Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
18 07 2016 Page 12
Загружено:
rajesh1924Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
18 07 2016 Page 12
Загружено:
rajesh1924Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cr*S l$
yMSt AlP rZ $
yls (GG).. $tMS$ : O 22
Ol>lZ G[M>tMS M>l B Cyl*
$syl (DIG) l {Z l]l$ Z..
sMSMS B, OsMS Ats, $ Btl,
$ Btl $tMS$: O 23
* ]ll l
MSZ l$l ]l* {s $syl
l V>Z A{s {sVS $tMS$:
O 23
]l$ 18-7-2016
{$]l GV>j$ll&2016..
BVS$t 7]l fVS]l$. A$$ CsMS
{l N^l Es$. MS E*VSyl
lV> jMS$t #$$ *_]l l*yl
st, ]llMS ]l*$ A$..
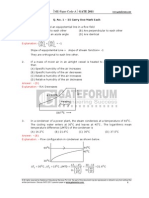
CIVILS PRELIMS-2016 MODEL TEST
Number of Questions: 100
1. Which of the following is not true about East
India Company's administration?
a. Lord Cornwallis was the pioneer of administrative setup in British India.
b. British Indian Army was always commanded
by British officers.
c. The Govt of India Act of 1858 provided for
the Civil Services exam to be held on an
open competition level for Indians too.
d. Cornwallis introduced the idea of 'Circle' as
a smaller unit in districts in police administration.
2. Which of the following is not an aspect of
Constructive programme of Gandhi?
a. Promotion of Khadi
b. Removing untouchability
c. Attaining 'poorna swaraj'
d. Promotion of Hindu-Muslim unity
3. Which of the following is not true about
Woods Despatch?
a. It contained a proposal to establish universities in all the Presidency towns on the model
of English Universities.
b. It provided for women education.
c. It did not allow private sector into education
as it expected the sector to go out of control
of the Britishers.
d. The aim of British education was to promote
western learning.
4. Which of the following is not true about the
Interim Government formed in 1946?
a. The government was formed from the newly
elected Constituent Assembly of India.
b. The Vice President of the Viceroy's
Executive Council was Jawaharlal Nehru.
c. Liaqat Ali Khan was very influential in All
India Muslim League and held the portfolio
of Home Affairs.
d. Mohammad Ali Jinnah was not a member of
the Council of Ministers of the Interim
Government.
5. Royal Indian Navy Mutiny refers to:
a. A revolt in the Royal Indian Navy arising due
to a tussle between an Indian and a British
naval officer.
b. A strike due to the hardships faced by the ratings in terms of the food, pay and racial discrimination.
c. The strike started as the ratings demanded
complete independence from the British rule
at the behest of the Congress and the Muslim
League.
d. The strike started as a part of the Quit India
Movement in the Indian Navy.
6. Which of the following is true about the
Dyarchy established by the Government of
India Act 1919?
1. The Dyarchy was established in the central
legislature.
2. Dyarchy means some part of the government
was responsible to the legislature, while
some powers vested exclusively with the
Governor General.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct.
7. Which of the following are proposed in the
Fourteen Points of Jinnah?
1. Cabinet both at central and provincial levels
must consist of one-third Muslim strength.
2. Muslim representation in central legislature
must not be less than one third.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct.
8. Which of the following is true about Bhagat
Singh?
1. As per the plans of the HSRA, Bhagat Singh
was involved in throwing a bomb in the
Central Legislative Assembly against the
passage of Public Safety Bill and the Trade
Disputes Bill.
2. Bhagat Singh was also involved in the assassination of a police official involved in the
lathi-charge of Lala Lajput Rai, which led to
his death.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct
Civils Prelims Model Test-KEY & EXPLANATION
1. Ans: c
Exp: First tenure of Cornwallis was from 1786 to
1793. He introduced Permanent Settlement
of Bengal, Judicial reforms, police reforms,
and reforms to curb corruption in the East
India Company.
Open competition in civil services was
provided by the Charter Act of 1853.
2. Ans: c
Exp: Constructive Program (CP) is a term coined
by Mahatma Gandhi to describe one of the
two branches of his satyagraha, the other
being some form on nonviolent resistance,
e.g. Civil Disobedience, sometimes referred
to as "obstructive program". CP is a way of
carrying out a struggle through community
and self-improvement by building structures, systems, processes, and resources that
are alternatives to oppression and promote
self-sufficiency and unity in the resisting
community.
3. Ans: c
Exp: An education department was to be set in
every province.
Universities on the model of the London
University be established in big cities such
as Bombay, Calcutta and Madras.
At least one government school be opened
in every district.
Affiliated private schools should be given
grant-in- aid.
The Indian natives should be given training
in their mother tongue also.
Wood's Despatch is called MagnaCarta of
English Education in India.
In accordance with Wood's despatch, Education Departments were established in every province and universities were opened at
Calcutta, Bombay and Madras in 1857 on
the model of the London University.
Later more universities were opened in
Punjab in 1882 and at Allahabad 1887.
4. Ans: c
Exp: After the end of the World War II, the
British authorities in India released all
political prisoners who had participated in
the Quit India movement. The Indian
National Congress, the largest Indian
political party, which had long fought for
national independence, agreed to participate
in the elections for a Constituent Assembly,
as did the Muslim League. The newly
elected government of Clement Attlee
dispatched the 1946 Cabinet Mission to
India to formulate proposals for the
formation of a government that would lead
to an independent India. Nehru was the Vice
President. Home affairs were under
Vallabhai Patel and Liaqat Ali Khan held
Finance portfolio. Jinnah had no portfolio.
5. Ans: b
Exp: On February 18, 1946, a section of noncommissioned officers and sailors known as
Ratings, serving in the Royal Indian Navy,
mutinied against the British Officers. The
mutiny started as a strike by the ratings to
protest against the hardships regarding pay,
food and racial discrimination.
6. Ans: b
Exp: In Government of India Act 1919 the spheres of the central and provincial governments were demarcated by a division of
subjects into "central" and "provincial". Generally speaking, the central subjects included all subjects directly administered by the
Government of India or in which extra-provincial interests were dominant. The provincial subjects included subjects in which
the interests of the provinces essentially
predominated. The Dyarchy was for the
Provincial Governments. The provincial
subjects were divided into two categories
viz., reserved and transferred. The reserved
subjects were kept with the Governor and
transferred subjects were kept with
Governor acting with the Indian Ministers.
7. Ans: b
Exp: 14 points:
The form of the future constitution should
be Federal, with the residuary power vested
in the provinces.
A uniform measure of the autonomy shall
be granted to all provinces.
All legislatures in the country and other
elected bodies shall be constituted on the
definite principle of adequate and effective
representation of minorities in every
province without reducing the majority in
Marks: 200
Time : 120 Min
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct
9. Which of the following is true about the
Rowlatt Act?
1. The Act was in the light of the lapsing of the
Defence of India Regulations Act 1915.
2. The Act was a result of perception of the
British Government that some revolutionary
nationalists would engage in some conspiracies.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct.
10. Which of the following is true about the moderates and extremists in Congress during the
split of 1907?
1. Moderates supported the partition of Bengal
while the extremists did not support the partition.
2. Moderates did not support the expansion of
boycott movement to the other parts of the
country, while the extremists supported.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct.
11. Which of the following is true about the Indian
economy during the British rule?
1. The drain theory was central to the criticism
made by Indian leaders.
2. The British imports ruined the Indian handicrafts and textile industry and the tariff policies served the interests of British Capitalist
classes.
3. The benefits of railways were reaped by
British in terms of capital investment and the
encouragement of their iron and steel industry.
a. 1 and 3 only
b. 1 and 2 only
c. 2 and 3 only
d. All are correct
any province to minority or even equality.
In the Central legislature, Muslim representation shall not be less than one third.
Representation of the communal groups
shall continue to be by separate electorates
provided that it shall be open to any
community at any time to abandon its
separate electorate in favour of the joint
electorates.
Any terrestrial redistribution that might at
any time be necessary shall not in any way
affect the Muslim majority in Punjab,
Bengal and NWF Province.
Full religious liberty that is liberty of belief,
worship and observance, propaganda,
association and education shall be
guaranteed to all communities.
No bill or resolution or any part thereof
shall be passed in any legislature or any
other elected body if three fourths of the
members of any community in that
particular body oppose it being injurious to
that of the community.
Sind should be separated from the Bombay
Presidency.
Reforms should be made in the NWF
Province and Baluchistan.
Provision should be made in the
Constitution giving Muslims an adequate
share along with the other Indians in all the
services of the State and Local self
governing bodies having due regard to the
requirements of efficiency.
The Constitution should embody adequate
safeguards to the protection of the Muslim
Culture, education, language, religion,
personal laws, and Muslim charitable
institutions. They should get their due share
in grant-in-aid.
No cabinet, either central or provincial,
should be formed without there being at
least one third of the Muslim Ministers.
No change shall be made in the constitution
by the Central legislature except with the
concurrence of the states constituting the
Indian Federation
8. Ans: c
Exp: Singh's plan was to explode a bomb inside
the Central Legislative Assembly. The
nominal intention was to protest against the
Public Safety Bill, and the Trade Dispute
12. Which of the following is true about the period
around 5th century AD?
1. Bhakti tradition started during the Pallava
regime in the Southern peninsula region.
2. Cholas tried to establish their supremacy in
the land lying between Krishna and
Tungabhadra.
a. Only 1 is correct. b. Only 2 is correct.
c. Both 1 and 2 are correct.
d. Neither 1 nor 2 is correct.
13. Which god/goddess among the following is not
a part of "Panchadeva" during the post-Gupta
times?
a. Surya b. Durga c. Agni d. Vishnu
14. Which of the following is not a part of the
navarasas in the Bharata's Natya shastra?
a. Roudra
b. Veera
c. Sahitya
d. Bhayanaka
15. Consider the following statements related to
Livestock resource and its contribution to
human livelihood:
1. It provides cash income or income in kind
through the sale of animals.
2. It promotes gender equity.
3. The growth in livestock sector remained
about 1.5 times larger than in the crop sector.
Which of the statements given above are incorrect?
a. Only 1 & 2
b. Only 2 & 3
c. Only 1 & 3
d. None of the above.
16. Consider the following statements about
Montane Temperate forests:
1. Wet Montane temperate forests are found in
east of Nepal into Arunachal Pradesh in the
North and in the Nigliris in the South.
2. The forests in the northern region are less
denser than in the South.
3. Montane forests have oak, alder, chestnut,
birch, and cherry trees. There are a large
variety of orchids, bamboo and creepers in
such forests.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a. Only 1
b. Only 2 & 3
c. Only 1 & 3
d. All of the above.
17. Consider the following statements related to the
term "Reserve Forests":
1. The term was first introduced in the Indian
Forest Act, 1927 in British India, to refer to
certain forests that are granted protection
under the British crown in British India.
2. Rights to activities like hunting and grazing
are given to communities living on the
Act, which had been rejected by the
Assembly but were being enacted by the
Viceroy using his special powers; the actual
intention was for the perpetrators to allow
themselves to be arrested so that they could
use court appearances as a stage to
publicize their cause. To avenge the killing
of LalaLajpat Rai, Bhagat Singh, Raj guru,
Jai Gopal and Sukh Dev conspired to kill
the police chief, Scott. But they shot on the
DSP - J. P. Saunders, who was killed on the
spot. Bhagat Singh immediately fled from
Lahore and to avoid recognition, he cut his
beard and hair. Later he was trailed in this
Lahore Conspiracy Case when he was
captured after throwing bomb in Delhi
Assembly.
9. Ans: c
Exp: An extension to the Defense of India
Regulations Act 1915 was passed as
"Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act
of 1919", in March of that year. This was
also known as Rowlatt Act, which were
intended to crush subversive movements,
provided for stricter control of the press,
arrests without warrant, indefinite detention
without trial, and in camera trials of
political prisoners, without juries. These
Acts moreover denied the accused the right
to know who his accusers were or to
challenge the evidence on which he was
being tried, and required ex-political
offenders to deposit securities and forbade
them from taking part in any political,
educational, or religious activities.
10. Ans: b
Exp: Extremists wanted to spread the movement
outside the regions of Bengal and also to
include other forms of associations like
government service, law courts, legislative
councils etc. and thus start a nationwide
mass movement. Moderates were totally
opposed to boycott councils and other
associations. Moderates also did not like to
extend the boycott beyond Bengal.
However, they supported Swadeshi
Movement and condemned the policies of
Curzon and the partition of Bengal.
11. Ans: d
Exp: Indian industries such as silk and textiles
collapsed. The new manufacturing methods
fringes of the forest, who sustain their livelihood partially or wholly from forest
resources or products.
3. The first Reserve Forest of India was Corbett
National Park.
4. They are declared by respective State governments.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a. Only 2, 3 & 4
b. Only 1, 2 & 3
c. Only 1, 3 & 4
d. All of the above.
18. To improve the quality of air resource, Clean
Development Mechanism has been introduced.
Consider the following statements related to the
advantages of CDM:
1. Provides credits to developing countries for
technology transfer.
2. The prices of credits are flexible as it crowds
out legitimate projects.
3. Benefits developed countries more as it provides technological and environmental markets.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a. Only 1
b. Only 2
c. Only 1 & 3
d. Only 2 & 3
19. Consider the following statements about the
Ecological Sensitive Area (ESA).
1. It is a bio-climatic unit wherein human
impacts have locally caused irreversible
changes in the structure of biological communities and their natural habitats.
2. Protected areas in contrast to ESA, largely
focused on flagship species and their habitats, leave out small, unique habitats.
3. ESA's may have Protected Areas embedded
in them, of various extents.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a. Only 1 & 2
b. Only 1 & 3
c. Only 2 & 3
d. All of the above
20. Consider the following statements:
1. Leadership in Energy and Environmental
Design (LEED) is a set of rating systems for
the design, construction, operation, and
maintenance of green buildings only.
2. LEED is developed by the U.S. Green
Building Council (USGBC).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a. Only 1
b. Only 2
c. Both 1 & 2
d. Neither 1 nor 2
replaced the old manufacturing methods in
ship building, metal works, glass works,
paper and many other crafts. In summary,
after losing the industries, Indians were
confined with the only industry- that was
agriculture. If Indians wanted to export,
there was a heavy duty imposed over there
for entry in the market. The acts and
legislations excluded the Indian goods from
British markets and other foreign markets.
12. Ans: a
Exp: Rise of Cholas took place only in the 9th
century. Alvars and Nayanars were also
considered to be part of the Bhakti movement around 8-9 century AD.
13. Ans: c
Exp: Panchadeva puja is the worship of five gods
in Hinduism. The five deities worshipped
are Ganesha, Vishnu, Shiva, Goddess
Durga, and Surya.
14. Ans: c
Exp: Shringara, hasya, karuna, raudra, veera,
bhayanaka, bhibatsa, adbhuta and shanta
are the navarasas.
15. Ans: d
16. Ans: a
Exp: The trees found in the western section are
broad-leaved oak, brown oak, walnut,
rhododendron, etc. The forests in the
northern region are denser than in the
South.
17. Ans: c
Exp: Rights to all activities like hunting, grazing,
etc. in reserved forests were banned unless
specific orders are issued otherwise. The
first Reserve Forest of India was Satpura
National Park.
18. Ans: a
19. Ans: d
20. Ans: a
Exp: Leadership in Energy and Environmental
Design (LEED) is a set of rating systems for
the design, construction, operation, and
maintenance of green buildings, homes and
neighbourhoods.
(Continued in
Tomorrow's Bhavitha)
Вам также может понравиться
- Active DSA ListДокумент42 страницыActive DSA ListMukul Nagwekar67% (3)
- ICSE Apendix II - Prescribed Books ListДокумент7 страницICSE Apendix II - Prescribed Books Listpankaj koliОценок пока нет
- CseДокумент292 страницыCsePritesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Indian Polity Chapter 1 - Historical Background MCQДокумент13 страницIndian Polity Chapter 1 - Historical Background MCQniit cts91% (11)
- Dasarathi Rangacharya PDFДокумент6 страницDasarathi Rangacharya PDFrajesh1924100% (1)
- Dasarathi Rangacharya PDFДокумент6 страницDasarathi Rangacharya PDFrajesh1924100% (1)
- Herbal Hair OilДокумент26 страницHerbal Hair Oilrajesh1924100% (2)
- Class 8 History CH 12Документ4 страницыClass 8 History CH 12SushilОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12-India After Independence: Page No: 172Документ4 страницыChapter 12-India After Independence: Page No: 172Piyush KashyapОценок пока нет
- Chapter Wise Indian Polity MCQ'S With Explanations Historical BackgroundДокумент198 страницChapter Wise Indian Polity MCQ'S With Explanations Historical BackgroundDon Sen100% (1)
- CH 12Документ2 страницыCH 12SHABAJ KHANОценок пока нет
- 4th Sem Pol SC Complete NotesДокумент29 страниц4th Sem Pol SC Complete NotesSomnath PahariОценок пока нет
- Indian Polity: Question Set 1: Q1-50Документ14 страницIndian Polity: Question Set 1: Q1-50mail2svenkatesh2792Оценок пока нет
- Constitutional Dev Set 2Документ21 страницаConstitutional Dev Set 2gitansh sharmaОценок пока нет
- VIII History Ch. 10 India After Independence QAДокумент1 страницаVIII History Ch. 10 India After Independence QASharad MusaleОценок пока нет
- 13 India After IndependenceДокумент5 страниц13 India After IndependenceanjanaОценок пока нет
- Government of India Act 1919Документ9 страницGovernment of India Act 1919Sarthak KapoorОценок пока нет
- PCX - ReportДокумент15 страницPCX - ReportUmar GondalОценок пока нет
- ICSE - History & Civics Sample Paper-1-solution-Class 10 Question PaperДокумент9 страницICSE - History & Civics Sample Paper-1-solution-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh Khan100% (1)
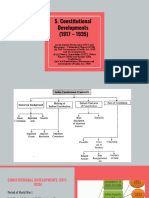
- Constitutional DevelopmentsДокумент24 страницыConstitutional DevelopmentsArjun SinghОценок пока нет
- 0 GKBKB S8 ROq B3 I2 Nro ATДокумент65 страниц0 GKBKB S8 ROq B3 I2 Nro ATArun Kumar Panda.Оценок пока нет
- Montagu Chemsford FileДокумент12 страницMontagu Chemsford FileMuhammad Zehadul IslamОценок пока нет
- History 'India After Independence' Notes 12.02.2022Документ3 страницыHistory 'India After Independence' Notes 12.02.2022tribhuvanr138Оценок пока нет
- Impact of 1970 Election in BangladeshДокумент9 страницImpact of 1970 Election in BangladeshMd AkteruzzamanОценок пока нет
- History ch-3Документ13 страницHistory ch-3Sadik farhat MollaОценок пока нет
- 202004132156500043abha Trivedi Government of India Act 1919Документ16 страниц202004132156500043abha Trivedi Government of India Act 19199824528679Оценок пока нет
- Act of Parliament in 1858Документ4 страницыAct of Parliament in 1858Dhanush D RОценок пока нет
- Indian National Movements Modern History PYQ 1995 2020Документ64 страницыIndian National Movements Modern History PYQ 1995 2020isha eslavathОценок пока нет
- His Ch.9 The Making of The National MovementДокумент3 страницыHis Ch.9 The Making of The National MovementMohammad AayanОценок пока нет
- History Prelims PaperДокумент7 страницHistory Prelims Papershauryasahu2004Оценок пока нет
- Mod His Vis 10Документ194 страницыMod His Vis 10sony priya valluruОценок пока нет
- The Government of India Act, 1858Документ3 страницыThe Government of India Act, 1858Sana MОценок пока нет
- CDS I 2021 Previous Year Paper: General Knowledge: WWW - Gradeup.coДокумент26 страницCDS I 2021 Previous Year Paper: General Knowledge: WWW - Gradeup.coVidit DixitОценок пока нет
- Social Science Holiday HomeworkДокумент39 страницSocial Science Holiday HomeworkNitinОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 Rise of Muslim Nationalism in Subcontinent (A Struggle Reform 1909,1919)Документ4 страницыTopic 2 Rise of Muslim Nationalism in Subcontinent (A Struggle Reform 1909,1919)KARIMA IFTIKHARОценок пока нет
- Complete Hios PyqДокумент107 страницComplete Hios Pyqricafol638Оценок пока нет
- 08 Social Ncert History ch12 India After Independence QuesДокумент4 страницы08 Social Ncert History ch12 India After Independence QuesMurtaza YousufОценок пока нет
- Section 2 NotesДокумент5 страницSection 2 NotesHamna MinhasОценок пока нет
- Modern History 1Документ47 страницModern History 1Ekta AgrawalОценок пока нет
- History Assignment 2nd SemДокумент9 страницHistory Assignment 2nd SemAarya ChhanganiОценок пока нет
- HU107 - Khilafat Movement, Nehru Report and Jinnah's 14 PointsДокумент5 страницHU107 - Khilafat Movement, Nehru Report and Jinnah's 14 PointsTouseef IsmailОценок пока нет
- The National MovementДокумент18 страницThe National MovementaggkanishkaaОценок пока нет
- 20191bal0032 - K.A. Nithin KishoreДокумент7 страниц20191bal0032 - K.A. Nithin KishoreNithin KishoreОценок пока нет
- Weekly Premix Compilation 3Документ25 страницWeekly Premix Compilation 3NRОценок пока нет
- 1st War of Independence-2Документ4 страницы1st War of Independence-2ginger teathОценок пока нет
- Indian National MovementДокумент14 страницIndian National MovementNEOMENTORS EXAMS360Оценок пока нет
- Government of India Act of 1909Документ2 страницыGovernment of India Act of 1909Pratyush mishraОценок пока нет
- Emergence of GandhiДокумент7 страницEmergence of GandhisumerОценок пока нет
- Let Us CДокумент5 страницLet Us CWajahat RiazОценок пока нет
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 Solutions EngДокумент23 страницыPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 14 Solutions EngKrishna PrintsОценок пока нет
- Indian Constitutional History: M. S. RAMA RAO B.SC., M.A., M.LДокумент18 страницIndian Constitutional History: M. S. RAMA RAO B.SC., M.A., M.LSatyam PathakОценок пока нет
- History Question BankkДокумент30 страницHistory Question BankkSAHIL GUPTAОценок пока нет
- The Road To Partition - 1Документ25 страницThe Road To Partition - 1lulapottyОценок пока нет
- The Montague-Chelmsford Reforms (1919)Документ9 страницThe Montague-Chelmsford Reforms (1919)Sayed Zameer ShahОценок пока нет
- The Montague Chelmsford Reforms (Indian Council Act 1919) : Topic 13Документ2 страницыThe Montague Chelmsford Reforms (Indian Council Act 1919) : Topic 13KIRAN BUTTОценок пока нет
- 2020 Day 16 Solutions HistoryДокумент23 страницы2020 Day 16 Solutions HistoryRaghavОценок пока нет
- Modern Indian History FactsДокумент15 страницModern Indian History FactsChethan rajОценок пока нет
- Outsourced - Romeet (1-50)Документ32 страницыOutsourced - Romeet (1-50)Prestorming PrefitОценок пока нет
- MCQ 2022 Part 1Документ33 страницыMCQ 2022 Part 1MITALI BAGHELОценок пока нет
- Government of India Act 1919Документ20 страницGovernment of India Act 1919Ojasvi Arora100% (1)
- Answers 2023 of Political Science IVДокумент56 страницAnswers 2023 of Political Science IVSyed Misbahul IslamОценок пока нет
- Unit-10 Emergence of Organised NationalismДокумент11 страницUnit-10 Emergence of Organised NationalismPavan KalyanОценок пока нет
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: History Iii: Final DraftДокумент18 страницDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: History Iii: Final DraftPrachi VermaОценок пока нет
- PRELIMS TEST 15 AnsДокумент25 страницPRELIMS TEST 15 AnsPawani GuptaОценок пока нет
- Sbi Pos: Prelims Model Paper - 2018Документ1 страницаSbi Pos: Prelims Model Paper - 2018rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Sbi Pos: Prelims Model Paper - 2018Документ1 страницаSbi Pos: Prelims Model Paper - 2018rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Î Në Uj - Þœé - Êÿ-Ùšíj Úæ°-Ô Ù-#Ì Ú ÷ - Óÿ Ù..?Документ1 страницаÎ Në Uj - Þœé - Êÿ-Ùšíj Úæ°-Ô Ù-#Ì Ú ÷ - Óÿ Ù..?rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Page 3Документ1 страницаPage 3rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- TOP MECHANICAL Engineering Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент24 страницыTOP MECHANICAL Engineering Interview Questions and Answersrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- IndexДокумент1 страницаIndexrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- ME-Paper Code-A GATE 2011: Answer: - (B) ExplanationДокумент22 страницыME-Paper Code-A GATE 2011: Answer: - (B) ExplanationIMLOGANОценок пока нет
- Mechanical PDFДокумент2 страницыMechanical PDFrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Convert Now WhiteoutДокумент1 страницаConvert Now Whiteoutrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Published From: OnlineДокумент16 страницPublished From: Onlinerajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Resume Template PDFДокумент1 страницаResume Template PDFrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- 02Документ1 страница02rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: G.V.S.PrasannaДокумент1 страницаCurriculum Vitae: G.V.S.Prasannarajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: M.Suma Bindu D/O M.Vijay Kumar Hydearabad PH - No: +91-738642xxxxДокумент4 страницыCurriculum Vitae: M.Suma Bindu D/O M.Vijay Kumar Hydearabad PH - No: +91-738642xxxxrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Rajesh Reddy: ObjectiveДокумент2 страницыRajesh Reddy: Objectiverajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Ð) L*Æý‡$Μëmýs$) M>Æý‡…: Sets - ProblemsДокумент1 страницаÐ) L*Æý‡$Μëmýs$) M>Æý‡…: Sets - Problemsrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- 20160711a 012137004Документ1 страница20160711a 012137004rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Theory of Machines Questions and Answers OldДокумент123 страницыTheory of Machines Questions and Answers OldSaajal Sharma81% (27)
- History EraserДокумент1 страницаHistory Eraserrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Page 12Документ1 страницаPage 12rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .Документ1 страницаVøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .. Vøïºìœæ Mìs Všæ Ð) L Qå .rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Bitbank79Документ4 страницыCurrent Affairs Bitbank79rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Bitbank80Документ5 страницCurrent Affairs Bitbank80rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Current Affairs Bitbank81Документ3 страницыCurrent Affairs Bitbank81rajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Ùî Ü M °-Õüt-º$Ìœæ DÐÐL - SœæþìzДокумент1 страницаÙî Ü M °-Õüt-º$Ìœæ DÐÐL - Sœæþìzrajesh1924Оценок пока нет
- Ahluwalia 1966, Sultanate's Penetration Into Rajasthan and Central IndiaДокумент10 страницAhluwalia 1966, Sultanate's Penetration Into Rajasthan and Central IndiakamakarmaОценок пока нет
- GR 7-Term II Hstory Ls 6 Revision SheetДокумент10 страницGR 7-Term II Hstory Ls 6 Revision SheetPOOJYA SRITHA NОценок пока нет
- 8 Hadapsar 888 BranchДокумент303 страницы8 Hadapsar 888 BranchrubabshaikhОценок пока нет
- Final Merit List After Cap IIIДокумент37 страницFinal Merit List After Cap IIILaukik DesaiОценок пока нет
- Salaam Namaste Magazine, November 2008Документ109 страницSalaam Namaste Magazine, November 2008rkolluri100% (14)
- Corporate Database22Документ126 страницCorporate Database22Dhiren PatilОценок пока нет
- The Miracle Plays of Mathura. - Hein, NorvinДокумент344 страницыThe Miracle Plays of Mathura. - Hein, Norvinszalerp100% (1)
- Ist of ParticipantsДокумент2 страницыIst of ParticipantsSamridhh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Paul Brunton - A TributeДокумент5 страницPaul Brunton - A TributeDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -KОценок пока нет
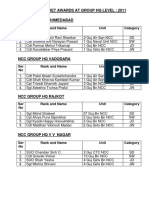
- Best Cadet Awards at Group HQ Level: 2011: Ser No Rank and Name Unit CategoryДокумент2 страницыBest Cadet Awards at Group HQ Level: 2011: Ser No Rank and Name Unit CategoryRajput Jai Verma NittuОценок пока нет
- Mughalempire PDFДокумент20 страницMughalempire PDFAngad KumarОценок пока нет
- SCSDFSDFSDFДокумент6 страницSCSDFSDFSDFasdasdОценок пока нет
- BAXA GarageList (Updated 20.04.2013)Документ105 страницBAXA GarageList (Updated 20.04.2013)Ashish KumarОценок пока нет
- Manu Sangh and IДокумент95 страницManu Sangh and I791987Оценок пока нет
- Sri Badrinath Yatra MurPriya Blog 2016 JuneДокумент55 страницSri Badrinath Yatra MurPriya Blog 2016 JunePadmavathy Ramamoorthy100% (1)
- Nam PallyДокумент4 страницыNam PallyRamesh Reddy BhanuriОценок пока нет
- Cipremi Customer ListДокумент56 страницCipremi Customer Listmahwish khanОценок пока нет
- Jivanmukti in SikhismДокумент10 страницJivanmukti in SikhismGordon LeeОценок пока нет
- Shiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - िशवताǷवˑोũम्Документ9 страницShiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - Shiv Tandav Stotra - िशवताǷवˑोũम्superangel2000in913Оценок пока нет
- Merit - Journalism and Mass Comunication - General - 2020Документ23 страницыMerit - Journalism and Mass Comunication - General - 2020OENDRIL DASОценок пока нет
- List of Art Galleries in Rajahmundry - Pythondeals3Документ5 страницList of Art Galleries in Rajahmundry - Pythondeals3SRINIVASARAO JONNALAОценок пока нет
- MadhyaPradesh DV List1Документ119 страницMadhyaPradesh DV List1Sanjeev MishraОценок пока нет
- Not Return Teachers Book ListДокумент1 страницаNot Return Teachers Book ListDAMBALEОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For Identifying Census Centres: WWW - Censusindia.gov - inДокумент9 страницGuidelines For Identifying Census Centres: WWW - Censusindia.gov - inAkshayОценок пока нет
- Indus Aryan CultureДокумент38 страницIndus Aryan CultureMuhammad Haider AliОценок пока нет
- Prices Effective Dated April 01 2016Документ13 страницPrices Effective Dated April 01 2016Adnan AkhtarОценок пока нет
- CLASS XII Painting SyllabusДокумент8 страницCLASS XII Painting SyllabusAshishSethi50% (2)
- 71Документ285 страниц71gaurav chauhanОценок пока нет