Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p20
Загружено:
MeMe AmroОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p20
Загружено:
MeMe AmroАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
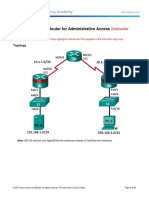
Lab - Securing the Router for Administrative Access
IP Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Switch Port
Fa0/1
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S1 Fa0/5
S0/0/0 (DCE)
10.1.1.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
N/A
S0/0/0
10.1.1.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
N/A
S0/0/1 (DCE)
10.2.2.2
255.255.255.252
N/A
N/A
Fa0/1
192.168.3.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S3 Fa0/5
S0/0/1
10.2.2.1
255.255.255.252
N/A
N/A
PC-A
NIC
192.168.1.3
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
S1 Fa0/6
PC-C
NIC
192.168.3.3
255.255.255.0
192.168.3.1
S3 Fa0/18
R1
R2
R3
Objectives
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Configure basic IP addressing for routers and PCs.
Configure static routing, including default routes.
Verify connectivity between hosts and routers.
Part 2: Control Administrative Access for Routers
Configure and encrypt all passwords.
Configure a login warning banner.
Configure enhanced username password security.
Configure enhanced virtual login security.
Configure an SSH server on a router.
Configure an SSH client and verify connectivity.
Part 3: Configure Administrative Roles
Create multiple role views and grant varying privileges.
Verify and contrast views.
Part 4: Configure Cisco IOS Resilience and Management Reporting
Secure the Cisco IOS image and configuration files.
Configure a router as a synchronized time source for other devices using NTP.
Configure Syslog support on a router.
Install a Syslog server on a PC and enable it.
Configure trap reporting on a router using SNMP.
Make changes to the router and monitor syslog results on the PC.
Part 5: Configure Automated Security Features
Lock down a router using AutoSecure and verify the configuration.
2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 61
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p14Документ1 страницаCCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p14MeMe AmroОценок пока нет
- CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p37Документ1 страницаCCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p37MeMe AmroОценок пока нет
- CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p19Документ1 страницаCCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p19MeMe AmroОценок пока нет
- CCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p7Документ1 страницаCCNA Security Instructor Lab Manual v1 - p7MeMe AmroОценок пока нет