Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
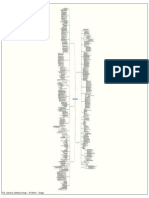
One Page Overview of ITILV3
Загружено:
athmavАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
One Page Overview of ITILV3
Загружено:
athmavАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
One
Page Overview of ITILV3
KEY AREAS
WHAT IS ITIL?
SERVICE
STRATEGY
SERVICE DESIGN
SERVICE
TRANSITION
KEY POINTS TO CONSIDER
SERVICE MANAGEMENT
Service Management is a set of
organisa.onal capabili.es for delivering
value and outcomes customers want
without the ownership of specic costs
and risks
ITIL
DEFINITION
ITIL
is
a
set
of
best
prac.ces
that
oers
advice
and
guidance
on
the
implementa.on
and
con.nued
delivery
of
service
management
ITIL
OBJECTIVES
Aligns
IT
services
with
the
current
and
future
needs
of
the
business
and
its
customers
Enables
standard
terminology
across
business
and
IT
Improves
the
quality
of
the
IT
services
delivered
Reduces
the
long-term
cost
of
service
provision
SERVICE
OBJECTIVES
Iden.fy
business
needs
The
type
of
services
required
Who
are
the
customers?
Are
these
services
available
in
the
marketplace?
How
will
outcomes,
availability,
capacity,
con.nuity
and
security
of
services
be
measured?
INPUTS & OUTPUTS
These needs, the level of u.lity
and warranty
are iden.ed and agreed
within a Service Level Package
Strategies
Policies
Resources & constraints
SLP from requirements
SOURCING STRTEGY & SERVICE PROVISIONING MODELS
Making informed decisions on service sourcing in terms of internal
services, shared services or outsourcing
Managed Service where a business unit requiring a service fully
funds the provision of that service for itself
Shared Services is the provisioning of mul.ple services to one or
more business units via shared infrastructure
UJlity Services are provided on the basis of demand by each
customer, how oXen, and at what .mes needed
SERVICE DESIGN OBJECTIVES
It starts with a set of requirements, and ends with the development of a service
solu.on to meet business needs Services meet business needs
Processes for service lifecycle
Iden.fy and manage risks
Resilient IT infrastructures Design methods and metrics
Produce and maintain plans, processes, policies, standards, architectures,
frameworks and documents to support the design of quality solu.ons
Develop skills within IT
Contribute to service quality
SERVICE DESIGN ASPECTS
1. New or changed service
solu.ons
2. Service management
systems and tools
3. Technology architectures
and management systems
4. Processes, roles and
capabili.es
5. Measurement and metrics
EFFECTIVE & SUCCESSFUL SERVICE TRANSITION
The role of Service Transi.on is to deliver services that are required by the
business into opera.onal use
Eec.ve Service Transi.on is delivered by involving all relevant par.es,
ensuring appropriate knowledge is available
KEY
PRINICPLES
Understanding
all
services,
their
u.lity
and
warran.es
Establishing
a
formal
policy
and
common
framework
for
implementa.on
of
all
required
changes
Suppor.ng
knowledge
transfer,
decision
support
and
re-use
of
processes,
systems
and
other
elements
Being
proac.ve
and
determining
likely
course
of
issues,
and
when
elements
of
a
service
do
need
to
be
adjusted,
this
is
undertaken
logically
and
is
fully
documented
For successful transiJon to take place, the following is needed:
Poten.al business value and who it is delivered to
Iden.ca.on of all stakeholders within supplier, customer and other areas
Resources available for modica.on of the service design where the need is
detected during transi.on
SERVICE
OPERATION
OBJECTIVES
Service
Opera.on
is
to
deliver
agreed
levels
of
service
to
users
and
customers,
and
to
manage
the
applica.ons,
technology
and
infrastructure
that
support
delivery
of
the
services
It
is
during
this
stage
of
the
lifecycle
that
services
actually
deliver
value
to
the
business
PURPOSE
Con.nual
Service
Improvement
(CSI)
is
concerned
with
maintaining
value
for
customers
through
the
con.nual
evalua.on
and
improvement
of
the
quality
of
services
Third i Consul.ng
ADOPTION & COMPLIANCE
Although ITIL has been adopted by thousands of companies, it is a
set of best prac.ces and not a standard therefore, neither tools,
processes, or people can be deemed ITIL compliant
Processes and organisa.ons can be assessed against ISO 20000 (IT
Service Management standard based on ITIL)
KEY PROCESSES AND ACTIVITIES
STRATEGY GENERATION
The vision and direc.on
The basis on which the
provider will compete
Plan to achieve their vision
Their approach in the way of
doing things
FINANCIAL
MGT
Financial
Management
covers
the
func.on
and
processes
responsible
for
managing
an
IT
service
providers
budge.ng,
accoun.ng
and
charging
requirements
SERVICE PORTFOLIO MGT
SPM is proac.ve management
of IT investments across the
service lifecycle (concept,
design, transi.on pipeline, live
services)
DEMAND
MANAGEMENT
The
purpose
of
Demand
Management
is
to
understand
and
inuence
customer
demand
for
services
and
the
provision
of
capacity
to
meet
these
demands
SERVICE CATALOG MGT
SCM provides a single,
consistent source of
informa.on all of the services
SERVICE LEVEL MGT
The SLM process ensures all
opera.onal services and
performance are measured
CAPACITY
MGT
This
is
a
point
of
focus
for
all
capacity
and
performance
service
&
resource
issues
AVAILABILITY
MGT
This
provides
a
point
of
focus
or
all
availability-related
issues
(services
&
resources)i
IT SERVICE CONTINUITY ITSCM
is to maintain the appropriate
on-going recovery capability
within IT services to match the
agreed requirements
INFORMATION
SECURITY
The
ISM
process
aligns
IT
security
with
business
security
and
ensures
informa.on
security
is
n
all
IT
services
SUPPLIER
MANAGEMENT
This
ensures
suppliers
and
the
services
they
provide
are
managed
to
support
IT
service
targets
&
business
needs
KEY
ACTIVITIES
Business
needs
analysis
Design
&
development
of
services,
technology,
processes
&
metrics
CHANGE
MANAGEMENT
A
standardised
methods
used
for
the
handling
of
all
changes
recorded
in
the
CMS
SERVICE ASSET &
CONFIGURATION MGT
SACM iden.es, controls and
accounts for IT assets & CIs
KNOWLEDGE
MGT
This
ensures
the
right
person
has
the
right
knowledge,
at
the
right
.me
to
deliver
&
support
TRANSITION PLANNING &
SUPPORT
Plan resources & control risks
to transi.ons service to OPS
RELEASE & DEPLOYMENT
This process assembles all
aspects of services into
produc.on and establish
eec.ve use of new or
changed services
SERVICE & VALIDATION
TESTING
This process provide evidence
that the new/changed service
supports business needs &
SLAs
EVALUATION
This
ensure
services
meets
business
needs
by
establishing
the
appropriate
metrics
and
measurement
techniques
SERVICE
TRANSITION
ACTIVITIES
Managing
the
following:
Communica.ons
in
IT
Organisa.onal
change
Stakeholders
IT
OPERATION
MGT
For
the
management
and
maintenance
of
the
IT
infrastructure
required
to
deliver
the
agreed
SLAs
IT
Opera.ons
Control
is
usually
staed
by
shiXs
of
operators
who
carry
out
rou.ne
opera.onal
tasks.
Facili.es
Management
is
responsible
for
management
of
data
centres,
computer
rooms
and
recovery
sites
INCIDENT
MANAGEMENT
It
is
to
restore
normal
service
as
quickly
as
possible,
and
to
minimise
the
adverse
impact
on
business
opera.ons
REQUEST
FULFILLMENT
Enable
users
to
request
and
receive
standard
services,
to
source
and
deliver
them
&
to
provide
informa.on
on
them
ASSET
MANAGEMENT
Provides
the
rights
for
users
to
be
able
to
access
services
&
preven.ng
access
to
non-
authorised
users
EVENT MANAGEMENT
PROBLEM MANAGEMENT
OPERATION ACTIVITIES
An event may indicate that
something is not func.oning
correctly, leading to an incident
being logged
Prevents problems and
resul.ng incidents from
happening, and to eliminate
recurring incidents
Management
of
the
infrastructure
A
central
point
to
monitor
and
managing
services
5. ANALYSE THE DATA
Data analysis transforms the
informa.on into knowledge
of the events that are
aec.ng the organisa.on
Once the data is processed
into informa.on, the results
can be analyzed to answer
ques.ons such as:
Are targets being met?
Are there any clear
trends?
Are correc.ve ac.ons
required?
What would be the cost?
6. PRESENT & USE THE
INFORMATION
The informa.on needs to be
presented in the right
format, at the right level and
in the right way for the
intended audience
IT needs invest the .me to
understand specic business
goals and translate IT metrics
to reect an impact against
these business goals
7.
IMPLEMENT
THE
CORRECTIVE
ACTION
The
knowledge
gained
is
used
to
op.mise,
improve
and
correct
services,
processes,
and
all
other
suppor.ng
ac.vi.es
and
technology
The
correc.ve
ac.ons
required
to
improve
the
service
should
be
iden.ed
and
communicated
to
the
organisa.on
The
7-Step
Improvement
Process
is
con.nual
and
loops
back
to
the
beginning
KEY FUNCTIONS
CONTINUAL
SERVICE
IMPROVEMENT
4
Ps
OF
DESIGN
1. People:
the
IT
people,
skills
&
competencies
2. Products:
technology
used
for
delivery
of
IT
services
3. Processes:
the
processes,
roles
and
ac.vi.es
for
provision
of
IT
services
4. Partners:
Suppliers
suppor.ng
IT
services
SERVICE
LIFECYCLE
ITIL
has
5core
books
for
each
stage
of
the
service
lifecycle
Service
Strategy
Service
Design
Service
Transi.on
Service
Opera.ons
Con.nual
Service
Improvement
SERVICE
DESK
Service
Desk
provides
a
single
central
point
of
contact
for
all
IT
users
Logs
all
incidents
and
requests,
categorising
and
priori.sing
them
First-line
inves.ga.on
and
diagnosis
Managing
the
lifecycle
of
incidents
and
requests
Inform
users
of
status
of
services,
incidents,
requests
TECHNICAL
MGT
This
func.on
includes
all
the
people
who
manage
the
IT
infrastructure
Knowledge
&
exper.se
Design
new
services
Dene
architecture
standards
Con.nual
service
improvement
projects
Assistance
with
service
management
tools
APPLICATION
MGT
This
technical
unc.on
includes
all
the
people
who
provide
exper.se
for
management
&
support
of
applica.ons
Applica.on
Management
works
closely
with
Development
Applica.on
Management
is
usually
organized
by
the
lines
of
business
that
each
team
supports
2. DEFINE WHAT YOU CAN
MEASURE
Perform a gap analysis on
what can be measured today
and the "TO BE"
measurements desired
The gaps and poten.al
impacts can then be
reported to the business and
IT management
3. GATHER THE DATA
Quality monitoring and data
collec.on is the goal of CSI
which focuses on the
eec.veness of a service,
process, tool, organisa.on or CI
to iden.fy where changes can
be made to improve the
exis.ng level of service or IT
performance
THE 7 STEP IMPROVEMENT PROCESS
1.DEFINE WHAT YOU SHOULD
MEASURE
Dene a set "TO BE"
measurements to fully support
the goals of the organisa.on
4. PROCESS THE DATA
Raw data is processed into
the required format, typically
providing an end- to-end
perspec.ve on the
performance of services and
processes
It is key to understand that
components impact on the
larger infrastructure and IT
service
Kigospace.com
Вам также может понравиться
- ITIL Core Concepts Summary PDFДокумент31 страницаITIL Core Concepts Summary PDFRafael SolisОценок пока нет
- Change And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОт EverandChange And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОценок пока нет
- Service Desk Transformation A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionОт EverandService Desk Transformation A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionОценок пока нет
- Disaster Recovery Service-Level Management Complete Self-Assessment GuideОт EverandDisaster Recovery Service-Level Management Complete Self-Assessment GuideОценок пока нет
- Pragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachОт EverandPragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachОценок пока нет
- The SAM Leader Survival Guide: A Practical Success Guide for Software Asset Management ProfessionalsОт EverandThe SAM Leader Survival Guide: A Practical Success Guide for Software Asset Management ProfessionalsОценок пока нет
- Release Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsОт EverandRelease Management Process Documentation Standard RequirementsОценок пока нет
- ITIL Service Operation in PolicyДокумент7 страницITIL Service Operation in PolicyilayavplОценок пока нет
- ITIL Process Flows PDFДокумент11 страницITIL Process Flows PDFdanroddОценок пока нет
- Checklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enДокумент18 страницChecklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enFeleke AfeworkОценок пока нет
- Third Party Risk Management Framework A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОт EverandThird Party Risk Management Framework A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОценок пока нет
- Maturing Security Operations Centers A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОт EverandMaturing Security Operations Centers A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОценок пока нет
- ISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОт EverandISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionОценок пока нет
- CHG Mindmap v4Документ1 страницаCHG Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallОценок пока нет
- Computer security incident management Standard RequirementsОт EverandComputer security incident management Standard RequirementsОценок пока нет
- ITIL BasicsДокумент22 страницыITIL Basicshescribd100% (2)
- ITIL Service DeliveryДокумент1 страницаITIL Service DeliverygringoricanОценок пока нет
- ISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОт EverandISO IEC 27001 Lead Implementer A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОценок пока нет
- Incident Management for Procurement A Clear and Concise ReferenceОт EverandIncident Management for Procurement A Clear and Concise ReferenceОценок пока нет
- Information Technology Security Audit A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОт EverandInformation Technology Security Audit A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionОценок пока нет
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingДокумент17 страницITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloОценок пока нет
- ITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideДокумент2 страницыITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideMadhur Sawant100% (2)
- Template For IT Service Continuity PlanДокумент4 страницыTemplate For IT Service Continuity Plangigioa100% (1)
- ITIL Strategy Design Transition Operation ProcessДокумент32 страницыITIL Strategy Design Transition Operation ProcessrkamundimuОценок пока нет
- Stepping Heavenward by Prentiss, E. (Elizabeth), 1818-1878Документ181 страницаStepping Heavenward by Prentiss, E. (Elizabeth), 1818-1878Gutenberg.orgОценок пока нет
- Nebula - 150 User ManualДокумент94 страницыNebula - 150 User ManualSamuel MongeОценок пока нет
- CemeraДокумент84 страницыCemerashyam prakash sharmaОценок пока нет
- QuestionДокумент6 страницQuestionVj Sudhan100% (3)
- Gas Reservoir Engineering Application ToolkitДокумент20 страницGas Reservoir Engineering Application Toolkitnishant41288100% (1)
- Ford OBD2 MonitorДокумент282 страницыFord OBD2 MonitorAnonymous 4IEjocОценок пока нет
- Information Security PolicyДокумент16 страницInformation Security Policymohammed oumerОценок пока нет
- Industrial Report On InfosysДокумент14 страницIndustrial Report On InfosysMitesh ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Tps60403-q1 (Charge Pump) Signal CondДокумент29 страницTps60403-q1 (Charge Pump) Signal CondCH Pavan KumarОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Quiz Section A Chapter 1 - SolutionДокумент29 страницModule 2 Quiz Section A Chapter 1 - SolutionSaad RashidОценок пока нет
- Let'S Learn Algebra in Earl'S Way The Easy Way!Документ23 страницыLet'S Learn Algebra in Earl'S Way The Easy Way!Cristinejoy OletaОценок пока нет
- General Format Purdue Writing LabДокумент1 страницаGeneral Format Purdue Writing LabAriana QuilesОценок пока нет
- Color Palettes For Graphic DesignДокумент19 страницColor Palettes For Graphic DesignClarence Tuazon FloresОценок пока нет
- Control System Applied Principles of ControlДокумент23 страницыControl System Applied Principles of ControlAngelus Vincent GuilalasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ19 страницChapter 3Mohamad Hafizi PijiОценок пока нет
- Audio Engineering Advice - January2023 2023 V1.6Документ31 страницаAudio Engineering Advice - January2023 2023 V1.6jeremy hartigОценок пока нет
- 5713 How Microsoft Moves Their SAP Landscape Into AzureДокумент41 страница5713 How Microsoft Moves Their SAP Landscape Into AzureHaitham DesokiОценок пока нет
- Cornet-ED-78S UserManualQeng PDFДокумент2 страницыCornet-ED-78S UserManualQeng PDFpdfjunkieОценок пока нет
- MCA 2020 - List of Applicants Shortlisted For Interview (F) - 30 May 2020Документ21 страницаMCA 2020 - List of Applicants Shortlisted For Interview (F) - 30 May 2020shatabdi mukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Management Information System: Case Study ofДокумент7 страницManagement Information System: Case Study ofAnonymous YSA8CZ0Tz50% (1)
- English 6 - EJE 4 - Week 10Документ3 страницыEnglish 6 - EJE 4 - Week 10Yan Carlos Morales MurciaОценок пока нет
- Coal Combustion TechnologiesДокумент31 страницаCoal Combustion TechnologiesFawad MushtaqОценок пока нет
- Design of 400kV200kV SSДокумент62 страницыDesign of 400kV200kV SSAbinav AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Datasheet LIGO SP Series Fuel Level SensorДокумент24 страницыDatasheet LIGO SP Series Fuel Level SensorPACKWOODS COMPANYОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ67 страницChapter 4longtran1191Оценок пока нет
- Math Lecture 1Документ37 страницMath Lecture 1Mohamed A. TaherОценок пока нет
- Case RCBДокумент76 страницCase RCBSaurabh KatariaОценок пока нет
- SAS Part-1 SyllabusДокумент7 страницSAS Part-1 Syllabusnagarjuna_upsc100% (1)
- Target Market Profile WorksheetДокумент6 страницTarget Market Profile WorksheetMabel WilliamОценок пока нет