Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ME415 Condensers
Загружено:
agafina0Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ME415 Condensers
Загружено:
agafina0Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
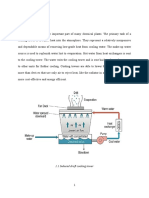
Condensation & Condensers
Condensation Process
Condensers & Cooling Towers
When saturated vapour comes in contact with a surface having a
temperature below the saturation temperature, condensation occurs. There
are two types of condensation:
Dr. M. Zahurul Haq
Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
Film-wise condensation: condensed liquid wets the surface and
forms a film covering the entire surface.
Drop-wise condensation: surface is not totally wetted by the
saturated vapour, and the condensate forms liquid droplets that fall
from the surface.
Compared to film-wise condensation, drop-wise condensation has a greater
surface heat-transfer coefficient as it has a greater area exposed to the
saturation vapour.
ME 415: Refrigeration & Building Mechanical Systems
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
1 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensation & Condensers
2 / 16
Types of Condensers
De-superheating of the hot gas
Condensing of the gas to liquid state and release of the latent heat.
Sub-cooling of the liquid refrigerant.
Based on the cooling medium used, condensers used in refrigeration
systems can be classified into the following three categories:
1 Water-cooled condensers
1
Sub-cooling only occupies a small portion of condensers surface area.
Therefore, an average heat transfer coefficient is used for the whole
condensers surface area, and the condensation is assumed to occur at the
condensing temperature.
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
Condensation & Condensers
Stages in Condensation
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
3 / 16
Double-tube condenser
Shell-and-tube condenser
Air-cooled condensers
Evaporative condensers
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
4 / 16
Condensation & Condensers
Condensation & Condensers
Double-tube Condenser
Shell-and-tube Condenser
e223
e222
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
5 / 16
Condensation & Condensers
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
6 / 16
Condensation & Condensers
The choice of water-cooled condenser depends on the following
factors:
Quality and availability of water
Space requirements
Water treatment costs
Noise
Advantages of water cooled-condensers are:
Easy to operate
Requires less surface area
Low energy requirement for the compressor.
e229
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
7 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
8 / 16
Condensation & Condensers
Condensation & Condensers
Air-cooled Condenser
Characteristics of Air-cooled Condenser
Compact, easy and economical to install.
Flexibility in changing capacity by varying air flow.
Hot air may be disposed of easily.
Easy to clean fin and tube surface by blowing air.
Required less maintenance.
Higher power requirement per ton of refrigeration
On days when maximum cooling is needed, the least is available.
e224
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
9 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensation & Condensers
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
10 / 16
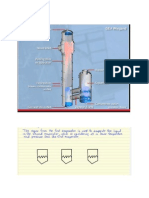
Cooling Tower
Evaporative Condenser
Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a device in which recirculating condenser water
from a condenser or cooling coils is evaporatively cooled by contact
with atmospheric air.
It consists of a fan to extract intake air, a heat-transfer medium or fill,
a water basin, a water distribution system, and an outer casing.
According to the location of the fan corresponding to the fill and to
the flow arrangements of air and water, cooling towers can be
classified into the following categories:
1
2
3
e225
Counterflow induced draft
Cross-flow induced draft
Counterflow forced draft.
Evaporation of water spray is used to condense the refrigerant
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
11 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
12 / 16
Cooling Tower
Cooling Tower
Counterflow Induced Draft
Cross-flow Induced Draft
e226
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
e227
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
13 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Cooling Tower
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
14 / 16
Cooling Tower
Counterflow Forced Draft
Cooling Tower Terminology
Approach: temperature difference between the temperature of
condenser water leaving the tower and the wet-bulb temperature of
the air entering the tower.
Range: temperature difference between the temperature of condenser
water entering the tower and the temperature leaving the cooling
tower.
Blow-down: water discharged to the drain periodically to avoid
build-up of dissolved solid.
Make-up: water added to the circulating water to compensate for the
loss of water to evaporation, drift and blow-down.
e228
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
15 / 16
c Dr. M. Zahurul Haq (BUET)
Condensers & Cooling Towers
ME 415 (2011)
16 / 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Analysis of Grape and WineДокумент116 страницAnalysis of Grape and WineElenaTrofimОценок пока нет
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsОт Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- FWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFДокумент49 страницFWC Air Cooled Exchanger PDFdinakaranpatelОценок пока нет
- Hvac For Offshore Platforms..Документ15 страницHvac For Offshore Platforms..hiepcpp100% (1)
- Heller System PPT 3 Cooling SystemsДокумент34 страницыHeller System PPT 3 Cooling SystemsShrey DattaОценок пока нет
- P Hazz Er Enforcer Us A ManualДокумент23 страницыP Hazz Er Enforcer Us A ManualArif TjoeripОценок пока нет
- Case Study of HVACRДокумент8 страницCase Study of HVACRAmit Kushwaha 42Оценок пока нет
- The Impact of Air Cooled Condensers On Plant Design and OperationsДокумент12 страницThe Impact of Air Cooled Condensers On Plant Design and Operationsandi_babyОценок пока нет
- CFD SimulationДокумент39 страницCFD SimulationSambhav JainОценок пока нет
- CFDДокумент34 страницыCFDSambhav JainОценок пока нет
- Nirma University Study on Performance of Air-Cooled CondensersДокумент6 страницNirma University Study on Performance of Air-Cooled Condenserstarun_aseriОценок пока нет
- Cleaning Air Cooled Condensers Improve PerformanceДокумент8 страницCleaning Air Cooled Condensers Improve PerformanceKroya HunОценок пока нет
- Cooling TowersДокумент5 страницCooling TowerssuganthОценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsДокумент10 страницCooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsLiu YangtzeОценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsДокумент8 страницCooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsThieuhuyen Ky100% (1)
- Cooling Tower REPORTДокумент25 страницCooling Tower REPORTSaroj KumarОценок пока нет
- Power plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesДокумент7 страницPower plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesMustafam98Оценок пока нет
- Lec 10 - Cooling TowersДокумент28 страницLec 10 - Cooling TowersHager ArefОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower ProjectДокумент50 страницCooling Tower ProjectRahul Wavdekar100% (1)
- Evaporative Cooling Technology TodayДокумент10 страницEvaporative Cooling Technology TodayWinwin07Оценок пока нет
- Cooling Technology Institute "Why Every Air Cooled System Condensor Needs A Cooling Tower" (2003)Документ16 страницCooling Technology Institute "Why Every Air Cooled System Condensor Needs A Cooling Tower" (2003)Amir AbbaszadehОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower AssignmentДокумент11 страницCooling Tower AssignmentSaad khan100% (2)
- Cooling System PresentationДокумент34 страницыCooling System PresentationzamijakaОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower - Design ConsiderationsДокумент6 страницCooling Tower - Design Considerationsofelherrera77Оценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers: Codes and Standards Enhancement ReportДокумент19 страницCooling Towers: Codes and Standards Enhancement ReportAIYODOT DOTОценок пока нет
- Types of Cooling TowersДокумент9 страницTypes of Cooling TowersPalitha Seneviratne100% (1)
- Cooling Towers ExplainedДокумент10 страницCooling Towers ExplainedHamza NeweraОценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers: Industrial MediumДокумент5 страницCooling Towers: Industrial Mediumaneesh awasthiОценок пока нет
- How Cooling Towers FunctionДокумент18 страницHow Cooling Towers Functionindrachandra100% (1)
- Cooling Towers: Design of Tall Structures Me Structural Engineering DrspdalalДокумент21 страницаCooling Towers: Design of Tall Structures Me Structural Engineering DrspdalalMegha LakhaniОценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers - Downloaded SkillsДокумент22 страницыCooling Towers - Downloaded SkillsVuthpalachaitanya KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Basics of AHU, FCU, DX and Chilled Water SystemsДокумент113 страницBasics of AHU, FCU, DX and Chilled Water SystemsDum AccountОценок пока нет
- Basic Components of Ahu and Fcu, Fan and Duct SystemsДокумент113 страницBasic Components of Ahu and Fcu, Fan and Duct SystemsSka dooshОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower Basics Calculation Formulas - Cooling Tower EfficiencyДокумент9 страницCooling Tower Basics Calculation Formulas - Cooling Tower EfficiencySantosh JayasavalОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower DesignДокумент11 страницCooling Tower DesignSmrutiОценок пока нет
- Hybrid Cooling TowerДокумент12 страницHybrid Cooling TowerEka SafitriОценок пока нет
- Cooling TowerДокумент13 страницCooling TowerMuhammad TayyabОценок пока нет
- Ijmet 08 01 011Документ10 страницIjmet 08 01 011Abhinav VermaОценок пока нет
- General Types of Cooling Tower IllustrationsДокумент10 страницGeneral Types of Cooling Tower IllustrationsanisalyaaОценок пока нет
- Back to Basics Cooling Towers GuideДокумент4 страницыBack to Basics Cooling Towers GuideWalter J Naspirán Castañeda100% (1)
- Desalination: M. Deziani, Kh. Rahmani, S.J. Mirrezaei Roudaki, M. KordlooДокумент6 страницDesalination: M. Deziani, Kh. Rahmani, S.J. Mirrezaei Roudaki, M. KordlooMustafa KaddouraОценок пока нет
- Heat and Mass Transfer Analysis of Evaporative Condenser: V. W. BhatkarДокумент12 страницHeat and Mass Transfer Analysis of Evaporative Condenser: V. W. BhatkarDr Vijay BhatkarОценок пока нет
- CONDENSER AND COOLING WATER PLANT DESIGNДокумент4 страницыCONDENSER AND COOLING WATER PLANT DESIGNAhmed HelmyОценок пока нет
- Forced Draft Cooling Tower ExperimentДокумент28 страницForced Draft Cooling Tower ExperimentIbrahim DanladiОценок пока нет
- Cooling TowersДокумент35 страницCooling TowersSingaravelu MariappanОценок пока нет
- Cooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsДокумент6 страницCooling Towers Design and Operation ConsiderationsvanmurthyОценок пока нет
- Surface CondenserДокумент33 страницыSurface CondensershivvaramОценок пока нет
- Air Cooled CondensersДокумент13 страницAir Cooled CondensersSyed ShoebОценок пока нет
- Internal Epoxy Coating in Surface CondenserДокумент14 страницInternal Epoxy Coating in Surface CondenserChaudhari SanketОценок пока нет
- R&AC Lecture 22Документ37 страницR&AC Lecture 22rchandra2473Оценок пока нет
- 02 - Condensers & Cooling Towers PDFДокумент61 страница02 - Condensers & Cooling Towers PDFVimleshKumarSharmaОценок пока нет
- Project - 1 PPT (Cooling Tower)Документ16 страницProject - 1 PPT (Cooling Tower)harshilshah122Оценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower1Документ66 страницCooling Tower1Er Bali Pandhare100% (1)
- Comparative Evaluation of Hybrid (Dry Wet) Cooling TowerДокумент11 страницComparative Evaluation of Hybrid (Dry Wet) Cooling TowerFernandoОценок пока нет
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AОт EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Ejectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsОт EverandEjectors for Efficient Refrigeration: Design, Applications and Computational Fluid DynamicsОценок пока нет
- Warm Air Heating: International Series of Monographs in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationОт EverandWarm Air Heating: International Series of Monographs in Heating, Ventilation and RefrigerationОценок пока нет
- Small Wind: Planning and Building Successful InstallationsОт EverandSmall Wind: Planning and Building Successful InstallationsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Industrial Heat Exchangers: Selection, Design, Construction, and OperationОт EverandFundamentals of Industrial Heat Exchangers: Selection, Design, Construction, and OperationОценок пока нет
- Carbide K20Документ1 страницаCarbide K20hadeОценок пока нет
- Moment FlechДокумент1 страницаMoment Flechagafina0Оценок пока нет
- MCQ-Diodes and TransistorsДокумент102 страницыMCQ-Diodes and Transistorsaksaltaf913774% (23)
- MCQ-Diodes and TransistorsДокумент102 страницыMCQ-Diodes and Transistorsaksaltaf913774% (23)
- 2013 June Regents Diagnostic GuideДокумент1 страница2013 June Regents Diagnostic Guideagafina0Оценок пока нет
- 4Документ1 страница4agafina0Оценок пока нет
- Impression RDM 6Документ1 страницаImpression RDM 6agafina0Оценок пока нет
- Physics Test 2 FinalДокумент3 страницыPhysics Test 2 Finalagafina0Оценок пока нет
- 2013-2014 Liturgical Calendar-Year AДокумент12 страниц2013-2014 Liturgical Calendar-Year Aagafina0Оценок пока нет
- Lectionary General IntroductionДокумент44 страницыLectionary General IntroductionVSL Regional VicariateОценок пока нет
- Practical Visual Inspection of WeldsДокумент40 страницPractical Visual Inspection of WeldsAmit Sharma100% (1)
- Medical TourismДокумент18 страницMedical TourismdhnaushОценок пока нет
- Is411 8Документ1 страницаIs411 8amoghimiОценок пока нет
- BOM Eligibility CriterionДокумент5 страницBOM Eligibility CriterionDisara WulandariОценок пока нет
- MAstering IATFДокумент20 страницMAstering IATFGyanesh_DBОценок пока нет
- Product and Service Costing: Job-Order System: Questions For Writing and DiscussionДокумент22 страницыProduct and Service Costing: Job-Order System: Questions For Writing and Discussionsetiani putriОценок пока нет
- WILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Документ32 страницыWILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Toyour EternityОценок пока нет
- QIMA - Ethical Audit Preparation Document - ENДокумент3 страницыQIMA - Ethical Audit Preparation Document - ENMD Nurul HudaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonДокумент17 страницIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Personrovie andes100% (1)
- M Shivkumar PDFДокумент141 страницаM Shivkumar PDFPraveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Catalogue of DDSY23S Energy Meter: Smart Metering and System Solution ProviderДокумент2 страницыCatalogue of DDSY23S Energy Meter: Smart Metering and System Solution ProviderNadine MichaelsОценок пока нет
- Causes & Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseДокумент41 страницаCauses & Prevention of Coronary Artery DiseaseeenagpurcongОценок пока нет
- SBR2018 - AbstractsДокумент115 страницSBR2018 - AbstractsGustavo ResendeОценок пока нет
- 0 BOSH FrameworkДокумент18 страниц0 BOSH Frameworkharold fontiveros100% (1)
- Palm Avenue ApartmentsДокумент6 страницPalm Avenue Apartmentsassistant_sccОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryДокумент6 страницSolutions To Exercises, Chapter 19: Okuyama & Maskill: Organic ChemistryM Irfan KhanОценок пока нет
- Form-Ii (See Regulation 4) Postal Bill of Export - II (To Be Submitted in Duplicate)Документ1 страницаForm-Ii (See Regulation 4) Postal Bill of Export - II (To Be Submitted in Duplicate)mrthilagamОценок пока нет
- Humiseal Thinner 73 MSDSДокумент3 страницыHumiseal Thinner 73 MSDSibnu Groho Herry sampurnoОценок пока нет
- Badhabits 2022Документ53 страницыBadhabits 2022Sajad KhaldounОценок пока нет
- Allen: Chemical KineticsДокумент4 страницыAllen: Chemical KineticsBidhan Chandra SarkarОценок пока нет
- Fabrication and Installation of Vertical Steel Pressure ShaftДокумент23 страницыFabrication and Installation of Vertical Steel Pressure ShaftPasan RajasingheОценок пока нет
- CIVIL BILL OF QUANTITIESДокумент16 страницCIVIL BILL OF QUANTITIESTomОценок пока нет
- R02.4 Standard III (A) - AnswersДокумент11 страницR02.4 Standard III (A) - AnswersShashwat DesaiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 EconomicsДокумент5 страницChapter 1 Economicsjordan cedeñoОценок пока нет
- Effective Determinantsof Consumer Buying Decisionon OTCДокумент13 страницEffective Determinantsof Consumer Buying Decisionon OTCThinh PhamОценок пока нет
- Sugar Crisis in Pakistan Research PaperДокумент10 страницSugar Crisis in Pakistan Research Paperrehan9891Оценок пока нет
- Primary Healthcare Centre Literature StudyДокумент32 страницыPrimary Healthcare Centre Literature StudyRohini Pradhan67% (6)
- Navi Cure prospectus summaryДокумент50 страницNavi Cure prospectus summaryGaurav SrivastavaОценок пока нет