Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
α−decay X He X: Four principal decay modes of unstable nuclei
Загружено:
kevinucamОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
α−decay X He X: Four principal decay modes of unstable nuclei
Загружено:
kevinucamАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Four principal decay modes of unstable nuclei:
1.
decay :
The emission of a nucleus
A4
Z2
X N2
A
Z
XN
particle
of a
4
2
H e 2 , and a
( daughter nucleus).
A
Z
X N Z2 y N2 + particle+Q
A4
A
Z
X N Z2 y N2 + 2H e 2 +Q
A
Z
A4
is the parent nucleus, and
A4
Z2
is the daughter nucleus, and Q is
the energy released by the reaction.
2.
decay :
The emission by a nucleus of an electron or positron.
There are 2 type of Beta decay:
decay
decay
+decay
(Electron-beta decay):
+ +Q
+ Q} AZ X Z+1A y +e
A
A
Z X N Z+1 y N 1+
+decay
A
Z
(Positron-beta decay):
++ +Q
X N Z1A y N +1 +e
General formula:
A
Z
X N Z 1A y N 1+ e + +Q
Note:* When there is
is positive,
the
correspond to the
will be negative. Vice versa.
. In other words, if
3.
decay :
The emission by a nucleus of an energetic (MeV) photon:
A
Z
X AZ X +
Where
is the photon of energy. MeV is mega-electron Volt where 1MeV=
1.60217657 X 1013 J
Note: * shows that nucleus is excited.(Excited state means the nucleus has
more energy than usual)
,
4.
decays are known as spontaneous decay.
fission :
The splitting of a heavy nucleus into 2 smaller ( more or less equal sized)
fragments plus neutrons and
A
Z
rays :
X N AZ X N + AZ X N + neutron+ ' s
1
1
Z 1 + Z2 Z , N 1 + N 2 < N , A 1 + A 2 < A
Uranium- 235 nuclear fission
236
141
92
n+ 235
92 U 92 U 56 B a+ 36 K r +3 n+ Q(energy)
This one is the most famous nuclear fission, since nuclear fission is not very
predictable, if it is on the test it must be this one.
Вам также может понравиться
- Week 1 - Introduction & GDPДокумент24 страницыWeek 1 - Introduction & GDPkevinucamОценок пока нет
- Accounts Receivable T Account AnalysisДокумент2 страницыAccounts Receivable T Account AnalysiskevinucamОценок пока нет
- Current Events AssignmentДокумент1 страницаCurrent Events AssignmentkevinucamОценок пока нет
- PSYB10 Syllabus Fall 2016, P. 1 of 6: ProfessorДокумент7 страницPSYB10 Syllabus Fall 2016, P. 1 of 6: ProfessorkevinucamОценок пока нет
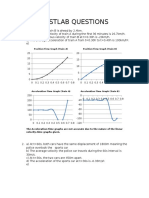
- Postlab Questions: Position-Time Graph (Train A) Position-Time Graph (Train B)Документ3 страницыPostlab Questions: Position-Time Graph (Train A) Position-Time Graph (Train B)kevinucamОценок пока нет
- EconomicsssДокумент2 страницыEconomicssskevinucamОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)