Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Civil 2yr Syllabus
Загружено:
kkАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Civil 2yr Syllabus
Загружено:
kkАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NME-302: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
UNIT-I
Compound stress and strains: Introduction, normal stress and strain, shear stress and strain, stresses on
inclines sections, strain energy, impact loads and stresses, state of plane stress, principal stress and strain,
maximum shear stress, Mohrs stress circle, three dimensional state of stress & strain, equilibrium equations,
generalized Hooks law, theories of failure
UNIT II
Stresses in Beams: Pure Bending, normal stresses in beams, shear stresses in beams due to transverse and axial
loads, composite beams.
deflection of Beams: Equation of elastic curve, cantilever and simply supported beams, Macaulays method,
area moment method, fixed and continuous beams
Torsion: Torsion, combined bending & torsion of solid & hollow shafts, torsion of thin walled tubes
UNIT-III
Helical and Leaf Springs: Deflection of springs by energy method, helical springs under axial load and under
axial twist (respectively for circular and square cross sections) axial load and twisting moment acting
simultaneously both for open and closed coiled springs, laminated springs.
Columns and Struts: Buckling and stability, slenderness ratio, combined bending and direct stress, middle
third and middle quarter rules, struts with different end conditions, Eulers theory for pin ended columns, effect
of end conditions on column buckling, Ranking Gordon formulae, examples of columns in mechanical
equipments and machines.
UNIT-IV
Thin cylinders & spheres: Introduction, difference between thin walled and thick walled pressure vessels, Thin
walled spheres and cylinders, hoop and axial stresses and strain, volumetric strain.
Thick cylinders:
Radial, axial and circumferential stresses in thick cylinders subjected to internal or external pressures,
compound cylinders, stresses in rotating shaft and cylinders, stresses due to interference fits.
UNIT-V
Curved Beams: Bending of beams with large initial curvature, position of neutral axis for rectangular,
trapezoidal and circular cross sections, stress in crane hooks, stress in circular rings subjected to tension or
compression.
Unsymmetrical Bending: Properties of beam cross-section, slope of neutral axis, stress and deflection in
unsymmetrical bending, determination of shear center and flexural axis (for symmetry about both axis and
about one axis) for I-section and channel section.
NCE 301 FLUID MECHANICS
Unit - I
Fluid and continuum, Physical properties of fluids, Rheology of fluids. Pressure-density-heigh Types of fluid
flows: Continuum & free molecular flows. Steady and unsteady, uniform and non-uniform, laminar and
turbulent t relationship, manometers, pressure transducers, pressure on plane and curved surfaces, centre of
pressure, buoyancy, stability of immersed and floating bodies, fluid masses subjected to linear acceleration and
uniform rotation about an axis.
Unit II
flows, rotational and irrigational flows, compressible and incompressible flows, subsonic, sonic and supersonic
flows, sub-critical, critical and supercritical flows, one, two and three dimensional flows, streamlines, continuity
equation for 3D and 1D flows, circulation, stream function and velocity potential. Dimensional analysis,
Buckinghams Pi theorem, important dimensionless numbers and their significance,
Unit - III
Potential Flow: source, sink, doublet and half-body. Equation of motion along a streamline and its integration,
Bernoullis equation and its applications- Pitot tube, orifice meter, venturi meter and bend meter, Hot-wire
anemometer and LDA, notches and weirs, momentum equation and its application to pipe bends.
Similarity Laws: geometric, kinematics and dynamic similarity, undistorted and distorted model studies.
Unit - IV
Equation of motion for laminar flow through pipes, Stokes law, transition from laminar to turbulent flow,
turbulent flow, types of turbulent flow, isotropic, homogenous turbulence, scale and intensity of turbulence,
measurement of turbulence, eddy viscosity, mixing length concept and velocity distribution in turbulent flow
over smooth and rough surfaces, resistance to flow, minor losses, pipe in series and parallel, power transmission
through a pipe, siphon, water hammer, three reservoir problems and pipe networks.
Unit - V
Boundary layer thickness, boundary layer over a flat plate, laminar boundary layer, application of momentum
equation, turbulent boundary layer, laminar sub layer, separation and its control, Drag and lift, drag on a sphere,
a two dimensional cylinder, and an aerofoil, Magnus effect. Introduction to compressible flow
NCE 302 Building Materials & Construction
Unit-1
Classification of building materials, buildingmaterialsandtheirperformance,economicsofthebuildingmaterials.
Stones, Requirement of good building stone, characteristics of building stones and their testing. Common
building stones. Methods of preservation of stones.
Bricks: Manufacturing process of clay bricks, classification of clay bricks. Properties of clay bricks, testing
methods for clay bricks .Problems of efflre scence & lime bursting in bricks & tiles.
Gypsum: properties of gypsum plaster, building products made of gypsum and their uses.
Lime: Manufacture of lime, classifications of limes, properties of lime.
Cement: Raw materials used, Process of Manufacturing, Chemical composition, compounds formed and their
effect on strength, Types of cement, Testing of cement properties, Uses of cement
Cement Concrete: Constituent materials and their properties, Grades of concrete, Factors affecting strength,
Properties of concrete at fresh and hardened stage, Testing of concrete, Methods of Curing of concrete.
Pozzolona: Chemical composition and requirements for uses, Natural and Artificial flash, Surkhi (burnt clay
pozzolona), ricehusk and ashpozzolona, properties and specifications for use in construction.
Timber: Classification and identification of timber, Fundamental Engineering Properties of timber, Defects in
timber, Factors affecting strength of timber, Methods of seasoning and preservation of timber. Wood based
products.
Asphalt, Bitumen and Tar: Terminology, specifications and uses, Bituminous materials.
Unit II
Chemistry of Plastics manufacturing process, classification, advantages of plastics, Mechanical properties and
use of plastic in construction.
Paints varnishes and distempers, Common constituents, types and desirable properties, Cement paints.
Ferrous metals, Desirable characteristics of reinforcing steel. Principles of cold working. Reinforcing steel
mechanical and physical properties chemical composition. Brief discussion on properties and uses of Aluminum
and lead.
Glass: Ingredients, properties types and use in construction.
Insulating Materials: Thermal and sound insulating material, desirable properties and types of insulating
materials.
Unit III
Components of building, area considerations, Construction Principle and Methods for layout, Damp proofing,
anti termite treatment in buildings, Vertical circulation means: staircases and their types, design and
construction. Different types of floors, and flooring materials (Ground floor and upper floors). Bricks and stone
masonry construction. Cavity wall hollow block construction.
Unit- IV
Doors, Windows and Ventilations, Construction details, types of doors and windows and their relative
advantages & disadvantages. Types of roof and roof treatments, Lintels and Chhajja, Functional efficiency of
Buildings.
Unit-V Natural Ventilation, Water Supply and Sanitary fittings (Plumbing), Electricity. Heating Ventilation &
Air conditioning, Mechanical Lifts and Escalators, Fire Fighting, Acoustics. Plastering different types, pointing,
Distempering, Color washing, Painting etc. Principles & Methods of building maintenance
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Gmail - New Examiner Allotment - 559Документ1 страницаGmail - New Examiner Allotment - 559kkОценок пока нет
- Anu Image Maker Size 38x 25 950: Continued...Документ1 страницаAnu Image Maker Size 38x 25 950: Continued...kkОценок пока нет
- Surveying ManualДокумент84 страницыSurveying ManualGSKReddyОценок пока нет
- BillDesk Payment GatewayДокумент1 страницаBillDesk Payment GatewaykkОценок пока нет
- Sanju Yada 9568400686 Ashish Kum 8057113727 Bhunesh Kumar9411Документ1 страницаSanju Yada 9568400686 Ashish Kum 8057113727 Bhunesh Kumar9411kkОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetkkОценок пока нет
- After This All SceneДокумент1 страницаAfter This All ScenekkОценок пока нет
- Malikhan Singh Inter College Thulai Block Sasni: SR No Student Name Father's Name Course/yr Mobile NoДокумент4 страницыMalikhan Singh Inter College Thulai Block Sasni: SR No Student Name Father's Name Course/yr Mobile NokkОценок пока нет
- Arjun SinghДокумент1 страницаArjun SinghkkОценок пока нет
- Wish Him Success in Provisional - Cum-ChaДокумент2 страницыWish Him Success in Provisional - Cum-ChakkОценок пока нет
- National Apprenticeship Training SchemeДокумент1 страницаNational Apprenticeship Training SchemekkОценок пока нет
- 559 Full Students List 2016Документ19 страниц559 Full Students List 2016kkОценок пока нет
- NCE 302 Building MaterialsДокумент7 страницNCE 302 Building MaterialskkОценок пока нет
- GP 801Документ1 страницаGP 801kkОценок пока нет
- ECE023Документ2 страницыECE023kkОценок пока нет
- National Apprenticeship Training SchemeДокумент1 страницаNational Apprenticeship Training SchemekkОценок пока нет
- K NДокумент14 страницK NkkОценок пока нет
- Cse 2ndyear SyllabusДокумент11 страницCse 2ndyear Syllabusashish jainОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam UniversityДокумент1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam UniversitykkОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)Документ1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)kkОценок пока нет
- Btech II Civil Engg 2014 20aug14Документ17 страницBtech II Civil Engg 2014 20aug14singhsaurabh1995Оценок пока нет
- ECE014Документ2 страницыECE014kkОценок пока нет
- B Tech 3april2014 PDFДокумент27 страницB Tech 3april2014 PDFParveen DhullОценок пока нет
- Ece-023 Transportation System and Planning 2011-12Документ4 страницыEce-023 Transportation System and Planning 2011-12kkОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)Документ1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)kkОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)Документ1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)kkОценок пока нет
- NGP601Документ1 страницаNGP601kkОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam UniversityДокумент1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam UniversitykkОценок пока нет
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)Документ1 страницаDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow (Uttar Pradesh)kkОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Segment RoutingДокумент375 страницSegment RoutinglillibithОценок пока нет
- Molten Salt Heat Storage PDFДокумент20 страницMolten Salt Heat Storage PDFchuckhsu1248Оценок пока нет
- Lab Report Welding (SMAW) - FizaДокумент13 страницLab Report Welding (SMAW) - FizaCheng Yee71% (7)
- 9702 w22 QP 36 PDFДокумент16 страниц9702 w22 QP 36 PDFsangdeepОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Leuco DyesДокумент312 страницChemistry Leuco Dyeskarel470% (1)
- Grade 7 MathДокумент3 страницыGrade 7 MathMarie Antonette SandiegoОценок пока нет
- Info Sphere Information Analyzer - Methodology and Best PracticesДокумент127 страницInfo Sphere Information Analyzer - Methodology and Best PracticesRoshava KratunaОценок пока нет
- NUS Past Year PaperДокумент8 страницNUS Past Year PaperSteven KuaОценок пока нет
- Nicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The NetworkДокумент9 страницNicira - It Is Time To Virtualize The Networkcsp_675491Оценок пока нет
- ST-2500FH: Part No. Description Part No. Description Part No. DescriptionДокумент1 страницаST-2500FH: Part No. Description Part No. Description Part No. DescriptionGergely IvánovicsОценок пока нет
- DMSM10 Espinosa Fiche de Stage Parachute GBДокумент2 страницыDMSM10 Espinosa Fiche de Stage Parachute GBHasan Junaid HashamОценок пока нет
- AHU ControlДокумент30 страницAHU Controlvn_hung3137Оценок пока нет
- Us 20060145019Документ11 страницUs 20060145019Raymond100% (4)
- SeepageДокумент25 страницSeepagesheikh jamilОценок пока нет
- ASME B1.16 - B1.16M - 1984 (Reaffirmed 2006) PDFДокумент184 страницыASME B1.16 - B1.16M - 1984 (Reaffirmed 2006) PDFKristin Jones100% (1)
- Summative Test Gr7Документ1 страницаSummative Test Gr7Les Angelz100% (1)
- Lab ReportДокумент4 страницыLab ReportSyafiq MTОценок пока нет
- 3Документ8 страниц3K@mR@N D@uD P@nHw@RОценок пока нет
- Alkane and AlkeneДокумент40 страницAlkane and AlkenePawankumar Gupta91% (11)
- Landscape Products: Technical GuideДокумент124 страницыLandscape Products: Technical Guidegabbo24Оценок пока нет
- Lasal: Laser Cutting SolutionsДокумент4 страницыLasal: Laser Cutting SolutionsGeorge ZiovasОценок пока нет
- 21 10 26 Tastytrade ResearchДокумент7 страниц21 10 26 Tastytrade ResearchCSОценок пока нет
- PT 849 Req D PatchesДокумент34 страницыPT 849 Req D PatchesxwОценок пока нет
- Elementary Data Organisation-1Документ15 страницElementary Data Organisation-1zidhi bachaОценок пока нет
- Cooling Water Sump Model Studies Through CFD AnalysisДокумент6 страницCooling Water Sump Model Studies Through CFD AnalysisvijayasarathiОценок пока нет
- Prelims Solution Ce18Документ6 страницPrelims Solution Ce18Mark Lester LualhatiОценок пока нет
- R1218x SERIES: Step-Up DC/DC Converter For White LED BacklightДокумент21 страницаR1218x SERIES: Step-Up DC/DC Converter For White LED Backlight666667Оценок пока нет
- 34centaxcx Sec en 12 16 PDFДокумент110 страниц34centaxcx Sec en 12 16 PDFbogodavidОценок пока нет
- CD30LA0011EДокумент357 страницCD30LA0011EMichael Naím Dévora QuintanarОценок пока нет
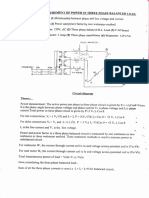
- Experiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadДокумент2 страницыExperiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadTripti GuptaОценок пока нет