Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Reviewer - Cardio
Загружено:
Lizzy Way0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров3 страницыCardio
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCardio
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
12 просмотров3 страницыReviewer - Cardio
Загружено:
Lizzy WayCardio
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
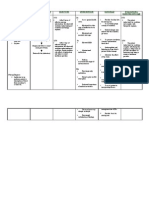
Valvular Disorders
Regurgitation valves do not
close/open properly and theres a
backflow
Stenosis valve does not open
completely and flow of blood is
reduced
Prolapse - a slippage or sinking of a
valve of the heart from its usual
position
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Produces no symptoms; occurs
more frequently in women; usually
inherited connective tissue disorder
resulting in enlargement of one or
both of mitral valve leaflets
Fatigue,
SOB,
lightheadedness,
dizziness, syncope, palpitations,
chest pain, anxiety
Extra heart sound, mitral click
Prophylactic meds (antibiotics),
mitral valve repair
Patient teaching
Mitral Regurgitation
Involves blood flowing back from
the left ventricle into the left
atrium during systole
Dyspnea,
fatigue,
weakness,
palpitations, SOB, cough
Prophylactic meds (antibiotics),
restrict
activity
level,
mitral
valvuloplasty/valve replacement
Mitral Stenosis
Obstruction of blood flowing from
the left atrium into the left
ventricle
Often
caused
by
rheumatic
endocarditis
Dyspnea, progressive fatigue, low
cardiac
output,
enlarged
left
atrium, dry cough, wheezing,
palpitations,
orthopnea,
PND,
repeated respi infections
Anticoagulants to dec rick for
developing atrial thrombus, Tx for
anemia, avoid strenuous activities,
valvuloplasty,
mitral
valve
replacement
Aortic Regurgitation
Flow of blood back into left
ventricle from aorta during diastole
May be caused by inflammatory
lesions,
infective/rheumatic
endocarditis,
congenital
abnormalities, syphilis, blunt chest
trauma
Forceful
heartbeat,
orthopnea,
PND, dyspnea, fatigue
Avoid physical exertion, Tx for
dysrhymias and HF, vasodilators,
CCB, ACE inhibitors, hydralazine
Aortic
valvuloplasty/valve
replacement
Aortic Stenosis
Narrowing of the orifice bet the LV
and
the
aorta;
result
of
degenerative calcifications
Asymptomatic; exertional dyspnea,
orthopnea,
PND,
pulmonary
edema, dizziness, syncope, angina
pectoris
Meds to treat dysrhythmia of LV
failure
VALVULOPLASTY
COMMISSUROTOMY
fused leaflets
separate
ANNULOPLASTY repair of valve
annulus
LEAFLET REPAIR
CHORDOPLASTY
tendinae
repair chordae
VALVE REPLACEMENT
Occurs most often in school-age
children
May develop after an episode of
group
A
beta-hemolytic
streptococcal pharyngitis
Prompt Tx of strep throat with
antibiotics
can
prevent
the
development of rheumatic fever
Infective Endocarditis
Cardiomyopathy
Heart muscle dse accoc with
cardiac dysfxn
Dilated: most common form;
dilation of the ventricles without
simultaneous
hypertrophy;
pregnancy,
heavy
alcohol
intake,
viral
infection,
chemotherapeutic
meds,
Chagas dse.
Hypertrophic: rare autosomal
dominant condition; occurring in
all age groups, often detected in
puberty
Restrictive: right ventricular
walls that impair diastolic filling
and ventricular stretch
HF s/sx, PND, cough, orthopnea,
peripheral edema, fluid retention,
dizziness,
palpitations,
nausea,
syncope, chest pain
Correcting
HF,
low-Na
diet,
exercise/rest regimen, controlling
dysrhythmias, fluid intake may be
limited to 2L each day, limit
physical activity, heart transplant
Rheumatic Endocarditis
Microbial
infection
of
the
endothelial surface of the heart
Develops in people with prosthetic
heart valves
Myocarditis
Inflammatory process involving the
myocardium
Heart dilation, thrombi on the heart
wall (mural thrombi), infiltration of
circulating blood cells around the
coronary vessels and bet the
muscle fibers and degeneration of
the muscle fibers themselves
Prevention!
Appropriate
immunizations
Tx of underlying cause if known,
physical activity is inc slowly, BR,
dec cardiac workload
Monitor patient, for tachycardia,
fever,
cardiac
activity,
antiembolism stockings, active and
passive ROM exercises
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the pericardium;
primary illness or may develop into
a disorder
Asymptomatic; chest pain (may be
located beneath the clavicle, neck ,
scapula regions), creaky, scratchy
friction rub at left lower sternal
border
NSAIDS, analgesics, Tx of cause
Health teachings!
Cellulitis
Most common infectious cause of
limb swelling
Can occur as a single isolated
event or a series or recurrent
events
Swelling, fever, chills, sweating,
redness, tender and enlarged
lymph nodes
Antibiotic therapy
Elevate affected area above heart
level and apply warm, moist packs
to the site every 2-4 hrs
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- A.M. No. 02-11-10-SCДокумент8 страницA.M. No. 02-11-10-SCLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Honda Cars Philippines, Inc., Vs - Honda Cars Technical Specialist and Supervisors UnionДокумент1 страницаHonda Cars Philippines, Inc., Vs - Honda Cars Technical Specialist and Supervisors UnionOlivia JaneОценок пока нет
- Duty Free v. COAДокумент1 страницаDuty Free v. COALizzy Way100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- CIR-vs-Isabela-Cultural-CorpДокумент1 страницаCIR-vs-Isabela-Cultural-CorpLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Arches v. BellosilloДокумент1 страницаArches v. BellosilloLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Winebrenner Inigo Insurance Brokers Inc vs. CIRДокумент1 страницаWinebrenner Inigo Insurance Brokers Inc vs. CIRLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Medicard v. CirДокумент1 страницаMedicard v. CirLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- MERALCO, Et Al. Vs LimДокумент2 страницыMERALCO, Et Al. Vs LimLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- 2004 Rules On Notarial PracticeДокумент14 страниц2004 Rules On Notarial PracticeLizzy Way100% (3)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Special Edition Philippine Mythology FolkloreДокумент34 страницыSpecial Edition Philippine Mythology FolkloreSon Michael MarianoОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Phantom of The OperaДокумент18 страницPhantom of The OperaLizzy Way100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- PLDT Vs Province of LagunaДокумент1 страницаPLDT Vs Province of LagunaLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Cases in Taxation I: Submitted ToДокумент44 страницыCases in Taxation I: Submitted ToJwilfred CarpizoОценок пока нет
- Basilan Estates vs. CirДокумент1 страницаBasilan Estates vs. CirLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- 21.board of Assessment Appeals of Laguna vs. Cta, NwsaДокумент1 страница21.board of Assessment Appeals of Laguna vs. Cta, NwsaHappy KidОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- UST Golden Notes 2011 - Torts and Damages PDFДокумент50 страницUST Golden Notes 2011 - Torts and Damages PDFpot420_aivan50% (2)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Sy Po Vs CTAДокумент1 страницаSy Po Vs CTALizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Electronic Commerce Act (RA No. 8792)Документ2 страницыElectronic Commerce Act (RA No. 8792)Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Intellectual Property Code (RA No. 8293)Документ8 страницIntellectual Property Code (RA No. 8293)Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- AMLAДокумент6 страницAMLALizzy WayОценок пока нет
- 22-1 Aglipay V Ruiz Case DigestДокумент1 страница22-1 Aglipay V Ruiz Case DigestemyОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Abakada Guro Party List Vs Ermita GR 168056Документ1 страницаAbakada Guro Party List Vs Ermita GR 168056Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- PLDT Vs City of BacolodДокумент1 страницаPLDT Vs City of BacolodLizzy Way100% (1)
- Mendez Vs People 726 SCRA 203 (2014)Документ1 страницаMendez Vs People 726 SCRA 203 (2014)Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Data Privacy Act (RA No. 10173)Документ4 страницыData Privacy Act (RA No. 10173)Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Cir vs. Marubeni Corp., 372 Scra 577 - VelosoДокумент1 страницаCir vs. Marubeni Corp., 372 Scra 577 - VelosoAlan GultiaОценок пока нет
- People Vs LiceraДокумент1 страницаPeople Vs LiceraLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Tan Tiong Bio vs. CIR, G.R. No. L-15778, April 23, 1962Документ1 страницаTan Tiong Bio vs. CIR, G.R. No. L-15778, April 23, 1962Lizzy WayОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Lorenzo vs. Posadas Jr.Документ2 страницыLorenzo vs. Posadas Jr.Lizzy Way100% (1)
- CIR Vs PinedaДокумент1 страницаCIR Vs PinedaLizzy WayОценок пока нет
- Instruction: Check Under Correctly Done If Identified Skill Is Correctly Performed Incorrectly Done If Skill IsДокумент3 страницыInstruction: Check Under Correctly Done If Identified Skill Is Correctly Performed Incorrectly Done If Skill IsSIR ONEОценок пока нет
- Materi Dasar EkgДокумент52 страницыMateri Dasar EkgFirsandiPrasastyaFikryGozali100% (2)
- Gerry B. Acosta, MD, FPPS, FPCC: Pediatric CardiologistДокумент51 страницаGerry B. Acosta, MD, FPPS, FPCC: Pediatric CardiologistChristian Clyde N. ApigoОценок пока нет
- Management of Cardiac Disease in LaborДокумент6 страницManagement of Cardiac Disease in LaborHassan osmanОценок пока нет
- Final CirculatoryДокумент44 страницыFinal CirculatoryKeiko-Kaori NebresОценок пока нет
- Postsurgical Anatomy: Lung Transplantation Lobectomy and PneumonectomyДокумент36 страницPostsurgical Anatomy: Lung Transplantation Lobectomy and PneumonectomyYui Phitchaya MonsintornОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyДокумент13 страницCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariОценок пока нет
- MCQs InternalДокумент20 страницMCQs InternalOsama AlhumisiОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Shock: Dr. Refli Hasan SPPD, SPJP (K) FihaДокумент37 страницDiagnosis and Treatment of Shock: Dr. Refli Hasan SPPD, SPJP (K) FihaWinson ChitraОценок пока нет
- Dextrocardia With Situs Inversus and Associated Cardiac MalformationДокумент51 страницаDextrocardia With Situs Inversus and Associated Cardiac MalformationAbdul Haris Khoironi100% (1)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasДокумент3 страницыCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis FlyerДокумент2 страницыDeep Vein Thrombosis FlyerMuhammad Reza Syahli PiliangОценок пока нет
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Документ2 страницыNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- ACLS 1 Answers & ExplanationsДокумент11 страницACLS 1 Answers & ExplanationsCarl SarsОценок пока нет
- 07 Blood Pressure Abnormality 1-8-2021 配布用Документ22 страницы07 Blood Pressure Abnormality 1-8-2021 配布用Lan NguyenОценок пока нет
- Spring 2016 NewsletterДокумент4 страницыSpring 2016 Newsletterapi-262611502Оценок пока нет
- Duchenne Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Cardiac Management From Prevention To Advanced Cardiovascular TherapiesДокумент18 страницDuchenne Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Cardiac Management From Prevention To Advanced Cardiovascular TherapiesKelvin SupriamiОценок пока нет
- Ginekologija Sa AkusertsvomДокумент2 страницыGinekologija Sa AkusertsvomZaklina RistovicОценок пока нет
- LWW BATES 10 Cardiovascular System Transcript FINALДокумент11 страницLWW BATES 10 Cardiovascular System Transcript FINALShivamОценок пока нет
- Tavi SurgeryДокумент10 страницTavi Surgeryapi-683799701Оценок пока нет
- Answer Diagnosis: 1. RhythmДокумент2 страницыAnswer Diagnosis: 1. RhythmSuggula Vamsi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Pneumonics For AclsДокумент2 страницыPneumonics For Aclskrishnaprasadm7100% (2)
- Arterijska Hipertenzija U Osoba Starije Životne DobiДокумент5 страницArterijska Hipertenzija U Osoba Starije Životne DobiRebecca BlackburnОценок пока нет
- Film-Coated Tablet 5mg & 7.5mg: CH O OCH CH N N OДокумент2 страницыFilm-Coated Tablet 5mg & 7.5mg: CH O OCH CH N N ObadrhashmiОценок пока нет
- Stages of ShockДокумент1 страницаStages of ShockronaОценок пока нет
- E-Book How To Identify A Normal EcgДокумент19 страницE-Book How To Identify A Normal EcgBisma TariqОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Inflammatory Markers in HTNДокумент6 страницComparison of Inflammatory Markers in HTNDan JohnstonОценок пока нет
- Health Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERДокумент4 страницыHealth Teaching Plan Tagalog About HYPERJaic Ealston D. TampusОценок пока нет
- Review Jurnal ProcainamidДокумент9 страницReview Jurnal ProcainamidEko FebryandiОценок пока нет
- Aortic DissectionДокумент5 страницAortic DissectionCosminNGDNОценок пока нет
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (80)