, sodium has an
electronic configuration of 2,8,1. It is in period 3 hence it has 3 electron shells.
4 How do metals react and how do non-metals react?
A: Metals react by losing electrons and non-metals react by gaining electron.
5 What are some common physical properties of metals?
A: Metals are ductile (able to be stretched into wires), malleable (able to form
and shape easily), good conductors of electricity, good conductors of heat,
sonorous (produce a tickling sound when struck), generally high melting and
boiling points (except for group 1 metals and mercury which have low melting
point).
6 What are the common chemical properties of metals?
A: Metals generally react with acids to form salt and hydrogen gas. They also
form ionic compounds when reacted with non-metals. The more reactive metals
like the group 1 metals can react with cold water to form aqueous group 1
hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
7 What is the name given to group 1 elements?
A: Group 1 elements are collectively called alkali metals.
8 What are some properties that are unique to group 1 elements only?
A: Group 1 metals are soft metal. Group 1 metals unlike most metals have low
melting and boiling point. Group 1 metals can react with water to form a metal
hydroxide and hydroxide.
9 Write the word and chemical equations, with state symbol, for
sodium's reaction with water.
A: Sodium + water --> sodium hydroxide + hydrogen gas.
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) --> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g).
10 Describe the reactions of group 1 metals.
A: Alkali metals react with water to form metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
They also react with acid to form salt and hydrogen gas. Group 1 metals react
with halogens (group 7 element) to form metal halide. For example, sodium
reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride and potassium reacts with bromine
to form potassium bromine.
11 What is the name given to elements in group 7?
A. Halogens.
12 What is the name given to elements in group 0?
A: Noble gas.
13 What is the name given to elements between group 2 and 3?
A: Transition metals.
14 How many valence electrons does group 1, group 2 and group 3
elements has?
A. Group 1 has 1, group 2 has 2 and group 3 has 3 valence electrons. (This is the
safest way to determine the number of valence electrons, do not do the
2,8,8,8.... it will be wrong).
15 What is the ionic charge expected of group 1, group 2 and group 3
ions?
A: Group 1 ions is +1, group 2 is +2 and group 3 is +3.
16 What are some of the common properties of group 1 metal? (state
only properties possessed by group 1 metals.
A: Soft metal, low melting boiling point (as opposed to most metals which are
high) and low density.
17 State the trends of properties of group 1 elements down the group.
A: Melting and boiling point decreases down the group, reactivity increases down
the group and density increases down the group.
18 Explain VERY briefly why melting point of group 1 metals decreases
down the group.
A: The metal bonds holding the positive ions and negative sea of electrons
weakens. So lesser energy is needed to overcome the forces of attraction and
hence melting and boiling point decreases.
19 Explain in detail why the melting point of group 1 metals decreases
down the group.
A: As the metals moved down the group, the atomic radius increases. The force
of attraction between the positive nucleus and negative sea of electrons
weakens. This weakens the metallic bonds and their melting point will decreases.
20 Explain why reactivity of metals increases down the group.
A: As the metals moved down the group, the atomic radius of the atoms
increases. The shielding effect between the positive nucleus and the valence
electrons increases. This weakens the force of attraction between the nucleus
and the valence electrons. Since the metals react by losing electrons, it is easier
to lose electrons down the group hence reactivity increases.
21 Describe a simple experiment to test the reactivity of lithium,
sodium and potassium with water.
A: Add same amount of the 3 metals into 3 separate beakers of water. Ensure all
the water is identical and of the same temperature. It will be observed that
lithium's reaction with water is fast, sodium is vigorous and potassium is
explosive. This shows that potassium is the most reactive of the 3 metals and
reactivity of metals increases down the group.
22 Describe what you will observe when sodium is added to water
mixed with universal indicator. Explain the changes to the solution.
A: Bubbles of gas (effervescence) observed, gas produced extinguished light
splint with a pop sound. Solution changes from green to violet. Water is a neutral
substance therefore; it appears green with universal indicator. When sodium
reacts with water, it forms sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Since sodium
hydroxide is a strong alkali, the universal indicator turns violet.
23 What are the states of the halogens at room temperature?
A: Both chlorine and fluorine are gases at room temperature, bromine is a liquid
at room temperature, iodine and astatine are both solids at room temperature.
24 What are the type colours of the halogens at room temperature?
A: Flourine is a pale yellow gas, chlorine is a greenish yellow gas, bromine is a
reddish brown liquid, iodine is a black solid (sometime it can be BROWN
SOLUTION) and astatine is a black solid.
25 State the trends of group 7 substances.
A: The colours of the molecules darkens down the group, the reactivity decreases
down the group, the melting boiling point increases down the group.
26 What is a displacement reaction with regards to halogen?
A: A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive element from its salt.
27 What are the colours of standard solutions?
A: Most of the solutions you will be encountering are colourless solutions.
Solutions of group 1 and group 2 salts are all colourless. the coloured solutions
are normally from transition metals. Like iron (II) salts are green, copper (II) salts
are blue and iron (III) salts are yellow.
28. Describe and explain what happen when bromine is added to
potassium chloride.
A: (First off bromine is reddish brown, potassium chloride is a group 1 salt so it is
a colourless solution.) There is no visible reaction. Bromine is less reactive than
chlorine so it is unable to displace chlorine from its salt.
29. Describe and explain what happen when chlorine is added to
potassium bromide.
A: (Again potassium bromide is a group 1 salt so it is a colourless solution and
chlorine is greenish yellow) When the greenish yellow gas is added to the
colourless solution, solution turns reddish brown. Chlorine is more reactive than
bromine hence it is able to displace bromine from potassium bromide. The
displaced bromine is reddish brown, causing the solution to turn reddish brown.
30 Write the chemical equation for the reaction in question 29
A: Cl2 + 2KBr --> 2KCl + Br2. Ionic equation: Cl2 + 2Br- --> 2Cl- + Br2
31 Describe and explain what happen when chlorine is added to
potassium iodide.
A: When greenish yellow gas is added to colourless solution, solution turns
brown. Chlorine is more reactive than iodine so it is able to displace iodine from
potassium iodide.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cargo ManagementДокумент45 страницCargo ManagementShubham Chaurasia75% (8)
- Chemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study GuideДокумент22 страницыChemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study Guidemannm26Оценок пока нет
- Periodic Table:: There Are Three Main Types of Elements: Metals, Non Metals and MetalloidsДокумент9 страницPeriodic Table:: There Are Three Main Types of Elements: Metals, Non Metals and MetalloidsTahmed HasanОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0Документ11 страницIGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0ChemistryKlipz100% (4)
- 4.04.. The Patterns Within Group 1 .Документ5 страниц4.04.. The Patterns Within Group 1 .Abrar JaheenОценок пока нет
- Chemistry End of Term Revision Term 2Документ18 страницChemistry End of Term Revision Term 2sohaila ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 The Periodic TableДокумент9 страницChapter 13 The Periodic TableTeck TieОценок пока нет
- S-Block Elements: Earth Metals. These Are So Called Because Their Oxides and Hydroxides Are Alkaline in NatureДокумент8 страницS-Block Elements: Earth Metals. These Are So Called Because Their Oxides and Hydroxides Are Alkaline in NatureAgamGoelОценок пока нет
- Halogen Grp7Документ7 страницHalogen Grp718gmillsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 The Periodic TableДокумент9 страницChapter 13 The Periodic Tablemonkeydluffy18935Оценок пока нет
- 1CONCEPTS SUMMARY WITH QUESTIONS - Docx 2Документ17 страниц1CONCEPTS SUMMARY WITH QUESTIONS - Docx 2haiqaОценок пока нет
- Form 2 7 Alkali MetalsДокумент24 страницыForm 2 7 Alkali MetalsHarshil PatelОценок пока нет
- The Periodic TableДокумент36 страницThe Periodic TableChaos InsurgencyОценок пока нет
- 2 Metals and Non-MetalsДокумент23 страницы2 Metals and Non-MetalsArmaanОценок пока нет
- Lectura Tabla PeriodicaДокумент5 страницLectura Tabla PeriodicaVERONICA ECHAVARRIA CARRASQUILLAОценок пока нет
- All DecksДокумент4 страницыAll Deckssujivaj7914Оценок пока нет
- Group 1 ElementsДокумент11 страницGroup 1 ElementsKIRAN ALLUОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table: Main Group or Fundamental ElementsДокумент3 страницыPeriodic Table: Main Group or Fundamental ElementsTahmed HasanОценок пока нет
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Документ34 страницыOxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Warren Mark ManguneОценок пока нет
- The Periodic TableДокумент4 страницыThe Periodic Tablekashvi kheraОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6-Group 1 & 2Документ34 страницыLecture 6-Group 1 & 2Kumar KeshavОценок пока нет
- Periodic TableДокумент9 страницPeriodic TableXGC Ahssn YtОценок пока нет
- The Periodic Ta-Wps OfficeДокумент3 страницыThe Periodic Ta-Wps OfficeAlan Gandidze MotifОценок пока нет
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsДокумент40 страницClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes The S-Block ElementsNair SidharthОценок пока нет
- C1 Chemistry - Group 1Документ19 страницC1 Chemistry - Group 1bipin jainОценок пока нет
- Alkaline Earth MetalДокумент33 страницыAlkaline Earth MetalSup FansОценок пока нет
- Textbook Chemistry Without The Useless InformationДокумент5 страницTextbook Chemistry Without The Useless Informationfathead4269Оценок пока нет
- Metals: Properties and ReactivityДокумент20 страницMetals: Properties and ReactivityKivaОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент23 страницыChemistryAbhishek PawarОценок пока нет
- S Block AДокумент5 страницS Block AMr BurgerОценок пока нет
- S BlockДокумент27 страницS BlockAditya BansalОценок пока нет
- Alkali MetalsДокумент16 страницAlkali MetalsFernanda BeltranОценок пока нет
- Group 1-AДокумент14 страницGroup 1-AShivam GuptaОценок пока нет
- F334 - The Steel StoryДокумент11 страницF334 - The Steel StoryBecky TenneyОценок пока нет
- 2958 - Periodic - Table 6.4Документ41 страница2958 - Periodic - Table 6.4ctp5wx6nbqОценок пока нет
- The Periodic Table - 9.3 LessonДокумент5 страницThe Periodic Table - 9.3 LessonSri Charitha AОценок пока нет
- Atoms, Bonds and Groups Chapter 1 - Atoms and ReactionsДокумент2 страницыAtoms, Bonds and Groups Chapter 1 - Atoms and ReactionsEleanorОценок пока нет
- The Periodic Table Power PointДокумент61 страницаThe Periodic Table Power PointAkaNayep ApОценок пока нет
- S - Block Elements Unit - 10: Group I Elements: Alkali MetalsДокумент15 страницS - Block Elements Unit - 10: Group I Elements: Alkali MetalsVivan TОценок пока нет
- 2324 T2 Chemistry C3 Elements and CompoundsДокумент66 страниц2324 T2 Chemistry C3 Elements and CompoundswilsonconcepcionОценок пока нет
- Interactive Textbook 5 2Документ9 страницInteractive Textbook 5 2api-240094705Оценок пока нет
- 15.1. Group 1 Elements: Li He 2s RB KR 5sДокумент33 страницы15.1. Group 1 Elements: Li He 2s RB KR 5sDurgeshTiwariОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 4Документ16 страницLecture Notes 4Deandra WhitelyОценок пока нет
- Activity of MetalsДокумент8 страницActivity of MetalsDaniel BerryОценок пока нет
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsДокумент4 страницыSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleОценок пока нет
- Metals: Bonding & Structure Properties Alloys Chemical Reactions Reactivity SeriesДокумент23 страницыMetals: Bonding & Structure Properties Alloys Chemical Reactions Reactivity SeriespenguinpowerrrrОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table File NotesДокумент12 страницPeriodic Table File NotesVeronica HanyОценок пока нет
- Lab-Activity - Reactivity of Alkali Metals - Group 1 - 2023Документ2 страницыLab-Activity - Reactivity of Alkali Metals - Group 1 - 2023careersОценок пока нет
- Halogens Task SheetДокумент1 страницаHalogens Task SheetMayraaj KhaanamОценок пока нет
- C3 Elements and CompoundsДокумент81 страницаC3 Elements and CompoundskarenelizabethjamiОценок пока нет
- The Periodic TableДокумент19 страницThe Periodic Tablejoannavera2020Оценок пока нет
- Periodic Table of Elements ChapterДокумент10 страницPeriodic Table of Elements ChapterReo RandoОценок пока нет
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Документ6 страницUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126Оценок пока нет
- L.O.13chemistry G 10Документ22 страницыL.O.13chemistry G 10bebo atefОценок пока нет
- Class 10th ChemistryДокумент17 страницClass 10th ChemistryasritakilanОценок пока нет
- Alkali MetalsДокумент12 страницAlkali MetalsSaki Sultana LizaОценок пока нет
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesДокумент14 страницClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- Obj:-Q) Can Anyone Answer How Many Halogens Are Der in PTДокумент5 страницObj:-Q) Can Anyone Answer How Many Halogens Are Der in PTSamia KhanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationДокумент5 страницChemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationNaomi JohnsonОценок пока нет
- S BlockДокумент6 страницS BlockSora RoseОценок пока нет
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- MkpsДокумент16 страницMkpsDeepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Paadukaasahasram PDFДокумент186 страницPaadukaasahasram PDFDeepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Museum DocentДокумент2 страницыMuseum DocentDeepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Guru-Ashtakam Tamil PDF File7816 PDFДокумент5 страницGuru-Ashtakam Tamil PDF File7816 PDFDeepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Kanchi Periva Forum - Maha Shivaratri Special Edition EbookДокумент35 страницKanchi Periva Forum - Maha Shivaratri Special Edition EbookNagendra KrishnamurthyОценок пока нет
- Totakashtakam Telugu PDF File1509Документ7 страницTotakashtakam Telugu PDF File1509phanindraОценок пока нет
- Sahasra Gayathri Procedure-1Документ9 страницSahasra Gayathri Procedure-1Deepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Distance LearningДокумент3 страницыAdvantages and Disadvantages of Distance LearningDeepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Lesson 7Документ20 страницLesson 7Deepa KarthikОценок пока нет
- Someone Who Believes in YouДокумент1 страницаSomeone Who Believes in YouMANOLO C. LUCENECIOОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3.c (Centroid by Intergration)Документ15 страницChapter 3.c (Centroid by Intergration)Ariff AziziОценок пока нет
- 12 Key Principles On Bhava AnalysisДокумент28 страниц12 Key Principles On Bhava AnalysisDhineshОценок пока нет
- Grade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaДокумент25 страницGrade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaPenke Mejado BelenОценок пока нет
- Solutions GoldsteinДокумент10 страницSolutions GoldsteinAnyiОценок пока нет
- The Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsДокумент34 страницыThe Light Fantastic by Sarah CombsCandlewick PressОценок пока нет
- SDHI18 - Komparativna Analiza Primene Vodostana I Sinhronih Regulatora TurbinaДокумент13 страницSDHI18 - Komparativna Analiza Primene Vodostana I Sinhronih Regulatora TurbinaAleksandar PetkovicОценок пока нет
- Irina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeДокумент4 страницыIrina Maleeva - Ariel Snowflake x6 - ENG - FreeMarinaKorzinaОценок пока нет
- ZF-FreedomLine TransmissionДокумент21 страницаZF-FreedomLine TransmissionHerbert M. Zayco100% (1)
- Unit 3Документ12 страницUnit 3Erik PurnandoОценок пока нет
- Parts Catalogue of Foton: (TC2A504-034K)Документ132 страницыParts Catalogue of Foton: (TC2A504-034K)МаксимОценок пока нет
- Basic Geriatric Nursing 6th Edition Williams Test BankДокумент10 страницBasic Geriatric Nursing 6th Edition Williams Test Bankmaryrodriguezxsntrogkwd100% (49)
- Board Replacement CasesДокумент41 страницаBoard Replacement CasesNadeeshОценок пока нет
- Emw 2007 FP 02093Документ390 страницEmw 2007 FP 02093boj87Оценок пока нет
- Ad149 Manual RДокумент69 страницAd149 Manual RCharityОценок пока нет
- Sika - Bitumen: Bitumen Emulsion Waterproof & Protective CoatingДокумент3 страницыSika - Bitumen: Bitumen Emulsion Waterproof & Protective Coatingdinu69inОценок пока нет
- Electrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент5 страницElectrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDwane AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Electric ScootorДокумент40 страницElectric Scootor01fe19bme079Оценок пока нет
- Significance of GodboleДокумент5 страницSignificance of GodbolehickeyvОценок пока нет
- Fighting Techniques of The Early Modern World AD 1500-AD 1763 - Equipment Combat Skills Amp Amp TacticsДокумент258 страницFighting Techniques of The Early Modern World AD 1500-AD 1763 - Equipment Combat Skills Amp Amp Tacticslupoeva100% (3)
- Market AnalysisДокумент4 страницыMarket AnalysisSaniya CharaniyaОценок пока нет
- 123 09-Printable Menu VORДокумент2 страницы123 09-Printable Menu VORArmstrong TowerОценок пока нет
- Potassium Fixation As Affected by Alternate Wetting and Drying in Some Soil Series of JharkhandДокумент4 страницыPotassium Fixation As Affected by Alternate Wetting and Drying in Some Soil Series of JharkhandDr Amrit Kumar JhaОценок пока нет
- Digging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Документ2 страницыDigging Deeper: Can Hot Air Provide Sustainable Source of Electricity?Рустам ХаджаевОценок пока нет
- Ensemble Averaging (Machine Learning)Документ3 страницыEnsemble Averaging (Machine Learning)emma698Оценок пока нет
- June 2021 QP - Paper 1 (H) Edexcel Chemistry GCSEДокумент28 страницJune 2021 QP - Paper 1 (H) Edexcel Chemistry GCSEmiapoppycollinsОценок пока нет
- Impact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFДокумент16 страницImpact of Retrofitting Existing Combined Heat and Power Plant With Polygeneration of Biomethane PDFAwais Salman0% (1)
- Goldhofer FTV 850 BrochureДокумент2 страницыGoldhofer FTV 850 BrochureMauroОценок пока нет
- Socialized HousingДокумент48 страницSocialized HousingJessieReiVicedoОценок пока нет