Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Discussion: Pneumonia (Fig. 1a)
Загружено:
غسن سمن المدنИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Discussion: Pneumonia (Fig. 1a)
Загружено:
غسن سمن المدنАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
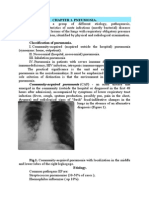
Pneumonia (Fig.
1a)
- The infl ammatory exudate within
air-spaces and interstitium of the
affected lung causes the
opacifi cation and air-fi lled
bronchioles outlined by adjacent
fl uid-fi lled alveoli in affected lung
produce the air bronchogram.
Discussion
- Pneumonia is a common disease
and is usually caused by bacterial
infection.
- Apart from the typical features of
lobar pneumonia, other probable
radiological fi ndings not seen on
this CXR include:
1. Pleural effusion
seen as blunting of lateral
costophrenic angle
2. Cavitation
more common in staphylococcus
pneumonia or pulmonary
tuberculosis
- Pneumonia caused by certain
organisms may produce
characteristic radiologic features
1. Unilateral lobar involvement in
streptococcus infection
2. Bilateral patchy involvement
(Fig. 1b), sometimes with
cavitation in staphylococcus
pneumonia (Fig. 1c)
3. Upper lobe involvement with
cavitation in pulmonary TB
(Fig. 1d)
4. Bilateral symmetrical perihilar
distribution which progresses
rapidly over 3-5 days in PCP
pneumonia in immune
Вам также может понравиться
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesОт EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesОценок пока нет
- 长沙医学院 国际教育学院 Pathology (病理学)Документ57 страниц长沙医学院 国际教育学院 Pathology (病理学)Ichsan FajriОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD (: Dr:Mie Ali Ali MohamedДокумент67 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD (: Dr:Mie Ali Ali MohamedzakwanОценок пока нет
- Presentation1 PneumoniaДокумент13 страницPresentation1 PneumoniaAmr An IIIОценок пока нет
- Syndrom of Consolidated Pulmonary Tissue. Pneumonia. Athelectasis. Andrei IchimДокумент114 страницSyndrom of Consolidated Pulmonary Tissue. Pneumonia. Athelectasis. Andrei IchimYan Sheng Ho100% (1)
- Lec 9 Respiratory Disorders Part 2Документ11 страницLec 9 Respiratory Disorders Part 2iam2117Оценок пока нет
- Pulmonary PathologyДокумент46 страницPulmonary PathologyMuostafa KamelОценок пока нет
- Chest X-Ray Manifestations of PneumoniaДокумент3 страницыChest X-Ray Manifestations of PneumoniaVishesh SoodОценок пока нет
- CASE 5 PnemoniaДокумент18 страницCASE 5 Pnemoniaabdulwahab ibn hajibushraОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia: ANAND. TO, 1ST MSC Student Nursinc NsgstudentДокумент11 страницPneumonia: ANAND. TO, 1ST MSC Student Nursinc NsgstudentArunОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia, Pleuropneumonia, Lung Abscess, and Pleuritis: Radiographic Appearance of PneumoniaДокумент9 страницPneumonia, Pleuropneumonia, Lung Abscess, and Pleuritis: Radiographic Appearance of PneumoniaEasti EmoraОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary InfectionДокумент9 страницPulmonary InfectionlalaОценок пока нет
- Diseases of Respiratory OrgansДокумент72 страницыDiseases of Respiratory OrgansEdi Kerina SembiringОценок пока нет
- (Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaДокумент86 страниц(Materi Dr. Heny) PneumoniaFathiyah SalsabilaОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia in Sheep and GoatДокумент32 страницыPneumonia in Sheep and Goataliabh2006100% (5)
- Bronchiectasis: DR Budi Enoch SPPDДокумент21 страницаBronchiectasis: DR Budi Enoch SPPDVito CuyОценок пока нет
- Wae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaДокумент14 страницWae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaRashed ShatnawiОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia & Lung AbscessДокумент61 страницаPneumonia & Lung AbscessnewtypeОценок пока нет
- BronchiectasisДокумент21 страницаBronchiectasisMuhammad Iyhan NuriansyahОценок пока нет
- Etiology: An Irreversible Airway Dilation That Involves The Lung inДокумент3 страницыEtiology: An Irreversible Airway Dilation That Involves The Lung inOlli TherineОценок пока нет
- 2.BE PathogenesisДокумент7 страниц2.BE PathogenesisJaya Semara PutraОценок пока нет
- Resp Patho McqsДокумент2 страницыResp Patho McqsChan ZiqiОценок пока нет
- Bronchial ObstructionДокумент137 страницBronchial ObstructionGrajdianu Natalia100% (1)
- PneumoniaДокумент3 страницыPneumoniaKami KhanОценок пока нет
- III. COPD Book 17-22Документ6 страницIII. COPD Book 17-22Maria OnofreiОценок пока нет
- Bronko PneumoniaДокумент33 страницыBronko PneumoniaNurul Hidayati SyarahОценок пока нет
- The Pneumonias: Associate Professor Dr. Lauren Ţiu ŞorodocДокумент60 страницThe Pneumonias: Associate Professor Dr. Lauren Ţiu ŞorodocCristina Georgiana CoticăОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент3 страницыChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJessica Corona - MarianoОценок пока нет
- Broncho PneumoniaДокумент5 страницBroncho PneumoniamarkkkkkkkheeessОценок пока нет
- Internal Medicine Mid TurmДокумент27 страницInternal Medicine Mid TurmAjay The RockerОценок пока нет
- Past Year RespiДокумент5 страницPast Year RespiThulasi tootsieОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Chest Findings 3rd Year 2023Документ54 страницыAbnormal Chest Findings 3rd Year 2023Abishek PrinceОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia: Eksudasi Cairan Perdarahan (Pada Alveolus & Bronchus) Membentuk Konsistensi HeparДокумент4 страницыPneumonia: Eksudasi Cairan Perdarahan (Pada Alveolus & Bronchus) Membentuk Konsistensi HeparDhita Budi WibowoОценок пока нет
- SGL6 - CoughДокумент63 страницыSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Tract Pathology New LectureДокумент63 страницыRespiratory Tract Pathology New Lectureabenezer isayasОценок пока нет
- Suppurative Lung Diseases: DR Taher El Naggar Prof of Pulmonary Medicine Ain Shams UniversityДокумент65 страницSuppurative Lung Diseases: DR Taher El Naggar Prof of Pulmonary Medicine Ain Shams UniversitykingmedicОценок пока нет
- Non Tuberculous Infections (Updated)Документ54 страницыNon Tuberculous Infections (Updated)ZijieОценок пока нет
- Study Guide 2Документ16 страницStudy Guide 2cОценок пока нет
- PATHOLOGIC CHANGES. Grossly, The Lungs Are Characteristically Stiff, Congested and Heavy. Microscopically, The Following Features Are EvidentДокумент6 страницPATHOLOGIC CHANGES. Grossly, The Lungs Are Characteristically Stiff, Congested and Heavy. Microscopically, The Following Features Are EvidentIsak ShatikaОценок пока нет
- Lect 8 Pneumonia PDFДокумент68 страницLect 8 Pneumonia PDFRaghad AbdullaОценок пока нет
- Gharib2001 Radiologi Pneumonia-DikonversiДокумент31 страницаGharib2001 Radiologi Pneumonia-Dikonversitsamara24_Оценок пока нет
- 1 Lung AbscessДокумент51 страница1 Lung AbscessЕвгений ХанькоОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaДокумент11 страницSchematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaanGel1115Оценок пока нет
- Respiratory-Renal Block, Practical IДокумент37 страницRespiratory-Renal Block, Practical Imina mounirОценок пока нет
- Classification of PneumoniaДокумент3 страницыClassification of PneumoniaRobelОценок пока нет
- Viral Pneumoni Dari 18Документ13 страницViral Pneumoni Dari 18Yoyada SitorusОценок пока нет
- Radiology Pulmonary Infections ReportДокумент33 страницыRadiology Pulmonary Infections ReportAngeline Fernandez-TwoОценок пока нет
- Pathology Lecture-Diseases Affecting The Lower Respiratory Tract & TBДокумент48 страницPathology Lecture-Diseases Affecting The Lower Respiratory Tract & TBSounds of MindОценок пока нет
- LP K RamliДокумент18 страницLP K RamliAtila FaОценок пока нет
- Acute Lung Abscesses. Definition of The Idea. Classification. Etiology and Pathogenesis. Clinical Picture. Diagnosis.Документ6 страницAcute Lung Abscesses. Definition of The Idea. Classification. Etiology and Pathogenesis. Clinical Picture. Diagnosis.Lucas Victor AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Fiopatologia EPOCДокумент9 страницFiopatologia EPOCJames D. EspinozaОценок пока нет
- PBL of PneumoniaДокумент9 страницPBL of PneumoniaRobelОценок пока нет
- Care of Patient With Respiratory DisordersДокумент35 страницCare of Patient With Respiratory Disorderskriiteeabns100% (1)
- Laporan Pendahuluan Asuhan Keperawatan Anak Pada Klien Dengan BronkhitisДокумент14 страницLaporan Pendahuluan Asuhan Keperawatan Anak Pada Klien Dengan BronkhitisDicky Aris SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Broncho PneumoniaДокумент21 страницаBroncho PneumoniaRiad GagahОценок пока нет
- B&lung AbscessДокумент21 страницаB&lung Abscessnathan asfahaОценок пока нет
- Pathology of The Respiratory System 2Документ76 страницPathology of The Respiratory System 2Fabian ChapimaОценок пока нет
- TherapyДокумент100 страницTherapyomolola adeogunОценок пока нет
- DR Chiranjibbhattacharyya Associateprofessor Dept - Ofanaesthesiology Ipgmer KolkataДокумент40 страницDR Chiranjibbhattacharyya Associateprofessor Dept - Ofanaesthesiology Ipgmer KolkataFadhli AzhimiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1. Pneumonia. Pneumonia - A Group of Different Etiology, PathogenesisДокумент14 страницChapter 1. Pneumonia. Pneumonia - A Group of Different Etiology, PathogenesisAbraham ChiuОценок пока нет
- CMB5Документ2 страницыCMB5غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- CMB2Документ1 страницаCMB2غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- CMB4Документ2 страницыCMB4غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- CMB1Документ1 страницаCMB1غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- CMB3Документ3 страницыCMB3غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Dan M. Roden-WPS OfficeДокумент1 страницаDan M. Roden-WPS Officeغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- AchalasiaДокумент4 страницыAchalasiaغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Emergency Tintin-WPS OfficeДокумент1 страницаEmergency Tintin-WPS Officeغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- AbortionДокумент3 страницыAbortionغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Abdominal AorticДокумент6 страницAbdominal Aorticغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Acanthamoeba In-WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыAcanthamoeba In-WPS Officeغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Antiplatelet THДокумент3 страницыAntiplatelet THغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Acanthamoeba In-WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыAcanthamoeba In-WPS Officeغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Not Seen in This Patient Include:: DiscussionДокумент1 страницаNot Seen in This Patient Include:: Discussionغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Lung CollapseДокумент1 страницаLung Collapseغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- The Major Fissures Have Similar Anatomy On The Two Sides. They Run Obliquely Forwards andДокумент1 страницаThe Major Fissures Have Similar Anatomy On The Two Sides. They Run Obliquely Forwards andغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Laminar EffusionsДокумент1 страницаLaminar Effusionsغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Recognize Partial or Complete Atelectasis of The Following On A Chest Radiograph or Computed TomographyДокумент1 страницаRecognize Partial or Complete Atelectasis of The Following On A Chest Radiograph or Computed Tomographyغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Imaging of The Breast Is Undertaken As Part of A ComprehensiveДокумент1 страницаImaging of The Breast Is Undertaken As Part of A Comprehensiveغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Types of AtelectasisДокумент1 страницаTypes of Atelectasisغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Recognizing A Pleural EffusionДокумент1 страницаRecognizing A Pleural Effusionغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Learning ObjectivesДокумент1 страницаLearning Objectivesغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- A Class I Incisor Relationship Is Defined by The British Standards Incisor Classification As FollowsДокумент2 страницыA Class I Incisor Relationship Is Defined by The British Standards Incisor Classification As Followsغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Short Incubation PeriodДокумент1 страницаShort Incubation Periodغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- The Primary Features of Established Illness Are Related To EndothelialДокумент1 страницаThe Primary Features of Established Illness Are Related To Endothelialغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- 17Документ2 страницы17غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Isolated Heart MuscleДокумент1 страницаIsolated Heart Muscleغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- The Development of The 12Документ1 страницаThe Development of The 12غسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulant andДокумент2 страницыAnticoagulant andغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет