Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nonlinear Modeling of Piles Using SAP2000
Загружено:
TuanQuachИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nonlinear Modeling of Piles Using SAP2000
Загружено:
TuanQuachАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
Non-Linear Modelling/Analysis of Pile using SAP 2000
Shrabony Adhikary
Research Scholar, Department of Earthquake Engineering, IIT Roorkee
For Queries please mail to: shrabonyeq@gmail.com
Step-1 Obtain the p-y,t-z and q-z curves at different depths along the pile
for the given soil profile
Soil Profile
Depth (m) Soil Type Undrained shear strength
(kN/m2)
0-2
Stiff Clay 80
2-8
Stiff Clay 100
8-12
Stiff Clay 120
12-16
Stiff Clay 150
16-22
Stiff Clay 180
22-40
Stiff Clay 200
Unit weight
(kN/m3)
17
18
19.5
20
20
21
Laterally loaded Piles in Stiff Clay
As per API (2005) the lateral soil resistance deflection relationship for stiff clay above water
table is nonlinear and in the absence of experimental data the following expression can be used
y
p
0.5
pu lt
y 50
0.25
(1)
where the value of p remains constant beyond y=16y50 in case of stiff clay and y50 =2.550D, is
the deflection at one-half the ultimate soil resistance and
50 =strain at one-half the maximum
difference in principal stresses of undisturbed soil sample.
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
p
pu lt
0
0.5
0.84
1
1
y
y50
0
1
8
16
pult can be obtained as described in the following section.
pult 3cu Z J
cu Z
D
(2)
pult 9cu
(3)
Z= depth under consideration, cu is the shear strength at depth Z, and D is the width of the pile. J
is taken as 0.5. pult is calculated at each depth where p-y curve is desired.
Table 1 Representative values of 50 and cu for normally consolidated clay
50
< 48
0.020
48-96
0.010
96-192 0.005
Consistency of clay cu(kPa)
Soft
Medium
Stiff
Derivation of p=y curve parameters
pult(Eq.2)
pult(Eq.3)
y50
z
cu
D
J
e50
283.67
720.00
0.02
17.00
1.00
80.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
327.33
720.00
0.02
17.00
2.00
80.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
454.00
900.00
0.02
18.00
3.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
505.33
900.00
0.02
18.00
4.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
556.67
900.00
0.02
18.00
5.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
608.00
900.00
0.02
18.00
6.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
659.33
900.00
0.02
18.00
7.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
710.67
900.00
0.02
18.00
8.00
100.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
895.50
1080.00
0.02
19.50
9.00
120.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
955.00
1080.00
0.02
19.50
10.00
120.00
1.50
0.50
0.01
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
Axially loaded Piles in Stiff Clay
As per API (2005) piles should be designed for static and cyclic axial loads. The total ultimate
axial load carrying capacity of the pile is provided through soil-pile skin friction and end bearing
resistance of the pile tip, i.e.
QAu Q fu Qpu f As q Ap
(4)
where, Q fu is the skin frictional resistance in kN; Q pu is the total end bearing capacity of the pile
in kN; f is the the unit skin friction in kN/m2 , As is the side surface area of the pile in m2 , q is
the end bearing capacity in kN/m2 , Ap is the gross end area of the pile in m2.
For clay
f cu
(5)
q 9cu
(6)
and = a dimensionless factor, cu is the undrained shear strength of the soil, and the factor
computed as per the following equations, 0.5 0.5 1.0 and 0.5 0.25 1.0 , and
is
1.0,
where cu / p0 and p0 is the effective overburden pressure
As per API (2005) the analytical expression to find the skin friction capacity of piles is given by
t
t max
z
z
zc zc
(7)
where, z is the local pile deflection in m, zc is the relative displacement required and is taken as
0.005 m in case of clay. tmax is the maximum shear stress in kN/m2 and t is the shear stress at
nodal point in kN/m2. The t-z curves as defined in API (2005) are the function of z/D and t/ tmax .
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
z
D
t max
0
0.0016
0.0031
0.0057
0.0080
0.01
0.02
0
0.3
0.5
0.75
0.9
1.0
0.7-0.9
0.7-0.9
Derivation of t=z curve parameters
z
cu
po'
17.00
1.00
80.00
17.00
4.71
0.34
27.16
17.00
2.00
80.00
34.00
2.35
0.40
32.30
18.00
3.00
100.00
52.00
1.92
0.42
42.46
18.00
4.00
100.00
70.00
1.43
0.46
45.73
18.00
5.00
100.00
88.00
1.14
0.48
48.43
18.00
6.00
100.00
106.00
0.94
0.51
51.48
18.00
7.00
100.00
124.00
0.81
0.56
55.68
18.00
8.00
100.00
142.00
0.70
0.60
59.58
19.50
9.00
120.00
161.50
0.74
0.58
69.61
As per API (2005) the analytical expression to find pile tip settlement curves is given by
q
qmax
1/ 3
z
zcb
(8)
where, qmax is the maximum bearing stress in kN/m2 ; z is the axial tip deflection of the pile in m
, and zcb is the maximum displacement required to develop qmax. The q-z curves as defined in
API (2005) are the function of z/D and q/ qmax .
z
D
qmax
0.002
0.013
0.042
0.073
0.1
0.25
0.5
0.75
0.9
1
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
19.50
10.00
120.00
181.00
0.66
0.61
73.69
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
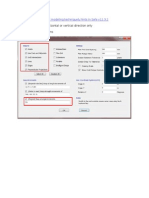
Step-2 Define section properties>Link support properties> Add new
properties
Define Multilinear Force-Deformation Parameters in terms of force-displacement curves as
obtained. It is to be noted that the p-y and t-z curves are to be defined in both tension and
compression however, the q-z curves should be defined only for compression.
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
Nonlinear Modelling of Pile using SAP 2000
References
American Petroleum Institute (API), 2005. Recommended Practice for Planning, Designing and
Constructing Fixed Offshore Platforms. API-RP2A-WSD, Washington, D.C.
Erhan, S., and Dicleli, M. 2014. Effect of dynamic soilbridge interaction modeling assumptions
on the calculated seismic response of integral bridges. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake
Engineering, 66 (0):42-55.
Shirato M, Koseki J, and Fukui J. 2006. A new nonlinear hysteretic rule for winkler type soil-pile
interaction spring that consider loading pattern dependency. Soil Found Jpn Geotech
Soc,46(2):17388.
Indo-Norwegian Training Programme on
Nonlinear Modelling and Seismic Response Evaluation of Structures
December 14-16, 2014 Continuing Education Center, IIT Roorkee
Вам также может понравиться
- Weld Design SymbolsДокумент63 страницыWeld Design Symbolspriyoc6100% (15)
- 10 Week Size Surge Diet and Workout PlanДокумент15 страниц10 Week Size Surge Diet and Workout Planjosgerardo200092% (12)
- Composite Materials 1Документ29 страницComposite Materials 1JisselAroraОценок пока нет
- 550.2r 13 Design Guide For Connections in Precast Jointed SystemsДокумент20 страниц550.2r 13 Design Guide For Connections in Precast Jointed SystemsMohd Sulahuddin RamlyОценок пока нет
- Sofistik Tutorials 2020: General Workflow Bridge DesignДокумент51 страницаSofistik Tutorials 2020: General Workflow Bridge Designnepoznati1111Оценок пока нет
- Seismic Design Guide For Metal Building SystemsДокумент212 страницSeismic Design Guide For Metal Building Systemsgaposso100% (9)
- Two Column Hammerhead Pier Structural Analysis TutorialДокумент35 страницTwo Column Hammerhead Pier Structural Analysis TutorialMohd FaizalОценок пока нет
- Connections: Best Tips of The 21st CenturyДокумент4 страницыConnections: Best Tips of The 21st Centurysymon ellimac100% (1)
- Design of Neoprene Bearing Pads - DupontДокумент25 страницDesign of Neoprene Bearing Pads - Dupontnigst2100% (1)
- Vibration Analysis of Steel Pedestrian BridgesДокумент35 страницVibration Analysis of Steel Pedestrian BridgesYasela100% (1)
- Draft Amendment in IRC 6 Fatigue Load Clause 204.6Документ4 страницыDraft Amendment in IRC 6 Fatigue Load Clause 204.6Santhoshkumar RayavarapuОценок пока нет
- Prestressed Concrete Design To Eurocodes PDFДокумент13 страницPrestressed Concrete Design To Eurocodes PDFashwini thakurОценок пока нет
- Abutment Design Example To Eurocodes and UK National AnnexesДокумент53 страницыAbutment Design Example To Eurocodes and UK National AnnexesVikash AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Decoduct Cable Management Systems 03-04-2013Документ54 страницыDecoduct Cable Management Systems 03-04-2013Giemy P GeorgeОценок пока нет
- MSS SP 67 - 1995 PDFДокумент18 страницMSS SP 67 - 1995 PDFVelibor StokicОценок пока нет
- PSC Design (Aashto-Lrfd Tyu07) TutorialДокумент44 страницыPSC Design (Aashto-Lrfd Tyu07) TutorialMohammad Tawfiq WaraОценок пока нет
- Marriot StandarsДокумент409 страницMarriot StandarsJose Buitrago100% (10)
- Step-by-Step Pushover Analysis Using CSiBridgeДокумент26 страницStep-by-Step Pushover Analysis Using CSiBridgekejspmОценок пока нет
- Compression Member PDFДокумент45 страницCompression Member PDFSanjeevJadhav100% (1)
- "Asce705W" - Asce 7-05 Code Wind Analysis ProgramДокумент32 страницы"Asce705W" - Asce 7-05 Code Wind Analysis ProgramTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Structural Bolting GuideДокумент14 страницStructural Bolting GuideLintang Jarai0% (1)
- SPC Manual PDFДокумент11 страницSPC Manual PDFNgiuyen Viet TienОценок пока нет
- Design of Concrete ShearWallДокумент34 страницыDesign of Concrete ShearWallOmar HadriОценок пока нет
- RC-Pier LRFD 3 Column Frame Pier ExampleДокумент160 страницRC-Pier LRFD 3 Column Frame Pier ExampleMTCLS100% (2)
- Composite Bridge Steel Girder Design in BSДокумент131 страницаComposite Bridge Steel Girder Design in BSSANDIPОценок пока нет
- Welcome: All Faculty Members & All Participants of Integrated Course-10109Документ39 страницWelcome: All Faculty Members & All Participants of Integrated Course-10109structure12367% (3)
- Prestressed Concrete IIT-M PDFДокумент490 страницPrestressed Concrete IIT-M PDFsandeepgolu19100% (2)
- Task00-MultiLinearPlasticLink 20160126 MD DRAFTДокумент9 страницTask00-MultiLinearPlasticLink 20160126 MD DRAFTAryОценок пока нет
- Soil Stiffness Vesic Vs BowlesДокумент1 страницаSoil Stiffness Vesic Vs BowlesAtul Kumar EngineerОценок пока нет
- Road Project Work OrderДокумент4 страницыRoad Project Work Ordernandini50% (4)
- Wood& ArmerДокумент9 страницWood& ArmerthirumalaichettiarОценок пока нет
- Diaphargm Wall DesignДокумент24 страницыDiaphargm Wall Designsurajoffshore75% (4)
- Vol.02 - Complete Guide To PrestressingДокумент14 страницVol.02 - Complete Guide To PrestressingShadiОценок пока нет
- Adsec8.3 Manual PDFДокумент98 страницAdsec8.3 Manual PDFLeeОценок пока нет
- Integral Abutment Bridges Accommodate Thermal MovementДокумент12 страницIntegral Abutment Bridges Accommodate Thermal Movementsoniafaisal100% (1)
- (1966) Basic Facts Concerning Shear Failure PDFДокумент37 страниц(1966) Basic Facts Concerning Shear Failure PDFMohammad AshrafyОценок пока нет
- Pile Cap Design With 7 Piles: Calculation Note Project: AppartmentДокумент9 страницPile Cap Design With 7 Piles: Calculation Note Project: AppartmentChanthy RathedОценок пока нет
- 05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015Документ26 страниц05.40.00 Cold-Formed Metal Framing Specification Updated June 2015mishikhanОценок пока нет
- Flexural Behavior of Circular Hollow ColumnsДокумент92 страницыFlexural Behavior of Circular Hollow ColumnsArnold TunduliОценок пока нет
- Magnets and Magnetism (Grade 3) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingДокумент1 страницаMagnets and Magnetism (Grade 3) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachinglanie.taneco100% (5)
- Bridge DesignДокумент21 страницаBridge DesignattartouseefahemedОценок пока нет
- Manual Fagus 7Документ157 страницManual Fagus 7Ramon Gutierrez100% (1)
- Special Modeling Technique in Safe v12Документ15 страницSpecial Modeling Technique in Safe v12thailecanadaОценок пока нет
- FEM - Report LUSAS SoftwareДокумент27 страницFEM - Report LUSAS SoftwareSiti Rohani IsdrisОценок пока нет
- Issues of Vibrations in Footbridges by Mahesh TandonДокумент17 страницIssues of Vibrations in Footbridges by Mahesh TandonAnonymous YHcvra8Xw6Оценок пока нет
- Target Issuance 30 May 2023Документ4 страницыTarget Issuance 30 May 2023Achmad OktafionoОценок пока нет
- Triple Frictional Pendulum PDFДокумент18 страницTriple Frictional Pendulum PDFpsh1979Оценок пока нет
- MIDAS MCT File Quick ReferenceДокумент90 страницMIDAS MCT File Quick ReferenceromanoscotchОценок пока нет
- PT EUrocodeДокумент90 страницPT EUrocodeKilaru HareeshОценок пока нет
- Losses in Prestress-Friction, Anchorage SlipДокумент16 страницLosses in Prestress-Friction, Anchorage SlipSravanthi MeharОценок пока нет
- Strut Tie Model Transfer SlabДокумент182 страницыStrut Tie Model Transfer Slabshish0iitrОценок пока нет
- Sofistik Training Level 2 - Dynamic & Convoys: Tutorial For Rolling Stock AnalysisДокумент40 страницSofistik Training Level 2 - Dynamic & Convoys: Tutorial For Rolling Stock AnalysisAlexandros Gi100% (1)
- Strut and Tie Model For Deep Beam Design (To ACI Building Code)Документ8 страницStrut and Tie Model For Deep Beam Design (To ACI Building Code)yyanan1118Оценок пока нет
- Tubular Film Blowing Process ExplainedДокумент9 страницTubular Film Blowing Process ExplainedAlmir MachadoОценок пока нет
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОт EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000Документ34 страницыAnalysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000qwerty qwerty75% (4)
- Allowable Tensile Stress For Webs of Prestressed Segmental Concrete BridgesДокумент8 страницAllowable Tensile Stress For Webs of Prestressed Segmental Concrete BridgesShikhar SinghОценок пока нет
- Macro For Design of Beam in Excel STAAD ProДокумент3 страницыMacro For Design of Beam in Excel STAAD ProdrajkumarceОценок пока нет
- SAM Design ExampleДокумент110 страницSAM Design Exampleyyanan1118100% (3)
- Prof Ashok Jain-Example On Torsion - IRC 112 PDFДокумент5 страницProf Ashok Jain-Example On Torsion - IRC 112 PDFrahuljoagОценок пока нет
- Numerical Modeling of Laterally Loaded PilesДокумент6 страницNumerical Modeling of Laterally Loaded PilesMatteo Izzi100% (1)
- VSL Strand Post Tensioning Systems PDFДокумент41 страницаVSL Strand Post Tensioning Systems PDFJonathan GallegosОценок пока нет
- Coherent Gravity I K StiffesДокумент8 страницCoherent Gravity I K Stiffesgrga piticОценок пока нет
- End Block Design AidДокумент6 страницEnd Block Design AidAhsan KhanОценок пока нет
- CSiBridge Bridge Seismic Design ReportДокумент18 страницCSiBridge Bridge Seismic Design ReportMarcos MorrisonОценок пока нет
- Free Cantilever Method (Método Del Voladizo Libre)Документ48 страницFree Cantilever Method (Método Del Voladizo Libre)German SanchezОценок пока нет
- Tendon Elongation Calculation - BeamДокумент1 страницаTendon Elongation Calculation - Beamvikramjain66Оценок пока нет
- Transforming Railways Seismic CodeДокумент39 страницTransforming Railways Seismic CodevigneshrajamanickamОценок пока нет
- XTRACT - Fall2012 ManualДокумент15 страницXTRACT - Fall2012 ManualEdgarFloresGonzalesОценок пока нет
- Load Capaciy of Piles by SPT - CPT Dhimitri Et - AlДокумент8 страницLoad Capaciy of Piles by SPT - CPT Dhimitri Et - AlSaroj BhattaraiОценок пока нет
- Stochastic nonlinear p-y analysis of laterally loaded pilesДокумент8 страницStochastic nonlinear p-y analysis of laterally loaded pilesHusseinali HusseinОценок пока нет
- Tubular King Pile Foundation AppendicesДокумент100 страницTubular King Pile Foundation AppendicesNizar HalabiОценок пока нет
- CE 407 Earthquake Engineering Final Exam QuestionsДокумент2 страницыCE 407 Earthquake Engineering Final Exam QuestionsSteve BariaОценок пока нет
- Bulding Design Rsap2015Документ32 страницыBulding Design Rsap2015TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Design of Fully Restrained Moment Connections AISC LRFD 3rd EditionДокумент28 страницDesign of Fully Restrained Moment Connections AISC LRFD 3rd EditionMIRCEA1305Оценок пока нет
- Lec-8. Moving Loads Compatibility ModeДокумент14 страницLec-8. Moving Loads Compatibility ModeAfia S Hameed100% (1)
- Lecture 16Документ14 страницLecture 16TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- SSB03 ActionsДокумент64 страницыSSB03 ActionsCristi BudauОценок пока нет
- Data Input:: 205 14 210 8 LW 345 450 8000 8000 Uniform GradientДокумент6 страницData Input:: 205 14 210 8 LW 345 450 8000 8000 Uniform GradientTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Screw Connections Subject To Tension Pull-Out and Shear ForcesДокумент64 страницыScrew Connections Subject To Tension Pull-Out and Shear ForcesTuanQuach100% (1)
- Architects Guide 2010-03-18 PDFДокумент47 страницArchitects Guide 2010-03-18 PDFSharath JagadeeshanОценок пока нет
- C PhiДокумент1 страницаC PhiTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Columns: CIE429 - RC DesignДокумент11 страницColumns: CIE429 - RC DesignTuanQuach100% (1)
- Preliminary Design Guide For Cold-Formed Steel C - and Z-Members-1993Документ44 страницыPreliminary Design Guide For Cold-Formed Steel C - and Z-Members-1993TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Lecture19 PDFДокумент17 страницLecture19 PDFTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Rclect6 12Документ24 страницыRclect6 12monkeyDivanОценок пока нет
- CIE429 - RC Design: Lecture #23 FootingsДокумент17 страницCIE429 - RC Design: Lecture #23 FootingsTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Lecture 22Документ16 страницLecture 22TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Rclect4 12Документ14 страницRclect4 12Marshall BravestarОценок пока нет
- Llogaritje Statike Per ShkalletДокумент19 страницLlogaritje Statike Per ShkalletgertjaniОценок пока нет
- Lecture19 PDFДокумент17 страницLecture19 PDFTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Rclect14 Composite 12 PDFДокумент27 страницRclect14 Composite 12 PDFAbera MamoОценок пока нет
- Rclect10 12Документ25 страницRclect10 12Abera MamoОценок пока нет
- Rclect7 12 PDFДокумент19 страницRclect7 12 PDFTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- The Uncracked (1st), Cracked (2nd) and Plastic (3rd) State of StressesДокумент17 страницThe Uncracked (1st), Cracked (2nd) and Plastic (3rd) State of StressesTuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Rclect5 12Документ22 страницыRclect5 12TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Rclect2 12Документ20 страницRclect2 12TuanQuachОценок пока нет
- Engineering Physics-II - PH151Документ2 страницыEngineering Physics-II - PH151uday vivekОценок пока нет
- Auditorium Acoustic G 3 3Документ10 страницAuditorium Acoustic G 3 3TharunОценок пока нет
- RCC Pile Works ChecklistДокумент1 страницаRCC Pile Works ChecklistAyush PuriОценок пока нет
- Current Practice of CFA Piling in Australia and New Zealand: June 2018Документ10 страницCurrent Practice of CFA Piling in Australia and New Zealand: June 2018Vetriselvan ArumugamОценок пока нет
- Screw DetailsДокумент21 страницаScrew DetailsHans HamiltonОценок пока нет
- Indoor Unit Outdoor Unit CS-S10JKP CS-S13JKP CS-S15JKP CU-S10JKP CU-S13JKP CU-S15JKPДокумент93 страницыIndoor Unit Outdoor Unit CS-S10JKP CS-S13JKP CS-S15JKP CU-S10JKP CU-S13JKP CU-S15JKPVinh LeОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +97455034994, +97433252400Документ4 страницыCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +97455034994, +97433252400Satya BysaniОценок пока нет
- Comp 12Документ36 страницComp 12Tanu RdОценок пока нет
- Liebert HimodДокумент71 страницаLiebert HimodlincolnОценок пока нет
- International Equipment: CatalogueДокумент24 страницыInternational Equipment: CatalogueFahmi FahreziОценок пока нет
- LED Lighting CatalogДокумент10 страницLED Lighting CatalogNguyen Anh TuОценок пока нет
- Chilean Steel Design ManualДокумент295 страницChilean Steel Design ManualshakibbrОценок пока нет
- Ball ValvesДокумент28 страницBall ValvesRAVINDR.KОценок пока нет
- Itp Ralgo HssДокумент5 страницItp Ralgo Hssmark quijlvoОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Bridge StructuresДокумент158 страницAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Bridge StructuresINARQ1979Оценок пока нет
- LRFD 1.5B 36 1.5BI 36 1.5PLB 36 - GR80 - Roof - DeckДокумент2 страницыLRFD 1.5B 36 1.5BI 36 1.5PLB 36 - GR80 - Roof - DeckXiomara M Santiago OramaОценок пока нет
- An Investigation of Microstructure/property Relationships in Dissimilar Welds Between Martensitic and Austenitic Stainless SteelДокумент13 страницAn Investigation of Microstructure/property Relationships in Dissimilar Welds Between Martensitic and Austenitic Stainless SteelOrhan BAYLANОценок пока нет
- Type 1 Surge Protective Device SPD FeaturesДокумент2 страницыType 1 Surge Protective Device SPD FeaturesYasim AbidinОценок пока нет