Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Molecular Biology Midterm Study Guide
Загружено:
Samer MetriАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Molecular Biology Midterm Study Guide
Загружено:
Samer MetriАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bio99B Study Guide: Boiko half of the course
Textbook: Molecular Biology: Principles and Practice, by Cox, Doudna,
ODonnell, either full or custom edition (from last year)
Please visit our Website for all of the materials available for your use
The sitting chart will be posted before the exam on the website
There will be very few if any multiple-choice questions this year and most of the
questions require problem-solving skills, which we developed during our lectures,
along with the molecular biology language you learned.
Study strategy:
Follow class notes; re-read the material you highlighted in pre-lecture reading
assignments; follow the notes you took during the discussion sessions.
Most importantly (as I pointed out in class) you should be able to:
Know differences between RNA and DNA building blocks (dNTPs, dNMPs, NTPs,
NMPs) and know what is on the 5 and 3 ends of a monomer and how the
polymer looks like.
Know what 5 and 3 mean for DNA polarity and for the activity of the enzymes
operating on nucleic acids (e.g. 53 activity of DNA polymerase etc.)
Draw the 5 common bases, nucleosides and nucleotides structure and correct
nomenclature with numbering (including nomenclature for base alone or as part
of nucleotide). I am allowing you to have these in a one-page summary note.
Know Central Dogma and Exceptions
Know how deamination, oxidation, alkylation affects structure of nucleotides;
what groups get modified and what are the consequences for the double-helix
Know the chemistry of phosphodiester bond formation and breakage
What conditions stabilize the DNA helix and what destabilize it (salt, temperature,
pH, GC content)
Nucleic acid hybridization: know principle, probe design, what conditions affect
the outcome of hybridization experiment
Define Tm and use it in experiments
Know Frederick Griffiths and Oswald Averys transformation experiments
Know Hershey/Chase experiment
Know Genome content, simple sequence repeats
Define what gene is, how alternative splicing leads to one gene encoding for
several proteins
Being able to explain chromosome packaging, nuclease experiment
Being able to experimentally validate chromosome components (Murrays
experiment): ORI, Centromere, Telomere
Explain Meselson/Stahl experiment
Know diffreneces between Polymerisation-Pyrophosphorolysis-Proofreading
Know Lagging vs leading strand concept, small bubble, large bubble, trombone
model
Diagram steps in DNA synthesis, replication termination
PCR: primer design for acquisition of a particular product, being able to diagram
several cycles with primers annealed and extended
Knowing what the linking number is is not required, but you need to know what
overwound and underwound DNA is and how it affects replication/transcription,
as well as how topoisomerases contribute to this
Diagram Pre-RC, RC, details not important
Be able to explain the end replication problem and how to solve it, diagram
several rounds of replication and point out where the DNA gets lost
For the enzymes involved in phosphodiester bond formation and breakage
please pay attention to energy of the reaction in terms of ATP and dNTPs
I introduced you to the triplet genetic code used for translation, understanding it
is important for understanding insertion and deletion mutations
Being able to define mutation
Being able to design an Ames test for the compounds you are testing for
mutagenicity and analyze the data
In mismatch repair you need to know how cell distinguishes between parental
and daughter strands to conduct repair in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Please pay attention to the cell cycle phase: each type of DNA repair is cell
phase specific
Know what is the genetic basis of XP, and explain the consequences at cellular
and organism level
Being able to diagram how a single strand break can potentially become a
double-strand break (replication fork collapse)
Being able to diagram what happens in the five types of DNA repair we
discussed (mismatch, BER, NER, HR, NHEJ)
Know what positive and negative controls are (see H.pilori experiment)
Know how to design a gene knockout cassette and how the technique works
We are using selection markers, ori, transformation, selection media throughout
the course, its important to learn that and be able to use the knowledge for
solving the problems
Genomic library vs cDNA library, DNA Sequencing and Complementation will be
included in the cumulative final, not in the midterm!
Being able to follow the experiments we analyzed in class. Play with
experimental conditions at home, its the best way to prepare for solving
the problems (change the selection marker and see how it will affect your
choice for selection media etc.)
2
Take a look at the Learning Goals before each lecture and ask yourself if
you achieved those
Take a look at the topics listed at the first slide of each lecture, you should
know these
Learn your molecular biology language well: know the difference between
telomere and telomerase, antibiotic and gene of antibiotic resistance,
adenine and gene for adenine synthesis etc.
These are just the highlights any topic covered in class/book can be
included on the exam.
Since the discussion sections were designed to reinforce the lecture
material, I will not include any questions directly from the Discussion
sections, which were not covered in the class.
Вам также может понравиться
- Preclass Quiz 8 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFДокумент3 страницыPreclass Quiz 8 - Fa19 - MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (47940) PDFElizabeth DouglasОценок пока нет
- BIO 516-Advance Molecular Biology-Shaper MirzaДокумент4 страницыBIO 516-Advance Molecular Biology-Shaper MirzaAnonymous sF8ZuiGОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology ExamДокумент8 страницMolecular Biology Exam畏Оценок пока нет
- Examn of Molecular BiologyДокумент11 страницExamn of Molecular BiologycegfracОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Evolution VocabДокумент3 страницыAP Biology Evolution VocabOhhgeeee100% (1)
- Alan's Bio NotesДокумент19 страницAlan's Bio Notesluongc4100% (1)
- Biotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentДокумент40 страницBiotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentnescafeforeverОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology Notes 1 PDFДокумент23 страницыMolecular Biology Notes 1 PDFChris_Barber09100% (3)
- Leah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFДокумент32 страницыLeah4Sci OrgChem Cheat Sheet PDFhОценок пока нет
- Some Study Questions For USABOДокумент32 страницыSome Study Questions For USABORay Sanchez100% (1)
- Phylogenetic Tree Creation Morphological and Molecular Methods For 07-JohnsonДокумент35 страницPhylogenetic Tree Creation Morphological and Molecular Methods For 07-JohnsonCHRISTEROP100% (2)
- B. BiochemistryДокумент22 страницыB. BiochemistryRadhika SarawagiОценок пока нет
- Transcription Prokaryotes 2012-cДокумент27 страницTranscription Prokaryotes 2012-cAnupama PatiОценок пока нет
- BiologySATIISubjTest 1Документ28 страницBiologySATIISubjTest 1helenОценок пока нет
- Study GuideДокумент3 страницыStudy GuideSam Khader100% (1)
- BIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandBIOCHEMISTRY, CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology IntroductionДокумент1 страницаCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFДокумент3 страницыProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Оценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology: Handbook & Selection GuideДокумент32 страницыMolecular Biology: Handbook & Selection GuideKiki Dtvt100% (1)
- Chapter 5-Large BiomoleculesДокумент24 страницыChapter 5-Large Biomoleculesprehealthhelp100% (4)
- Molecular Biology Lecture NotesДокумент7 страницMolecular Biology Lecture NotesChristineОценок пока нет
- Biology IB SLДокумент28 страницBiology IB SLRaynaahОценок пока нет
- MCAT MetabolismДокумент4 страницыMCAT MetabolismNawledge9308100% (1)
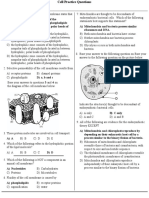
- Cell Practice Questions-Answer KeyДокумент7 страницCell Practice Questions-Answer KeyJoohyun LeeОценок пока нет
- AS Biology BYB1 Core Principles 10.4 Enzymes TestДокумент5 страницAS Biology BYB1 Core Principles 10.4 Enzymes TestormattОценок пока нет
- Fire Emblem Fates - Friendship Seal ChartДокумент13 страницFire Emblem Fates - Friendship Seal ChartHilu FicОценок пока нет
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsОт EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 1, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsОценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology Practice QuestionsДокумент9 страницMolecular Cell Biology Practice Questionssahana2791100% (1)
- CH 45 Guided ReadingДокумент7 страницCH 45 Guided ReadingmharirajОценок пока нет
- The Edaphic Factors and The Soil Inhabitants: Exercise No.. 2Документ7 страницThe Edaphic Factors and The Soil Inhabitants: Exercise No.. 2Sakib R SiddiqueОценок пока нет
- Molecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study GuideДокумент22 страницыMolecular Biology of The Cell Cumulative Final Exam Study Guiderazgriz1211Оценок пока нет
- A Molecular Biology GlossaryДокумент24 страницыA Molecular Biology GlossaryNabaneeta MukhopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 TestДокумент5 страницUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Оценок пока нет
- Protein Structure and Folding LectureДокумент18 страницProtein Structure and Folding Lecturemaryscribd241Оценок пока нет
- Sterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsОт EverandSterling Test Prep OAT General Chemistry Practice Questions: High Yield OAT General Chemistry Practice QuestionsОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5 - Protein Localization & Prediction of Protein StructureДокумент3 страницыAssignment 5 - Protein Localization & Prediction of Protein StructureViệt Lê Nguyễn HoàngОценок пока нет
- Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes V1От EverandPhytopathogenic Prokaryotes V1Mark MountОценок пока нет
- 2021 Aamc 10aДокумент4 страницы2021 Aamc 10aNadiaОценок пока нет
- Recombinant DNA And Cell ProliferationОт EverandRecombinant DNA And Cell ProliferationGary SteinОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Notes - Unit OneДокумент24 страницыMicrobiology Notes - Unit OneMalavikaNОценок пока нет
- USABO Competition: Answers Saved QДокумент25 страницUSABO Competition: Answers Saved QChanguoi YOtoОценок пока нет
- MCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet: Nuclear and Atomic Chemistry Electron ConfigurationsДокумент2 страницыMCAT G-Chem Formula Sheet: Nuclear and Atomic Chemistry Electron ConfigurationsGreenINVОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - ClassificationДокумент59 страницChapter 2 - ClassificationgoodmushroomsoupОценок пока нет
- AP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesДокумент7 страницAP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesBellony SandersОценок пока нет
- AP Chemistry Practice 1998-1992Документ10 страницAP Chemistry Practice 1998-1992Mary TaklaОценок пока нет
- Characteristics and Genotyping (Semi-Automated and Automated), Apparatus Used in GenotypingДокумент45 страницCharacteristics and Genotyping (Semi-Automated and Automated), Apparatus Used in GenotypingKhalid HameedОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 6Документ5 страницAP Biology Outline - Chapter 6Omar LopezОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Midterm 1 QuestionsДокумент2 страницыBiochemistry Midterm 1 Questionselfin_treeОценок пока нет
- Overview: Cellular Messaging: © 2011 Pearson Education, IncДокумент69 страницOverview: Cellular Messaging: © 2011 Pearson Education, IncbbyiknowОценок пока нет
- Alkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsДокумент10 страницAlkanes - Saturated HydrocarbonsJuan Carlos SihotangОценок пока нет
- Biology Unitwise MCQ - S (MCAT)Документ41 страницаBiology Unitwise MCQ - S (MCAT)M Noaman Akbar100% (1)
- Gacan Qabad Chemistry Book With AnswersДокумент32 страницыGacan Qabad Chemistry Book With Answerscazmi Andirahman100% (1)
- Ap Bio Practice Exam Section IДокумент6 страницAp Bio Practice Exam Section INaama GoutiОценок пока нет
- The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATPДокумент38 страницThe Structure and Hydrolysis of ATPBellony SandersОценок пока нет
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesДокумент24 страницыDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- AP BiologyДокумент5 страницAP BiologyAnil ChauhanОценок пока нет
- General Chem All ReactionsДокумент3 страницыGeneral Chem All ReactionsSamer MetriОценок пока нет
- Midterm 2 SummaryДокумент6 страницMidterm 2 SummarySamer MetriОценок пока нет
- OChem Reaction ListДокумент2 страницыOChem Reaction ListSamer MetriОценок пока нет
- Samer Metri TA: Steve Juarez Section 4Документ2 страницыSamer Metri TA: Steve Juarez Section 4Samer MetriОценок пока нет
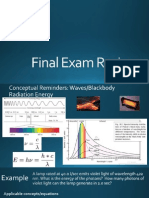
- FinalExamReview StudentsДокумент34 страницыFinalExamReview StudentsSamer MetriОценок пока нет
- Samer Metri TA: Steve Juarez Section 4Документ2 страницыSamer Metri TA: Steve Juarez Section 4Samer MetriОценок пока нет
- AP Stats ReviewДокумент59 страницAP Stats ReviewSamer MetriОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ2 страницыUnit 1Samer MetriОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 (Energy)Документ2 страницыUnit 2 (Energy)Samer MetriОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 (Energy)Документ2 страницыUnit 2 (Energy)Samer MetriОценок пока нет
- Interdependence of Organism in An EcosystemДокумент10 страницInterdependence of Organism in An EcosystemJennilyn LumacadОценок пока нет
- Anion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending ToДокумент24 страницыAnion Ide: Monoatomic: Change Ending TodjkedslОценок пока нет
- Lab 25Документ5 страницLab 25Nor Ashikin IsmailОценок пока нет
- Red Ox TitrationДокумент13 страницRed Ox Titrationabdirizak Haji MohammedОценок пока нет
- ClustersДокумент2 страницыClustersسمير العطارОценок пока нет
- TDS Rheobyk-7410 Et enДокумент4 страницыTDS Rheobyk-7410 Et enNelОценок пока нет
- Prakash Khude UV ProtectionДокумент29 страницPrakash Khude UV ProtectionariefОценок пока нет
- 5090 w16 QP CompleteДокумент120 страниц5090 w16 QP CompleteAyra MujibОценок пока нет
- PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM ALUMINUM SULFATE, KAl (SO4) 2 - 12H2O (Alum)Документ5 страницPREPARATION OF POTASSIUM ALUMINUM SULFATE, KAl (SO4) 2 - 12H2O (Alum)vinsmoke1Оценок пока нет
- EUPIA March 2021Документ6 страницEUPIA March 2021Ellen De Oliveira DeОценок пока нет
- Chem 101 Lab Report 4Документ8 страницChem 101 Lab Report 4ArvindVishakОценок пока нет
- Buffered and Isotonic Solutions: Lecturer Ghaidaa S Hameed Physical PharmacyДокумент63 страницыBuffered and Isotonic Solutions: Lecturer Ghaidaa S Hameed Physical PharmacyloloОценок пока нет
- Workshop Oxidation StatesДокумент3 страницыWorkshop Oxidation StatesgarangoОценок пока нет
- Modern Drymix Mortars: Performance Additives ForДокумент15 страницModern Drymix Mortars: Performance Additives Form_shahbaghiОценок пока нет
- Zahid Article - Wide Visible-Range Activatable Fluorescence QDs - J Mat Chem B 2021Документ15 страницZahid Article - Wide Visible-Range Activatable Fluorescence QDs - J Mat Chem B 2021Latif Ullah KhanОценок пока нет
- Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) : Experiment No. 01Документ4 страницыCation Exchange Capacity (CEC) : Experiment No. 01manurihimalshaОценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRY 1 - Worksheet 1.1: Pure or Mixture?Документ2 страницыCHEMISTRY 1 - Worksheet 1.1: Pure or Mixture?CJ VauseОценок пока нет
- Route Evaluation and Analytical HPLC Method Development of Buprenorphine, Naloxone, and Comparison OverallSJFN - ms.ID.000105Документ19 страницRoute Evaluation and Analytical HPLC Method Development of Buprenorphine, Naloxone, and Comparison OverallSJFN - ms.ID.000105Drkrishnasarma pathyОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - Chemistry Lab 3 - Esterification With Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Sem 1 16-17Документ2 страницыUnit 2 - Chemistry Lab 3 - Esterification With Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Sem 1 16-17kelon scottОценок пока нет
- Modified Guidelines For Geopolymer Concrete Mix Design Using Indian StandardДокумент13 страницModified Guidelines For Geopolymer Concrete Mix Design Using Indian StandardDl Divakar LОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4 PDF UPLOADДокумент18 страницChemistry Form 4 PDF UPLOADRahmat Syafiq MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Ingevity Capa CoatingsДокумент4 страницыIngevity Capa CoatingsKanagarajan VijayakumarОценок пока нет
- Chemistry (Nmat)Документ4 страницыChemistry (Nmat)John Rhel DenqueОценок пока нет
- ADSORPTIONДокумент6 страницADSORPTIONSatyamGupta0% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: According To EC Directive 91/155/EECДокумент6 страницSafety Data Sheet: According To EC Directive 91/155/EECTitiОценок пока нет
- Molar Mass Activity For Grade 11 ChemistryДокумент2 страницыMolar Mass Activity For Grade 11 ChemistryMatthew GreesonОценок пока нет
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1Документ36 страницNCERT Exemplar For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1gudiОценок пока нет
- Indian Standard: Symbols and Abbreviations FOR Use in Geological Maps, Sections and Subsurface Exploratory LogsДокумент18 страницIndian Standard: Symbols and Abbreviations FOR Use in Geological Maps, Sections and Subsurface Exploratory Logsgini associatesОценок пока нет
- Reaction Rates: BIG IdeaДокумент34 страницыReaction Rates: BIG Ideacarleston thurgoodОценок пока нет
- Poster Suci Ingrid Daniati 20505005Документ3 страницыPoster Suci Ingrid Daniati 20505005ZakiAbdullahОценок пока нет