Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Purchase Risk Register
Загружено:
S Sinha RayАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Purchase Risk Register
Загружено:
S Sinha RayАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
example
Procurement Risk Register
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Name of tender: [name]
Risk
Impact
What would stop our procurement
objectives being met?
What would be the result of this risk?
Example: Suppliers do not
understand the business need.
Proposals fail to address the
requirements, no proposals meet the
need.
How risky is this if left uncontrolled?
Likelihood
Possible
Consequence
High
Risk rating
(uncontrolled)
Does Procurement Plan mitigate risk?
What is in place to reduce the risk?
Make sure the description of goods/services
is comprehensive. Double-check the final
draft with the business owner. Set
appropriate weightings.
What level of risk remains if mitigated?
Likelihood
Rare
Consequence
Low
Risk rating
(controlled)
Do we need additional controls?
What else could we do to reduce this
risk?
Test the description of goods/services
with someone not involved in the
drafting. Provide supplier briefings
before issuing tender.
RISK RATING = use colour + letter
G
green
yellow
amber
red
How to define your risks
Once you have identified specific risks, use the steps below to identify the likelihood, consequence and risk rating.
STEP 1 - choose one of the following to define the likelihood of the risk happening
Likelihood
level of risk
your assessment
Almost certain
Likely
Possible
Unlikely
Rare
Is expected to occur in most circumstances
Would probably occur in most circumstances
Could occur at some time
Is not expected to occur
May occur only in exceptional circumstances
STEP 2 - choose one of the following to define the consequence if the risk happens
Consequence
level of risk
your assessment
Extreme
High
Moderate
Low
Negligible
Significant impact on the achievement of goals/objectives
High impact on the achievement of goals/objectives
Moderate impact on the achievement of goals/objectives
Impacts on a limited aspect of the activity
The consequences are dealt with by routine operations
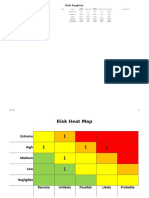
STEP 3 - use these two ratings to determine the overall risk rating (green/yellow/amber/red)
Plot the likelihood and consequence ratings on the matrix to identify the colour of the risk rating.
For example: a risk with a 'possible' likelihood and 'moderate' consequence would be rated as AMBER (where the two intersect on the matrix).
Likelihood
Consequence
Risk rating
rare
rare
unlikely
unlikely
rare
rare
unlikely
possible
possible
likely
rare
unlikely
possible
possible
likely
likely
almost certain
almost certain
unlikely
possible
likely
likely
almost certain
almost certain
almost certain
negligible
low
negligible
low
moderate
high
moderate
negligible
low
negligible
extreme
high
moderate
high
low
moderate
negligible
low
extreme
extreme
high
extreme
moderate
high
extreme
green
green
green
yellow
yellow
yellow
yellow
yellow
yellow
yellow
amber
amber
amber
amber
amber
amber
amber
amber
red
red
red
red
red
red
red
Examples of potential risks*
Identifying the need
Understatement of the need
Overstatement of the need
Insufficient funding
Impractical target dates
Probity failure
Misinterpretation of user needs
Political environment
Likely media interest
Developing the specification
Narrow definition or commercial specification (e.g. brand name)
Definition of inappropriate product or service
Biased specification
Inadequate specification or statement of work (for services)
Detrimental environmental impacts
Selecting the procurement method
Failure to identify potential sources
Selecting inappropriate method
Supplier collusion
Strength of New Zealand and international market
Contract documents
Terms and conditions unacceptable to service providers
Providing inadequate information method
Seeking, clarifying and closing offers
Failure to address service provider enquiries adequately
Actual or perceived favouritism in providing information
Actual or perceived breach of confidentiality
Insufficient number of responses
No response from known quality service providers
Evaluating offers
Failure to follow effective evaluation procedures
Breaches of security
Offers fail to meet needs
Failure to identify a clear winner. Decision made on subjective grounds
Selecting the preferred service provider
Selecting an inappropriate service provider
Selecting inappropriate product
Seeking, clarifying and closing offers
Not matching the expectations of buyer and service provider
Deadlock on details of agreement
Failure to secure mandatory conditions
Unfair or onerous requirements on the service provider in the contract conditions
Failure to reflect the terms offered and agreed in the contract
Inadvertently creating a contract without the delegates prior approval. Inappropriate product
Contract management
Variations in price and foreign exchange
Unwillingness of the service provider to accept the contract
Unwillingness of the service provider to accept the contract
Inadequately administering the contract
Commencement of work by the service provider before contract is exchanged or letter of acceptance issued
Unauthorised increase in scope of work
Loss of intellectual property
Failure to meet liabilities of third parties (e.g. royalties or third party property insurance)
Loss of or damage to goods in transit
Fraud
Key personnel not available
Supplier goes out of business
Disposal
Collusive bidding at auction
Inadequate tender management
Evaluating the procurement process
Failure to evaluate procurement and management processes
Failure to identify and address problem management
[* Source: NSW Government Procurement Guidelines]
Вам также может понравиться
- Risk Register PurchaseДокумент40 страницRisk Register PurchaseRahul Kumar100% (1)
- Risk Assessment (Draft)Документ2 страницыRisk Assessment (Draft)audideadОценок пока нет
- Procurement Risk RegisterДокумент3 страницыProcurement Risk RegisterYogender Singh Rawat100% (2)
- Procurement Risk Register 2Документ5 страницProcurement Risk Register 2Tarek YehiaОценок пока нет
- Contract Risk RegisterДокумент4 страницыContract Risk Registeralex11230% (1)
- Bhushan Power and Steel Limited: Draft Internal Audit Report - Production and Maintenance ReviewДокумент26 страницBhushan Power and Steel Limited: Draft Internal Audit Report - Production and Maintenance ReviewJagdish MishraОценок пока нет
- Record-to-Report Risk Control MatrixДокумент30 страницRecord-to-Report Risk Control MatrixAswath SОценок пока нет
- Final Report - Audit of City of Shreveport Insurance ProcurementДокумент25 страницFinal Report - Audit of City of Shreveport Insurance Procurementshreveporttimes0% (1)
- Purchasing Payables ControlДокумент9 страницPurchasing Payables ControljenjenheartsdanОценок пока нет
- Risk Register - ERMДокумент22 страницыRisk Register - ERMSuman Mandal50% (2)
- Inventory Audit Work ProgramДокумент19 страницInventory Audit Work ProgramAdnan MohammedОценок пока нет
- Audit Plan 2021Документ12 страницAudit Plan 2021GARUIS MELI100% (1)
- SM - ChecklistДокумент17 страницSM - ChecklistAdeline MokОценок пока нет
- It Audit Risk MatrixДокумент16 страницIt Audit Risk MatrixChinh Lê ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Internal Audit of Procurement Activity - A Case StudyДокумент5 страницInternal Audit of Procurement Activity - A Case StudyGurvinder Mann Singh PradhanОценок пока нет
- QMS - Risk Register SummaryДокумент26 страницQMS - Risk Register SummaryTigor GurningОценок пока нет
- CMS Control of Internal AuditingДокумент6 страницCMS Control of Internal AuditingAmine RachedОценок пока нет
- Foi 11 38 Procurement Process ReviewДокумент41 страницаFoi 11 38 Procurement Process ReviewSaid AliОценок пока нет
- Risk ControlДокумент7 страницRisk ControlDinesh AravindhОценок пока нет
- Internal Audit ChecklistДокумент80 страницInternal Audit ChecklistdinuindiaОценок пока нет
- QMS Audit Plan & Schedule: Clauses NoДокумент1 страницаQMS Audit Plan & Schedule: Clauses NosbtharanОценок пока нет
- Risk assessment and mitigation worksheetДокумент4 страницыRisk assessment and mitigation worksheetkapil ajmaniОценок пока нет
- Risk Register ProjectДокумент749 страницRisk Register ProjectmanojmoryeОценок пока нет
- Risk AssessmentДокумент3 страницыRisk AssessmentsalmanОценок пока нет
- PCF Product MatrixДокумент1 страницаPCF Product MatrixDebabrata Paul100% (1)
- Internal Audit Planning and Scheduling Sample FormatДокумент3 страницыInternal Audit Planning and Scheduling Sample Formatsameh100% (2)
- The Biggest Internal Audit Challenges in The Next Five YearsДокумент3 страницыThe Biggest Internal Audit Challenges in The Next Five YearsBagusОценок пока нет
- (Full Client Name Reg Caps) Procedure: (Receiving Proc. Title) Rev. (Rev Number)Документ3 страницы(Full Client Name Reg Caps) Procedure: (Receiving Proc. Title) Rev. (Rev Number)dellanadia putriОценок пока нет
- Samples of Internal Audit Forms For Construction CompanyДокумент28 страницSamples of Internal Audit Forms For Construction CompanyMohammed Rahimuddin HabeebОценок пока нет
- Compliance Test Program: State Accounting OfficeДокумент10 страницCompliance Test Program: State Accounting OfficeChristen CastilloОценок пока нет
- Internal Audit Procedure With FlowchartДокумент4 страницыInternal Audit Procedure With FlowchartEric Anastacio100% (1)
- Construction Auditingby Ron RisnerДокумент2 страницыConstruction Auditingby Ron RisnerdemirciferhatОценок пока нет
- ERA Risk and Opportunity Management - Project Details SummaryДокумент5 страницERA Risk and Opportunity Management - Project Details SummaryHailegebriel Mulugeta100% (1)
- Internal Audit Process ScheduleДокумент2 страницыInternal Audit Process Schedule25900solon50% (2)
- Internal Audit PlanДокумент48 страницInternal Audit PlankokoОценок пока нет
- Risks and Controls in ProcurementДокумент3 страницыRisks and Controls in Procurementzae nuddinОценок пока нет
- Relief International Competitive Bid AnalysisДокумент5 страницRelief International Competitive Bid AnalysisVassay KhaliliОценок пока нет
- FIN-01. Purchasing ProcedureДокумент7 страницFIN-01. Purchasing ProcedureVu Dinh ThietОценок пока нет
- 2020 Moving Forward - 201910029Документ10 страниц2020 Moving Forward - 201910029Razak MisbanОценок пока нет
- Risk Management Plan SampleДокумент12 страницRisk Management Plan SampleAryaan RevsОценок пока нет
- Checklist of Potential Risks - Goods and Services Procurement ProcessДокумент11 страницChecklist of Potential Risks - Goods and Services Procurement ProcessDarshit Thakkar100% (1)
- IFC-Template - InventoryДокумент21 страницаIFC-Template - InventoryCA Rahul Gupta100% (2)
- 03 - FoAM Form-02 - Fraud Risk Assessment TemplateДокумент3 страницы03 - FoAM Form-02 - Fraud Risk Assessment Templatenonavi lazoОценок пока нет
- Audit Methodology As Per ISO 9000:2000Документ45 страницAudit Methodology As Per ISO 9000:2000sbsharmaОценок пока нет
- 18.1 - App - 1 - IMS - Internal - System - Checklist - (ISO9001.14001 45001)Документ15 страниц18.1 - App - 1 - IMS - Internal - System - Checklist - (ISO9001.14001 45001)HenryОценок пока нет
- IA Audit Report - SampleДокумент6 страницIA Audit Report - SampleMounirDridi100% (1)
- Procurement Compliance ChecklistsДокумент8 страницProcurement Compliance Checklistsedzky69Оценок пока нет
- Risk RegisterДокумент6 страницRisk Registergroup2sd1314100% (2)
- Checklist Internal AuditДокумент69 страницChecklist Internal AuditTrang Đỗ Thu0% (1)
- Audit Risk Register TemplateДокумент3 страницыAudit Risk Register TemplateMAHESH SHAW100% (1)
- Nicks (India) Tools Unit-II Khakat: Quality Management System AuditДокумент1 страницаNicks (India) Tools Unit-II Khakat: Quality Management System Auditrajesh sharmaОценок пока нет
- Control Testing Vs Substantive by CPA MADHAV BHANDARIДокумент59 страницControl Testing Vs Substantive by CPA MADHAV BHANDARIMacmilan Trevor JamuОценок пока нет
- Internal Audit Report FormatДокумент3 страницыInternal Audit Report FormatSaket TibrewalОценок пока нет
- Project Risk Register GuidanceДокумент8 страницProject Risk Register GuidanceGabriel LepadatuОценок пока нет
- Project risk register analysisДокумент3 страницыProject risk register analysisTejendrasinh GohilОценок пока нет
- Risk-Based Internal Prescription For Audit FunctionДокумент7 страницRisk-Based Internal Prescription For Audit FunctionnitinОценок пока нет
- Financial Controls Closing ProcessДокумент16 страницFinancial Controls Closing Processvikrant durejaОценок пока нет
- Factsheet: Internal Audit Report Ratings: Connect Support AdvanceДокумент2 страницыFactsheet: Internal Audit Report Ratings: Connect Support AdvanceWajdi AlissawiОценок пока нет
- HeadFirstPMP RiskMgmtToolsДокумент10 страницHeadFirstPMP RiskMgmtToolssranjeetОценок пока нет
- Practical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelДокумент10 страницPractical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Practical Guidelines for Drawing the Human FigureДокумент9 страницPractical Guidelines for Drawing the Human FigureS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Practical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelДокумент10 страницPractical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Admission Test For Programme 2009-11: B C D B C AДокумент51 страницаAdmission Test For Programme 2009-11: B C D B C ATuku SinghОценок пока нет
- Practical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelДокумент10 страницPractical Guidelines for Creating Compositions (Secondary LevelS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Block 1 FEG 2 Unit 1Документ10 страницBlock 1 FEG 2 Unit 1Manisha BhavsarОценок пока нет
- Drawing - Object StudyДокумент5 страницDrawing - Object StudyS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Drawing Animal BirdДокумент10 страницDrawing Animal BirdS Sinha Ray100% (1)
- Drawing - Object StudyДокумент5 страницDrawing - Object StudyS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Drawing Animal BirdДокумент10 страницDrawing Animal BirdS Sinha Ray100% (1)
- Calcutta University PhD Admission TestДокумент4 страницыCalcutta University PhD Admission TestDebi GhoshОценок пока нет
- Vendor List GSPLДокумент11 страницVendor List GSPLS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Patent Draft Howtodraftapatentbyshivangchaudharyciieiima-151023091611-Lva1-App6891Документ12 страницPatent Draft Howtodraftapatentbyshivangchaudharyciieiima-151023091611-Lva1-App6891S Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Sample Statement of PurposeДокумент2 страницыSample Statement of PurposeSanhoihpa Khaineu0% (3)
- Patent Search Strategy WIPO Wipo - Tiscs - ZNZ - 16 - T - 6 PDFДокумент51 страницаPatent Search Strategy WIPO Wipo - Tiscs - ZNZ - 16 - T - 6 PDFS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- SMES Open Innovation and IP Management - Advancing Global DevelopДокумент10 страницSMES Open Innovation and IP Management - Advancing Global DevelopS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Patent Book Protect Your Ideas Ebook EditionДокумент152 страницыPatent Book Protect Your Ideas Ebook EditionS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Ip Panorama 3 Learning Points PDFДокумент34 страницыIp Panorama 3 Learning Points PDFRenuka KhatkarОценок пока нет
- Psoriatic Arthritis Professor Neil McHugh - Management of Psoriatic Arthritis - 0Документ48 страницPsoriatic Arthritis Professor Neil McHugh - Management of Psoriatic Arthritis - 0S Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Patent SearchingДокумент240 страницPatent SearchingPankaj GargОценок пока нет
- IP Valuation Ip - Business PDFДокумент69 страницIP Valuation Ip - Business PDFS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- FTO SearchesДокумент42 страницыFTO SearchesKrishna RamavarapuОценок пока нет
- Essar Coal Bed Methane Training ReportДокумент60 страницEssar Coal Bed Methane Training ReportS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- CLAT IMS SimCLAT 2020 Ques Ans Paper MergedДокумент36 страницCLAT IMS SimCLAT 2020 Ques Ans Paper MergedS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- IP Valuation Ip - Business PDFДокумент69 страницIP Valuation Ip - Business PDFS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- TN PWD Sor 2018-19Документ118 страницTN PWD Sor 2018-19vivek0630100% (2)
- Patent Search Strategy WIPO Wipo - Tiscs - ZNZ - 16 - T - 6 PDFДокумент51 страницаPatent Search Strategy WIPO Wipo - Tiscs - ZNZ - 16 - T - 6 PDFS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Standard OISD - Standard - 226Документ92 страницыPipeline Standard OISD - Standard - 226S Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- ASA 301L 301LA Cement Additives SLSHДокумент1 страницаASA 301L 301LA Cement Additives SLSHS Sinha RayОценок пока нет
- City Gas Distribution IndiaДокумент6 страницCity Gas Distribution IndiaS Sinha Ray0% (1)
- Analyze financial statementsДокумент3 страницыAnalyze financial statementsVINOD KUMARОценок пока нет
- 202202040501089359661LATESTUPDATEupto28 01 2022Документ330 страниц202202040501089359661LATESTUPDATEupto28 01 2022Aaiza YusufОценок пока нет
- Tqm-Stmicroelectronics Case Study JoseДокумент4 страницыTqm-Stmicroelectronics Case Study JosekringtrezОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 3rd Edition by WisnerДокумент36 страницSolution Manual For Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 3rd Edition by Wisnerkatevargasqrkbk100% (29)
- CARROT OR STICK_ NUDGING CONSUMERS TOWARDS HEALTHIER CHOICES THROДокумент81 страницаCARROT OR STICK_ NUDGING CONSUMERS TOWARDS HEALTHIER CHOICES THRONwogu PromiseОценок пока нет
- PCN Certification for Non-Destructive TestingДокумент7 страницPCN Certification for Non-Destructive TestingtomcanОценок пока нет
- M1 Case AnalysisДокумент27 страницM1 Case AnalysisWILYN MAE JIEN GASATAN100% (1)
- TayoДокумент7 страницTayomogaliess sultanОценок пока нет
- ARTA - Annual Report - 2018Документ155 страницARTA - Annual Report - 2018Rohadatul AisyОценок пока нет
- Standard CostingДокумент9 страницStandard CostingRoselyn LumbaoОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Auditing Indonesia Mapping The Results of Management Accounting Research in IndonesiaДокумент13 страницJurnal Akuntansi Dan Auditing Indonesia Mapping The Results of Management Accounting Research in IndonesiaOva NamusОценок пока нет
- Fairmount Partners - CTS Report Q3 2022Документ13 страницFairmount Partners - CTS Report Q3 2022Kevin ParkerОценок пока нет
- GRAANA - Final Project Group 3Документ11 страницGRAANA - Final Project Group 3Muhammad Saad UmarОценок пока нет
- Project TerminationДокумент5 страницProject TerminationNoor NabiОценок пока нет
- Project Manager TasksДокумент19 страницProject Manager TasksRodagom MogОценок пока нет
- Full Download Introduction To Risk Management and Insurance 10th Edition Dorfman Test BankДокумент36 страницFull Download Introduction To Risk Management and Insurance 10th Edition Dorfman Test Bankfockochylaka100% (20)
- Product CostingДокумент12 страницProduct CostinghanumaОценок пока нет
- CH 23 Pure CompetitionДокумент25 страницCH 23 Pure CompetitionPj Sorn100% (2)
- Final Preboard May 08Документ21 страницаFinal Preboard May 08Ray Allen PabiteroОценок пока нет
- Colorbar MesmerEyesДокумент17 страницColorbar MesmerEyesSwatiGoelОценок пока нет
- Meta Ads Video FrameworkДокумент4 страницыMeta Ads Video FrameworkFakhzan BadiranОценок пока нет
- Corporate PPT Template 9Документ10 страницCorporate PPT Template 9Suyog BhujbalОценок пока нет
- TAX-301 (VAT-Subject Transactions)Документ10 страницTAX-301 (VAT-Subject Transactions)Edith DalidaОценок пока нет
- Amo GLB PP 101195Документ2 страницыAmo GLB PP 101195Prakash JadhavОценок пока нет
- The Effects of Fuel Price Hike To Tricycle Drivers in Zamboanga CityДокумент4 страницыThe Effects of Fuel Price Hike To Tricycle Drivers in Zamboanga CityRIZLE SOGRADIELОценок пока нет
- 5.1.1b.1 PENYIMPANAN BAHAN PENGEMASДокумент2 страницы5.1.1b.1 PENYIMPANAN BAHAN PENGEMASThunder GunturОценок пока нет
- Pitch DeckДокумент19 страницPitch Deckakshaysingh211Оценок пока нет
- Muller PhippsДокумент2 страницыMuller PhippsIqra SameerОценок пока нет
- Continuous Improvement BasicsДокумент6 страницContinuous Improvement BasicsAbraham SorianoОценок пока нет
- Original Document Control ListsДокумент2 страницыOriginal Document Control Listswater labОценок пока нет