Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Controlling Function
Загружено:
Eric MugaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Controlling Function
Загружено:
Eric MugaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter Three
Overview of management functions
Part Four: Directing and Controlling
Functions
1.
2.
3.
Planning
Organizing
Staffing
4.
Directing
5.
Controlling
CONTROLLING FUNCTION.
Definition:
Controlling can be defined as the process of measuring actual performance
against standards and taking any corrective action in case of deviations from
standards.
An organization involved in production of goods/services must measure the
level of actual performance of the employees and compare with the
standards laid down by the organization in order to ensure that employees
perform as per the standards.
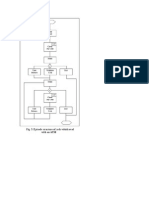
Controlling process
As a management function controlling involves the following steps:
1. Setting standards/ objectives to be achieved.
2. Measuring the level of actual performance
3. Comparing actual performance against standards.
4. Taking corrective action in case of any deviation.
METHODS OF CONTROLLING AN ORGANIZATION
1. Steering/feed forward controls (before)
2. Screening/ yes or no controls (during)
3. Feedback/post action controls (after)
STEERING/FEEDFORWARD CONTROLS.
These are controls directed towards the future. They are designed to detect
deviations from some standards or goals to allow corrective action before
implementation of activity. Involves the following methods:
a) Setting standards and defining objectives clearly.
b) Feasibility studies on the proposed activities to be undertaken.
c) Establishment of steering committee to steer the activities to be
undertaken.
d) Budgeting: - to plan the resources required and control the future
expenditure on proposed activities.
e) Establishment of proper work procedures to direct the flow of work or
activity from the beginning to the end.
f) Establishment of appropriate organizational structures to ensure that
activities will be effectively coordinated.
g) Appropriate organizational policies to provide guidelines for the
implementation process.
h) Rules and regulations to be followed to restrict the actions of managers
and subordinates and ensure that activities are implemented as per
organizational requirements.
i) Forecasting: to reduce the level of environmental and certainty before
setting objectives and strategies.
j) Inspection/involving suppliers in drawing up the specifications of the
quality of materials needed.
k) Appointment of managers and supervisors to be in charge/direct
activities to be implemented etc.
SCREENING /YES OR NO CONTROLS
These control systems monitor activities while in progress: they are intended
to detect deviation in a timely manner so that necessary actions are taken
implementation process is continued. They are commonly used in
manufacturing systems which implements automated controls.
Methods of screening controls.
a) Progress reports should be prepared on daily, weekly, monthly or
quarterly basis.
b) Managers
and
supervisors
should
constantly
monitor
the
implementation process
c) Periodic review of performance through performance appraisal
d) Establishment of check points on the production process or in the
course of undertaking an activity e.g. a system which requires that 3
managers must verify a document or a bank cheque.
e) Periodic inspection of departmental activities (management audit)
f) Internal audit systems.
g) Computerized monitoring systems applied in production controls
h) Meeting organized on daily weekly or monthly basis e.g. management
committee meetings to review performance etc.
Feedback/post action controls
This type of control is implemented after an activity has taken place i.e. it
evaluates the results of an activity after it has been completed. It is suitable
to control activities which the process is not well known but after completion
the management can find out whether the actual performance met the
standards. It uses feedback from the output of the system and measuring
outputs as a means of controlling it shows deficiency over historical data
such as those received from accounting reports.
One of the difficulties with such historical data is that they tell business
managers e.g. in November that they lost money in October because of
something that was done in July. This type of control system is therefore not
the best. What managers need for effective control is a system that will tell
them in time to take corrective actions and that problems will occur if they
dont do something about them now?
Methods of post action controls
a) Annual accounting reports
b) Annual performance appraisal reports
c) External auditors reports
d) Final inspection of finished goods before dispatch.
e) Any other report which is prepared upon the completion of the project
or activity.
IMPORTANCE OF CONTROLLING.
1. Contributes to achievement of set standards/organizational goals.
2. Directs behavior of employees towards goal achievements. Control
systems monitor rewards and reinforce the behavior and activities desired
by the management.
3. Leads to efficient utilization of organizations resources e.g. budgeting,
financial and purchases records could improve the utilization of resources.
4. Improves the coordination of organizations activities: -control systems
ensures that efforts of all members will be coordinated through standards,
norms, budgets and reporting systems hence integration of organizational
activities. In a sense control provides the mechanism for achieving
diverse activities of the organization.
5. Useful in managing uncertainty: -control system limits options in decision
making by setting rules and regulations to handle repetitive activities i.e.
It ensures conformity to standards e.g. commercial bank have
credit standards and regulations that loan officers uses in issuing
loans. If these standards do not exist each officer could use
different standards for issuing loans.
DRAWBACKS/LIMITATIONS OF CONTROLS
1. Controls may contribute to dysfunctional effects
Such bureaucratic red tape i.e. a system characterized by excessive controls,
which affects operations of the organizational.
2. Time consuming:
Too many procedures or monitoring systems may affect the smooth flow of
work resulting into delays of goals accomplishment.
3. Less customer/client satisfaction:
Dissatisfaction with too many procedures to be followed in an organization
may send customers away.
4. Effect on creativity and innovation:-
Controls may affect the level of creativity of individual employees.
Employees will tend to forecast on activities, which strictly leads to goal
attainment. This may affect their level of creativeness and innovativeness.
5. Demoralized work force: Too many control systems may lower workers satisfaction or morale and
productivity.
6. Conflicts between managers and subordinates:
Managers who are very strict in enforcing controlling systems may affect
team spirit and performance.
7. Expensive to implement: Certain control systems e.g. computerized control systems are very
expensive to set up and to train employees to operate them etc.
Directing
DIRECTING is said to be a process in which the managers instruct, guide
and oversee the performance of the workers to achieve predetermined
goals. Directing is said to be the heart of management process. Planning,
organizing, staffing have got no importance if direction function does not
take place.
Directing initiates action and it is from here actual work starts. Direction is
said to be consisting of human factors. In simple words, it can be described
as providing guidance to workers is doing work. In field of management,
direction is said to be all those activities which are designed to encourage
the subordinates to work effectively and efficiently. According to Human,
Directing consists of process or technique by which instruction can be
issued and operations can be carried out as originally planned. Therefore,
Directing is the function of guiding, inspiring, overseeing and instructing
people towards accomplishment of organizational goals.
Direction has got following characteristics:
1. Pervasive Function - Directing is required at all levels of
organization. Every manager provides guidance and inspiration to his
subordinates.
2. Continuous Activity - Direction is a continuous activity as it
continuous throughout the life of organization.
3. Human Factor - Directing function is related to subordinates and
therefore it is related to human factor. Since human factor is complex
and behaviour is unpredictable, direction function becomes important.
4. Creative Activity - Direction function helps in converting plans into
performance. Without this function, people become inactive and
physical resources are meaningless.
5. Executive Function - Direction function is carried out by all managers
and executives at all levels throughout the working of an enterprise, a
subordinate receives instructions from his superior only.
6. Delegate Function - Direction is supposed to be a function dealing
with human beings. Human behaviour is unpredictable by nature and
conditioning the peoples behaviour towards the goals of the enterprise
is what the executive does in this function. Therefore, it is termed as
having delicacy in it to tackle human behaviour.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Strategic Position - Part 4Документ34 страницыStrategic Position - Part 4Eric MugaОценок пока нет
- Simplex MethodДокумент16 страницSimplex MethodShantanu Dutta100% (1)
- Case Study-Mary RobertsДокумент2 страницыCase Study-Mary RobertsEric Muga50% (2)
- SFA Matrix Learning Strategic ChoiceДокумент5 страницSFA Matrix Learning Strategic ChoiceAmna Mirza100% (1)
- Case StudyДокумент1 страницаCase StudyjaijohnkОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis ApproachДокумент2 страницыCase Analysis ApproachEric MugaОценок пока нет
- 4 Mini Case StudiesДокумент18 страниц4 Mini Case Studiesali400250% (2)
- Wardle Storeys - Case StudyДокумент4 страницыWardle Storeys - Case StudyEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Science ST NDДокумент61 страницаScience ST NDAaronRamosОценок пока нет
- ATM LogicДокумент1 страницаATM LogicEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Competitor Analysis: Chapter FourДокумент9 страницCompetitor Analysis: Chapter FourEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Lit Policy ReviewДокумент29 страницLit Policy ReviewEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Economics ArticleДокумент26 страницEconomics ArticleEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Taxation (United Kingdom) : Tuesday 4 June 2013Документ22 страницыTaxation (United Kingdom) : Tuesday 4 June 2013Eric MugaОценок пока нет
- 28 Deadlock SolutionsДокумент37 страниц28 Deadlock SolutionsEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Kenya Fiscal Guide 2011Документ8 страницKenya Fiscal Guide 2011Eric MugaОценок пока нет
- Contextual Design ProcessДокумент4 страницыContextual Design ProcessEric MugaОценок пока нет
- Affinity DiagramДокумент21 страницаAffinity DiagramMarco Bernabe JumaquioОценок пока нет
- Vector DifferentiationДокумент6 страницVector DifferentiationEric MugaОценок пока нет
- 1 IntroductionДокумент21 страница1 IntroductionEric MugaОценок пока нет
- International Strategy: Globalization Drivers - Assess Dual PressuresДокумент29 страницInternational Strategy: Globalization Drivers - Assess Dual PressuresamarraajОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Curriculum OverviewДокумент3 страницыCurriculum OverviewJoshua EUSTACE [11R04S]Оценок пока нет
- Cognitive Rehabilitation Programs in Schizophrenia PDFДокумент26 страницCognitive Rehabilitation Programs in Schizophrenia PDFMeindayaniОценок пока нет
- Maharishi Vedic Psychology Brings FulfillmentДокумент27 страницMaharishi Vedic Psychology Brings FulfillmentAMTR100% (1)
- CinderellaДокумент3 страницыCinderellalauracurleyОценок пока нет
- 16-00400-21 Masteravhandling - Reading Comprehension, Elin Jorde Hansen - Docx 267995 - 1 - 1Документ70 страниц16-00400-21 Masteravhandling - Reading Comprehension, Elin Jorde Hansen - Docx 267995 - 1 - 1Lamhot NaibahoОценок пока нет
- Functions of Organization CultureДокумент9 страницFunctions of Organization CultureAbdul Mateen RahimОценок пока нет
- The Job Demands-Resources Model: State of The ArtДокумент20 страницThe Job Demands-Resources Model: State of The ArtHarpreet AjimalОценок пока нет
- David Grove Basic Clean Language QuestionsДокумент2 страницыDavid Grove Basic Clean Language QuestionsAnonymous 2a1YI92k9L100% (4)
- Types of MotionДокумент20 страницTypes of MotionMelanie Panza ManibaleОценок пока нет
- Possiveis Selfs - A Teoria de MarkusДокумент17 страницPossiveis Selfs - A Teoria de MarkusCésar OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Coaching College Students With Executive Function Problems (2017, The Guilford Press)Документ258 страницCoaching College Students With Executive Function Problems (2017, The Guilford Press)Vicente Rodrigues100% (1)
- Abdul WahabДокумент9 страницAbdul WahabAlexanderОценок пока нет
- Sociocultural Theory Model of Reading 1986-1995Документ7 страницSociocultural Theory Model of Reading 1986-1995api-353329890Оценок пока нет
- Animal ConditioningДокумент27 страницAnimal ConditioningpolypeptideОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 ReportДокумент5 страницUnit 1 Reportlehsem20006985Оценок пока нет
- MOHANTY - 1984 - Philosophical Description and Descriptive PhilosophyДокумент22 страницыMOHANTY - 1984 - Philosophical Description and Descriptive PhilosophyrosenbergalapeОценок пока нет
- Marketing Friday, June 3, 2016 20-Minute Oral Presentation (Including Questions) Abstract 2016-099 8:50 AM (Legacy South 2)Документ2 страницыMarketing Friday, June 3, 2016 20-Minute Oral Presentation (Including Questions) Abstract 2016-099 8:50 AM (Legacy South 2)Luiz SilvaОценок пока нет
- Power and Organizational PoliticsДокумент20 страницPower and Organizational Politicsharmanguliani88Оценок пока нет
- Astington EdwardANGxpДокумент7 страницAstington EdwardANGxpAndris C BeatriceОценок пока нет
- George Herbert MeadДокумент5 страницGeorge Herbert MeadRen Bernardo100% (1)
- Red TeamingДокумент100 страницRed TeamingbmurilloОценок пока нет
- No More Heidegger, No More Genius LogiДокумент10 страницNo More Heidegger, No More Genius LogiCristina DumitruОценок пока нет
- Eisenhardt 1989 SummaryДокумент9 страницEisenhardt 1989 SummaryAdelson NascimentoОценок пока нет
- Quiz # 1 Practical ResearchДокумент2 страницыQuiz # 1 Practical ResearchAriel Nube100% (2)
- McCandless's Journey To Self-ActualizationДокумент5 страницMcCandless's Journey To Self-ActualizationZack R. Smith100% (3)
- ENGLISH 119 - DraftДокумент5 страницENGLISH 119 - DraftBrod LenamingОценок пока нет
- Mindfulness Training and Neural Integration: Differentiation of Distinct Streams of Awareness and The Cultivation of Well-BeingДокумент5 страницMindfulness Training and Neural Integration: Differentiation of Distinct Streams of Awareness and The Cultivation of Well-BeingGretchen Marie Aristud AquinoОценок пока нет
- Creative Movement An Opportunity For Affective EducationДокумент10 страницCreative Movement An Opportunity For Affective EducationMisrah SulimanОценок пока нет
- Role of Multicultural CounselorДокумент3 страницыRole of Multicultural CounselorChuah Yee LinОценок пока нет
- ILC Fragamenation of ILДокумент256 страницILC Fragamenation of ILAziz SalibaОценок пока нет