Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDF
Загружено:
illuminatehОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDF
Загружено:
illuminatehАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
*Formulas highlighted in yellow are found in the formula list of the exam paper.
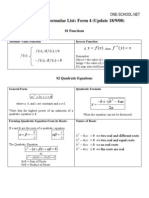
Quadratic Equation
b2 - 4ac > 0
Real and Distinct Roots
Also known as Unequal Roots
b2 - 4ac = 0
Real and Equal Roots
Also known as Repeat Roots or Coincident Roots.
b2 - 4ac < 0
Imaginary roots
Also known as Complex Roots.
b2 - 4ac > 0
Real and Distinct Roots
Also known as Unequal Roots
b2-4ac = 0
Real and Equal Roots
Also known as Repeat Roots or Coincident Roots.
b2-4ac < 0
Imaginary roots
Also known as Complex Roots
Page 1 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Roots of Quadratic Equation
The Quadratic Equation has solutions and
Sum of Roots is + =
Product of Roots is =
The Equation is x2 (Sum of Roots) x + (Product of Roots) = 0
2 + 2 = ( + )2 2
= ( )2
4 + 4 = ( 2 + 2 )2 2()2
Indices
Same Base Number
Same Power
x a xb =
x a +b
a b =( a b )
xa
= x a b
xb
a
a
=
m
b
b
(x )
a b
Same Base Number Power Add or Subtract
Same Power same Base Number Multiply or Divide.
= x ab x a xb =
x a +b
Other Laws of Indices
1
b
1
xa
xa =
x a y b =
x = b x1
xa
yb
1
= xa
xa
a
b
x = x
b
b
x=
x
y
a
b
x=
1
=
1
b
x
a
x0 = 1
1
b
x1
y
=
x
1
=
a
xb
1
b
xa
Page 2 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Surds
a
a b=
b
a b = ab
( a )=
m a n b =
m n ab
a a=
m a +n a =
( m + n) a
m a n a =
( m n) a
Rationalizing Denominator
1
n a
=
n+ a n a
(n
n (
1
n+ a
=
n a n+ a
(n +
n (
1
n+
1
n
)
a)
(n
)
a)
(n
=
2
=
2
n a
2
n a
2
n a
=
n a
( n a=
)
(n a )
na
( n) ( a)
n+ a
=
n+ a
( n + a=
)
(n + a )
na
( n) ( a)
Partial Factions
Linear Factor
Check if the highest coefficient of the
mx + n
A
B
=
+
(ax + b)(cx d ) (ax + b) (cx + d )
NUMERATOR is the SAME or LARGER
that the DENOMINATOR. If it is, do
LONG DIVISION first before partial
Repeat Factor
fractions.
mx + n
A
B
C
=
+
+
2
(ax + b)(cx d )
(ax + b) (cx + d ) (cx + d ) 2
Page 3 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Quadratic Factor
mx + n
A
Bx + C
=
+
2
(ax + b)(cx d ) (ax + b) (cx 2 + d )
Logarithm
log b 1 = 0
ln1 = 0
log b b = 1
ln e x = x
by = x
can be covert to
y = log b x
log b bx = x
log b m + log b n = log b (m n)
log b m log b n = log b (m n)
ln e xa = xa
* log b (m n) log b m log b n
ln x = log e x
ln e =1 as log e e=1
log b m a = a log b m
log v u =
log a u
log a v
log
=
vu
log u u
1
=
log u v log u v
Binomial Expansion
n
n!
=
r r !(n r )!
n n
= Cr
r
n
n
n
n
n
n
bx)n a n (bx)0 + a n 1 (bx)1 + a n 2 (bx)2 + a n 3 (bx)3 .... a n r (bx)r + a n n (bx)n
(a +=
0
1
2
3
r
n
OR
n
n
n
n
a n + a n 1 (bx)1 + a n 2 (bx) 2 + a n 3 (bx)3 .... a n r (bx) r + (bx) n
(a + bx) n =
1
2
3
r
Page 4 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
n
(n)(n 1) n 2
(n)(n 1)(n 2) n 3
a n + a n 1 (bx)1 +
a (bx) 2 +
a (bx)3 .... + (bx) n
(a + bx) n =
1
1 2
1 2 3
n n
n n 1
n n2
n n ( n 1)
n
0
1
2
n 1
n
( kx ) + 1nn ( kx )
1 ( kx ) + 1 ( kx ) + 1 ( kx ) + ....
1
0
1
2
n 1
n
kx )
(1 +=
n
OR
(1 + kx )
n
n
n
n 1
n
1
2
=
1 + ( kx ) + ( kx ) + ....
( kx ) + ( kx )
1
2
n 1
Trigonometry
cos ec =
1
sin
sin 2 + cos 2 =
1
sec =
1
cos
1 + cot 2 =
cos ec 2
cot
1
cos
=
tan sin
1 + tan 2 =
sec 2
Compound Angle Formula
sin ( A=
B ) sin A cos B cos A sin B
cos ( A B ) =
cos A cos B sin A sin B
Page 5 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
tan A tan B
tan ( A B ) =
1 tan A tan B
Double Angle Formula
sin 2 A = 2sin A cos A
cos
=
2 A cos 2 A sin 2 A
tan 2 A =
=
cos 2 A 2 cos 2 A 1
2 tan A
1 tan 2 A
cos 2 A = 1 2sin 2 A
Half Angle Formula
sin
A
1 cos A
=
2
2
cos
A
1 + cos A
=
2
2
A
=
tan
2
1 cos A 1 cos A
=
1 + cos A
sin A
R-Formula
aCos bSin =
RCos ( )
R
Where=
aSin bCos = RSin( )
tan =
a 2 + b2
b
a
Co-ordinate Geometry
Gradient(m) =
y2 y1
x2 x1
Linear Graph
Y= m x + c
y2 y=
m( x2 x1 )
1
m= gradient
General Equation
c= y-intercept (point on the graph
that intersects the y-axis)
Y y1= m( X x1 )
where
( x1 , y1 ) is a point on the
graph.
Page 6 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Mid-point of a line = (
x1 + x2 y1 + y2
,
)
2
2
Distance between two points =
( x2 x1 ) 2 + ( y2 y1 ) 2
If two lines have the same gradient
If two line have perpendicular
m1 = m2
gradient
i.e. 90 to each other.
m1 =
1
or m1 m2 =
1
m2
Perpendicular Bisector
1. The two lines AB and PQ must intersect at 90
m1 ( AB ) =
1
m2 ( PQ)
2. One Line (AB) will cut the mid-point of the other line (PQ)
x2 + x1 y2 + y1
,
2
2
Mid-point PQ =
Area of Plane Figure (Polygon Figure)
Vertices A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2),C (x3,y3)
1 1
2 1
*It does NOT matter if you calculate in a
2 3
2 3
4
4
1
1
clockwise or anti-clockwise direction. The
is a |modulus| in the formula
1
|( + 2 3 + 3 4 + 4 1 ) (2 1 + 3 2 + 4 3 + 1 4 )|
2 1 2
Page 7 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Circles
Radius of a circle
r=
( x a ) 2 + ( y b) 2
Equation of a Circle
( )2 + ( )2 = 2 or
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + = 0
where = , =
and = 2 + 2
Proofs in Plane Geometry
Midpoint Theorem
Tangent Chord Theorem (Alternate Segment Theorem)
sin
If X and Y are midpoints, then
Angle W = Angle X
YZ // WX
Angle Y = Angle Z
YZ = WX
Differentiation
dy
(ax n ) = anx n 1
dx
dy
(ax) = a
dx
dy
(a) = 0
dx
Where a is a constant and n is an
integer.
Page 8 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Chain Rule
Sum/Difference of Function
dy dy du
=
dx du dx
d
du dv
(u v) =
dx
dx dx
Product Rule
Quotient Rule
d
dv
du
(=
uv) u + v
dx
dx
dx
du
dv
v
u
d u
dx
dx
=
dx v
v2
d
(sin x) = cos x
dx
d
(cos x) = sin x
dx
d
(tan x) = sec 2 x
dx
The functions below are obtained using chain rule.
d
c ) ab cos(bx + c)
a sin ( bx +=
dx
d
ab sin(bx + c)
a cos ( bx + c ) =
dx
d
+ c ) ab sec 2 (bx + c)
a tan ( bx =
dx
d
a sin n ( bx
=
+ c ) anb sin n 1 (bx + c) cos(bx + c)
dx
d
a cos n ( bx + c ) =
anb cos n 1 (bx + c) sin(bx + c)
dx
d
ata n n ( bx
=
+ c ) anb tan n 1 (bx + c) sec 2 (bx + c)
dx
Exponential/Natural Logarithm Function
d x
(e ) = e x
dx
d ax +b
(e ) = ae ax +b (where a and b are constants)
dx
d
1
(ln x) = (where x>0)
dx
x
d
a
[ln(ax + b)] = (where ax +b>0)
dx
ax + b
Page 9 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Integration
n
dx
ax=
ax n +1
+ c where n1
n +1
a dx= ax + c
( ax + b )
( ax + b )
=
dx
n +1
(n + 1)(a )
+c
n1,a0; a & b are constants
Product of constant and a function
Sum and Difference of function
af ( x)dx = a f ( x)dx
[ f ( x) g ( x)]dx = f ( x)dx g ( x)dx
bx dx
a cos=
where f(x) is a function
a
sin bx + c
b
cos bx + c
a sin bx dx =
b
bx dx
a sec=
2
a
tan bx + c
b
where x is in radian.
1
dx ln x + c where x>0
x=
dx= e x + c
1
ln( + )
=
+
+
+
=
+
1
ln( 2 + )
=
+
2 +
2 +
2 +
+
=
+
2 +
Page 10 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Integration of Area
Area between Curve and X-axis
()
Area between Curve and X-axis
()
Area between Curve and Y-axis
()
Area between Curve and Y-axis
()
Area between the Curves f(x) (u-shape) and g(x)(n-shape).
() ()
Area between the Curves g(x)(n-shape) and f(x)(u-shape).
[ () ()]
Page 11 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047)
Area between the Curves g(y) (inverted c-shape) and f(y) (c-shape).
() ()
Area between the Curves f(y) (c-shape) and g(y) (inverted c-shape).
[ () ()]
Kinematics
Velocity is the RATE of CHANGE of
Acceleration is the RATE of CHANGE of
Displacement
Velocity
v=
ds
dt
a=
where v: velocity,s:displacement, t:time
=
v
where a:accleration
Some other methods to find acceleration
dv
a dt
dt
=
dt
=
a
Displacement (s)
dv
dt
Velocity (v)
d 2s
dt 2
=
a
dv ds
ds dt
Acceleration (a)
The End
Page 12 of 12
www.tuitionwithjason.sg
Вам также может понравиться
- Apti Booklet NewДокумент79 страницApti Booklet NewMegha PatilОценок пока нет
- 5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyДокумент16 страниц5.integral Calculus Objectives:: DX DyAndyMavia100% (1)
- Mathematics FormulasДокумент2 страницыMathematics FormulasgopalmyneniОценок пока нет
- Age problems solved step-by-stepДокумент20 страницAge problems solved step-by-stepAli Syed100% (1)
- Partial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsДокумент9 страницPartial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsChandini ManoharanОценок пока нет
- Complex NumbersДокумент21 страницаComplex NumbersAditya BansalОценок пока нет
- Linear Law Formulas Module 3 Additional Mathematics Form 5Документ30 страницLinear Law Formulas Module 3 Additional Mathematics Form 5Tan Chun HeeОценок пока нет
- C2 Algebra - Remainder and Factor TheoremДокумент37 страницC2 Algebra - Remainder and Factor TheoremDermot ChuckОценок пока нет
- Solving quadratic equationsДокумент5 страницSolving quadratic equationsAdam NaqibОценок пока нет
- Materi PolynomialДокумент20 страницMateri PolynomialnormasulasaОценок пока нет
- Solve Simultaneous Equations Year 9 MathsДокумент4 страницыSolve Simultaneous Equations Year 9 Mathseshal meОценок пока нет
- SL Practice For Exp Logs Key PDFДокумент8 страницSL Practice For Exp Logs Key PDFLeo DennisОценок пока нет
- Secondary 1 - Maths - SA1 - 2019 - 2Документ20 страницSecondary 1 - Maths - SA1 - 2019 - 2DigitalTransformation MitrpholОценок пока нет
- SMK PENDING KUCHING SA1 MATHS 2017Документ3 страницыSMK PENDING KUCHING SA1 MATHS 2017Loo Siaw ChoonОценок пока нет
- Sets & Relation TheoryДокумент8 страницSets & Relation TheorySushila TanwarОценок пока нет
- Equations and Inequalities IДокумент4 страницыEquations and Inequalities IElvir CrncevicОценок пока нет
- Surds and IndicesДокумент12 страницSurds and IndicesAbhishek PandeyОценок пока нет
- SM SAINS SERI PUTERI, KUALA LUMPUR: INDICES AND LOGARITHMSДокумент25 страницSM SAINS SERI PUTERI, KUALA LUMPUR: INDICES AND LOGARITHMSadeskitoku100% (1)
- C BX Ax: Math 154B Name - Completing The Square WorksheetДокумент2 страницыC BX Ax: Math 154B Name - Completing The Square Worksheetapi-241187529Оценок пока нет
- Log 30 Question Only 2022Документ16 страницLog 30 Question Only 2022Jaia Cher (Chijktcs)Оценок пока нет
- Add Math Coordinate GeometryДокумент14 страницAdd Math Coordinate Geometrykamil muhammad67% (3)
- Remainder Factor TheoremsДокумент3 страницыRemainder Factor TheoremsJohn Goh100% (1)
- The Function of Composition and InverseДокумент20 страницThe Function of Composition and InversenormasulasaОценок пока нет
- MATHEMATICS 2 DIPLOMA MODULEДокумент30 страницMATHEMATICS 2 DIPLOMA MODULEAzizul Anwar100% (1)
- 10 - Integration WorksheetДокумент18 страниц10 - Integration WorksheetAs EdОценок пока нет
- ComplexДокумент33 страницыComplexDipin Preet SinghОценок пока нет
- Add Math Revision 2Документ3 страницыAdd Math Revision 2Cannon HwaОценок пока нет
- Algebra IДокумент694 страницыAlgebra IKristi Rogers0% (1)
- Solving Logarithmic and Exponential EquationsДокумент2 страницыSolving Logarithmic and Exponential EquationsJo JoyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 QuadraticДокумент15 страницChapter 2 Quadratickym poon100% (1)
- Exponential & Logarithmic EquationsДокумент19 страницExponential & Logarithmic EquationsutpОценок пока нет
- O Level Additional Mathematics Past QuestionsДокумент16 страницO Level Additional Mathematics Past QuestionsnurlОценок пока нет
- BC MC P1ansДокумент17 страницBC MC P1anssharon cha100% (1)
- Additional Mathematics Paper 2Документ14 страницAdditional Mathematics Paper 2qnik9192% (12)
- Exercise 5 Sequence and SeriesДокумент5 страницExercise 5 Sequence and SeriesNurul SamsuddinОценок пока нет
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsДокумент8 страницExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsJas Dhillon0% (1)
- Functions, Limits and ContinuityДокумент3 страницыFunctions, Limits and ContinuityMohd AfzalОценок пока нет
- Math Foundations Session 1 ArithmeticДокумент42 страницыMath Foundations Session 1 ArithmeticBen HollowayОценок пока нет
- Derivatives of FungtionДокумент15 страницDerivatives of FungtionnormasulasaОценок пока нет
- Formula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Документ12 страницFormula Sheet - EM1 - EM2Ziyang XieОценок пока нет
- LCM and HCFДокумент66 страницLCM and HCFcoolmagaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Module IndicesДокумент38 страницChapter 5 Module IndicesCorey LopezОценок пока нет
- Integration Partial Fractions PDFДокумент10 страницIntegration Partial Fractions PDFrendie100% (1)
- Mathematics TДокумент97 страницMathematics TPh'ng Jiun YanОценок пока нет
- FP1 Chapter 1 PDFДокумент31 страницаFP1 Chapter 1 PDFkokleongОценок пока нет
- Important Formulas in AlgebraДокумент6 страницImportant Formulas in AlgebraAJ Christian MalacapoОценок пока нет
- Binary Operation - WikipediaДокумент15 страницBinary Operation - WikipediaFrank Clint100% (1)
- C1.1 Algebra and Functions 1Документ38 страницC1.1 Algebra and Functions 1nchauhan212Оценок пока нет
- Simultaneous Equations - Past-Year QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSimultaneous Equations - Past-Year QuestionsCgzam ZamОценок пока нет
- Exponential LogarithmicДокумент54 страницыExponential LogarithmicShella M LuarОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Function - 2011: Form 4Документ6 страницQuadratic Function - 2011: Form 4Hayati Aini AhmadОценок пока нет
- Permutations and Combinations Study PackageДокумент21 страницаPermutations and Combinations Study PackageSandeep KunalОценок пока нет
- Indefinite IntegrationДокумент24 страницыIndefinite IntegrationAditya BansalОценок пока нет
- Equation of A Circle ProblemsДокумент12 страницEquation of A Circle ProblemsEdward LactamОценок пока нет
- Basic Rules of AlgebraДокумент4 страницыBasic Rules of AlgebraRogelyn Manalo100% (1)
- IGP CSAT Paper 2 Basic Numeracy Number SystemДокумент13 страницIGP CSAT Paper 2 Basic Numeracy Number SystemAnonymous Ia9LPzОценок пока нет
- Functions Paper 1 1 1993: Past Year Questions Functions Additional Mathematics SPMДокумент8 страницFunctions Paper 1 1 1993: Past Year Questions Functions Additional Mathematics SPMyen 1978100% (1)
- Essential FormulasДокумент7 страницEssential FormulasShinigami01001Оценок пока нет
- MATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmДокумент16 страницMATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Contents of Mathematics Capsule For RRB NTPC With 100 + Prevous Year Questions by ADDA247Документ47 страницContents of Mathematics Capsule For RRB NTPC With 100 + Prevous Year Questions by ADDA247bharath devasothОценок пока нет
- Ganit Pravinya Past Year PapersДокумент37 страницGanit Pravinya Past Year PapersSaketh Maddamsetty100% (2)
- MATH 9 - Q3 - Module 1Документ17 страницMATH 9 - Q3 - Module 1An Neh GynОценок пока нет
- Similar Right Triangles: You Should LearnДокумент8 страницSimilar Right Triangles: You Should Learneugenio100% (1)
- SOLID MENSURATION FORMULASДокумент35 страницSOLID MENSURATION FORMULASKate ReyesОценок пока нет
- Maths SSC Tier 2Документ21 страницаMaths SSC Tier 2Sai Swaroop AttadaОценок пока нет
- INMO-2018 Paper & Solution..Документ6 страницINMO-2018 Paper & Solution..Ajay KumarОценок пока нет
- Draw 101 SimДокумент50 страницDraw 101 SimRenz KristoffОценок пока нет
- Find Area of Rectangular Field in HectaresДокумент64 страницыFind Area of Rectangular Field in HectaresKrishna Agrawal100% (1)
- BDT Cua Tran Quoc AnhДокумент19 страницBDT Cua Tran Quoc AnhPhạm Quốc BảoОценок пока нет
- Ch1 Geometry 2Документ47 страницCh1 Geometry 2trantuanan123Оценок пока нет
- 04-Complex Numbers, Quadratic EquationsДокумент22 страницы04-Complex Numbers, Quadratic EquationsGeeta MОценок пока нет
- LOCI IN TWO DIMENSION Form2Документ10 страницLOCI IN TWO DIMENSION Form2Rosmah Abdullah100% (16)
- Provincial Department of Education TestДокумент7 страницProvincial Department of Education Testenaya de alwisОценок пока нет
- G 1 3 2013 PDFДокумент8 страницG 1 3 2013 PDFmsmithmail21Оценок пока нет
- CLASS-10 MATH CASE STUDIESДокумент32 страницыCLASS-10 MATH CASE STUDIESHima ShettyОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 1988 Paper 2Документ11 страницMathematics 1988 Paper 2api-3826629Оценок пока нет
- iGCSE Edexcel Maths Jan 22 Paper 1HR QPДокумент32 страницыiGCSE Edexcel Maths Jan 22 Paper 1HR QParcreanderОценок пока нет
- Test Coordinate Geometry: A B A B A B A B A B A B PK A BДокумент2 страницыTest Coordinate Geometry: A B A B A B A B A B A B PK A BSuresh KumarОценок пока нет
- Elementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadДокумент38 страницElementary Geometry For College Students 6th Edition Alexander Solutions Manual DownloadCharles Vanhorne100% (30)
- Past Papers CXC MathsДокумент77 страницPast Papers CXC MathsShanice Henry96% (27)
- Orca Share Media1547387158090Документ2 страницыOrca Share Media1547387158090menma chanОценок пока нет
- $R1R10S7Документ16 страниц$R1R10S7aaaawfdwaedОценок пока нет
- Q4 Math 9 Week 2Документ4 страницыQ4 Math 9 Week 2Jiles M. MasalungaОценок пока нет
- Calculate Volume of a SphereДокумент11 страницCalculate Volume of a SphereNaz OmarОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT Teacherapptemproot280 20230821123852Документ7 страницASSIGNMENT Teacherapptemproot280 20230821123852syaОценок пока нет
- Rectangles and Squares Lesson Plan KindergartenДокумент4 страницыRectangles and Squares Lesson Plan KindergartenAl IkhwatОценок пока нет
- LCD in Math 4-6.V2Документ31 страницаLCD in Math 4-6.V2Crail ManikaОценок пока нет
- Second Periodical Test in G10 MathematicsДокумент5 страницSecond Periodical Test in G10 MathematicsEmelyn V. CudapasОценок пока нет