Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MOOC Petersen 2 1 VoltageGatedChannels 20140525
Загружено:
Juhi Neogi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1 просмотров15 страницThis document discusses voltage-gated ion channels. It explains that the open probability of voltage-gated ion channels depends on the membrane potential. Voltage-gated sodium channels cause explosive depolarization, while voltage-gated potassium channels stabilize the hyperpolarized membrane potential. The document also notes that voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels have single channel conductances of around 20 pS and are important for generating voltage-dependent currents.
Исходное описание:
voltage gated ion channels
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses voltage-gated ion channels. It explains that the open probability of voltage-gated ion channels depends on the membrane potential. Voltage-gated sodium channels cause explosive depolarization, while voltage-gated potassium channels stabilize the hyperpolarized membrane potential. The document also notes that voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels have single channel conductances of around 20 pS and are important for generating voltage-dependent currents.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1 просмотров15 страницMOOC Petersen 2 1 VoltageGatedChannels 20140525
Загружено:
Juhi NeogiThis document discusses voltage-gated ion channels. It explains that the open probability of voltage-gated ion channels depends on the membrane potential. Voltage-gated sodium channels cause explosive depolarization, while voltage-gated potassium channels stabilize the hyperpolarized membrane potential. The document also notes that voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels have single channel conductances of around 20 pS and are important for generating voltage-dependent currents.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 15
2.
1 Voltage-gated channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Prof. Carl Petersen
Voltage-gated ion channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-gated ion channels
Linear
Non-linear
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Protein structure of voltage-gated ion channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-gating mechanisms
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-dependent open probability
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-dependent conductance
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-dependent currents
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-dependent ion channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-dependent Na + and K + channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Voltage-gated Na + and K + channels
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Some numbers single channel conductance
gNa and gK: ~20 pS
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Some numbers explosive Na + conductance
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Some numbers stabilising K + conductance
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
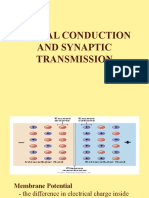
Voltage-gated ion channels
The open probability of a
voltage-gated ion channel
depends strongly upon the
membrane potential (Vm).
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
drive explosive depolarisation.
Voltage-gated K+ channels
stabilise hyperpolarised Vm.
Cellular Mechanisms of Brain Function
Вам также может понравиться
- Cellular Biology of EpileptogenesisДокумент10 страницCellular Biology of EpileptogenesisandreacamachogonОценок пока нет
- Neurobiology Block 4Документ24 страницыNeurobiology Block 4ashmitashrivasОценок пока нет
- Neuro 4Документ20 страницNeuro 4AKОценок пока нет
- NeuronsДокумент104 страницыNeuronsMolina ThirumalОценок пока нет
- Unit1 BERS Notes-Part2Документ11 страницUnit1 BERS Notes-Part2Mr. PavanОценок пока нет
- Physics ReportДокумент6 страницPhysics Reportابراهيم ماهر سلوم حسينОценок пока нет
- Electrical Potentials of NervesДокумент6 страницElectrical Potentials of Nervesابراهيم ماهر سلوم حسينОценок пока нет
- Advanced Cell BiologyДокумент14 страницAdvanced Cell BiologyUmair AneesОценок пока нет
- L2-Bioe345-EC Coupling - 2020Документ58 страницL2-Bioe345-EC Coupling - 2020asdfghjklОценок пока нет
- Blakely Ion Channels 2023 Cell and Molec Lecture V2Документ29 страницBlakely Ion Channels 2023 Cell and Molec Lecture V2farzadcop1Оценок пока нет
- Channelopathies: Ion Channel Defects Linked To Heritable Clinical DisordersДокумент12 страницChannelopathies: Ion Channel Defects Linked To Heritable Clinical Disorderscote_cote6951Оценок пока нет
- 1.0 The Origin of Biopotentials (New)Документ62 страницы1.0 The Origin of Biopotentials (New)Hanif HussinОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Rhythm Disorders With RMP and Inactivcating Sodium ChannelsДокумент37 страницCardiac Rhythm Disorders With RMP and Inactivcating Sodium ChannelsAniket MittalОценок пока нет
- Action Potentials Week 11Документ8 страницAction Potentials Week 11boultonbaileyОценок пока нет
- Action Potential FinalДокумент28 страницAction Potential FinalKawish AliОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NeurophysiologyДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Neurophysiologyvenkata ramakrishnaiahОценок пока нет
- Electrophysiology of HeartДокумент46 страницElectrophysiology of HearthafizahhoshniОценок пока нет
- Membrane PotentialДокумент51 страницаMembrane PotentialDr. R. PeriasamyОценок пока нет
- BME 7505 - Inv - Prac - Lecture No. 1 - 2Документ109 страницBME 7505 - Inv - Prac - Lecture No. 1 - 2Sk. Laila AyeshaОценок пока нет
- Neuro 1Документ21 страницаNeuro 1AKОценок пока нет
- Biology 4822: Resting Membrane Potential Reviewed and ContinuedДокумент30 страницBiology 4822: Resting Membrane Potential Reviewed and ContinuedKimberly Parton BolinОценок пока нет
- Ion ChannelsДокумент35 страницIon ChannelsnancyОценок пока нет
- Functional Organization of The Nervous SystemДокумент37 страницFunctional Organization of The Nervous SystemMsKizzyОценок пока нет
- Principles of Cardiac ElectrophysiologyДокумент98 страницPrinciples of Cardiac ElectrophysiologyAbnet WondimuОценок пока нет
- Action PotentialДокумент21 страницаAction PotentialjolilarmatarОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Electrophysiology: William MakdinataДокумент13 страницCardiac Electrophysiology: William MakdinataWilliam MakdinataОценок пока нет
- L3-Bioe345-EC Coupling - 2020Документ76 страницL3-Bioe345-EC Coupling - 2020asdfghjklОценок пока нет
- Physiol 01 B5Документ1 страницаPhysiol 01 B5DonkeyManОценок пока нет
- Action Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Документ42 страницыAction Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Maxamed Cali AtomОценок пока нет
- Nernst Equation: BY Dr.S.RajyalakshmiДокумент12 страницNernst Equation: BY Dr.S.RajyalakshmiRohit SreeramaОценок пока нет
- Resting Membrane PotentialДокумент22 страницыResting Membrane PotentialSanchezОценок пока нет
- NeurophysiologyДокумент117 страницNeurophysiologyRachel CajilesОценок пока нет
- Action PotentialДокумент15 страницAction PotentialAdam PrabowoОценок пока нет
- NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - ReadyДокумент83 страницыNEURON ACTION POTENTIAL - PPT - Readyelle leeОценок пока нет
- Ion ChannelsДокумент22 страницыIon ChannelsGanesh V GaonkarОценок пока нет
- 1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsДокумент35 страниц1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsDwi Amalia husnaОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Medicine Medical Education-Damietta UniversityДокумент43 страницыFaculty of Medicine Medical Education-Damietta UniversityMohamed ElnadyОценок пока нет
- 12 17 PDFДокумент71 страница12 17 PDFVikiОценок пока нет
- Ion ChannelsДокумент6 страницIon ChannelsNicolas IsformermynameОценок пока нет
- Patch Clamp TechniquesДокумент52 страницыPatch Clamp TechniquesRohitGuptaОценок пока нет
- Final ReviewДокумент29 страницFinal ReviewTín Đức ĐoànОценок пока нет
- Arrythmia by AbnetДокумент509 страницArrythmia by AbnetAbnet WondimuОценок пока нет
- 3 Excitable TissuesДокумент32 страницы3 Excitable TissuesSenthereng MoaisiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9Документ28 страницLecture 9sachinshah9845789999Оценок пока нет
- Aim of This Class 2. A First Order Approximation of Neuronal BiophysicsДокумент24 страницыAim of This Class 2. A First Order Approximation of Neuronal BiophysicsrajatОценок пока нет
- Synaptic TransmissionДокумент35 страницSynaptic TransmissiondehaОценок пока нет
- Action Potential in NeuronsДокумент109 страницAction Potential in NeuronsAdmin0% (1)
- Action PotentialДокумент24 страницыAction PotentialzzzОценок пока нет
- Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionДокумент87 страницNeural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionRose BernardoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Origins of Biopot CH 4Документ42 страницыLecture 2 Origins of Biopot CH 4api-27535945Оценок пока нет
- Electro-Physiology of HeartДокумент7 страницElectro-Physiology of HeartEhtiram HuseynovОценок пока нет
- Nerve PhysiologyДокумент75 страницNerve PhysiologyMemory MahwendaОценок пока нет
- 2.nerve PhysiologyДокумент43 страницы2.nerve Physiologycongresarad2022Оценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts 9 APДокумент35 страницBasic Concepts 9 APdevdsantoshОценок пока нет
- Ion Channel Structure and FunctionДокумент24 страницыIon Channel Structure and Functionshivanibhat1612Оценок пока нет
- BIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesДокумент37 страницBIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesOkikiola JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Synaptic Transmission and IntegrationДокумент19 страницSynaptic Transmission and IntegrationilincaОценок пока нет
- 2 02-Electrocardiography PDFДокумент17 страниц2 02-Electrocardiography PDFMiguel DomingoОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Topic 2 Lecture 4 5Документ22 страницыNervous System Topic 2 Lecture 4 5amjad.46987Оценок пока нет
- COMBINED SCREENING TEST - DR JuhiДокумент9 страницCOMBINED SCREENING TEST - DR JuhiJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- CEE Final PresentationДокумент7 страницCEE Final PresentationJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Candidates' User Manual For Registration & Choice Filling: WB PG Medical Counselling 2021Документ29 страницCandidates' User Manual For Registration & Choice Filling: WB PG Medical Counselling 2021Juhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Part 1 MRCOG Eligibility Application Form: Section 1: Personal DetailsДокумент6 страницPart 1 MRCOG Eligibility Application Form: Section 1: Personal DetailsJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Final Counselling Result PG 2021Документ1 820 страницFinal Counselling Result PG 2021Juhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Block Mountains Also Known As Mountain of UpliftmentДокумент3 страницыBlock Mountains Also Known As Mountain of UpliftmentJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Brexit Is TheДокумент9 страницBrexit Is TheJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Ccu Del Del Ixj: Booking Reference: MF117JДокумент4 страницыCcu Del Del Ixj: Booking Reference: MF117JJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Cee Project-A ReportДокумент4 страницыCee Project-A ReportJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- At KumartuliДокумент2 страницыAt KumartuliJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- A Change of Heart: The Tryst Between Indian Surgeons and Heart TransplantsДокумент4 страницыA Change of Heart: The Tryst Between Indian Surgeons and Heart TransplantsJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- As The Name SuggestsДокумент2 страницыAs The Name SuggestsJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- BarantiДокумент5 страницBarantiJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент2 страницыAssignmentJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- Assessment (Soils of India)Документ3 страницыAssessment (Soils of India)Juhi NeogiОценок пока нет
- 1001987548link of Advt With Inductus WebsiteДокумент9 страниц1001987548link of Advt With Inductus WebsiteJuhi NeogiОценок пока нет