Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Shock Types
Загружено:
RLI23ny0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страницаShock Types
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документShock Types
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страницаShock Types
Загружено:
RLI23nyShock Types
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
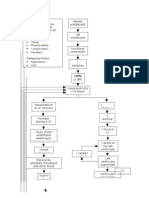
Type of shock
Signs/Symptoms
Bodys Total Volume Loss
o <20% Pale, Cool and
Clammy skin with HR
o 2040% RR,
orthostasis, possibly
confusion, poor capillary
refill, peripheral pulses
o 40% Hypotension,
oliguria, and obtundation
Cardiogenic
Pale and Cool Ashen gray
Cool and clammy extremities
Narrowed pulse pressure
Diaphoresis
JVP
Rales/Crackles
Muffled heard sounds
Neurogenic Warm
Bradycardia
Flaccid paralysis
RA
CVP
PCWP/
LVEDP
SVR
HR
CO
Distributive
Hypovolemic
Warm and Faint
Flushing
(MCC: E. RR acute hyperventilation
Coli, and S.
(resp. alkalosis, (PCO2 < 30
Aureus)
mm Hg))
At-risk patients diabetics
and immunocompromised
Nl or
Septic
Etiology
Treatment
Lack of enough blood (due to loss) to
properly perfuse the bodymost
commonly due to trauma
o Massive Infarction
Fluids and
o Fluid loss (i.e., vomiting, diarrhea,
pressors
burns, or trauma)
o Preexisting heart disease may
exacerbate the effects of hypovolemic
shock.
Failure of the heart as a pump
o Myocardial Infarction myocardium
damaged heart cant effectively pump
Treat
o Acute mitral regurgitation heart is
cardiac
pumping enough blood, but much of it is problem
leaking back into LA instead of being
propelled out into aorta
Defect in the central nervous system
control of vascular tone results in
Fluids and
generalized dilation of vessels and
Pressors
consequent pooling of blood
o Spinal Cord Injury (Cervical/Thoracic)
2550% mortality rate;
Generalized vascular dilation caused by
infectious organism, usually due to
Fluids,
lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in cell wall of
Antibiotics,
gram-negative bacterial organisms such as
and
E. Coli, Pseudomonas, and Klebsiella.
Pressors
o Blood pools in venous system and
peripheral vasculature and not enough
returns to the heart to be pumped out
Mechanical obstruction of blood flow
through central circulation due to
Results in Right Heart Failure
o Right Heart Pressure
o Impaired venous return
Obstructive
RV infarct
Massive
Pulm.
Nl or
Embolism
Pneumothorax
Pericdial
Tamponade
CO=Cardiac Output; SVR=Systemic Vascular Resistance; PCWP=Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure; LVEDP = Left Ventricular End Diastolic Pressure;
CVP=Central Venous Pressure; JVP = Jugular Venous Pressure; HR = Heart Rate; RR = Respiration Rate; = Increase; = Decrease; = No Change; Nl = normal
Page 4 of 8
Вам также может понравиться
- Shock: Dr. Heny Anggraeny LenapДокумент19 страницShock: Dr. Heny Anggraeny LenapRatna PermatasariОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент47 страницRheumatic Heart DiseaseGideon K. MutaiОценок пока нет
- Cardiology Notes by Wasim AhmadДокумент28 страницCardiology Notes by Wasim AhmadAshna moeenОценок пока нет
- Presentor: DR - Kumar Moderator: DR - VamsidharДокумент71 страницаPresentor: DR - Kumar Moderator: DR - VamsidharJayaprakash KuppusamyОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure By: DR - Nagwa AlmahallawiДокумент17 страницHeart Failure By: DR - Nagwa Almahallawiazir22Оценок пока нет
- Wk7 PLP Cardiovascular Disorder Part 1,2,3,4Документ210 страницWk7 PLP Cardiovascular Disorder Part 1,2,3,4claire yowsОценок пока нет
- ShockДокумент61 страницаShocktantosatuОценок пока нет
- PedsnotesДокумент18 страницPedsnoteskp13oyОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure FileДокумент31 страницаCongestive Heart Failure FileAbas AhmedОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент6 страницCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanОценок пока нет
- 8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)Документ6 страниц8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)AsmaaYL100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesОценок пока нет
- Duct Dependent Lesions - PPSXДокумент41 страницаDuct Dependent Lesions - PPSXSindujaОценок пока нет
- Medsurg NursingДокумент3 страницыMedsurg NursingGeraldine TeneclanОценок пока нет
- Aortic StenosisДокумент30 страницAortic Stenosisloknath reddyОценок пока нет
- Review Sheet AP2 Test #1 (19, 20 & 21) EXAM 1Документ2 страницыReview Sheet AP2 Test #1 (19, 20 & 21) EXAM 1Charity KiplagatОценок пока нет
- Aortic Stenosis - LecturioДокумент13 страницAortic Stenosis - Lecturiokujtimepira2Оценок пока нет
- Erythema Marginatum Chorea: Migratory Polyarthritis Cardiac Involvement Subcutaneous NodulesДокумент27 страницErythema Marginatum Chorea: Migratory Polyarthritis Cardiac Involvement Subcutaneous NodulesMisbah KaleemОценок пока нет
- Congestive Cardiac FailureДокумент38 страницCongestive Cardiac FailureSalman KhanОценок пока нет
- 3 CRHD CMP and CHDДокумент73 страницы3 CRHD CMP and CHDDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Shock Abdurrab UniversityДокумент124 страницыKuliah Shock Abdurrab UniversityVivi AnggrainyОценок пока нет
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент58 страницCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseasegolden37Оценок пока нет
- Kuliah MITRAL STENOSISДокумент19 страницKuliah MITRAL STENOSISAdi TrisnoОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteeДокумент65 страницPulmonary Edema: Prepared By: South West Education CommitteedanradulescuОценок пока нет
- Heart FailureДокумент39 страницHeart FailureMuhammad AsifОценок пока нет
- Aortic RegurgitationДокумент12 страницAortic RegurgitationSanjeet SahОценок пока нет
- Heart FailureДокумент41 страницаHeart FailureJared Khoo Er HauОценок пока нет
- Heart Failure Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыHeart Failure Cheat SheetNicolle GaleОценок пока нет
- CHD Fetal CirculationДокумент31 страницаCHD Fetal CirculationNandita ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- ShockДокумент124 страницыShockRahman Mukti AjiОценок пока нет
- Cardiology FMДокумент25 страницCardiology FMtrushaОценок пока нет
- Cardiogenic ShockДокумент27 страницCardiogenic ShockIgor StefanetОценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart DseДокумент8 страницValvular Heart DseJane Pineda CuraОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapyДокумент206 страницCardiovascular Physical TherapyJuanitoCabatañaLimIII100% (2)
- Valvular Heart Disease: Bekele T. (MD)Документ47 страницValvular Heart Disease: Bekele T. (MD)alehegn beleteОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Artery Catheters and Hemodynamic MonitoringДокумент32 страницыPulmonary Artery Catheters and Hemodynamic Monitoringjpsahni100% (1)
- 1.06 - 1.07 Pathophysiology of Clinical Features in Heart Failure - Pathological Consequences (To Students) Final 2020Документ59 страниц1.06 - 1.07 Pathophysiology of Clinical Features in Heart Failure - Pathological Consequences (To Students) Final 2020JedoОценок пока нет
- Acute Biologic CrisisДокумент10 страницAcute Biologic CrisisEniryz M. Salomon100% (1)
- Shock: Ron Michael N. Olaguera 2 Year Surgery ResidentДокумент40 страницShock: Ron Michael N. Olaguera 2 Year Surgery ResidentErick Anca100% (2)
- Shock Def ClassДокумент20 страницShock Def ClassctОценок пока нет
- ShockДокумент2 страницыShockYousef El3alameyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ShockДокумент56 страницIntroduction To ShockPaolo VegaОценок пока нет
- 5.2 DR - Yusuf Assegaf SPJP - Syok KardiogenikДокумент33 страницы5.2 DR - Yusuf Assegaf SPJP - Syok KardiogenikAfdol Triatmojo SikumbangОценок пока нет
- Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy: Ventricular DilatationДокумент1 страницаAlcoholic Cardiomyopathy: Ventricular DilatationDee SarajanОценок пока нет
- Shock PresentationДокумент108 страницShock PresentationWiDya EmiLiaОценок пока нет
- Case Study Congestive Heart Failure Patho)Документ8 страницCase Study Congestive Heart Failure Patho)Mj Silva100% (3)
- Aortic Regurgitation CaseДокумент38 страницAortic Regurgitation CaseIka MagfirahОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsДокумент127 страницNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac Problemssarah morleyОценок пока нет
- Hemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DДокумент59 страницHemodynamic Disorders: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент35 страницRheumatic Heart DiseaseSAYMABANUОценок пока нет
- Cardiogenic Shock Patofisiologi and TreatmentДокумент40 страницCardiogenic Shock Patofisiologi and TreatmentRichi Aditya100% (1)
- Coronary Circulation & Pathologies: Arif Hussain Demonstrator Anesthesia Ipms-KmuДокумент28 страницCoronary Circulation & Pathologies: Arif Hussain Demonstrator Anesthesia Ipms-Kmuayub khanОценок пока нет
- Aortic StenosisДокумент2 страницыAortic StenosishollyuОценок пока нет
- Acute Trauma Care:: ShockДокумент45 страницAcute Trauma Care:: ShockGeoffrey100% (1)
- (K7) Valvular Heart DiseaseДокумент79 страниц(K7) Valvular Heart DiseaseXeniel AlastairОценок пока нет
- Shock: Karolina Doskocz gr2BДокумент4 страницыShock: Karolina Doskocz gr2BKarolina DoskoczОценок пока нет