Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
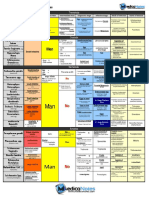
Endocrine Gland Hormone Released Chemical Class Target Tissue/Organ Major Function of Hormone
Загружено:
billyОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Endocrine Gland Hormone Released Chemical Class Target Tissue/Organ Major Function of Hormone
Загружено:
billyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Human Physiology/The endocrine system
Endocrine
Gland
Hormone Released
Chemical Class Target Tissue/Organ
Major Function of Hormone
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamic releasing and
inhibiting hormones
Peptide
Anterior pituitary
Regulate anterior pituitary hormone
Posterior
Pituitary
Antidiuretic (ADH)
Peptide
Kidneys
Stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys
Oxytocin
Peptide
Uterus, mammary
glands
Stimulates uterine muscle contractions and
release of milk by mammary glands
Thyroid stimulating (TSH)
Glycoprotein
Thyroid
Stimulates thyroid
Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH)
Peptide
Adrenal cortex
Stimulates adrenal cortex
Gonadotropic (FSH, LH)
Glycoprotein
Gonads
Egg and sperm production, sex hormone
production
Prolactin (PRL)
Protein
Mammary glands
Milk production
Growth (GH)
Protein
Soft tissue, bones
Cell division, protein synthesis and bone growth
Thyroxine (T4) and
Triiodothyronie (T3)
Iodinated amino All tissue
acid
Increase metabolic rate, regulates growth and
development
Calcitonin
Peptide
Bones, kidneys and
intestine
Lowers blood calcium level
Parathyroids
Parathyroid (PTH)
Peptide
Bones, kidneys and
intestine
Raises blood calcium level
Adrenal Cortex
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Steroid
All tissue
Raise blood gluclose level, stimulates breakdown
of protein
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Steroid
Kidneys
Reabsorb sodium and excrete potassium
Sex Hormones
Steroid
Gonads, skin, muscles
and bones
Stimulates reproductive organs and brings on sex
characteristics
Adrenal
Medulla
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Modified amino
acid
Cardiac and other
muscles
Released in emergency situations, raises blood
glucose level, fight or flight response
Pancreas
Insulin
Protein
Liver, muscles,
adipose tissue
Lowers blood glucose levels, promotes formation
of glycogen
Glucagon
Protein
Liver, muscles,
adipose tissue
Raises blood glucose levels
Testes
Androgens (testosterone)
Steroid
Gonads, skin, muscles
and bone
Stimulates male sex characteristics
Ovaries
Estrogen and progesterone
Steroid
Gonads, skin, muscles
and bones
Stimulates female sex characteristics
Thymus
Thymosins
Peptide
T lymphocytes
Stimulates production and maturation of T
lymphocytes
Pineal Gland
Melatonin
Modified amino
acid
Brain
Controls circadian and circannual rhythms,
possibly involved in maturation of sexual organs
Anterior
Pituitary
Thyroid
Hormones can be chemically classified into four groups:
1. Amino acid-derived: Hormones that are modified amino acids.
2. Polypeptide and proteins: Hormones that are chains of amino acids of less than or more than about 100 amino
acids, respectively. Some protein hormones are actually glycoproteins, containing glucose or other carbohydrate
groups.
Вам также может понравиться
- Women and Their Clitoris Personal Discovery, Signification, and UseДокумент25 страницWomen and Their Clitoris Personal Discovery, Signification, and UsebillyОценок пока нет
- Bradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFДокумент514 страницBradley Nelson - Body Code System of Natural Healing - Manual (2009) PDFJhon Talbot80% (49)
- MCAT MnemonicsДокумент14 страницMCAT Mnemonicskmulqs100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemДокумент2 страницыEndocrine SystemHerlene Suelto Tingle100% (1)
- Polyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistryДокумент2 страницыPolyatomic Ions List: Honors ChemistrymandaОценок пока нет
- Endocrine Hormone Table WordДокумент4 страницыEndocrine Hormone Table Wordkatgrey87Оценок пока нет
- Cushings Addisons and Acromegaly EdДокумент45 страницCushings Addisons and Acromegaly Edsamehseef100% (1)
- Cytokines 2Документ102 страницыCytokines 2api-273068056Оценок пока нет
- Hormon GDSДокумент23 страницыHormon GDSBRI KUОценок пока нет
- Endocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranДокумент78 страницEndocrinology: Prof - DR. Didik Tamtomo, DR PAK, MM, MKK Pakar Anatomi KedokteranAnnisaInayati-msОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of Hormones 1Документ21 страницаBiochemistry of Hormones 1Hazel Grace BellenОценок пока нет
- Integration by PartsДокумент39 страницIntegration by PartsJose Villegas100% (1)
- 2020 Disease Detectives 071619Документ71 страница2020 Disease Detectives 071619Sharynn Kew MooreОценок пока нет
- Histology of Lymphoid Organ PDFДокумент82 страницыHistology of Lymphoid Organ PDFRionaldy TaminОценок пока нет
- Chemical Co - OrdinationДокумент21 страницаChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurОценок пока нет
- Organization and Structure of Genome: Genome Size VariationДокумент27 страницOrganization and Structure of Genome: Genome Size Variationarun231187Оценок пока нет
- Base (Path Anatomy) 2014 FIRSTДокумент39 страницBase (Path Anatomy) 2014 FIRSTHarsh NimavatОценок пока нет
- Collins CSEC Biology Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент120 страницCollins CSEC Biology Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsAlvesia Weatherhead100% (2)
- As 595 Commondiseases PDFДокумент12 страницAs 595 Commondiseases PDFZohaib PervaizОценок пока нет
- Diet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Документ52 страницыDiet & Nutrition Advanced Ver 1Ina100% (1)
- Classification of Endocrine GlandsДокумент3 страницыClassification of Endocrine GlandsReine100% (1)
- What's in Breast Milk?Документ1 страницаWhat's in Breast Milk?Sunny SideОценок пока нет
- The Biology of Apoptosis: Fouad Boulos, MD August 2010Документ4 страницыThe Biology of Apoptosis: Fouad Boulos, MD August 2010ans11Оценок пока нет
- HydroxyureaДокумент2 страницыHydroxyureaBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- NCP DMДокумент4 страницыNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalДокумент33 страницыAnatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalRizha Zhetira100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of FeverДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of FeverEasha Jamil AbbasiОценок пока нет
- Nature of DiseaseДокумент14 страницNature of DiseaseLambo Ignacio Queen Quin100% (1)
- Sources Hormone FunctionДокумент2 страницыSources Hormone FunctionKatherine Joy MaderajeОценок пока нет
- ProtozoaДокумент2 страницыProtozoaAbdullah FauziОценок пока нет
- Proteinuria in Adults and Diagnostic ApproachДокумент9 страницProteinuria in Adults and Diagnostic ApproachCindy JAОценок пока нет
- Endocrine Pathophysiology: Doc. Mudr. Ing. Rndr. Peter Celec, DRSC., MPHДокумент121 страницаEndocrine Pathophysiology: Doc. Mudr. Ing. Rndr. Peter Celec, DRSC., MPHS ARUNA100% (1)
- Easy Gynaecology PDFДокумент9 страницEasy Gynaecology PDFDinesh PantОценок пока нет
- (Jean Langhorne (Editor) ) Immunology and ImmunopatДокумент239 страниц(Jean Langhorne (Editor) ) Immunology and Immunopatclaudia lilianaОценок пока нет
- Endocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1Документ130 страницEndocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1api-19824701Оценок пока нет
- Body System ChecklistДокумент6 страницBody System Checklistapi-422967453Оценок пока нет
- Normal FloraДокумент30 страницNormal FloraRaul DuranОценок пока нет
- The Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsДокумент41 страницаThe Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsSaddamix AL OmariОценок пока нет
- Endocrinology Notes: Veterinary PhysiologyДокумент16 страницEndocrinology Notes: Veterinary PhysiologyBrian AllanОценок пока нет
- Inborn Errors of MetabolismДокумент4 страницыInborn Errors of Metabolismcurly perkyОценок пока нет
- AVS 172 Reproductive Physiology: Amin Ahamdzadeh Department of Animal and Veterinary Science University of IdahoДокумент41 страницаAVS 172 Reproductive Physiology: Amin Ahamdzadeh Department of Animal and Veterinary Science University of IdahoCristina CarvalhoОценок пока нет
- NeurolepticsДокумент6 страницNeurolepticsVantaku Krishna Swamy NaiduОценок пока нет
- Vaginal CytologyДокумент20 страницVaginal CytologyDaisy Sullcahuamán ElgueraОценок пока нет
- Metabolic Biochemistry, Volume - T. P. MommsenДокумент511 страницMetabolic Biochemistry, Volume - T. P. MommsenJesus Daniel Morales MarquezОценок пока нет
- GastrointestinalДокумент104 страницыGastrointestinalNugroho AnisОценок пока нет
- Summary of Different Parasites: Man ManДокумент1 страницаSummary of Different Parasites: Man ManNurhayati HasanahОценок пока нет
- The Adrenal GlandДокумент41 страницаThe Adrenal GlandRujha Haniena Ahmad RidzuanОценок пока нет
- Dna and Rna Powerpoint 2Документ46 страницDna and Rna Powerpoint 2api-267309851Оценок пока нет
- Ap Cell Tour 1 ProteinДокумент28 страницAp Cell Tour 1 Proteinapi-235744933100% (1)
- Endo 3 Notes PDFДокумент9 страницEndo 3 Notes PDFDilОценок пока нет
- The HPO AxisДокумент4 страницыThe HPO AxisBilal Irshan Eka RiselioОценок пока нет
- Blood Clotting ChartДокумент1 страницаBlood Clotting ChartBianca SimionescuОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Liver SamДокумент28 страницPathology of Liver SamJaks RipperОценок пока нет
- Chapter 29 - Endocrine FunctionДокумент6 страницChapter 29 - Endocrine Functionhgfree41392Оценок пока нет
- Food Science Resources-Sci OlympiadДокумент2 страницыFood Science Resources-Sci Olympiadjared boОценок пока нет
- Gland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusДокумент2 страницыGland Hormone Function Target Organ (Name or Picture) : HypothalamusRoya ImaniОценок пока нет
- Allergy and HypersensitivityДокумент73 страницыAllergy and HypersensitivityAdi PomeranzОценок пока нет
- Beneficial Effects of The Normal FloraДокумент4 страницыBeneficial Effects of The Normal FloraSyazmin KhairuddinОценок пока нет
- Developmental Biology, 12th Edition (Michael J.F. Barresi, Scott F. Gilbert)Документ48 страницDevelopmental Biology, 12th Edition (Michael J.F. Barresi, Scott F. Gilbert)Nita DelinaОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Identification KeyДокумент8 страницBacterial Identification KeyPaddyFlavellMartinОценок пока нет
- False Pregnancy or Pseudo Pregnancy in DogsДокумент2 страницыFalse Pregnancy or Pseudo Pregnancy in DogsEyüp Eren GültepeОценок пока нет
- Intermediate FilamentsДокумент4 страницыIntermediate FilamentsSai SridharОценок пока нет
- Digestive System 3Документ11 страницDigestive System 3Shubham HarishОценок пока нет
- Question BankДокумент131 страницаQuestion BankAdarshBijapurОценок пока нет
- CESTODESДокумент10 страницCESTODEScole_danielleОценок пока нет
- Cellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseОт EverandCellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseAlfredo Ulloa-AguirreОценок пока нет
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyОт EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinОценок пока нет
- BL5106 Basic Molecular Genetics Laborato PDFДокумент17 страницBL5106 Basic Molecular Genetics Laborato PDFbillyОценок пока нет
- Plasmid StudyДокумент5 страницPlasmid StudybillyОценок пока нет
- Bios116-Cloning in E PDFДокумент8 страницBios116-Cloning in E PDFbillyОценок пока нет
- Bios116-Cloning in E PDFДокумент8 страницBios116-Cloning in E PDFbillyОценок пока нет
- OverviewДокумент6 страницOverviewbillyОценок пока нет
- 13.2 Modeling Projectile MotionДокумент6 страниц13.2 Modeling Projectile MotionbillyОценок пока нет
- BRY's Microbiology 1st SemesterДокумент95 страницBRY's Microbiology 1st SemesterbillyОценок пока нет
- Keystone Biology Review Guide 1Документ9 страницKeystone Biology Review Guide 1billyОценок пока нет
- BRY's Microbiology 2nd SemesterДокумент80 страницBRY's Microbiology 2nd SemesterSaba ParkarОценок пока нет
- Basic Mendelian GeneticsДокумент31 страницаBasic Mendelian GeneticsbillyОценок пока нет
- BIOL 3456 - Course SyllabusДокумент8 страницBIOL 3456 - Course SyllabusbillyОценок пока нет
- Ch. 18 Notes EndocrineДокумент73 страницыCh. 18 Notes EndocrinebillyОценок пока нет
- School of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: Irina - Borovkov@utdallas - EduДокумент4 страницыSchool of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: Irina - Borovkov@utdallas - EdubillyОценок пока нет
- Gel ElectrophoresisДокумент32 страницыGel ElectrophoresisbillyОценок пока нет
- Evaluating Definite IntegralsДокумент9 страницEvaluating Definite IntegralsbillyОценок пока нет
- The Fundamental Theorem of CalculusДокумент8 страницThe Fundamental Theorem of CalculusbillyОценок пока нет
- Basic Mendelian GeneticsДокумент31 страницаBasic Mendelian GeneticsbillyОценок пока нет
- The Endocrine SystemДокумент18 страницThe Endocrine SystemRishabh DangiОценок пока нет
- Liquid CultureДокумент30 страницLiquid CultureSumesh ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Vet Obst Lecture 4 Congenital Fetal Defects (Teratology)Документ34 страницыVet Obst Lecture 4 Congenital Fetal Defects (Teratology)gnpobsОценок пока нет
- Keratosis PilarisДокумент25 страницKeratosis PilarisAntoninus HengkyОценок пока нет
- Pathology MBBS MCQsДокумент7 страницPathology MBBS MCQsShahzad Asghar Arain100% (3)
- Valores Hematologicos en Maine CoonsДокумент8 страницValores Hematologicos en Maine CoonsAngelo CardenasОценок пока нет
- A Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantДокумент4 страницыA Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantIJIRSTОценок пока нет
- Lupus - Client Brochure Rdramirez v2Документ4 страницыLupus - Client Brochure Rdramirez v2api-437843157Оценок пока нет
- Cartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTДокумент34 страницыCartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTAesthetics MinОценок пока нет
- Submission Guideline Iconic 2018Документ6 страницSubmission Guideline Iconic 2018Riska Awalia LestariОценок пока нет
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0338100 A1Документ15 страницUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0338100 A1sohair farag hassan ahmedОценок пока нет
- Selection of TransgenicsДокумент15 страницSelection of TransgenicsKV DeepikaОценок пока нет
- Protein MicroarrayДокумент5 страницProtein Microarraysudhu sudsОценок пока нет
- Redox-Potential and Immune-Endothelial Axis States of Pancreases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in ExperimentsДокумент6 страницRedox-Potential and Immune-Endothelial Axis States of Pancreases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in ExperimentsEdisher TsivtsivadzeОценок пока нет
- Histochemistry Print PDFДокумент4 страницыHistochemistry Print PDFEka Putra PratamaОценок пока нет
- Altitude Adaptation Through Hematocrit Change RevisarДокумент8 страницAltitude Adaptation Through Hematocrit Change RevisarMiguel Angel Santacruz VasquezОценок пока нет
- Bacteria Transformation - Activity - TeachEngineeringДокумент4 страницыBacteria Transformation - Activity - TeachEngineeringMarcela Stevie HadinataОценок пока нет
- Allergic Rhinitis History and Presentation PDFДокумент6 страницAllergic Rhinitis History and Presentation PDFJimena LopezОценок пока нет
- Genetics Extra CreditДокумент3 страницыGenetics Extra CreditNicole Leigh KleinasОценок пока нет
- Kolej Genius@Pintar Negara Research Skill Proposal Form (Cadangan Penyelidikan)Документ8 страницKolej Genius@Pintar Negara Research Skill Proposal Form (Cadangan Penyelidikan)saadhana elangovanОценок пока нет
- Background : BDH Polices & Procedures On Universal Newborn ScreeningДокумент21 страницаBackground : BDH Polices & Procedures On Universal Newborn ScreeningJnana YumnaОценок пока нет
- Layers of The Abdominal WallДокумент3 страницыLayers of The Abdominal WallRosemarie Cunanan GrifoniОценок пока нет
- Kul Bioprocess DevelopmentДокумент25 страницKul Bioprocess Developmentuntia_sariОценок пока нет
- Antenatal CounsellingДокумент56 страницAntenatal CounsellingDr. Prashant JainОценок пока нет
- ExplanationДокумент6 страницExplanationMoses SiahaanОценок пока нет