Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Skin - Structure and Function Flashcards - Quizlet
Загружено:
Dani AnyikaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Skin - Structure and Function Flashcards - Quizlet
Загружено:
Dani AnyikaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
9/20/2015
SkinStructureandFunctionflashcards|Quizlet
Skin - Structure and Function
39 terms by dani_mcfarlane
Like this study set? Create a free account to save it.
Create a free account
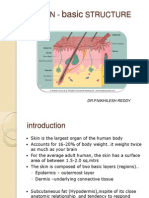
What are the four functions of skin?
1. Protection (UV, mechanical,
chemical, thermal plus is a physical
barrier to invasion)
2. Thermoregulation
3. Sensation (Rc for touch, pressure,
pain, temp)
4. Metabolic (Subcutaneous fat as
energy, VitD synthesis)
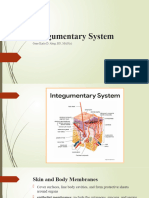
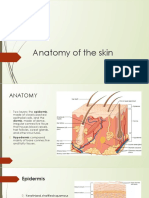
What are the three layers of the skin?
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Subcutaneous fat
What are the four types of cells in the
epidermis? What are their functions?
1. Keratinocytes (squamous cells - 95%)
2. Melanocytes - melanin/colour
production
3. Langerhans' cells - immune function
4. Merkel cells - tactile function
What type of epithelium is the
epidermis (cell type)
keratinized stratified squamous
What two openings can be found in the
epidermis?
1. Endocrine sweat ducts
2. Hair follicles
https://quizlet.com/18141694/skinstructureandfunctionflashcards/
1/5
9/20/2015
SkinStructureandFunctionflashcards|Quizlet
What are the four layers of the
Epidermis? In what layer does cell
division occur? What layer is the most
differentiated?
S. Basalis - basal cell layer = cell division
S. Spinosum
S. Granulosum
S. Corneum - most differentiated,
mainly dead cells, looks like a basket
weave
What is the main difference observed
in the epithelium between thick and
thin skin?
Thick skin has very dense and thick
stratum corneum. Thin skin has a think
layer of s. corneum where you can still
see the basket weave pattern
How are keratinocytes attached to one
another?
Desmosomes
What is the renewal rate of the
epidermis?
4 weeks. 2 weeks to get from basal
layer --> granular layer + 2 weeks to
cross s. corneum
The junction between the epidermis
and dermis is characterized by
downward folds of the epidermis called
________ which integrate with upward
projections of the dermis called
__________.
Rete Ridges (epidermis)
Dermal papillae (dermis)
What is hyperkeratosis? What are the
two different subtypes? How does this
present clinically?
Increased thickness of the stratum
corneum (chronic)
1. Orthokeratosis = no nuclei in s.
corneum
2. Parakeratosis - nuclei present in s.
corneum
Both present clinically as SCALE
Often occurs with acanthosis
Spongiosis
(Acute Dermatitis)
Intracellular edema (edema btw
keratinocytes), looks like a juicy papule
Acanthosis
Epidermal hyperplasia = thickening of
the epidermis (chronic)
Often occurs with hyperkeratosis
Atrophy
Thinning of the skin
https://quizlet.com/18141694/skinstructureandfunctionflashcards/
2/5
9/20/2015
SkinStructureandFunctionflashcards|Quizlet
Acantholysis
Loss of attachment between
keratinocytes (desmosomes). Cell
separate and assume round shapes
Lichenification
Thickening of all layers of epidermis
and dermis
What type of epidermal change occurs
(histologically) in acute eczematous
dermatitis?
Spongiosis
What type of epidermal change occurs
(histologically) in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Acantholysis - loss of desmosomal
connection, keratinocytes round up
and separate
What type of epidermal change has
occurred (histologically) when someone
has rough skin with increased skin
markings as a result of chronic
rubbing?
Lichenification
Melanocytes produce and secrete
melanin. What is melanin synthesized
from and where does this synthesis
take place?
Melanin is synthesized from tyrosine by
typrosinase enzyme. Synthesis occurs
in melanosomes
What factors contribute to the
difference in skin pigmentation?
1. Number and Size of melanosomes
2. Melanosome dispersion in the skin
Note: People of all races have similar
number of melanocytes
How do melanocytes help protect
against UV damage.
Melanocytes produce and secrete
melanin. Melanin synthesis occurs in
melanosomes. Melanosomes are
transferred to keratinocytes and cap
the keratinocyte nucleus protecting it
from UV damage.
The lips, digits and oral cavity are
abundant in what cell type? (in the
epidermis)
Merkel cells (tactile sensation)
Bullous pemphigoid is a blistering
disease that causes separation of _____
from ______.
Epidermis (basement membrane) from
dermis
https://quizlet.com/18141694/skinstructureandfunctionflashcards/
3/5
9/20/2015
SkinStructureandFunctionflashcards|Quizlet
Where are BPAg1 and BPAg2 located?
(Bullous Pemphigoid Antigens)
In the hemidesmosome
What are the two zones of the dermis?
Which one is superficial and which one
is deep? How are collagen fibers
arranged in each?
1. Papillary Dermis = superficial,
collagen is fine and loosely arranged
2. Reticular Dermis = deep, collagen is
thick and densely packed
Where in the skin are blood vessels,
lymphatics and nerves located?
Dermis.
Dermis contains two plexuses,
superficial and deep with connecting
capillaries. Free nerve endings convey
sensory info for touch, temp and pain
What are two functions of blood
vessels in the skin?
Temperature regulation and nutrition
With regards to temperature and heat
regulation, shunting blood to the
superficial plexus results in _______,
shunting blood to deep plexus results
in __________.
Superficial = heat loss
Deep = heat conservation
What is the function of eccrine sweat
glands? Where are they located?
Help regulate body temp by excreting
sweat onto the skin surface. Located
almost everywhere. Structure looks like
a ball of spaghetti with a straw to the
surface of the skin.
What glands are responsible for body
odour?
Apocrine sweat gland. Odour produced
by bacteria on the skin surface with the
apocrine sweat which is actually
odourless.
Where are apocrine glads located (both
in the skin microscopically and around
the body?)
Gland located deep in the dermis. Duct
drains into mid-hair follicle. Located in
axilla, anogenital region, and as
modified glands in the external ear
canal, eyelid, and breast (mammary
gland).
What are the two types of hairs?
Vellus (light and fine)
Terminal (dark and thick - hormonal
dependent)
https://quizlet.com/18141694/skinstructureandfunctionflashcards/
4/5
9/20/2015
SkinStructureandFunctionflashcards|Quizlet
What determines the pigment of a
hair?
The amount of melanocytes in the cells
of the hair bulb (matrix).
What are the two components of the
pilosebaceous unit? What disease is
produced by messed up pilosebaceous
units?
1. Sebaceous gland
2. Hair follicle (with pore at the top)
Acne (open or closed comedone)
What is the primary event in the
pathogenesis of acne?
Development of comedones
What are the three phases of the hair
growth cycle and what occurs in each
phase?
1. Anagen - growing
2. Catogen - regressing
3. Telogen - resting
What is secreted by sebaceous glands?
Where are they located
(microscopically and on the body)?
Sebum, secretion controlled by
androgen activity
Located in the dermis, drain into hair
follicle
Most prominent on scalp, face and
trunk. Palms and soles are the only
regions WITHOUT sebaceous glands
What part of the skin helps insulate the
body from cold and cushions deep
tissue from trauma?
https://quizlet.com/18141694/skinstructureandfunctionflashcards/
Subcutaneous fat
5/5
Вам также может понравиться
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinДокумент40 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinRicko Ciady100% (1)
- The Integumentary System: Dermatology ExaminationДокумент28 страницThe Integumentary System: Dermatology ExaminationCasey EngelОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент21 страницаIntegumentary SystemErnie SyarinaОценок пока нет
- CH 5 PowerpointДокумент71 страницаCH 5 PowerpointAnonymous HvuDls6eОценок пока нет
- SDL IntegumentaryДокумент4 страницыSDL IntegumentaryMonique Eloise GualizaОценок пока нет
- Integumentary System 15 16Документ26 страницIntegumentary System 15 16api-305436791Оценок пока нет
- 1- Anatomy of the SkinДокумент15 страниц1- Anatomy of the Skinumart4843Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1 The Integumentary SystemДокумент3 страницыUnit 1 The Integumentary SystemSharva BhasinОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент46 страницIntegumentary SystemDainah ArticuloОценок пока нет
- 04 INTEGUMENTARY PowerpointДокумент22 страницы04 INTEGUMENTARY Powerpointct328100% (3)
- AnaPhy Integumentary SystemДокумент4 страницыAnaPhy Integumentary SystemLeah Valerie EstolasОценок пока нет
- Skin Structure and DevelopmentДокумент45 страницSkin Structure and DevelopmentNikhileshReddyОценок пока нет
- Name The Components of Integumentary SystemДокумент3 страницыName The Components of Integumentary SystemNorman Vryne CaduaОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент35 страницIntegumentary Systembellechristine.roxasОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Physiology Pointers on the Integumentary SystemДокумент21 страницаAnatomy & Physiology Pointers on the Integumentary SystemDarwin DicoОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент18 страницIntegumentary SystemRenjyl Gay DeguinionОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент27 страницIntegumentary Systemzjz4k684c9Оценок пока нет
- Function of The SkinДокумент69 страницFunction of The SkinapermatagamaОценок пока нет
- Skin and Breast HistologyДокумент8 страницSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganОценок пока нет
- Integumentary System LectureДокумент157 страницIntegumentary System LecturesnpjavierОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент27 страницIntegumentary SystemKit KathОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Function of The SkinДокумент9 страницAnatomy & Function of The Skinعبدالعزيز احمد علي عتشОценок пока нет
- The Integumentary System (Skin) : HistologyДокумент6 страницThe Integumentary System (Skin) : HistologyNurani AtikasariОценок пока нет
- Skin Structure and Function: Applied Dermatotoxicology. DOI: © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedДокумент10 страницSkin Structure and Function: Applied Dermatotoxicology. DOI: © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedArsene AngelaОценок пока нет
- The Integumentary System - The Epidermis: T. RickДокумент17 страницThe Integumentary System - The Epidermis: T. Rickapi-464344582Оценок пока нет
- TDDSДокумент110 страницTDDSp.ishaanpawarОценок пока нет
- Learning Outcomes:: Layers of The SkinДокумент4 страницыLearning Outcomes:: Layers of The SkinRumaisa ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Lit SkinStruct Bensouillah Ch01 PDFДокумент11 страницLit SkinStruct Bensouillah Ch01 PDFisaco1531012Оценок пока нет
- ANA 222 Intergumentry System HistologyДокумент7 страницANA 222 Intergumentry System HistologyprincessmakklisОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент34 страницыIntegumentary SystemALAN MAGPANTAYОценок пока нет
- Integumen - Anatomi, Histologi Dan Fisiologi - ArinSДокумент42 страницыIntegumen - Anatomi, Histologi Dan Fisiologi - ArinSJack Flow ClickОценок пока нет
- Integumentary System: Skin, Glands & FunctionsДокумент28 страницIntegumentary System: Skin, Glands & Functionstamilvanan3Оценок пока нет
- The Integumentary System: Functions and DisordersДокумент5 страницThe Integumentary System: Functions and DisordersVivi rikkaОценок пока нет
- ANA 101 Lab: University of Northern PhilippinesДокумент12 страницANA 101 Lab: University of Northern PhilippinesAesthethic findsОценок пока нет
- Layers of The SkinДокумент49 страницLayers of The SkinBakri MustafaОценок пока нет
- The Integumentary SystemДокумент23 страницыThe Integumentary Systemtareqhaddad123Оценок пока нет
- Integumentary System: Chapter OutlineДокумент7 страницIntegumentary System: Chapter OutlineRiy KimОценок пока нет
- Ch 5 Skin FunctionsДокумент36 страницCh 5 Skin FunctionsPopa EmilОценок пока нет
- Intergumentary SystemДокумент8 страницIntergumentary SystemJSeasharkОценок пока нет
- Skin ShortДокумент10 страницSkin ShortKashar SaeedОценок пока нет
- Physiological Support Systems - The Integumentary SystemДокумент16 страницPhysiological Support Systems - The Integumentary Systemzedy gullesОценок пока нет
- Integumentary ReviewДокумент8 страницIntegumentary ReviewCharli ParachinniОценок пока нет
- Module 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMДокумент25 страницModule 3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMMisha WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Questions and AnsДокумент147 страницDermatology Questions and AnsEl FaroukОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2023-09-18 at 2.25.38 AMДокумент1 страницаScreenshot 2023-09-18 at 2.25.38 AMMichelle FloresОценок пока нет
- Topical Corticosteroids BinderДокумент108 страницTopical Corticosteroids BinderElena DragomirОценок пока нет
- Topic 5 - Integumentary SystemДокумент32 страницыTopic 5 - Integumentary SystemAllysa Megan OrpillaОценок пока нет
- Lecture Presented by:-ALI Waheed /yasmin Falah /zainab Mazin Supervised By:-Dr. Sattar Jabbar Jasim /cell and Tissue BiomedicalДокумент24 страницыLecture Presented by:-ALI Waheed /yasmin Falah /zainab Mazin Supervised By:-Dr. Sattar Jabbar Jasim /cell and Tissue BiomedicalAli Waheed jolan100% (1)
- The Integumentary SystemДокумент43 страницыThe Integumentary SystemRameen ZahraОценок пока нет
- Zoology 100 Notes 1Документ8 страницZoology 100 Notes 1Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The SkinДокумент28 страницAnatomy of The Skinay254Оценок пока нет
- M13 - Dermatology - Chapter 1Документ10 страницM13 - Dermatology - Chapter 1Idham BaharudinОценок пока нет
- Skin AnatomyДокумент21 страницаSkin Anatomyayesha khanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Dermatology: Marwa El-SamongyДокумент16 страницIntroduction To Dermatology: Marwa El-SamongyAbdalla esayedОценок пока нет
- Role of Skin in HomeostasisДокумент34 страницыRole of Skin in Homeostasissalehazahid83Оценок пока нет
- Intug SystemДокумент42 страницыIntug SystemdrkumaranОценок пока нет
- Core Curriculum WOCNSДокумент1 212 страницCore Curriculum WOCNSJerry MaguireОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemДокумент64 страницыLecture 9 Integumentary Systemhafiz patahОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент52 страницыIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5От EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Thrombolysis: By: Sachin Kumar M-Pharm (Pharmacology) Dept. of Pharma. Sci. M.D.U Rohtak, HaryanaДокумент18 страницThrombolysis: By: Sachin Kumar M-Pharm (Pharmacology) Dept. of Pharma. Sci. M.D.U Rohtak, HaryanaDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Pubh 6914 - 001 Community Nutrition Intervention Spring 2017: I. Course DescriptionДокумент19 страницPubh 6914 - 001 Community Nutrition Intervention Spring 2017: I. Course DescriptionDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Depression Among University Students in Kenya: Prevalence and Sociodemographic CorrelatesДокумент7 страницDepression Among University Students in Kenya: Prevalence and Sociodemographic CorrelatesDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- DigestionДокумент46 страницDigestionFaisal NasirОценок пока нет
- Medical Microbiology and Parasitology Quiz 1 KeyДокумент1 страницаMedical Microbiology and Parasitology Quiz 1 KeyDani Anyika100% (1)
- Endocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesДокумент7 страницEndocrine Pancreas & Fuel Homeostasis: Learning ObjectivesEmmanuel NhandaraОценок пока нет
- The Catholic University of Eastern Africa A. M. E. C. E. AДокумент2 страницыThe Catholic University of Eastern Africa A. M. E. C. E. ADani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- CUEA Medical Microbiology and Parasitology ExamДокумент3 страницыCUEA Medical Microbiology and Parasitology ExamDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Rubric For Scoring Oral PresentationДокумент5 страницRubric For Scoring Oral PresentationBosco BonillaОценок пока нет
- Courtship TopicsДокумент5 страницCourtship TopicsMayowa AdelekunОценок пока нет
- Community Nutrition AssignmentДокумент3 страницыCommunity Nutrition AssignmentDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- CHD 221 Community Nutrition CAT 1Документ2 страницыCHD 221 Community Nutrition CAT 1Dani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- MalnutritionДокумент43 страницыMalnutritionsharm1208100% (3)
- CHD 122 Biochemistry Quiz 1Документ2 страницыCHD 122 Biochemistry Quiz 1Dani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- CHD 125 CAT 1 May-Aug 2020 OPEN BOOKДокумент3 страницыCHD 125 CAT 1 May-Aug 2020 OPEN BOOKDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Cranial NervesДокумент54 страницыCranial NervesDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- CHD 128 Communicable Diseases and Control AssignmentДокумент2 страницыCHD 128 Communicable Diseases and Control AssignmentDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Kenya Immunization ScheduleДокумент1 страницаKenya Immunization ScheduleDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Biochemistry Class Lecture NotesДокумент14 страницChapter 1 Introduction To Biochemistry Class Lecture NotesDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- CDC's Zika Virus Guidance for CliniciansДокумент68 страницCDC's Zika Virus Guidance for CliniciansDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- 10.29.08.HISTO .Velkey - BloodBoneMarrow-1Документ56 страниц10.29.08.HISTO .Velkey - BloodBoneMarrow-1nerissaОценок пока нет
- Glossary of Exam Terms PDFДокумент2 страницыGlossary of Exam Terms PDFDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- #4 Fao / Who Codex Alimentarius Commission and Related ActivitiesДокумент38 страниц#4 Fao / Who Codex Alimentarius Commission and Related ActivitiesDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Student Survival Tips in Anatomy & Physiology byДокумент35 страницStudent Survival Tips in Anatomy & Physiology byDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Malaria StrategyДокумент17 страницMalaria StrategyDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesДокумент27 страницSpinal Cord and Spinal NervesDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology - Prokaryotic Cell Biology: Bacterial Surface Structures Bacterial Cell Wall StructureДокумент5 страницMicrobiology - Prokaryotic Cell Biology: Bacterial Surface Structures Bacterial Cell Wall StructureDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Morphological Characterization of Enteric Pathogens-1959Документ10 страницMorphological Characterization of Enteric Pathogens-1959Dani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of Life For LectureДокумент90 страницChemistry of Life For LectureDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 19 Isolation of Bacterial DNAДокумент5 страницExperiment 19 Isolation of Bacterial DNADani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Training Manual W Appendix 3-20-14 RsДокумент193 страницыTraining Manual W Appendix 3-20-14 RsZakir Ullah100% (5)
- Unit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL NotesДокумент2 страницыUnit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL Notesapi-264764674Оценок пока нет
- SF3300Документ2 страницыSF3300benoitОценок пока нет
- HandwritingДокумент25 страницHandwritingajeshtnОценок пока нет
- Real Estate Development Business PlanДокумент5 страницReal Estate Development Business PlanA. FranciscoОценок пока нет
- English Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'Документ5 страницEnglish Test: Dash-A-Thon 2020 'The Novel Coronavirus Pandemic'William Phoenix75% (4)
- Coventor Tutorial - Bi-Stable Beam Simulation StepsДокумент45 страницCoventor Tutorial - Bi-Stable Beam Simulation Stepsrp9009Оценок пока нет
- Indonesian Hotel Annual ReviewДокумент34 страницыIndonesian Hotel Annual ReviewSPHM HospitalityОценок пока нет
- Queueing in The Linux Network StackДокумент5 страницQueueing in The Linux Network StackusakОценок пока нет
- Math 20-2 Unit Plan (Statistics)Документ4 страницыMath 20-2 Unit Plan (Statistics)api-290174387Оценок пока нет
- Open NNДокумент2 страницыOpen NNsophia787Оценок пока нет
- 21 V-Ax Formation ENДокумент49 страниц21 V-Ax Formation ENMauro SousaОценок пока нет
- JavaScript ArraysДокумент5 страницJavaScript Arraysursu_padure_scrОценок пока нет
- Life Orientation September 2022 EngДокумент9 страницLife Orientation September 2022 EngTondaniОценок пока нет
- Parameter ranges and attenuation values for RRH configurationsДокумент121 страницаParameter ranges and attenuation values for RRH configurationscharantejaОценок пока нет
- Paul of Aegina LaminectomyДокумент9 страницPaul of Aegina LaminectomypepepartaolaОценок пока нет
- Lista SindroameДокумент28 страницLista SindroameFeier CristianОценок пока нет
- Under DronesДокумент336 страницUnder DronesRobert LewisОценок пока нет
- FPGA Based Digital Electronic Education, Data Entry Organization For A CalculatorДокумент5 страницFPGA Based Digital Electronic Education, Data Entry Organization For A CalculatorAkhilОценок пока нет
- CNS - Types of CiphersДокумент47 страницCNS - Types of Ciphersmahesh palemОценок пока нет
- Bulletin 13.9.22Документ4 страницыBulletin 13.9.22dbq088sОценок пока нет
- Slides Iso 17021 Be LacДокумент117 страницSlides Iso 17021 Be Lacjorge.s1943Оценок пока нет
- Pe Unit2Документ2 страницыPe Unit2srikaanth06Оценок пока нет
- AVD 370 Installation Manual WEBДокумент72 страницыAVD 370 Installation Manual WEBLuis Anselmo CastilloОценок пока нет
- Baseline Switch 2226 Plus: User GuideДокумент92 страницыBaseline Switch 2226 Plus: User GuideOswaldoОценок пока нет
- Trung Tâm Anh NG Nhung PH M 27N7A KĐT Trung Hòa Nhân Chính - 0944 225 191Документ5 страницTrung Tâm Anh NG Nhung PH M 27N7A KĐT Trung Hòa Nhân Chính - 0944 225 191Duy Khánh Nguyễn ĐăngОценок пока нет
- Curso de GaitaДокумент24 страницыCurso de GaitaCarlosluz52Оценок пока нет
- Chennai Contact - 1Документ12 страницChennai Contact - 1Jvr SubramaniaraajaaОценок пока нет
- Parallel Merge Sort With MPIДокумент12 страницParallel Merge Sort With MPIIrsa kanwallОценок пока нет
- Motivation and Rewards StudyДокумент6 страницMotivation and Rewards StudyBea Dela CruzОценок пока нет