Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ib Bio Questions Digestion Wans
Загружено:
Shreya DasОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ib Bio Questions Digestion Wans
Загружено:
Shreya DasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:
Questions on Digestion
Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on
Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a
study guide for the next quiz.
Due Date: Thursday March 15
1.
What is absorption?
A.
Food entering the mouth and being chewed
B.
Food entering the stomach for digestion
C.
Taking digested food into the blood stream
D.
Making complex organic molecules in cells using digested foods
(Total 1 mark)
2.
Ducts connect the liver, gall bladder and pancreas to the alimentary canal. Which diagram
shows the correct pattern of duct connections?
A.
liver
B.
gall bladder
liver
pancreas
gall bladder
pancreas
intestine
intestine
C.
liver
pancreas
D.
liver
gall bladder
gall bladder
intestine
pancreas
intestine
(Total 1 mark)
3.
What sequence of organs do substances pass through, as they move through the human digestive
system?
A. Mouth stomach pancreas small intestine liver large intestine anus
B. Mouth stomach small intestine pancreas liver large intestine anus
C. Mouth esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine anus
D. Mouth esophagus stomach large intestine small intestine anus
(Total 1 mark)
4.
Why is most food digested?
A.
Digestive enzymes require a variety of substrates.
B.
It ensures that the diet is balanced.
C.
Most ingested food molecules are large.
D.
To prevent disorders of the intestine.
(Total 1 mark)
5.
Two cellular activities that support human life are absorption and assimilation. What is needed
for assimilation but not for absorption?
A.
Enzymes to synthesize new molecules
B.
Blood capillaries
C.
Dissolved nutrients
D.
Microvilli
(Total 1 mark)
6.
Describe the role of enzymes in digestion with reference to two named examples.
(Total 5 marks)
7.
Draw a labelled diagram of the digestive system.
(Total 5 marks)
8.
State the sources, substrate, product, and optimum pH conditions for the enzyme amylase.
(Total 4 marks)
9.
Dietary factors are known to influence the incidence of colon cancer. The graphs below show
the correlation between meat consumption (eating meat) and colon cancer in sample countries
and the correlation between fat consumption and colon cancer.
50
40
Colon cancer incidence / 30
100 000 women
20
Sweden
10
Hungary
0
0
40
80 120 160 200 240 280 320
Meat consumption / grams day1
[Source: B Armstrong and R Doll, Environmental factors and cancer incidence and mortality in different countries, with special
reference to dietary practices, (1975), International J Cancer, 15, pp 617631]
30
25
20
Colon cancer incidence /
15
100 000 men
10
5
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Fat consumption / grams day1
[Source: http:members.aol.com/wantnomeat/page]
(a)
(i)
State the relationship between daily meat consumption and the incidence of colon
cancer in women.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
Using the data in the two graphs opposite, suggest reasons for the relationship
between daily meat consumption and the incidence of colon cancer in women.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
(i)
Calculate the difference in colon cancer incidence between Hungarian women and
Swedish women.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
Discuss whether meat consumption causes colon cancer in Sweden and Hungary.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 7 marks)
10.
Draw a diagram of a villus in vertical section.
(Total 5 marks)
11.
(a)
State two sources of disaccharides in the diet.
1.
.........................................................................................................................
2.
.........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Outline the use of absorbed carbohydrates.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(3)
(c)
Discuss the relationship between high levels of saturated lipids in the diet and health of
the individual.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
12.
(a)
Identify the parts of the human digestive system indicated below.
(2)
(b)
In the space below draw the structure of an amino acid.
(2)
(c)
The enzyme pepsin, involved in protein digestion in the stomach, requires an acid pH to
work properly. Explain the effect of pH on enzyme activity.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(d)
Explain how three structures of the villus are related to the role of the villus in
absorption.
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
13.
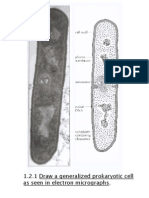
The electron micrograph below shows part of several pancreatic islet cells.
Capillary
I
Storage vesicles
II
III
(a)
Identify the structures labelled I, II and III in the micrograph above and give a role for
each one.
Structure
Role
A.
B.
C.
D.
(3)
(b)
(i)
Using the letter A, identify one location on the micrograph where transcription
takes place.
(1)
(ii)
Using the letter B, identify one location on the micrograph where chemiosmosis
occurs.
(1)
The large, black vesicles store products of the cells that are released into the capillaries of the
pancreas.
(c)
(i)
Suggest what product each cell is likely to be making.
..........................................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
Explain how the products are transported from the site of production and released
from the islet cells.
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
14.
Enzymes are used by living organisms to catalyse reactions. Some of these reactions occur in
the cytoplasm of cells. Other reactions take place outside cells, for example the digestion of
foods in the human gut.
(a)
State the name used by biochemists for the chains and cycles of reactions that occur
inside cells.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Enzymes of digestion in humans are secreted by glands. They have a pH optimum which
allows them to work efficiently in the part of the gut into which they are secreted.
(i)
In the table below, identify the missing enzyme, the two glands, and the pH
optimum
Name of
enzyme
amylase
Gland secreting
the enzyme
Substrate
Products
starch
maltose
triglycerides
fatty acids and
glycerol
pH optimum
7
(4)
(ii)
Outline the effect of pH values above and below the optimum on enzyme structure.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
10
(c)
Enzymes that work inside cells are sometimes affected by non-competitive inhibitors.
Explain how a non-competitive inhibitor affects the activity of an enzyme.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
15.
(a)
Outline the role of the liver in the storage of nutrients.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
Explain how the body overcomes the problem of lipid digestion in the alimentary canal.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 4 marks)
11
16.
(a)
List two glands that secrete digestive juices into the alimentary canal.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Describe the process of erythrocyte and hemoglobin breakdown in the liver.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 5 marks)
12
1.
C
[1]
2.
A
[1]
3.
C
[1]
4.
C
[1]
5.
A
[1]
6.
large food molecules must be broken down;
such as carbohydrates / proteins, etc;
by hydrolysis of bonds / to form monomers;
in preparation for absorption;
rate of reaction at body temperature too slow;
enzymes increase the rate of breakdown / act as catalysts;
first enzyme example name, substrate and product;
second enzyme example name, substrate and product;
Award [3 max] if no examples given.
[5]
7.
Award [1] for each two of the following structures clearly drawn and correctly labelled.
Connections between organs must be correct for full marks.
mouth / teeth / tongue;
esophagus;
stomach;
small intestine;
large intestine / colon;
anus;
pancreas;
liver;
gall bladder;
rectum;
salivary glands;
sphincters;
[5]
8.
source: salivary glands;
pancreas;
substrate: starch / glycogen; (do not accept carbohydrate)
product: maltose / disaccharide;
optimum pH: 78 / neutralslightly alkaline;
[4]
9.
(a)
(b)
(i)
positive correlation / higher incidence with higher meat consumption
(ii)
fat consumption is correlated with / causes colon cancer;
meat contains (high levels of) fat;
(i)
12( 1) deaths per 100000 women
(ii)
same meat consumption but higher colon cancer rate in Sweden;
other factors cause colon cancer (in Sweden) / eg genetic factors,
lack of fibre;
only some types of meat may cause colon cancer;
meat may contain more fat in Sweden / other chemical differences;
other foods may protect against cancer (in Hungary);
3 max
[7]
10.
(Award [1] for each of the following structures clearly drawn
and labelled correctly.)
lymph vessel;
arteriole;
venule;
(central) lacteal;
capillary network;
epithelial layer / lining / epithelium;
microvilli;
goblet cells;
[5]
11.
(a)
Award [1 max] for any two of the following.
cane sugar / honey / onion / milk / maple syrup / fruit / soft drinks
/ other answers
(b)
provide energy / cell respiration;
excess carbohydrate (glucose) can be converted into fat / glycogen for storage;
synthesis of glycoproteins / combine with proteins to form glycoproteins;
components of nucleic acids eg ribose in mRNA / deoxyribose in DNA;
required for the synthesis of some amino acids;
constituent of connective tissue;
3 max
(c)
diets high in saturated lipids increase risk of heart disease / atherosclerosis;
diets high in saturated lipids increase risk of obesity;
obesity linked to a variety of health problems eg diabetes;
atherosclerosis is narrowing of artery lumen;
atherosclerosis leads to high blood pressure / increased risk of coronary thrombosis /
stroke;
smoking / lack of exercise in combination with diet high in saturated lipids
compounds risk of heart disease;
relationship may be affected by genetic factors;
4 max
[8]
12.
(a)
I:
II:
III:
IV:
liver;
stomach;
pancreas;
large intestine / (descending) colon;
Award [1] for every two correct, up to [2 max].
2 max
(b)
amino group properly drawn;
acid group properly drawn;
C with H and R group attached; (no labels are required)
eg
H
N
H
C
R
O
C
;
OH
Award [2] if three are correct, [1 max] if two are correct and
[0] if one is correct.
N.B . A condensed formula is acceptable which shows H2Nand -COOH instead of the expanded amino group and
carboxyl group attached to the central carbon atom; N atom of
amino group must be joined to central C atom.
(c)
each enzyme has an optimum pH where enzyme functions best / drawing of
bell curve with optimal pH labelled;
changes in pH (from optimum pH) decrease activity / effectiveness;
pH slightly changes the shape of the active site / tertiary structure of protein
changed / enzyme denatured;
more difficult to form enzyme-substrate complex;
2 max
N.B . Accept above marking points if given through a specific
example such a s pepsinogen conversion to pepsin when
pH is lowered.
(d)
microvilli increase surface area of absorption;
epithelium / one layer of cells provides a thin layer to enhance absorption /
small distance for diffusion;
protein channels (in membrane of microvilli) allow facilitated diffusion;
mitochondria (for energy) present for active transport;
blood capillaries close to epithelium / surface membrane reduce distance /
increase speed for diffusion;
blood capillaries carry away glucose / amino acids / nutrients;
lacteal carry away fats / fatty acids / glycerol;
3 max
Accept any of the above points in a clearly drawn annotated
diagram.
[9]
13.
(a)
Award [1] for each correct structure and its role.
Structure
Role
mitochondria
produce ATP / site of (aerobic)
respiration;
II:
nucleus
contains genetic information / produces
RNA /
site of replication;
III:
(rough) endoplasmic
reticulum
(site of) translation / protein production /
protein
transport;
I:
(b)
(c)
(i)
A in nucleus / A in mitochondria
(ii)
B in a mitochondrion
(i)
insulin / glucagon
Do not accept proteins.
(ii)
vesicles formed at / bud off from RER;
product carried to Golgi apparatus (and modified there);
vesicles carry product to plasma membrane;
fuse with membrane;
release product (to lumen) / exocytosis;
ATP used / energy required;
3 max
[9]
14.
(a)
(b)
metabolic pathways / metabolic
reactions / metabolism / anabolism and catabolism
(i)
(ii)
salivary gland / pancreas;
pH 7.5 ( 0.5);
lipase; (accept lipidase)
pancreas;
ionic bonds / polar bonds broken / disrupted /
charge distribution altered;
ionization of amino / carboxyl groups altered;
conformation / shape of enzyme / active site altered /
tertiary structure altered;
enzyme denatured;
2 max
(c)
inhibitor binds (to the enzyme) away from the active site /
at allosteric site;
shape / (intramolecular) bonding / conformation of the protein /
enzyme is altered;
shape / properties of active site altered;
substrate no longer fits the active site /
no enzyme-substrate / ES complex formed;
no enzyme activity /
works more slowly (until the inhibitor dissociates);
Award [1 max] if competitive inhibition is described.
3 max
[10]
15.
(a)
(b)
liver stores excess glucose as glycogen / releases glucose from glycogen
(as levels drop);
liver breaks down red blood cells / hemoglobin and stores iron;
liver stores fat soluble vitamins / vitamin A / vitamin D / vitamin B12 /
folic acid;
2 max
lipids are hydrophobic / not water soluble;
bile helps to break up lipid droplets / bile emulsifies fats / increases
surface area of lipid droplets for lipase attack;
lipids more accessible to lipase / lipase breaks down lipids;
pancreatic juices brings up pH as optimal pH for lipase is alkaline / pH8;
2 max
[4]
(c)
inhibitor binds (to the enzyme) away from the active site /
at allosteric site;
shape / (intramolecular) bonding / conformation of the protein /
enzyme is altered;
shape / properties of active site altered;
substrate no longer fits the active site /
no enzyme-substrate / ES complex formed;
no enzyme activity /
works more slowly (until the inhibitor dissociates);
Award [1 max] if competitive inhibition is described.
3 max
[10]
16.
(a)
Two of the following needed for [1].
pancreatic;
salivary;
gastric pits / gastric glands;
glands in intestinal wall / krypts / Brunners gland;
liver
1 max
(b)
erythrocytes rupture when they reach the end of their life span / after 120 days;
absorbed by phagocytosis / Kupffer cells in liver from blood;
hemoglobin split into globin and heme groups;
iron removed from heme leaving bile pigment / bilirubin;
bilirubin released into alimentary canal;
digestion of globin to produce amino acids;
4 max
[5]
Вам также может понравиться
- Errors and Uncertainties in Biology Internal AssessmentДокумент4 страницыErrors and Uncertainties in Biology Internal AssessmentjnОценок пока нет
- IB Biology Photosynthesis IAДокумент12 страницIB Biology Photosynthesis IAAshwinОценок пока нет
- IB Biology, Human Health & Nutrition NotesДокумент17 страницIB Biology, Human Health & Nutrition NotesEvelyn LeversОценок пока нет
- SL Biology Syllabus NotesДокумент52 страницыSL Biology Syllabus NotesRyel MuchunkuОценок пока нет
- Internal Assesment Biology - 25Документ11 страницInternal Assesment Biology - 25lauraОценок пока нет
- Ecology QuestionsДокумент31 страницаEcology QuestionsBosco785Оценок пока нет
- Food TestsДокумент13 страницFood TestsBilal Shahid100% (1)
- I. II. Iii. IV. V. VI. Vii.: APES Final Review For AP EXAMДокумент12 страницI. II. Iii. IV. V. VI. Vii.: APES Final Review For AP EXAMRichi VasquezОценок пока нет
- Bio Paper FinalДокумент8 страницBio Paper FinalNiem PhamОценок пока нет
- Biology IaДокумент4 страницыBiology IaIndrani Goswami100% (1)
- Diffusion Osmosis Lab 2Документ3 страницыDiffusion Osmosis Lab 2briangkentОценок пока нет
- Ib Animal Experimental PolicyДокумент2 страницыIb Animal Experimental Policyapi-326269363Оценок пока нет
- Beano LabДокумент12 страницBeano Labapi-284496286Оценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY Sample IAДокумент12 страницBIOLOGY Sample IAVedant SainiОценок пока нет
- Cell Respiration: Samantha A. Price AP Biology 10-26-09 Lab #3Документ8 страницCell Respiration: Samantha A. Price AP Biology 10-26-09 Lab #3fallenangel32592100% (1)
- t2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeДокумент15 страницt2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeNicholas OwОценок пока нет
- Bio IA Possible TopicsДокумент5 страницBio IA Possible TopicskeziAОценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange Structured Questions IBДокумент9 страницGas Exchange Structured Questions IBJohn Osborne100% (1)
- IB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawДокумент33 страницыIB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawSchuyler Huff100% (1)
- Biology Catalase Experiment DesignДокумент6 страницBiology Catalase Experiment DesignNimisha SharmaОценок пока нет
- Bio IA TopsДокумент4 страницыBio IA TopsSanjana KumarОценок пока нет
- The Transport System IB Qq'sДокумент12 страницThe Transport System IB Qq'sJohn OsborneОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Ecology QuestionsДокумент69 страницChapter 4 Ecology QuestionsIndraneel BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Lab 1Документ10 страницAP Biology Lab 1Abby Loneker0% (1)
- Bio IAДокумент2 страницыBio IAbebelavida100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration in YeastДокумент11 страницCellular Respiration in YeastxshelyОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент17 страницMolecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianОценок пока нет
- Magnification QuestionsДокумент4 страницыMagnification QuestionsOmaimaОценок пока нет
- Biology SL Paper 1novДокумент10 страницBiology SL Paper 1novidkОценок пока нет
- Enzymes (AS Level Bio)Документ23 страницыEnzymes (AS Level Bio)DrMufaddal RampurwalaОценок пока нет
- 2022 FA DBQ Topic 4Документ11 страниц2022 FA DBQ Topic 4Zulkarnyne RezaОценок пока нет
- Ib Bio Answers OptioncДокумент5 страницIb Bio Answers Optioncshakar47Оценок пока нет
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabДокумент8 страницAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564Оценок пока нет
- Bio IAДокумент9 страницBio IAJuan VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- IB Bio IAДокумент16 страницIB Bio IAjunyiwuОценок пока нет
- Bio Ia PDFДокумент13 страницBio Ia PDFLia Marie BeloyОценок пока нет
- Ecology WorksheetДокумент7 страницEcology Worksheetsue.phan.0301Оценок пока нет
- Biology Revision BookletДокумент59 страницBiology Revision BookletSiddhant ShahОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Carbohydrates and LipidsДокумент42 страницы2.3 Carbohydrates and LipidsHelena GlanvilleОценок пока нет
- Biologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabДокумент8 страницBiologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabJames DaurayОценок пока нет
- IB Questions Cell Ultrastructure and ScaleДокумент10 страницIB Questions Cell Ultrastructure and ScaleJohn OsborneОценок пока нет
- Flashcards - CP 18 Production of Amylase in Germinating Cereal Grains - Edexcel Biology International A-LevelДокумент15 страницFlashcards - CP 18 Production of Amylase in Germinating Cereal Grains - Edexcel Biology International A-LevelBara' Hammadeh0% (1)
- Unit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Документ38 страницUnit 4 Revision Notes SNAB Topics 5 & 6 A2Olivia Panterka Vainilla100% (2)
- Biology Notes IB Free ResponseДокумент26 страницBiology Notes IB Free ResponseLarry LohОценок пока нет
- Chromatography Worksheet - (C) 2002 Ian Guch - All RightsДокумент2 страницыChromatography Worksheet - (C) 2002 Ian Guch - All RightsJulian Alberti100% (1)
- IB Biology Cells 2010Документ13 страницIB Biology Cells 2010tr4l100% (1)
- Bio IA - KwokДокумент12 страницBio IA - KwokSıla DenizОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Rate of Reaction of Enzyme ActivityДокумент6 страницThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Rate of Reaction of Enzyme ActivityMaan PatelОценок пока нет
- IB Biology Lab ReportДокумент21 страницаIB Biology Lab ReportAgnieszka100% (1)
- Regents Homeostasis and EnzymesДокумент5 страницRegents Homeostasis and Enzymesapi-3031203990% (1)
- Grade 11 Biology Midterm HLДокумент31 страницаGrade 11 Biology Midterm HLSaima SyedaОценок пока нет
- Biology IAДокумент8 страницBiology IAElise GalvanОценок пока нет
- 12 Cellular Communication-SДокумент5 страниц12 Cellular Communication-SadaОценок пока нет
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesДокумент8 страницAs Chemistry Unit 1 NoteshamzazzОценок пока нет
- IB Bio Topic 6.2 Transport Review MarkschemeДокумент4 страницыIB Bio Topic 6.2 Transport Review MarkschemeKatherineОценок пока нет
- Biology Extended Essay Final Draft.Документ33 страницыBiology Extended Essay Final Draft.Oliver Hernández100% (1)
- Heredity and VariationДокумент25 страницHeredity and VariationDre ParkerОценок пока нет
- Topic 5.1 - 5.3 IB TB Questions and AnswersДокумент28 страницTopic 5.1 - 5.3 IB TB Questions and AnswersYewande Oduwole100% (1)
- Recommendations For Rescue of A Submerged Unresponsive Compressed-Gas DiverДокумент10 страницRecommendations For Rescue of A Submerged Unresponsive Compressed-Gas Diverwyma01Оценок пока нет
- Thompson Coon, J. Et Al. Systematic Review Herbal Medicinal Products For Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002 16 1689-1699.Документ11 страницThompson Coon, J. Et Al. Systematic Review Herbal Medicinal Products For Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002 16 1689-1699.Pablo CrespoОценок пока нет
- Glossary of Psychiatry WikipediaДокумент153 страницыGlossary of Psychiatry WikipediaAkio OzaragaОценок пока нет
- Dalay Panishment of FormalinДокумент4 страницыDalay Panishment of Formalinmutiara defiskaОценок пока нет
- Scheduling: IndiaДокумент5 страницScheduling: IndiaCristinaОценок пока нет
- Microbial Control For Plant Disease in Thailand: Watchalee SopinДокумент80 страницMicrobial Control For Plant Disease in Thailand: Watchalee SopinImie S. Canaria100% (1)
- Https Covid-19.Pshealthpunjab - Gov.pk PublicSampleResults PatientPublicSampleResultДокумент2 страницыHttps Covid-19.Pshealthpunjab - Gov.pk PublicSampleResults PatientPublicSampleResultmuhammad imranОценок пока нет
- (NH4) 2co3Документ5 страниц(NH4) 2co3MuhafiОценок пока нет
- CASE STUDY PEDIA - SaavedraДокумент15 страницCASE STUDY PEDIA - SaavedraChryst Louise SaavedraОценок пока нет
- (Piper Crocatum) For Vaginal Discharge Among: The Effect of Using Red Betel Leaves Fertile Age Women (Faw)Документ6 страниц(Piper Crocatum) For Vaginal Discharge Among: The Effect of Using Red Betel Leaves Fertile Age Women (Faw)rezayantiquОценок пока нет
- Management of MenengitesДокумент8 страницManagement of Menengiteskhaled alsulaimОценок пока нет
- Picmonic Step 1 Study PlanДокумент32 страницыPicmonic Step 1 Study PlanrammyttaОценок пока нет
- Burn NotesДокумент4 страницыBurn NotesRiza Angela BarazanОценок пока нет
- Positive and Negative Filipino ValuesДокумент2 страницыPositive and Negative Filipino ValuesBrenty TablateОценок пока нет
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaДокумент19 страницInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaCJ M. Pablo100% (1)
- CeprofloxacinДокумент2 страницыCeprofloxacinGabby Robles PajeОценок пока нет
- Health Message & The SanctuaryДокумент14 страницHealth Message & The SanctuaryNick Bantolo100% (7)
- Chorti DictionaryДокумент285 страницChorti DictionaryLuis Bedoya100% (1)
- BangkasДокумент5 страницBangkasJulianne BangkasОценок пока нет
- Anchor Speech On WorkshopДокумент6 страницAnchor Speech On WorkshopPabhat Kumar100% (2)
- Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative and Exclusive Breast FeedingДокумент92 страницыBaby Friendly Hospital Initiative and Exclusive Breast Feedingvarshasharma05Оценок пока нет
- Domiciliary Midwifery RДокумент16 страницDomiciliary Midwifery Rswillymadhu83% (6)
- Eastfeeding StuartMacadamДокумент80 страницEastfeeding StuartMacadamDiana Fernanda Espinosa SerranoОценок пока нет
- Abc Abuso 1 PDFДокумент6 страницAbc Abuso 1 PDFMDMОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Infection and Semen Characteristics in Infertile MenДокумент6 страницBacterial Infection and Semen Characteristics in Infertile Menalia eltayebОценок пока нет
- Surgical Drains and TubesДокумент3 страницыSurgical Drains and TubesYusra ShaukatОценок пока нет
- OSPE DU MedicineДокумент101 страницаOSPE DU MedicinesaifОценок пока нет
- Dr. Anas Yasin - MDДокумент58 страницDr. Anas Yasin - MDMahfouzОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Sulfide FactДокумент2 страницыHydrogen Sulfide FactAgriSafeОценок пока нет
- NCP 1Документ3 страницыNCP 1itsmeayaОценок пока нет