Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
UMTS Network Planning Optimization and Inter Operation With GSM - p20 PDF
Загружено:
Amro GoneimОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UMTS Network Planning Optimization and Inter Operation With GSM - p20 PDF
Загружено:
Amro GoneimАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2
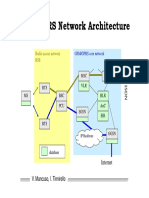
UMTS Network Planning, Optimization, and Inter-Operation with GSM
used GSM for the 2G network. UMTS is managed by the 3GPP organization, which also
became responsible for the GSM continued standardization from July 2000. CDMA2000 is
another significant 3G standard that is an outgrowth of the earlier 2G CDMA standard IS-95.
CDMA2000s primary proponents are mainly in the Americas, Japan, and Korea, though
UMTS is being tested and deployed at this time in the Americas by T-Mobile and Cingular.
CDMA2000 is managed by 3GPP2, which is separate and independent from UMTSs 3GPP.
The various types of transmission technology used in CDMA2000 include 1xRTT,
CDMA2000-1xEV-DO, and 1xEV-DV. China has also come up with a Standard of its
own, referred to as TD-SCDMA, which has been developed by the companies Datang and
Siemens, for which field trails have been taking place in Beijing and Shanghai.
The first commercial UMTS network was deployed by Japans NTT DoCoMo in 2001.
Since then UMTS networks have been deployed in more than 20 countries including
Germany, France, UK, Malaysia, Netherlands, Norway, Singapore, Spain, and Bahrain.
The 3G networks based on WCDMA continue to be deployed in more and more countries.
This situation is demanding that more and more radio planning professionals become
more familiar with the WCDMA technology to design and launch high quality 3G
networks. This book has been written with a heavy emphasis on radio planning and
optimization principles for RF engineering professionals. The book also contains four
extensive chapters (Chapters 13 to 16), which discuss the end-to-end QoS (Quality of
Service) inter-working, and the design, dimensioning, and optimization of the access
network, the core network, and the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) protocol for
wireless networks. Therefore this book is expected to benefit protocol and core network
engineering professionals as well, and provide a good reference for the end-to-end
network planning and optimization. 3G network planning involves a number of new
challenges over the 2G networks, which relate to the underlying WCDMA radio access,
the multi-service requirements, and opportunities to make use of new technologies in the
core network such as the split connection and call control architectures (soft switching)
for the design of efficient scaleable and flexible network architectures. These challenges
are briefly outlined in this introductory chapter, and then discussed in greater detail and
depth in the remaining chapters. This book is also expected to be highly valuable for
graduate level students and new researchers in the field with an interest in the WCDMA
technologies for network planning and optimization.
The development of the UMTS specifications based on W-CDMA in 3GPP has taken
several phases. The first release of the UMTS specifications is known as 3GPP R99, which
was functionally frozen in December 1999. The 3GPP R99 implementation offers the same
services with those of GSM Phase 2 (GPRS/EDGE). That is, all the same supplementary
services are available; teleservices and bearer services have different implementation but this
is not visible to the subscriber. The 3G network in this phase may offer some other services
not available in GSM, for example, a video call. The second phase known as 3GPP Release
4 introduces all-IP in the core network allowing separation of call control and signaling from
the actual connection or media used on the core network (CN) side to transport circuit
switched (CS) services such as voice. In the CN CS domain actual user data flow passes
through Media Gateways (MGW), which are elements that maintain the connection and
perform switching functions when required. The whole process is controlled by a separate
element evolved from MSC/VLR called MSC server. One MSC server can handle numerous
MGWs thus making the CN CS domain scalable. This approach is also referred to as soft
Вам также может понравиться
- Ts 129272v091300p p25Документ1 страницаTs 129272v091300p p25Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Table 5.2.2.1.1/1: Insert Subscriber Data RequestДокумент1 страницаTable 5.2.2.1.1/1: Insert Subscriber Data RequestAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- MME SGSN user data replacementДокумент1 страницаMME SGSN user data replacementAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Ts 129272v091300p p17Документ1 страницаTs 129272v091300p p17Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Freeze TMSI and P-TMSI on purgeДокумент1 страницаFreeze TMSI and P-TMSI on purgeAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- MME SGSN APN configuration profile updateДокумент1 страницаMME SGSN APN configuration profile updateAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Ts 129272v091300p p20Документ1 страницаTs 129272v091300p p20Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Table 5.2.1.1.1/2: Update Location Answer: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 14 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаTable 5.2.1.1.1/2: Update Location Answer: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 14 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 3 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 3 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 5.2 Mobility Services: 5.2.1 Location Management ProceduresДокумент1 страница5.2 Mobility Services: 5.2.1 Location Management ProceduresAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 15 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 15 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 7 Protocol Specification and Implementation ........................................................................................... 37Документ1 страница7 Protocol Specification and Implementation ........................................................................................... 37Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 3 Definitions and AbbreviationsДокумент1 страница3 Definitions and AbbreviationsAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Table 5.2.1.1.1/1: Update Location Request: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 13 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаTable 5.2.1.1.1/1: Update Location Request: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 13 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 3GPP TS 29.272 v9.13.0 Release 9 standardsДокумент1 страница3GPP TS 29.272 v9.13.0 Release 9 standardsAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- PS VersionДокумент1 страницаPS VersionAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 5 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 5 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Intellectual Property RightsДокумент1 страницаIntellectual Property RightsAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 5 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreДокумент1 страница5 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 1 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Документ1 страницаETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 1 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 129 272: Technical SpecificationДокумент1 страницаETSI TS 129 272: Technical SpecificationAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 3 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreДокумент1 страница3 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Ts 100614v070001pДокумент51 страницаTs 100614v070001pAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Unit Spec EEEN60141Optical Com and Adhoc Updated June213Документ30 страницUnit Spec EEEN60141Optical Com and Adhoc Updated June213Amro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Handover Success RatioДокумент1 страницаHandover Success RatioAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- Implementing Cisco Network Security Exam (210-260)Документ4 страницыImplementing Cisco Network Security Exam (210-260)Mohamed MkukОценок пока нет
- LearnEnglish EfE Unit 4 Support PackДокумент3 страницыLearnEnglish EfE Unit 4 Support PackAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- GSM/GPRS Network Architecture OverviewДокумент1 страницаGSM/GPRS Network Architecture OverviewAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 4 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreДокумент1 страница4 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- 1 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreДокумент1 страница1 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Types of Majority 1. Simple MajorityДокумент1 страницаTypes of Majority 1. Simple MajorityAbhishekОценок пока нет
- Forex Risk ManagementДокумент114 страницForex Risk ManagementManish Mandola100% (1)
- The Landmarks of MartinismДокумент7 страницThe Landmarks of Martinismcarlos incognitosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Part 1 - Measures of Central Tendency - Practice ProblemsДокумент8 страницChapter 2 - Part 1 - Measures of Central Tendency - Practice ProblemsTejas Joshi0% (3)
- Lesson Plan 2021Документ68 страницLesson Plan 2021ULYSIS B. RELLOSОценок пока нет
- Tso C139Документ5 страницTso C139Russell GouldenОценок пока нет
- Economics For Competition Lawyers - ADP Part OnlyДокумент44 страницыEconomics For Competition Lawyers - ADP Part Onlyeliza timciucОценок пока нет
- KEY TO THE SWIMMING POOL TIMETABLE AND PROGRAMMEДокумент2 страницыKEY TO THE SWIMMING POOL TIMETABLE AND PROGRAMMEthomas homerОценок пока нет
- Receivable Financing Pledge Assignment AДокумент34 страницыReceivable Financing Pledge Assignment AJoy UyОценок пока нет
- Canons of ST Basil The GreatДокумент67 страницCanons of ST Basil The Greatparintelemaxim100% (1)
- Boltanski Thevenot Los Usos Sociales Del CuerpoДокумент52 страницыBoltanski Thevenot Los Usos Sociales Del CuerpoAngélica VeraОценок пока нет
- 01082023-Stapled Visa ControversyДокумент2 страницы01082023-Stapled Visa Controversyakulasowjanya574Оценок пока нет
- Ebook Service Desk vs. Help Desk. What Is The Difference 1Документ18 страницEbook Service Desk vs. Help Desk. What Is The Difference 1victor molinaОценок пока нет
- AccountancyДокумент18 страницAccountancyMeena DhimanОценок пока нет
- Matrix of Activities For The Submission of Tasks For ResearchДокумент5 страницMatrix of Activities For The Submission of Tasks For ResearchJAY LORRAINE PALACATОценок пока нет
- In - Gov.uidai ADHARДокумент1 страницаIn - Gov.uidai ADHARvamsiОценок пока нет
- Criminal Investigation 11th Edition Swanson Test BankДокумент11 страницCriminal Investigation 11th Edition Swanson Test BankChristopherWaltonnbqyf100% (14)
- Wagner Group Rebellion - CaseStudyДокумент41 страницаWagner Group Rebellion - CaseStudyTp RayОценок пока нет
- Axis Priority SalaryДокумент5 страницAxis Priority SalarymanojОценок пока нет
- LP DLL Entrep W1Q1 2022 AujeroДокумент5 страницLP DLL Entrep W1Q1 2022 AujeroDENNIS AUJERO100% (1)
- Lec 2Документ10 страницLec 2amitava deyОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 7 MemoДокумент4 страницыCHAPTER 7 MemomunaОценок пока нет
- MBC and SAP Safe Management Measures, Caa 2020-05-28Документ9 страницMBC and SAP Safe Management Measures, Caa 2020-05-28Axel KruseОценок пока нет
- 3rd Yr 2nd Sem Business Plan Preparation Quiz 1 MidtermДокумент14 страниц3rd Yr 2nd Sem Business Plan Preparation Quiz 1 MidtermAlfie Jaicten SyОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Personality, Vision and Work of Aurobindo: 1.0 ObjectivesДокумент10 страницUnit 1 Personality, Vision and Work of Aurobindo: 1.0 ObjectivesAnkita RijhsinghaniОценок пока нет
- The Life of St. John of KronstadtДокумент47 страницThe Life of St. John of Kronstadtfxa88Оценок пока нет
- Capacity Building Series - Culturally Responsive PedagogyДокумент8 страницCapacity Building Series - Culturally Responsive Pedagogyapi-369226097Оценок пока нет
- ARP Poisoning Using ETTERCAP and WIRESHARKДокумент3 страницыARP Poisoning Using ETTERCAP and WIRESHARKBenny LangstonОценок пока нет
- Taste of IndiaДокумент8 страницTaste of IndiaDiki RasaptaОценок пока нет
- The Two Types of National SocialismДокумент5 страницThe Two Types of National SocialismSouthern FuturistОценок пока нет