Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Neck Axilla Back
Загружено:
moregutsАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Neck Axilla Back
Загружено:
moregutsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
NECK, AXILLA, ARM & BACK
POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF THE NECK
Anterior: Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Posterior: Anterior border of the trapezius
Inferior: Clavicle
Covered by the Investing layer of the deep cervical fascia
Floor is formed by the prevertebral layer of the deep cervical fascia
Subdivided by the inferior belly of the omohyoid into:
Occipital triangle
Inferior: Inferior belly of the omohyoid
Supraclavicular triangle
Superior: Inferior belly of the omohyoid
Inferior: clavicle
Both triangles:
Anterior: Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
Posterior: Anterior border of the trapezius
Floor: Splenius capitis, Levator scapula, Scalenus medius, Scalenus anterior
OCCIPITAL
Contents of the triangles
SUPRACLAVICULAR
Supraclavicular nerve
Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI)
Superior end of the sympathetic trunk
(Superior, Middle, Inferior cervical
sympathetic ganglion)
Cervical plexus
Semispinalis capitis muscle
Levator scapula muscle
Scalenus posterior muscle
Scalenus medius muscle
rd
3 part of the sublacian artrey
Subclavian vein
Apex of the lung
Roots of the brachial plexua
Deep cervical lymph nodes
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Muscles of the Posterior Triangle
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Splenius capitis
Ligamentum nuchae
Upper 4 thoracic spines
Superior nuchal line of occipital bone
Mastoid process of temporal bone
Dorsal primary rami of spinal
nerve
Levator Scapula
Transverse processes of C1-C4
Medial border of the scapula
Ventral primary rami (C3, C4)
Dorsal Scapular Nerve
Posterior
Transverse processes of C4-C6
2 rib
Medius
Transverse processes of C1-C6
Anterior
Transverse processes of C3-C6
Scalenus
nd
Anterior rami of cervical nerves
st
1 rib
C4-C6
Action
Bends neck laterally
Elevates medial border of the
scapula
Raises medial border of scapula
Bends neck laterally
nd
Elevates 2 rib, laterally flexes
and rotates cervical part of
vertebral column
Elevates 1st rib, laterally flexes
and rotates cervical part of
vertebral column
Scalenus Anterior muscles
1.
2.
3.
Key muscle in understanding the root of the neck and its relation to many neurovascular structures identified in the posterior triangle
Important relations:
Anteriorly related to carotid arteries, vagus nerve, IJV, and deep cervical lymph nodes
nd
Posteriorly related to the pleura, origin of the brachial plexus, and 2 part of the subclavian artery
Medially related to the vertebral artery and vein, sympathetic trunk, and thoracic duct (on the left side)
rd
Laterally - related to the emerging branches of the cervical plexus, roots of the brachial plexus, and the 3 part of the subclavian artery
Divides the subclavian artery into 3 parts
Fibers
1.
2.
Course
3.
4.
Areas of distribution
Phrenic Nerve
Spinal Accessory Nerve (XI)
Motor, Sensory
Motor
CRANIAL ROOT
1. Emerges from anterior surface of the medulla oblongata
2. Nerve runs laterally in the posterior cranial fossa and joins the spinal root
SPINAL ROOT
1. Emerges from nerve cells in the anterior gray horn of the upper 5 segments of the cervical part of
the spinal cord
2. Nerve ascends alongside the spinal cord and enters the skull through the foramen magnum
turns lateral to join cranial root
rd
th
Arises in the neck from the 3 , 4 ,
th
and 5 cervical nerves of the cervical
plexus (C3-C5)
Runs vertically downward across the
front of the scalenus anterior muscle
Enters the thorax by passing in front
of the subclavian artery
Further courses in the thorax
terminating at the diaphragm
Diaphragm
Cranial and Spinal root leave the skull through the jugular foramen and eventually separate:
Cranial root joins vagus nerve; distributed to soft palate, pharynx, and larynx muscles
Spinal root runs downward and laterally and enters SCM and over to the trapezius
Soft palate, pharynx, larynx, sternocleidomastoid, trapezius muscles
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Subclavian arteries
Origin
Commencement
Course
Termination
Left Subclavian
Right Subclavian
Arch of the aorta
Brachiocephalic artery
Behind manubrium sterni
Behind right sternoclavicular joint
Ascends to the root of the neck
Arches upward and laterally over the pleura between the scalenus
anterior and medius muscles
st
Outer border of the 1 rib
Scalenus anterior divides the subclavian artery into 3 parts
Vertebral artery
Basilar artery
Inferior thyroid artery
Posterior
cerebral artery
First Part of Subclavian Artery
Extends from the origin of the subclavian artery to the medial border of scalenus anterior
1st
Thyrocervical
trunk
Superficial cervical
artery
Suprascapular artery
Internal thoracic
artery
Subclavian artery
Superior epigastric
artery
Musculophrenic artery
2nd
Costocervical
trunk
Superior intercostal
artery
Deep cervical artery
3rd
Vertebral artery - ascends in the neck through foramina in the transverse processes of the
upper 6 cervical vertebrae ,ascends into the skull through the foramen magnum;
Forms the basilar artery at the anterior surface of the medulla oblongata at the level of the
lower border of the pons
Basilar artery - gives branches to the pons, cerebellum, and internal ear; contributes
to the formation of the Circle of Willis
Posterior cerebral artery - curves laterally and backward around the midbrain
Thyrocervical trunk
Inferior thyroid artery - closely related to recurrent laryngeal nerve; gives branches
to thyroid and inferior parathyroid glands
Superficial cervical artery - crosses the brachial plexus
Suprascapular artery - follows the suprascapular nerve onto the back of the scapula
st
Internal thoracic artery descends into the thorax behind the 1 costal cartilage and in front
of the pleura
Superior epigastric artery - supplies anterior abdomen
th th
Musculophrenic artery - supplies 7 -9 intercostal spaces and diaphragm
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
Second Part of Subclavian Artery
Lies behind the scalenus anterior
Costocervical trunk - runs backward over the dome of the pleura
st
nd
Superior intercostal artery supplies 1 and 2 intercostal spaces
Deep cervical artery - supplies deep muscles of the neck
Third Part of Subclavian Artery
Extends from the lateral border of the scalenus anterior across the posterior
st
triangle to the lateral border of the 1 rib
Continues to the axillary artery
No branches
Subclavian Vein
st
Commencement: Outer border of the 1 rib
From the axillary vein
Joins internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein
Receives the external jugular vein
Receives thoracic duct (left side) and right lymphatic duct (right side)
Relations:
Anterior: Clavicle
Posterior: Scalenus anterior and phrenic nerve
st
Inferior: upper surface of the 1 rib
Lymph Drainage
Superficial Cervical Lymph Nodes
Situated along the course of the External
Jugular Vein
Receive lymph from:
1. The skin over the angle of the jaw
2. Skin over the apex of the parotid gland
3. Lobe of the ear
Efferent lymph vessels drain into the deep
cervical lymph nodes
Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes
Form a vertical chain along the course of the Internal Jugular Vein
within the carotid sheath
Receive lymph from regional nodes:
1. Jugulodigastric node located below the angle of the jaw
Drainage of the tonsil and tongue
2. Jugulo-omohyoid node close to the omohyoid muscle
Drainage of the tongue
Efferent lymph vessels join to form jugular trunk drains into
thoracic duct (right lymph duct)
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
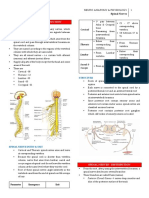
CERVICAL PLEXUS
st
Formed by the anterior rami of 1 4 cervical nerves
Joined by connecting branches form loops that lie in front of the
origins of the levator scapulae and scalenus medius
Covered in front by the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia
Related to the Internal Jugular Vein in the carotid sheath
Supplies the skin and muscles of the head, neck, and shoulders
Branches of the Cervical Plexus
Branches
Nerve Root
CUTANEOUS BRANCHES
Lesser Occipital nerve
C2
Greater auricular
nerve
Transverse cervical
nerve
C2, 3
Supraclavicular nerve
C3, 4
Distribution
Back of the scalp and
auricle
Skin over the angle of the
mandible
Skin over the front of the
neck
Skin over the shoulder
region
MUSCULAR BRANCHES TO THE NECK MUSCLES
Proprioceptive, C2, 3
Prevertebral muscles, SCM
C3, 4
Levator scapulae
Proprioceptive C3, 4
Trapezius
Branch of C1 joins with hypoglossal nerve
Some C1 fibers leave as a descending branch unites with
descending cervical nerve (C2, 3)
C1 descending branch + descending cervical nerve = ansa cervicalis
Ansa cervicalis innervates Sternohyoid, Omohyoid, Sternothyroid
MUSCULAR BRANCH TO THE DIAPHRAGM
Phrenic nerve
C3, 4, 5
Diaphragm
CERVICAL PART OF THE SYMPATHETIC TRUNK
st
Extends upward to the base of the skull below the neck of the 1 rib
Directly behind the internal and common carotid arteries, embedded in deep fascia
Three Ganglia of the Sympathetic Trunk and its Branches
Superior
Cervical
Ganglion
Middle
Cervical
Ganglion
Inferior
Cervical
Ganglion
Internal carotid nerve
Gray rami communicantes
Arterial branches
Cranial nerve brances
Phrayngeal branches
Superior cardiac branch
Gray rami communicantes
Thyroid branches
Middle cardiac branch
Stellate ganglion
Gray rami communicantes
Arterial branches
Inferior Cardiac branch
Postganglionic fibers; accompanies ICA
To the upper 4 anterior rami of cervical nerves
To the common and external carotid arteries
th
th
th
Join the 9 , 10 , and 12 cranial nerves
Unite with glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves
Descends in the neck; ends in cardiac plexus
th
To the anterior rami of 5 and 6th cervical nerves
Pass along inferior thyroid artery; to thyroid gland
Descends in the neck; ends in cardiac plexus
st
Fused inferior cervical with 1 thoracic ganglion
th
th
To the anterior rami of the 7 and 8 cervical nerve
To the subclavian and vertebral arteries
Descends to join the cardiac plexus
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
AXILLA, PECTORAL REGION, and MAMMARY GLAND
BREAST (Mammary gland)
Specialized accessory glands of the skin that secrete milk
Present in both sexes (similar structures in males and immature females)
nd
Superior: 2 rib
th
Inferior: 6 rib
Medial: Lateral margin of the sternum
Anterior: Skin
Posterior: Deep pectoral fascia
th
Nipples (at level of 4 intercostal space) are small and surrounded by a colored area of
the skin areola
Areolar glands produces tiny tubercles in the areola
Darkening of areola increased deposits of melanin in the epidermis
Axillary tail of Spence
Extension upward and laterally piercing the deep fascia at lower border of
pectoralis major
Enters the axilla
Each breast consist of 15-20 lobes radiate out from the nipple
Main duct of each lobe opens separately on the summit of the nipple each
possess a dilated ampulla (before termination)
Lobes are separated by fibrous septa serves as
suspensory ligaments of Cooper
Retromammary space - space behind the breast filled by loose connective tissue
Perforating branches of internal thoracic artery,
intercostal arteries
Axillary artery via
Lateral
lateral thoracic and thoracoacromial arteries
(correspond to arteries)
Medial
Into the internal thoracic group of nodes
Lateral
Into the anterior axillary or pectoral group of nodes
Posterior Into the posterior intercostal nodes
th th
4 -6 intercostal nerves
Medial
Arterial supply
Venous supply
Lymph
drainage
Innervation
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Muscles of the Pectoral Region
Origin
Insertion
Pectoralis major
Clavicle
Sternum
Upper 6 costal cartilages
Pectoralis minor
3 , 4 , and 5 ribs
Subclavius
1 costal cartilage
Clavicle
Serratus anterior
Upper 8 ribs
Medial border and inferior
border of scapula
rd
th
st
th
Lateral lip of bicipital
groove of humerus
Coracoid process of
scapula
Innervation
Medial and lateral pectoral
nerves from brachial
plexus
Medial pectoral nerve
from brachial plexus
Nerve to subclavius from
upper trunk of brachial
plexus
Long thoracic nerve
Nerve Roots
C5, 6, 7, 8, T1
C6, 7, 8
C5, 6
C5, 6, 7
Action
Adducts arm and rotates it medially
Clavicular fibers also flex arm
Depresses point of shoulder
if fixed scapula elevates ribs of origin
Depresses clavicle and steadies this
bone during movements of the
shoulder girdle
Draws the forward anterior around the
thoracic wall
Rotates the scapula
The Axilla
Axilla (armpit)
Pyramid-shaped space between the upper part of the arm and side of the
chest
Forms an important passage for nerves, blood, and lymph vessels as they
travel from root of the neck to the upper limb
Apex upper end of the axilla
Directed into the root of the neck
Bounded in front by the clavicle, behind by the upper border of the scapula,
st
and medially by the outer border of the 1 rib
Base lower end of the axilla
Bounded in front by anterior axillary fold (lower border of pectoralis major),
behind by posterior axillary fold (tendon of latissimus dorsi and teres
major), medially by the chest wall
Contents:
Axillary artery and its branches supply blood to upper limb
Axillary vein and tributaries drains blood from upper limb
Lymph vessels and lymph nodes - drain lymph from upper limb and breast
Brachial plexus innervates the upper limb
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
Walls of the Axilla
Anterior Wall: Pectoralis major
Subclavius
Pectoralis minor
Posterior Wall: Subscapularis
Latissimus dorsi
Teres major
Medial Wall: Upper 4 or 5 ribs
Intercostal spaces covered by serratus anterior
Lateral Wall: Coracobrachialis
biceps in the bicipital groove of the humerus
Base is formed by the skin stretching between anterior and posterior walls
Axilla contains principal vessels and nerves to upper limb and lymph nodes
Key Muscle in Axilla
Pectoralis minor
Crosses axillary artery and
brachial plexus of nerves
Used in describing the axillary
artery to divide into 3 parts
BRACHIAL PLEXUS
Complicated plexus allowing nerve fibers from different segments of the spinal cord to be arranged and distributed
efficiently in nerve trunks to the various parts of the upper limbs
th
th
st
Formed in the posterior triangle of the neck union of anterior rami of the 5 to 8 cervical and 1 thoracic spinal nerves
Important functions:
1. Sensory innervation to the skin and deep structures
2. Motor innervation to the muscles
3. Influence over the diameters of the blood vessels by the sympathetic vasomotor nerves
4. Sympathetic secretomotor supply to the sweat glands
Divided into roots, trunks, divisions, and cords
Roots, trunks, divisions reside in lower part of posterior triangle of the neck
Cords and its branches arranged around the axillary artery in the axilla; enclosed in axillary sheath
Lateral cord Upper (C5, 6) + middle (C7)
Posterior cord Upper (C5, 6) + middle (C7) + lower (C8, T1)
Medial cord Lower (C8, T1)
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
Branches of the Brachial Plexus
Branches
ROOTS
Dorsal Scapular nerve
Long Thoracic nerve
UPPER (SUPERIOR) TRUNK
Suprascapular nerve
Nerve to subclavius
(Accessory phrenic nerve)
LATERAL CORD
Lateral Pectroal nerve
Musculocutaneous nerve
POSTERIOR CORD
Upper subscapular nerve
Lower subscapular nerve
Axillary nerve
Thoracodorsal nerve
Radial nerve
MEDIAL CORD
Medial pectoral nerve
Medial cutaneous nerve
Medial cutaneous nerve of
forearm
Ulnar nerve
LATERAL + MEDIAL CORD
Lateral root of median nerve
Medial root of median nerve
Roots
C5
C5, 6, 7
C5, 6
C5, 6, 7
C5,6
C6, 7, 8
C5, 6, 7,
8, T1
C8, T1
Distribution
Rhomboid minor, Rhomboid major,
Levator scapulae muscles
Serratus anterior
Supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Subclavius
*Gives contribution to phrenic nerve
Pectoralis major
Coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis
Subscapularis
Subscapularis and teres major
Deltoid and teres mainor
Latissimus dorsi
Triceps, anconeus, part of brachialis,
forearm and hand and finger muscles
Pectoralis major and minor
Skin of medial side of arm
Skin of medial side of forearm
Hand and finger muscles
C5, 6, 7
C5, 6, 7,
8, T1
Forearm, hand and finger muscles
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
AXILLARY ARTERY and VEIN
AXILLARY ARTERY
Origin: Subclavian artery
st
Commencement: Lateral border of the 1 rib
Termination: Lower border of the teres major
Closely related to brachial plexus and their branches and with the axillary sheath
Pectoralis minor muscle divides axillary artery into 3 parts
st
1. First Part extends from lateral border of 1 rib to upper border of pectoralis minor
2. Second part behind the pectoralis minor
3. Third part extends from lower border of pectoralis minor to lower border of teres major
Axillary artery
st
1 part
Branch
Highest thoracic
artery
Thoracoacromial
artery
nd
2 part
Lateral thoracic
artery
Subscapular artery
rd
3 part
Anterior circumflex
humeral artery
Posterior circumflex
humeral artery
Relation
Anterior: Pectoralis major and skin
Posterior: Long thoracic nerve
Lateral: 3 cords of the brachial plexus
Medial: axillary vein
Anterior: Pectoralis minor, pectoralis major and the
skin
Posterior: Posterior cord of the brachial plexus,
subscapularis, shoulder joint
Lateral: Lateral cord of the brachial plexus
Medial: Medial cord of the brachial plexus and
axillary vein
Anterior: Pectoralis major, crossed by medial root
of median nerve
Posterior: Subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres
major, axillary and radial nerves
Lateral: Coracobrachialis, biceps, humerus, lateral
root of median and musculocutaneous nerve
Medial: Ulnar nerve, axillary vein, medial
cutaneous nerve of the arm
AXILLARY VEIN
Commencement: Lower border of the teres major
st
Termination: Lateral border of the 1 rib
Drains into subclavian vein
Formed from union of:
venae comitantes of the brachial artery and basilic vein
Vein receives tributaries corresponding to branches of the axillary artery
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
ARM and CUBITAL FOSSA
Skin
Superficial Sensory Nerves
Cutaneous nerves on lateral surface
1. Supraclavicular nerves (C3, 4)
Nerve supply to skin over the point of the shoulder halfway down the deltoid
2. Upper lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm (branch of axillary nerve C5, 6)
Nerve supply to skin over the lower half of the deltoid
3. Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm (branch of radial nerve C5, 6)
Nerve supply to skin over lateral surface of arm below the deltoid
Cutaneous nerves on medial surface
1. Medial Cutaneous nerve of the arm (T1)
Nerve supply of skin of the armpit and medial side of the arm
2. Intercostobrachial nerves (T2)
3. Posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm (branch of radial nerve C8)
Nerve supply of skin of the back of the arm
Veins of upper limb
Deep veins
Comprises the venae comitantes accompany
large arteries and the axillary vein
Superficial veins
Lie in the superficial fascia
Cephalic vein
Termination
Subcutaneous tissue from the lateral aspect
of the dorsum of the hand (lateral of the
wrist)
Deltopectoral groove
Drainage
Axillary vein
Commencement
Basilic vein
Medial border of the wrist
Lower border of teres major
Joins venae comitantes of brachial artery
into the axillary vein
Medial cubital vein and Median vein of the forearm - Communicating veins (links cephalic and basilica veins)
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
MUSCLES OF THE ARM
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Nerve Roots
Action
ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT
Biceps
brachii
Long head
Short head
Coracobrachialis
Brachialis
Supraglenoid tubercle of
scapula
Coracoid process of
scapula
Front of lower half of
humerus
POSTERIOR COMPARTMENT
Long head
Infraglenoid tubercle of
scapula
Lateral head
Upper half of posterior
Triceps
surface of humerus shaft
Medial head
Lower half of posterior
surface of humerus shaft
Lateral epicondyle of the
Anconeus
humerus
Tuberosity of radius
bicipital aponeurosis
Medial shaft of humerus
C5, 6
Musculocutaneous nerve
Coronoid process of ulna
C5, 6, 7
C5, 6
Supinator of forearm
flexor of elbow
Weak flexor of shoulder joint
Flexes arm, weak adductor
Flexor of elbow joint
Extensor of elbow joint
Olecranon process of ulna
Radial nerve
C6, 7, 8
Help stabilize elbow joint
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
Intermuscular septa Divides the arm into anterior and posterior compartment
Bicipital Aponeurosis reinforces antecubital area within the cubital fossa
Contents of the Fascial Compartment of the Upper Arm
Anterior
Posterior
Biceps brachii
Muscles
Coracobrachialis
3 heads of triceps
Brachialis
Blood supply
Brachial artery
Profunda brachii
Muscular Innervation
Musculocutaneous nerve
Radial nerve
Musculocutaneous
Median nerve
Ulnar nerve
Structures passing
Radial nerve
Brachial artery
through the compartment
Ulnar nerve
Basilica vein
Radial nerve (Present In Lower Part)
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
ANTERIOR FASCIAL COMPARTMENT
BRACHIAL ARTERY
Origin: Axillary artery
Commencement: Lower border of the teres major
Termination: Neck of the Radius
Divides into Radial and Ulnar arteries
Branches
Muscular branches to the anterior compartment of the upper arm
Nutrient artery to the humerus
Profunda artery - arises near beginning of the brachial artery; follows radial nerve into the spiral
groove of the humerus
Superior ulnar collateral artery - arises near the middle of the upper arm; follows the ulnar nerve
Inferior ulnar collateral artery - arises near the termination of the artery; takes part in the
anastomosis around the elbow joint
MUSCULOCUTANEOUS NERVE
From the lateral cord of the brachial plexus (C5,6, 7)
Pierces the coracobrachialis and passes between the biceps and brachialis
Appears at lateral margin of biceps tendon and pierces deep fascia above the elbow
Continues to the lateral aspect of the forearm as the lateral cutaneous nerve
Branches
Muscular branches to the biceps, coracobrachialis, and brachialis
Cutaneous branches - lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
Articular branches to the elbow joint
Median Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
Radial Nerve
From the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus
Runs downward on the lateral of the brachial artery
Halfway down the arm crosses brachial artery
At elbow crossed by bicipital aponeurosis
From medial cord of the brachial plexus
Runs downward on medial side of brachial artery up to middle of the arm
At coracobrachialis insertion pierces medial fascial septum and enters posterior
compartment of the arm; passes behind medial epicondyle of the humerus
Immediately enters posterior compartment of the arm
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
POSTERIOR FASCIAL COMPARTMENT
From posterior cord of the brachial plexus
Nerve winds around back of the arm in the spiral groove on back of the
humerus between head of triceps
Pierces lateral fascial septum above elbow and continues into cubital fossa
In spiral groove nerve is accompanied by profunda vessels
Radial Nerve
Ulnar Nerve
Profunda brachii Artery
Superior and Inferior
Ulnar Collateral
Arteries
Branches
In axilla -Posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm; branches given to
the long and medial heads of triceps
In spiral groove branches given lateral and medial heads of
triceps and anconeus
Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm
In anterior compartment of the arm gives branches to brachialis,
brachioradialis, extensor carpo radialis longus muscles
Articular branches to elbow joint
Descends behind the septum, covered posteriorly by the medial head
Accompanied by superior ulnar collateral vessels
At elbow lies behind medial epicondyle of the humerus on the medial
ligament of the elbow joint
Enters the forearm between 2 heads of origin of flexor carpi ulnaris
No articular branch to elbow joint
Origin: Brachial artery
Accompanies radial nerve through the spiral groove
Supplies triceps muscle, takes part in anastomosis around elbow joint
Origin: brachial artery
Take part in anastomosis around elbow joint
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Cubital Fossa
Triangle depression in front of the elbow
Roof: skin and fascia reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis
Floor: Brachialis
Base of the triangle: Imaginary line between the humeral
Lateral: brachioradialis
Medial: Pronator teres
Contents (medial to lateral):
Median nerve
Bifurcation of the brachial artery
Tendon of the biceps
Radial nerve and its deep branch
ELBOW JOINT
Articulation: between trochlea and capitulum of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna and head of the radius
articular surfaces covered with hyaline cartilage
Type: Synovial hinge joint
Capsule: Anterior: attached above to the humerus along upper margins of coronoid and radial fossae
to the front of the medial and lateral epicondyles and below to the margin of the coronoid process of the ulna and to the annular ligament
Posterior: attached above to margins of olecranon fossa of the humerus and below to the upper margin and sides of the olecranon process
Ligaments: Lateral ligament triangular; attached by its apex to lateral epicondyle of humerus
Medial ligament triangile; with 3 strong bands: anterior band, posterior band, transverse band
Synovial membrane : lines the capsule and covers fatty pads in the floors of the coronoid, radial, and olecranon fossae
Nerve supply: Branches from median, ulnar, musculocutaneous, and radial nerves
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
BACK, SHOULDER, & SCAPULAR MUSCLES
Bony Prominences
External occipital protuberance lies at junction of head and neck
th
Seventh (7 ) cervical vertebrae (vertebra prominens) most prominent
spinous process that can be felt in the neck
st
First (1 ) thoracic vertebra
Scapula
rd
Crest of the spine can be palpated at level of 3 thoracic spine
Medial border
st
Superior angle can be palpated opposite the 1 thoracic spine
th
Inferior angle can be palpated opposite the 7 thoracic spine
th
Iliac crest lie at the level of 4 lumbar spine
Superficial part of the back
Posterior rami of spinal nerves
Sensory nerve
st
th
(1 and 8 cervical nerves does not supply the skin)
supply
Arterial supply
Venous supply
Posterior branches of the:
posterior intercostal arteries and the lumbar arteries
Posterior intercostal vein and the lumbar vein
drain into azygos veins and the inferior vena cava
Deep Fascia of the back (Thoracolumbar Fascia)
Situated in the interval between the iliac crest and the 12th rib
Forms a strong aponeurosis
Gives origin to middle fibers of the transversus and the upper fibers of the
oblique muscle
Medially, splits into 3 lamellae
1. Posterior lamella covers deep muscles of the back;
attached to lumbar spines
2. Middle lamella attached to tips of transverse processes of the lumbar
vertebrae; lies anterior to deep muscles of the back and posterior to
the quadratus lumborum
3. Anterior lamella attached to anterior surface of the transverse
process of the lumbar vertebrae; anterior to quadratus lumborum
Muscles acting on the
vertebral column
Muscles acting on the
humerus
Erector spinae
Spinalis
Longissimus
Iliocostalis
Transversospinalis
Rotatores
Multifidus
Semispinalis
Interspinales
Intertrasnversarii
Deltoid
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres major
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
MUSCLES OF THE BACK
Origin
Insertion
Innervation
Nerve Roots
Action
SUPERFICIAL MUSCLES
Trapezius
Latissimus dorsi
Occipital bone
Ligamentum nuchae
th
Spine of 7 cervical vertebra
Spines of all thoracic vertebra
Iliac crest
Lumbar fascia
Spines of lower 6 thoracic
vertebrae
Lower 3-4 ribs
Inferior angle of the scapula
Upper fibers into lateral
third of clavicle
Middle and lower fibers
into acromion and spine
of scapula
Floor of bicipital groove of
humerus
Spinal part of
accessory nerve
(motor)
C3, C4 (sensory)
XI cranial nerve
(spinal part)
Upper fibers: elevate
the scapula
Middle fibers: pull
scapula medially
Lower fibers: pull
medial border of
scapula downward
Thoracodorsal nerve
C6, 7, 8
Extends, Adducts, and
medially rotates the arm
C3 and C4
Dorsal scapular nerve
C3, 4, 5
Raises medial border of
scapula
Dorsal Scapular nerve
C4, 5
INTERMEDIATE MUSCLES
st
Levator Scapula
Rhomboid Minor
Rhomboid major
Serratus Posterior
Superior
Serratus Posterior
Inferior
DEEP MUSCLES
Splenius capitis
Splenius cervicis
Transverse processes of 1 four
cervical vertebrae
Ligamentum nuchae
th
st
Spines of 7 cervical and 1
thoracic vertebrae
nd
th
2 5 thoracic spines
Lower cervical and upper thoracic
spines
Medial Border of scapula
Upper ribs
Intercostal Nerves
Upper lumber and lower thoracic
spines
Lower ribs
Lower part of ligamentum nuchae
Upper 4 thoracic spines
Superior nuchal line of occipital
bone and mastoid process of
temporal bone
Transverse process of upper
cervical vertebrae
Erector spinae, Transversospinalis, Interspinales, Intertransversarii
Posterior rami of spinal
nerves
Raises medial border of
scapula upward and medially
Raises ribs
Inspiratory muscle
Depresses ribs
Expiratory muscle
Bends neck laterally
Elevates medial border of the
scapula
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
SHOULDER and SCAPULAR MUSCLES
Origin
Deltoid
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Teres major
Subscapularis
Lateral third of the clavicle
Acromion
Spine of the scapula
Insertion
Middle lateral surface of shaft
of humerus
Supraspinous fossa of scapula
Infraspinous fossa of scapula
Upper two thirds of the
lateral border of scapula
Lower third of
lateral border of scapula
Subscapular fossa
Greater tuberosity of humerus
Capsule of shoulder joint
Innervation
Axillary nerve
Suprascapular nerve
Axillary nerve
Medial lip of bicipital groove of
humerus
Lesser tuberosity of humerus
Lower subscapular
nerve
Upper and lower
subscapular nerves
Nerve Roots
C5, 6
C4,5, 6
(C4), 5, 6
C6, 7
C5, 6, 7
Action
Abducts the arm
Anterior fibers: flex and
medially rotate arm
Posterior fibers: extend
and laterally rotate arm
Abducts arm and stabilizes
shoulder joint
Laterally rotates arm and
stabilizes shoulder joint
Medially rotates arm
Adducts arm
Stabilizes shoulder joint
Rotator Cuff Muscles:
SITS muscles
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Stabilizes shoulder joint
Acts in coordination to hold the head of the
humerus in the glenoid fossa
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Triangle of Auscultation
Site on the back where breath sounds may be most easily heard with a microscope
Inferior: Superior border of the latissimus dorsi
Medial: Inferior fibers of the trapezius
Lateral: Medial border of the scapula
Lumbar Triangle
Site where pus may emerge from the abdominal wall (pus accumulation may
occur)
Inferior: Iliac crest
Medial: Inferior border of latissimus dorsi
Lateral: posterior border of the external oblique of the abdomen
Suboccipital Triangle
Medial: Rectus capitis posterior major
Lateral: Oblique capitis superior
Oblique capitis inferior
Triangular space
Superior: Teres minor
Inferior: Teres major
Lateral: Long head of triceps brachii
Contains circumflex scapular artery
Quadrangular space
Superior: Subscapularis
Inferior: Teres major
Medial: Long head of triceps brachii
Lateral: surgical neck of humerus
Contains Axillary nerve and Posterior circumflex humeral artery
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
1st shift 2015-2016
Arterial anastomosis around the shoulder joint
Anastomosis between the branches of the subclavian artery and axillary artery
Ensures adequate blood flow in upper limb irrespective of arm positioning
Branches from Subclavian artery
Suprascapular artery - distributed to the supraspinous and infraspinous
fossae of the scapula
Superficial cervical artery - gives off a deep branch running down the
medial border of the scapula
Branches from Axillar artery
Subscapular artery and its circumflex scapular branch - supply the subscapular and
infraspinous fossae of the scapula respectively
Anterior circmflex humeral artery
Posterior circumflex humeral artery
Both Circumflex arteries form an anastomosing circle around the surgical neck of the humerus
SHOULDER JOINT
Articulation: between rounded head of the humerus and shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula
articular surfaces covered by hyaline cartilage; glenoid cavity deepened by glenoid labrum (fibrocartilaginous rim)
Type: Synovial ball-and-socket joint
Capsule: surrounds the joint and attached medially to the margin of the glenoid cavity outside the labrum
Thin and lax allows movement; strengthened by fibrous slips from the tendons of the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor
Ligaments: Glenohumeral ligaments 3 weak bands of fibrous tissue, strengthen front of the capsule
Transverse humeral ligament strengthens the capsule and bridges the gap between 2 tuberosities
Coracohumeral ligament strengthens capsule above and stretches from the root of the coracoid process to the greater tuberosity of the humerus
Synovial membrane : lines the capsule and attached to margins of the cartilage covering the articular surfaces
extends through anterior wall of the capsule forms subscapularis bursa beneath subscapularis
Nerve supply: Axillar and suprascapular nerves
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
TOPOGRAPHIC ANATOMY
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
MUSCLE ATTACHMENT and INSERTION
1st shift 2015-2016
Anatomy 1C Joshua Montelibano
CLAVICLE, SCAPULA and HUMERUS
1st shift 2015-2016
Вам также может понравиться
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1Документ20 страниц11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 1checkmateОценок пока нет
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THДокумент6 страницManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Back PDFДокумент4 страницыMuscles of The Back PDFjsdlzjОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Exam Review Muscles Innervations VasculatureДокумент27 страницAnatomy Exam Review Muscles Innervations Vasculaturegdubs215Оценок пока нет
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck JDVДокумент5 страницAnterior Triangle of The Neck JDVNica Lopez Fernandez100% (3)
- GRDA Intro NeckДокумент12 страницGRDA Intro NeckKingОценок пока нет
- Arterial Supply of Head and NeckДокумент41 страницаArterial Supply of Head and NeckKhadija VasiОценок пока нет
- Muscles and Their VAN Supply and FunctionДокумент8 страницMuscles and Their VAN Supply and FunctionVinothini Siva100% (1)
- HSB - Neck: Anterior TriangleДокумент8 страницHSB - Neck: Anterior TriangleRaki Iligan100% (1)
- Openings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedДокумент19 страницOpenings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedMacy Peralta100% (1)
- Spinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Документ5 страницSpinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Dr P N N ReddyОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsДокумент17 страницAnatomy 2 MnemonicsRosalie Catalan EslabraОценок пока нет
- Mnemonics Anatomy 1st SemДокумент4 страницыMnemonics Anatomy 1st SemNastassja Callmedoctor Douse67% (3)
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusДокумент22 страницыAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarОценок пока нет
- Head, Neck, Limbs OINAДокумент17 страницHead, Neck, Limbs OINAFrancis HenaresОценок пока нет
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckДокумент36 страниц6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyОценок пока нет
- ANATOMY: Pelvic 2Документ16 страницANATOMY: Pelvic 2Nur Liyana MohamadОценок пока нет
- Lower Limb - Clinical AnatomyДокумент18 страницLower Limb - Clinical Anatomyewijayapala100% (2)
- Anatomy Notes Awsome PDFДокумент210 страницAnatomy Notes Awsome PDFMuhammad RashidОценок пока нет
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck IIДокумент49 страницAnterior Triangle of The Neck IIvrajОценок пока нет
- Brainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaДокумент23 страницыBrainstem (Pons, Medulla, Midbrain) : Dr. MariaMuhammad Mustaqeem100% (1)
- Muscle of Upper LimbsДокумент5 страницMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsДокумент46 страницAnatomy MnemonicsMini ManraiОценок пока нет
- Lower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighДокумент8 страницLower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDОценок пока нет
- LMR ANATOMY by DR Shilpi Agarwal PDF Filename UTF 8''LMR ANATOMY PDFДокумент12 страницLMR ANATOMY by DR Shilpi Agarwal PDF Filename UTF 8''LMR ANATOMY PDFadiОценок пока нет
- Anatomy - Upper LimbДокумент72 страницыAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinОценок пока нет
- Head - Neck (Chapter 11)Документ14 страницHead - Neck (Chapter 11)Alenna Benitez50% (2)
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiДокумент4 страницыCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catОценок пока нет
- Head and Neck Arterial SystemДокумент30 страницHead and Neck Arterial SystemArifa parveenОценок пока нет
- Table of Head and Neck MusclesДокумент5 страницTable of Head and Neck Musclesororoangel0% (1)
- Head and Neck AnswersДокумент15 страницHead and Neck AnswersANDRE MAОценок пока нет
- Table A - TMJ and Infratemporal FossaДокумент9 страницTable A - TMJ and Infratemporal Fossaapi-422030113Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy - Cranial NervesДокумент3 страницыAnatomy - Cranial NervesKaradex DexondОценок пока нет
- Head and Neck AnatomyДокумент11 страницHead and Neck AnatomySaajid Amra100% (1)
- Anatomy MnemonicsДокумент51 страницаAnatomy MnemonicsDrKhawarfarooq SundhuОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationДокумент7 страницMuscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationKris GulleyОценок пока нет
- (ANA) 4.01 Abdomen in General - Dr. ElevazoДокумент22 страницы(ANA) 4.01 Abdomen in General - Dr. ElevazopasambalyrradjohndarОценок пока нет
- SkullДокумент48 страницSkulldavid100% (1)
- Head and Neck TumorsДокумент14 страницHead and Neck TumorsBarda GulanОценок пока нет
- Brachial Plexus: Summary Mnemonics Clinical RelationsДокумент19 страницBrachial Plexus: Summary Mnemonics Clinical RelationsGulmehr NoorОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerves and BranchesДокумент5 страницCranial Nerves and Branchesballer0417Оценок пока нет
- Upper LimbДокумент31 страницаUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojОценок пока нет
- Forearm & Hand AnatomyДокумент5 страницForearm & Hand AnatomyshivnairОценок пока нет
- Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)Документ58 страницMuscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)sdfs sdfdОценок пока нет
- PLM AbdomenДокумент11 страницPLM AbdomenClaudine Victoria Taracatac100% (1)
- MUSCLES OINA LavarnДокумент20 страницMUSCLES OINA LavarnStray KidsОценок пока нет
- 15 PharynxДокумент9 страниц15 Pharynxapi-3757921Оценок пока нет
- Bone SkullДокумент80 страницBone SkullKumarОценок пока нет
- 1.embryology Q AДокумент11 страниц1.embryology Q ADr P N N ReddyОценок пока нет
- Triangles of Neck (Anatomy)Документ36 страницTriangles of Neck (Anatomy)Dr Tahira Nihal100% (1)
- Brain CisternsДокумент44 страницыBrain CisternsRam Kirubakar Thangaraj100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFДокумент6 страницIdoc - Pub Anatomy-Viva PDFhieulee84Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The ARMДокумент17 страницAnatomy of The ARMJacob MasikaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of LarynxДокумент46 страницAnatomy of LarynxMayur Ingale100% (1)
- Osta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadДокумент22 страницыOsta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadslyfoxkittyОценок пока нет
- 02 Neck Axilla BackДокумент15 страниц02 Neck Axilla BackMonique BorresОценок пока нет
- 02 Neck Axilla BackДокумент15 страниц02 Neck Axilla BackMonique BorresОценок пока нет
- 02 Neck Axilla BackДокумент15 страниц02 Neck Axilla BackMonique BorresОценок пока нет
- 02 Neck Axilla BackДокумент15 страниц02 Neck Axilla BackMonique BorresОценок пока нет
- Rekap Tindakan MRI Feb 2020Документ7 страницRekap Tindakan MRI Feb 2020Metta WitariОценок пока нет
- 15 Spinal Cord External FeaturesДокумент81 страница15 Spinal Cord External FeaturesPraveen BaddipudiОценок пока нет
- Porcine Meat StandardДокумент27 страницPorcine Meat StandardoptimeatvaleriaОценок пока нет
- LegsДокумент28 страницLegsDevendar SharmaОценок пока нет
- Bobath ApproachДокумент22 страницыBobath ApproachCedricFernandez50% (4)
- Lab 9 Nervous TissueДокумент28 страницLab 9 Nervous TissueSarwar JafarОценок пока нет
- Gross Anatomy Practice Test #1Документ4 страницыGross Anatomy Practice Test #1Medicine4theMassesОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Upper AirwayДокумент13 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The Upper AirwayIgnacio VeraОценок пока нет
- Spinal Yoga Warm Up ExercisesДокумент1 страницаSpinal Yoga Warm Up ExercisesdrguruОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Radio GuidelinesДокумент4 страницыDiagnostic Radio Guidelinesrehan hayderОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of FreestyleДокумент7 страницBiomechanics of FreestylebrettОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Topografi Kepala-ParotisДокумент12 страницAnatomi Topografi Kepala-ParotisFeri IrawanОценок пока нет
- Paper Craft Skull Gart PDFДокумент12 страницPaper Craft Skull Gart PDFArmenie Ruth Tecne Due100% (1)
- Nursing Assessment in Tabular FormДокумент38 страницNursing Assessment in Tabular FormCas Tan100% (1)
- Histology of The Respiratory SystemДокумент62 страницыHistology of The Respiratory Systemmichelle100% (1)
- The Five Animal FrolicsДокумент113 страницThe Five Animal FrolicsEthual Smith100% (3)
- Groin AnatomyДокумент7 страницGroin AnatomyLorenzo Daniel AntonioОценок пока нет
- Guide To Agni SaraДокумент11 страницGuide To Agni SaraEnoch Gandhislilbrother Abraham100% (1)
- Three-Dimensional Anthropometry of The Lips in Young Japanese AdultsДокумент6 страницThree-Dimensional Anthropometry of The Lips in Young Japanese AdultsDrDejanDrakulОценок пока нет
- Ankle & Foot ExamДокумент18 страницAnkle & Foot ExamAlpar KissОценок пока нет
- Skeletal Muscle Tissue & Muscle OrganizationДокумент90 страницSkeletal Muscle Tissue & Muscle Organizationtiiandi100% (3)
- Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet GynecolДокумент6 страницInt J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecolpatrimonio79Оценок пока нет
- General Anatomy SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGeneral Anatomy SyllabusPatricia patriciaОценок пока нет
- Muscle Spindle SamarДокумент28 страницMuscle Spindle SamarHimanshu YadavОценок пока нет
- Atlas of Approaches in Neurosurgery - J.FischerДокумент7 страницAtlas of Approaches in Neurosurgery - J.FischerZdravko HeinrichОценок пока нет
- Orofacial Complex: Form and FunctionДокумент34 страницыOrofacial Complex: Form and FunctionAyushi Goel100% (1)
- Providing Range of Motion ExercisesДокумент5 страницProviding Range of Motion ExercisesKristine Faith AzcuetaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 9 Questions & AnswersДокумент2 страницыLesson 9 Questions & AnswersAnonymous nulAkhlY100% (2)
- Skull XrayДокумент13 страницSkull XrayEdgar BaniquedОценок пока нет
- Pier Paolo Maria Menchetti-Cervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFДокумент258 страницPier Paolo Maria Menchetti-Cervical Spine - Minimally Invasive and Open Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFLorena BurdujocОценок пока нет