Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aieee 2003
Загружено:
NCERT SolutionsИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aieee 2003
Загружено:
NCERT SolutionsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1.
A particle of mass M and charge Q moving with velocity "1 describes a circular path of radius R when subjected to a uniform transverse magnetic field of induction B. The work done by the field when the panicle completes one full circle is :
(a) (~2) 21tR (b) zero
(c) BQ 21tR Cd) BQv 2nR
2. A particle of charge - 16 x 10-'18 C moving with velocity 10 ms"! along the x-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along the y-axis and an electric field of magnitude 104 Vim is along the negative z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the x-axis, the magnitude of B is :
(a) 103 Wb/m2 (b) 105 Wb/m2
(c) 1016 Wh/m2 Cd) 10-3 Wb/m2
3. A thin rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely in the same field. If its period of oscillation is T " the ratio T 'IT is :
1 . 1
(a) 2.J2 (b) ·2
(c) 2
4. A magnetic needle lying parallel to a magnetic field requires W unit of work to turn it through 60°. The torque needed to maintain the needle in this position will be :
(a)./3W (b)W
(c) C..J3/2) W Cd) 2W
5. The magnetic Jinesofforce inside a Dar magnet : (al are from north-pole to south-pole of the magnet
(b) do not exist
(c) depend upon the area of cross-section of the bar magnet
(d) aloe from south-pole to north-pole of the magnet
6. Curie temperature is the temperature above which:
(a) a ferromagnetic material becomes para magnetic
(b) a paramagnetic material becomes
diamagnetic
(c) a ferromagnetic material becomes
diamagnetic
(d) a paramagnetic material becomes
ferromagnetic
7. A spring balance is attached to the ceiling of a lift. A man bangs his bag on the spring and the spring reads 49 N, when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves downward with an acceleration of 5 m/ 82, the reading of the spring balance will be:
(a) 24 N (c) 15 N
(b) 74 N (d) 49 N
8. The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 em, and the emf of its stand and cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the emf of a battery whose internal resistance is O.S n. If the balance point is obtained at l = 30 em from the
positive end, the emf of the battery is : °
30E
(a) roO.S
30£ (b) 100 - '0.5
( , 30 (E - 0.5i) h o. h ° h
C) 100 ' were l IS t e current ill t e
potentiometer wire
Cd) 30E
100
9. A strip of copper and another of germanium are cooled from room temperature to 80 K. The resistance of:
(a) each of these decreases
(b) copper strip increases and that of germanium decreases
(c) copper strip decreases and that of germanium increases
(d) each of the above increases
10. Consider telecommunication through optical fibres. :which of the following statements is not true?
(a) Optical fibres can be of graded refractive index
(b) Optical fibres are subjected to electromagnetic interference from outside
(c) Optical fibres have extremely low transmission loss
(d) Optical fibres may have homogeneous core with a suitable cladding
11. The thermo-emf of a thermocouple is 25 ~ V!"C
-at room temperature. A galvanometer of.400: resistance, capable of detecting current as low as 10-5 A, is connected with the thermocouple. The smallest temperature difference that can be detected by this system is :
(a) 16°C (b) 12°C
(c) 8°C (d) 20"C
12. The negative Zn pole of Daniell cell, sending a constant current through a circuit, decreases in mass by 0.13 g in 30 minutes. If the electrochemical equivalent of Zn arid Cu are 32.5 and 31.5 respectively, the increase in the mass of the positive Cu pole in this time is :
(a) 0.180 g (b) 0.141 g
ec) 0.126 g Cd) 0.242 g
13. Dimensions of_1_, where symbols have their f-lQ So
usual meaning, are ; (a) [L-1T]
ec) [l}T-2]
(b) [L2T2] Cd)[LT-1)
14. A circular disc X of radius R is made from an iron plate of thickness t, and another disc Y of radius 4R is made from an iron plate of thlcknessz/a . Then the relation between the moment of inertia I x and 1 y is :
(a) Iy = 32Ix . (b) Iy "" 16Ix
(c) Iy = l x (d) Iy = 64lx
15. The time period of a satellite of earth is 5 hours.
If the separation between the earth and the satellite is increased to 4 times the previous value, the new time petiod will become:
(a) 10 h (b) 80 h
(c) 40 h Cd) 20 h
16. A particle performing uniform circular motion has angular momentum L. If its angular frequency is doubled and its kinetic energy halved, then the new angular momentum is ;
L (a) - 4
(c) 4L
(b) 2L Cd) _!,_ 2
"
17. Which of the follOwing radiations has the least wavelength?
(a) y-rays (b) ll"-rays
(c) a-rays Cd) X·rays
18. When U23S nucleus originally at rest, decays py .: emitting an alpha particle having a speed u, the recoil speed of the residual nucleus is :
4u 4u
(a) 238 (b) - 234
4u 4u
(e) 234 Cd) - 238
19. Two spherical bodies of mass M and SM and radii Rand 2R respectively are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body JUSt before collision
is :
(a) 2.SR (c) 7.SR
(b) 4.SR Cd) 1.SR
20. The difference in with temperature semiconductor arises difference .in the:
(a) crystal structure
(b) variation of the number of charge carriers with temperature
(c) type of bonding
(d) variation of scattering mechanism with temperature
21. A car moving/with a speed of 50 km/h, can be stopped by brakes after at least 6 rn, If the same car is moving at a speed of 100 km/h, the minimum stopping distance is :
(a) 12 m (b) 18 m
(c) 24 m (d) 6 m
22. A boy playing on the roof of a 10 m high building throws a ball with a speed of 10 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal, How far from the throwing point will the ball be at the height of 10 m from the ground? [g == 10 m/s2, sin 30° = 1/2,
cos 30" = .J312]
(a) 5.20 m (b) 4.33 m
(c) 2.60 m (d) 8.66 m
23. An ammeter reads upto lAo Its Internal resistance is 0.81 n. To increase the range to 10 A, the value of the required shunt is :
the variation of resistance in a metal and a essentially due to die
(a) 0.03.0 (c) 0.9n
(b) 0.30 Cd) 0.090
24. The physical quantities not having same dimensions are:
(a) torque and work
(b) momentum and Planck's constant ec) Stress and Young's modulus
Cd) speed and (!J. oEorll2
25. Three forces stan acting C simultaneously oil a panicle moving with
velocity 1. These forces are represented in magnitude and direction
by the three sides of a A B triangle ABC (as shown). The particle will now move with velocity:
(a) less than 1
-+ (b) greater than v
(c) lv I in the direction of largest force Be Cd) It, remaining unchanged
26. If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is $1 and ~2' the electric charge inside the surface will be ;
(a) (lPz - +I)eo (b) (+1 + '2)/"0
eC) (92 - 91)/"0 (d) (~l + h) eo
27. A horizontal force of F
10 N is necessary to
JUSt hold a block _~l~ON~jllll stationary against a
wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is
0.2. The weight of the block is :
(a) 20 N (b) 50 N
ec) 100 N Cd) 2 N
28. A marble block of mass 2 kg lying on ice when given a velocity of 6 m/s is stopped by friction in 10 s. Then the coefficient of friction is ;
(a) 0.02 Cb) 0.03
(c) 0.06 (d) 0.01
29. Consider the following two statements :
A. Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero.
B. Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.
Then;
(a) A does not imply B and B does not imply A (b) A implies B butB does not imply A
(c) A does not imply B but B implies A
(d) A implies Band B implies A
30. Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon:
(a) the rates at which currents are changing in the tWO coils
(b) relative position and orientation of the two coils
ec) the materials of the wires of the coils (d) the currents in the two coils
31. A block of mass M is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a . rope of mass m. If a force P is applied at the free end of the rope, the force exerted by the rope on the block.is :
() Pm (b) Pm
a M+m M-m
(c)P (d)~
M+m
32. A light spring balance hangs from the hook of the other light spring balance and a block of mass M kg hangs from the former one. Then the true statement about the scale reading is :
(a) both the scales read M kg each
(b) the scale of the lower one reads M kg and of the upper one zero
(c) the reading of the two scales can be anything but the sum of the readings will be Mkg
(d) both the scales 'read M/2 kg
33. A wire suspended vertically from one of its ends is stretched by attaching a weight of 200 N to the lower end. The weight stretches the wire by 1 nun. Then the elastic energy stored in the wire is :
(a) 0.2 J " (b) 10 J
(c) 20 J Cd) 0.1 J
34. The escape velocity for a body projected vertically upwards from the surface of earth is 11 km/s. If the body is projected at an angle of 45" with the vertical, the escape velocity will be:
(a) 11 .J2 km/s (b) 22 krn/s
(c) 11 km/s Cd) 11/.J2 m/s
35. A mass M is suspended from a spring of negligible mass: The spring is pulled a little and then released so that the mass executes SHM of time period T. If the mass is increased by m, the
time period becomes 5T/3, then the ratio of r; is :
(a) ~ (b) 2S
5 9
(c) 16 (d) ~
9 3
- 36. ~Heat cannot be itself flow from a body at lower temperature [0 a body at higher temperature" is a statement or consequence of:
(a) second law of thermodynamics
(b) conservation of momentum
(c) conservation of mass
(d) first law of thermodynamics
37. Two particles A and B of equal masses are suspended from two massless springs of spring constants kl and k2' respectively. If the maximum velocities, during oscillations are equal, the ratio of amplitudes of A and B is :
(a) Jkl/k2 (b) kl/k2
(c) Jk21kl (d) kz/ kl
38. The length of a simple pendulum executing simple harmonic motion is increased by 21%. The percentage increase in the time period of the pendulum of increased length is:
(a) 11% (b) 21%
(c) 42% (d) 10.5%
39. The displacement y of a wave travelling in the x-direction is given by
y 0; 1O~4 sin (600t ~ 2x ;- -j) metre,
where, x is expressed in metres and t in seconds. The speed of the wave-motion, in ms'" is:
(a) 300 (c) 1200
(b) 600 (d) 200
40. When the current changes from + 2 A to - 2A in 0.05 s, an emf of 8 V is induced in a coil. The coefficient of self- induction of the coil is :
(a) 0.2 H (c) 0.8 H
(b) 0.4 H (d) 0.1 H
41. In an oscillating Le circuit the maximum charge on the capacitor is Q. The charge on the capacitor when the energy is stored equally between the electric and magnetic fields is :
(a) Q 12 (b) Q 1.J3
(c) Q 1../2 Cd) Q
42. The core of any transformer is laminated so as to:
(a) reduce the energy loss due to eddy currents (b) make it light weight
(c) make it robust and strong
(d) increase the secondary voltage ----)
· .. 43. Let P be the force acting ona particle having
position vector "1 and i be the torque of this force about the origin. Then:
----)----) ~4
(a) r . t ::: 0 and F . t ~ 0
44 4------}
(b) r . t ;t 0 and F .. t ::: 0
~-----}o -----}o~
(c) r .. t ~ 0 and F . t ~ 0
44 4---).
(d) r . t == 0 and F . 'C "" 0
44. A radioactive sample at any instant has its disintegration rate 5000 disintegrations per minute. After 5 minutes, the rate is 1250 disintegrations per minute. Then, the decay constant (per minute) is:
(a) 0.4 In 2 (b) 0.2 In 2
(c) 0.1 In 2 Cd) 0.8 In 2
45. A nucleus with Z "" 92 emits the following in a
sequence: 0:, 0:, .13~, Ir, 0:, 0:,0:,0:; 13-, ~~,
0:, 13+, W, Cl".. The Z of the resulting nucleus is :
Ca) 76 (b) 78
l:~!'~'
(e) 82 ~.i.. (d) 74
46. TWo identical, photocathodes receive light of frequencies 11. and f2• If the velocities of the photoelectrons (of mass m) coming out are respectively v1. and v2, then:
2 . 2 2h .
. (a) VI - V2 = - (iI - '2)
. . m
[2h ]112
(b) VI + V2 '" 1TI (fI + '2)
2 2 2h
(c) Vt + V2 ::: m (II + h)
[2h ]112
(d) VI - V2 == m (11 - (2)
47. Which of the following cannot be emitted by radioactive substances during their decay?
(a) Protons (b) Neutrinos
(c) Helium nuclei (d) Electrons
48. A 3V battery with negligible internal resistance is connected in a circuit as shown in the figure. The current 1, in the circuit will be :
·1
3V
(a) 1 A (c) 2A
3n (b) 1.5 A
Cd) ~A
49. A sheet of alurnini urn foil of negligible thickness is introduced between the plates of a capacitor. The capacitance of the capacitor:
(a) decreases (b) remains unchanged
(c) becomes infinite (d) increases
50. The displacement of a particle varies according co the relation x'" 4 (cosx; + sin 1fl'). The amplitude of the particle is :
(a) - 4 (b) 4
(c) 4 ./2. Cd) 8
51. A thin spherical conducting shell of radius R has a charge q. Another charge Q is placed at the centre of the shell. The electrostatic potential at a point P at a distance R/2 from the centre of the shell is:
2Q (a) 41lf-oR
(c) 2Q +_q_
41leoR 41ltuR
52. The work done in placing a charge of ? x 10- UI C on a condenser of capacity 100 1-1. F
is:
(a) 16 xlO-32 J (c) 4 x 10-10 J
(b) 3.1 x 10-26 J (d) 32 x 10-32 J
53. The co-ordinates of a moving particle at any time t are given by :x :=: at 3 and y '" (lr 3. The
speed of the panicle at time t is given by ;
(a) 3t Ju2 .,. ~/- (b) 3[2 Ju2 + ~i
(e) [2 ~U2 + p2 (d) Ju2 + (32
54. During an adiabatic process, the pressure of a gas is found to be proportional to [he cube' of its absolute temperature .. The ratio C p lev for the gas is:
(3) 4/3 (e) 5/3
(b) 2 (d) 3/2
55- Which of the following parameters does not characterise the thermodynamic state of matter?
(a) Temperature (b) Pressure
(e) Work (d) Volume
56. A Carnot enginetakes 3 x 106 cal of heat from a reservoir at 627°C and gives it to a sink. at.2 7°C. The work done by the engine is :
(a) 4.2 x 106 J (b) 8.4 x 106 J
(c) 16.8 x 106 J (d) zero
57. A spring of spring constant 5 x 103 N/m is stretched initially by 5 em from the unstretched position. Then the work required to stretch it
further by another 5 em is : -
(a) 12.50 N-m (b) 18.75 N·m
ee) 25.00 N-m (d) 6.25 N-m
58. A metal wire of linear mass density of 9.8 g/rn is stretched with a tension of 10 kg-wt between two rigid supports 1 m apart. The wire passes at its middle point between the poles of a permanent magnet and it vibrates in resonance when carrying an alternating current of frequency n. The frequency n of the alternating source is : (a) 50 Hz ec) 200 Hz
(b) 100 Hz (d) 25 Hz.
59. A tuning fork of known frequency 256 Hz makes 5 beats/s with the vibrating string of a piano. The beat frequency decreases [Q 2 beats!s when the tension in the piano string is slightly increased. The frequency of the piano string before increasing the tension was :
(a) (256 + 2) Hz. (b) (256 - 2) Hz
(c) (256 - 5) Hz (d) (256'1- 5) Hz
60. A body executes simple harmonic motion. The potential energy (PE), the kinetic energy eKE) and total energy (TE) are measured as function of displacement x. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) KE is maximum when x :. 0 (b) TE is zero when x == 0
(c) KE is maximum when x is maximum (d) PE is maximum when x = 0
61.ln the nuclear fusion reaction,
fH +rH __".1He +11
given that the repulsive potential energy between the two nuclei is 7.7 x IO-·14J, the temperature at which the gases must be heated to initiate the reaction is nearly [Boitl.mann's constant k == 1.38 x 10-23 J/K ] :
(a) 107 K (b) lOS K
ee) 101 K Cd) 10') K
62. Which of rhe following atoms has the lowest ionization potential?
(a) Ii N (b) 1~%Cs
(c)i~Ar Cd) 19O
63 .. The wavelengths involved in "the spectrum of deuterium CiD} are Slightly different from that
of hydrogen. spectrum, because:
(a) sizes of the two nuclei are different
(b) nuclear forces are djfferent in the two cases (c) masses of the two nuclei are different
(d) attraction between the electron and the nucleus is different in the two cases
64. In the middle of the depletion layer 01 reverse biased p·n junction, the:
(a) electric field is zero
(b) potential is maximum
(c) electric field is maximum (d) potential is zero
(a) q2 - q3 cos 8 (b)q~ ... qJ sin 6
b2 a2 b a
(c) q2 + q;J cos 0 (d) q2 - q3 sin e
b2 a2 b2 a2
70. A 220 V, 1000 W burt! is connected across a 110 V mains supply. The power consumed will be :
(a) 750 W (b) 500 W '
(c) 250 W (d) 1000 W
71. The image formed by an objective of a compound microscope is:
(a) virtual and diminished
(b) real and diminished
(e) real and enlarged
(d) virtual and enlarged
72. The earth radiates in the infra-red region of the spectrum. The spectrum is correctly given by: (a) Rayleigh Jeans law
(b) Planck's law of radiation (c) Stefan's law of radiation (d) Wien's law
73. To get three images of a single object, one should have two plane mirrors at an angle of :
(a) 600 (b) 90°
(c) 1200 (d) 300
74. According to Newton's law of cooling, the rate of cooling of a body is proportional to (6 8)", where
6, 0 is the difference of the temperature of the body and the surroundings, and n is equal to ;
(a) 2 (b) 3
(c) 4 (d) 1
75. The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by 100%. Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be :
(a) 200% (b) 100%
(c) 50% (d) 300%
...eIII\~ __
65 .. l.f the binding energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV, the energy required to remove the electron from the first excited state of Li2+ is :
(a) 30.6 eV (b) 13.6 eV
(e) 3.4 eV Cd) 12.2.4 eV
66. A body is moved along a straight line by a machine delivering a constant power. The distance moved by the body in rime r is proportional to :
(a) t 3/4 (b) t312
(c) tli~ (d) tin
67. A rocket with a lift-off mass 3.5 x 104 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 10 m/82 . Then the initial thrust of the blast is :
(a) 3.5 x lOS N (b) 7,Ox lOS N
(c) 14.0 X 105 N «n 1.75 x lOs N
68. To demonstrate the phenomenon of
interference we require two sources which emit radiations of :
(a) nearly the same frequency (b) the same frequency
(c) different wavelength
(d) the same frequency and having a definite phase relationship
69. Three charges - q l' + q 2 and - q3 are placed as shown in the figure. The x-component of the force on - ql is proportional to :
~!l3 y
~
II
~·~b
~ql
76. In Bohr series of lines of hydrogen spectrum, the third line from the red end corresponds to which one of the following inner-orbit jumps of the electron for Bohr orbits in an atom of hydrogen? (a) 3-,1> 2 (c) 4~ 1
(b).5~ 2 (d) 2-+ 5
77. The de-Broglie wavelength of a tennis ball of mass 60g moving with a velocity of 10 m/s is approximately:
(Planck's constant, h = 6.63 X 10-34 Js)
(a) 10-33 m (b) 10-31 m
(c) 10 .. 16 rn (d) 1O~2s m
78. The orbital angular momentum for anelecrron revolving in an orbit is given by JI(l + 1) !.
This momentum for an s-elecrron will be given by:
1 h (a) + -:-.- 2 2n
h (e)-
21t
(b) zero
r;:; h (d) 'oJ L.' .- 2n
79. How many unit cells are present in a cube shaped. idea] crystal of NaC! of mass LOO g? [Atomic masses : Na "" 23, Cl = 35.5]
Ca) 2.57 x 1021 (b) 5.14 x 1021
(c) 1.28 x 1021 (d) 1.7l x 1021
80. Glass is a :
(a) micro-crystalline solid (b) super-cooled liquid (c) gel
(d) polymeric mixture
81. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Manganese salts give a violet borax- bead test in the reducing flame
(b) From a mixed precipitate of AgCl and AgI, ammonia solution dissolves only AgCl
(c) Ferric ions give a deep green precipitate on adding potassium ferro cyanide solution
(d) On boiling a solution having K+, Ca2+ and HCO i ions we get a precipitate of K2Ca(C03)2
82. According to the periodic law of elements, the variation in properties of elements is related to their:
(a) atomic masses (b) nuclear masses (c) atomic numbers
(d) nuclear neutron-proton number ratios
83. Graphite is a soft solid lubricant extremely difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that graphite:
(a) is a non-crystalline substance (b) is an allotropic form of diamond
(c) has molecules of variable. molecular masses like polymers
(d) has carbon atoms arranged in farge plates of rings of strongly bound carbon atoms with weak interplate bonds
84. The IUPAC name ofCH3COCH(CH3h is : (a) isopropylrnethyl ketone
(1)) 2·methyJ·3-butanone
(c) 4-methylisopropyJ ketone (d) 3-methyl-2-butanone
85. When CH2 =CH-COOH is reduced with LiAIH4' the compound obtained will be :
(a) CH3 -OI2 -COOH
(b) CH2 =CH-CH20H
(c) CH3 -CH2 -CH20H
(d) CH3 -CH2 -CHO
86. According to the kinetic theory of gases, in an ideal gas, between two successive collisions a ga1 molecule travels :
(a) in a circular path
(b) in a wavy path
(c) in a straight line path
Cd) with an accelerated velocity
87, Which of the following group of transition metals is called coinage metals? .
(a) Cu, Ag, Au (b) Ru, Rh, pd (c) Fe, Co, Ni (d) Os, Ir, Pt
88. The general formula C "Hz"o z could be for open chain:
(a) diketones
(b) carboxylic acids (c) diols
(d) dialdehyde.s
89. An ether is more volatile than an alcohol having the same molecular formula. This is due to : (a) dipolar character of ethers
(b) alcohols having resonance structures
(c) inter-molecular hydrogen bonding in ethers (d) inter-molecular hydrogen bonding in
alcohols
90. Among the following four structures I to IV :
CH3 0 CH3
I II I
C2HS -CH-C3~ C}h-C -CH-C2HS
0) OQ
CH3
I
C2HS -CH-C2HS
H
I
H-C€I
I H (Ill)
(IV)
it is true that:
(a) all four are chiral compounds
(b) only I and II are chiral compounds (c) only III is a chiral compound
(d) only II and IV are chiral compounds
91. Which one of the following processes will produce hard water?
(a) Saturation of water with CaC03 (b) Saturation of water with MgC03 (c) Saturation of water with CaS04 (d) Addition of Na2S04 to water
92. Which one of the following compounds has the smallest bond angle in its molecule 7
(a) S02 (b) OH2
(c) SH2 (d) NH3
93. Which one of the following pairs of molecules will have permanent dipole moments for both .rnembers ?
(a) SiF4 and N02 (b) N02 andCOz
(c) N02 and 03 (d) SiF4 and CO2
94. Which one of the following groupings represents a collection of isoelectronic species? (At. numbers: Cs·SS, Br·3S)
(a) Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ (b) N3-, P-, Na+
(c) Be, AIH, cr (d) Ca2+, Cs+, Br
95.ln the anion HCOO- the two (arbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length, What is the. reason for it ?
(a) Electronic orbits of carbon atom are hybridised
(b) The C = ° bond is weaker than the C -0 bond
(c) The anion i-ICOO- has two resonating structures
(d) The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
96. The pair of species having identical shapes for molecules of both species is ~
(a) CF4, SF4 (b) XeF2, CO2
.. (c) Up:" PC13 (d) PFs, IPs
97. The atomic numbers of vanadium (V) , chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) are respectively 23,.24,25 and 26. Which one of these may beexpeeted to have the highest second ionization enthalpy?
(a) V (b) Cr
(c) Mn (d) Fe
98. Consider the reaction equilibrium; 2S02(g)+ 02(g)~ 2S03(g);
tI HO",-I98 kJ On the basis of Le-Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is : (a) lowering of temperature as well as pressure (b) increasing temperature as well as pressure (c) lowering the' temperature and increasing
the pressure
(d) any va lue of temperature and pressure
99. What volume of hydrogen gas, at 273K and 1 atm pressure will be consumed in obtaining 21.6g of elemental boron (atomic. mass = 10.8) from the reduction of boron trichloride by hydrogen? (a) 89.6 L (c) 44.8 L
eb) 67.2 L (d) 22.41.
100. For the reaction equilibrium,
Np 4(g)~· 2NOCg)
the concenrrations of N204 and N02 at equilibrium are 4.8 x 10-2 and 1.2x 10-2 mol L-1 respectively. The value of x, for the reaction is ;
(a) 3.3)( 102 mol r;l (b) 3)( 10-.1 mol L-1
ee) 3 x 10-3 mol L-) (d) 3 x 103 mol L-1
101. The solubility in water of a sparingly soluble salt AB2 is 1.0 x 10-5 mol 1-1. Its solubility product
number will be : (a) 4 x 1O-1S
(c) 1 x 10-15
(b) 4)( 10-10 Cd) 1 x 10-10
102. When during electrolysis of a sqlution of AgN03, 9650 coulombs of charge pass through the electroplating bath, the mass of silver deposited on the cathode will be ;
(a) 1.08 g (b) 10,8 g
(c) 21.6 g (d) 108 g
103. For the redox reaction
2n(s)+ Cu2+ (0.1 M),. 2n2+ (1M) + Cu(s)
taking place in a cell, E '~II is 1.10 volt. Hoell for thecell will be : ( 2.303 7' '" 0.0591)
(a) 2.14 V (b) LBO V
(c) l.07 V (d) 0.82 V
104. In a 0.2 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid HX, the degree of ionisation is 0.3. Taking Kf for water as 1.85, the freezing point of the solution will be nearest to :
(a) - 0.480°C (c) - O.260°C
(b) - 0.360" C (d) + 0.480°C
105. The rare law for a reaction between the substances A and B is given by rate '" k [ At [B)m. On doubling the concentration
of A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of the reaction will be as :
1
(a) 2m., ~. (b) em + n)
(c) (n - m) (d) 2(" - m)
106.25mL of a solution of barium hydroxide on titration with 0.1 molar solution of hydrochloric acid gave a titre value of 35 mL. The molarity of barium hydroxide solution was :
(a) 0.07 (b) 0 . .14
(e) 0.28 (d) 0.35
107. The correct relationship between free energy change in a reaction and the corresponding equilibrium constant K, is :
(a) IlG '" RT In Kc (b) - t.G '" RT In KG
(c) AGo", RT In Kc (d) - /lGo "" RT In K,
108. If at 298K the bond energies of C--l-I, C~C.
C = G and Ii-H bonds are respectively 414, 347, 615 and 435 k J mol:", the value of enthalpy change for the reaction
HlC - CHz{g) + H2(g) ----)0 H3C - CH3(g)
at 298K will be :
(a) +- 250 kJ (e) + 125 k J
(b) - 250 kJ (d) -12SkJ
~09. The enthalpy change for a reaction does not depend upon the:
(a) physical state of reactants and products
(b) use of different reactants for the same product
(c) nature of intermediate reaction steps
Cd) difference in initial or final temperatures of involved substances
110. A pressure cooker reduces cooking time for food because:
(a) heat is more evenly distributed in the cooking space
(b) boiling point of water involved in cooking is increased
(c) the higher pressure inside the cooker crushes the food material
(d) cooking involves chemical changes helped by a rise in temperature
111. If liquids A and B form an ideal solution, the; (a) enthalpy of mixing is zero
(b) entropy of mixing is zero
(c) free energy of mixing is zero
Cd), free energy as well as the entropy of mixing are each zero
112. For the reaction system;
2NO(g) + 02(g) ---+ 2N02(g) volume is suddenly reduced to half its value by increasing the pressure on it. If the reaction is of first order with respect to O2 and second order with respect to NO; the rate of reaction will : (a) diminish to one-fourth of its initial value (b) diminish to one-eighth of its initial value (c) increase to eight times of its initial value (d) increase to four times of its initial value
113. For a eel! reaction involving a two-electron change, the standard emf of the cell is found to be 0.295 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction at 25°C will be :
(a) 1 x 10-10 (b) 29.S x 10-2
(c) 10 Cd) 1 x 1010
,114;ln an irreversible process taking place at constant T and P and in which only pressure-volume work is being done, the change in Gibbs free energy (dG) and change in entropy (ciS), satisfy the criteria:
(a) (dS)v, Ii < 0, (dG).r, p < 0
(b) (dS)v,£ > 0, (dG)l'.p < 0
(c) (dS)v. E == 0, (dG~. P == 0
(d) (dS)v, E = 0, (dG)T, P > 0
115. Which cine of the following characteristics is not correct for physical adsorption?
(a) Adsorption on solids is reversible
(b) Adsorption increases with increase in
temperature
(c) Adsorption is spontaneous
(d) Both enthalpy and entropy of adsorption are negative
116.ln the respect of the equation k '" Ae-E"IRT in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) k is equilibrium constant (b) A is adsorption factor
ec) E« is energy of activation (d) R is Rydberg constant
117. Standard reduction electrode potentials of three metals A, Band C are+ O.5V, - 3.0Vand -1.2V respectively. The reducing power of these metals are:
(a) B >C > A (c) C > B > A
(b) A >B >C Cd) A>C >B
118. Which one of the following substances has the highest proton affinity ?
(a) H20 (b) H2S
(c) NH3 Cd) PH3
119. Which one of the following is an amphoteric oxide?
(a) ZnO Cb) Nap
(c) S02 (d) BP3
120. A red solid is insoluble in water. However it becomes soluble if some KI is added to water. Heating the red solid in a test tube results in liberation of some violet coloured fumes and droplets of a metal appear on the cooler parts of the test tube. The red solid is :
(a) (NH4hCr20", (b) Hg11
ec) HgO Cd) Pb304
121. Concentrated hydrochloric acid when kept in open air sometimes produces a cloud of white fumes. the explanation for it is that:
(a) concentrated hydrochloric acid emits strongly smelling HCI gas all the time
(b) oxygen in air reacts wtih the emitted HCI gas to form a cloudof chlorine gas
(c) strong affinity of HCl gas for moisture in air results in forming of droplets of liquid solution which appears like a cloudy smoke
(d) due to strong affinity for water, concentrated hydrochloric add pulls moisture of air towards itself. This moisture forms droplets of'water and hence thedS{ud
122. The substance used in Holmes signals of the ship is a mixture of:
(a) CaC:.! + Ca3P2 (b) Ca3(P04)2 + PbP4
(c) HjP04 + CaCl2 Cd) NHJ + HOC!
123. The number of d-electrons retained in Fe2+ (At. no. Fe == 26) ions is :
~a) 3 (b) 4
(e) 5 (d) 6
124. What would happen when a solution of potassium chromate is treated with an excess of dilute nitric acid?
(a) C1.3+ and Crpr are formed (b) Crp;~ and H20 are formed
(c) crO~- is reduced to + 3 state of Cr (d) None of the above
125. In the co-ordination compound, l(4[NiCCN)4]' the oxidation state of nickel is :
(a) -1 (b) 0
(c)+l (d)+2-
126. Ammonia forms the complex ion [Cu(NH3 )4] 2 ... with copper ions in the alkaline solutions but not in acidic solutions. What is the reason for it ? (a) In acidic solutions hydration protects
copper ions
(b) In acidic solutions protons co-ordinate with ammonia molecules forming NH~ ions and
NH3 molecules are not available
(c) In alkaline solutions insoluble Cu{OHh is precipitated which is soluble in excess of any alkali
(d) Copper hydroxide is an amphoteric substance
127. One mole of the 'complex compound Co(NH3 hCls, gives 3 moles of ions on' dissolution in water. One mole of the same complex reacts with twO moles of AgN03 solution to yield two moles of AgCI(s). The structureof the complex is :
(a) [Co(NH3 )5Cl]CI2
(b) [Co(NH3hCI2)· 2NH3 (c) [Co(NH3 ).; CJ:iJCI· NHs Cd) [Co(NH3)4C1]Clz ·NH3
128. The radius of La 3+ (Atomic number of La == 57) is 1.06 A. Which one of the following given values will be closest to the radius of Lu3., (Atomic number ofLu == 7l)?
(a) 1.60 A (b) 1.40 A
(c) 1.06 A Cd) 0.85 A
129. The radionudide 2~~Th undergoes two successive p-decays followed by one a-decay. The atomic number and the mass number respectively of the resulting radionudide are:
(a) 92 and 234 (b) 94 and 230
(c) 90 and 230 (d) 92 and 230
130. The half-life of a radioactive isotope is 3 h. If the initial mass ofthe isotope were 256 g, the mass - of it remaining undecayed after 18 h would be :
(a) 4.0 g (b) 8.0 g
(c) 12.0 g Cd) ]6.0 g
131. Several blocks of magnesium are fixed to the bottom of a ship to :
(a) keep away the sharks (b) make the ship lighter
(c) prevent action of water and salt
(d) prevent puncturing by under-sea rocks
132. In curing cement plasters water is sprinkled from time to time. This helps in :
(a) keeping it cool
(0) developing interlocking needle- like crystals of hydrated silicates
(c) hydrating sand and gravel mixed with cement
(d) converting sand into silicic acid
133. Which one of the following statements is not true?
(a) The conjugate base ofH2PO;; is HPO~(b) pH + pOH == 14 for all aqueous solutions (c) The pH ofl x 10-~ M Hel is 8
(d) 96,500 coulombs of electricity when passed through a CuSO 4 solution deposit 19 equivalent of copper at the cathode
134. The correct order of increasing basic nature for the bases NH~, CH)NH2 and (CH3hNH is:
(a) CH3NH2 < NH3 < (CH3)zNH
(b) (CH3)2NH < NH3 < CJ-I~NH2
(c) NH_., < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
Cd) CH1NH2 < (CH"hNH < NH3
135. Butene-l may be converted to butane by reaction with :
(a) Zn-HCI (b) Sn-HC\
(c) Zn-Hg (d) PdIH2
136. The solubilities of carbonates decrease down tile magnesium group due to a decrease in .:
(a) lattice energies of solids
(b) hydration energies of cations (c) inter-ionic attraction
(d) entropy of solution formation
137. During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with concentrated H2SO 4 the initiation step is :
(a) protonation of alcohol molecule (b) formation of carbocatlon
(c) elimination of water
(d) formation of an ester
138. Which one of the following nitrates win leave behind a metal Oil strong heating?
(a) Ferric nitrate (b) Copper nitrate
(c) Manganese nitrate(d) Silver nitrate
139. When rain is accompanied by a
thunderstorm, the collected rain water will have a pH value:
(a) slightly lower than that of rain water without thunderstorm
(b) slightly higher than that when the thunderstorm is not there
(c) uninfluenced by occurrence of
thunderstorm
(d) which depends on the amount of dust in air
140. Complete hydrolysis of cellulose gives :.
(a) D·fructose (b) D·ribose
(c) D-glucose (d) L-glucose
141. FOf making good quality mirrors, plates of float glass are used. These are obtained by floating molten glass over a liquid metal which does not . solidify before glass. The metal used can be :
(a) mercury (b) tin
(e) sodium Cd) magnesium
142. The substance nat likely to contain CaC03 is : (a) a marble statue (b) calcined gypsum
(c) sea shells (d) dolomite
143. The reason far double helical structure of DNA is operation of :
(a) van der waals' forces·
_ (b) dipole-dipole interaction (e) hydrogen bonding
(d) electrostatic attractions
144. Bottles containing C6HsI and C6HsCR2i lost their original labels. They were labelled A and B for testing. Aand B were separately taken in a test tube and boiled with NaOH
, solution. The end solution in each tube was made acidic with dilute HN03 and then some AgN03 solution was added. Substance B gave a yellow precipitate. Which one of the following statements is true far this experiment ?
(a) A was C6HsI
(b) A wasC6HsCH21 (c) B was C6HSI
Cd) Addition ofHN03 was unnece~sary
145. Ethyl isocyanide on hyd rolysis in acidic medium generates;
(a) ethylarnine salt and merhanolc acid (b) propanoic add and ammonium salt (c) ethanoic add and ammonium salt (d) methylamine salt and erbanoic acid
146. The internal energy change when a system goes from state A to B is4D kJ/mol. If the system goes from A to B bya reversible path and_ .. returns to state A by an irreversible path, what would be the net change in internal energy ?
(a) 40 kJ (b) > 40 kJ
(c) < 40 kJ (d) zero
147. The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic KOH and p-toluidine form :
(a) H3C-@-CN
(b) H3C-@-N2Cl'
(e) H3C-@-NHCHC12 Cd) H3C-@-NC
148. Nylon threads are made of: (a) polyvinyl polymer
(b) polyester polymer
(c) polyamide polymer
(d) polyethylene polymer
149. On mixing a certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, it forms only one monochloroalkane. This alkane could be;
(a) propane (b) pentane
(e) isopentane (d) neopentane
150. Which of the following could act as a propellant for rockets ?
(a) Liquid hydrogen + liquid nitrogen (b) Liquid oxygen + liquid argon
(c) Liquid hydrogen + liquid oxygen (d) Liquid nitrogen + liquid oxygen
~------------------
1. A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
{O-l h . dd
-y,wennlso
f(n) =
-%, when n is even
is:
(a) one-one but not onto
(b) onto but not one-one
(c) one-one and onto both (d) neither one-one nor onto
2. Let ZI and z2. be two roots of the equation Z2 +.az + b = 0, zheing complex. Further,
assume that the origin, Zl and Z2 form an equilateral triangle. Then:
(a) ci = b (h) a2 = 2b
(c) a2 = 3b (d) al = 4b
3. If z and 00 are two non-zero complex numbers such that] z roj = 1,. and
arg (z) - arg (00) = ~, then zro is equal to :
(a) 1 (b)-1
(e)i (d)-i
(1 + i)X
4- If 1 _ i = 1, then:
(a) x '" 4 0, where n is any positive integer (b) x", 211, where n is any positive integer
(c) x = 4 n + 1, where 11 is any positive integer . (d) x = 2 n 'I- 1, where n is any positive integer
a el- 1'1- a3
5. If b b2 1-1' b3 ",0
c e2 1 + ,3 and vectors (1, a, a2), (1, b, b2) and (1, C, (2) are non-coplanar, then the product abc equals :
(a) 2 (b) -1
(c) 1 (d) 0
6. If the system of linear equations 'x+2ay+az=0
x +3by + bz = 0 x+4cy+cz=0
has a non-zero solution, then a, b, c : (a) are in AP
(b) are in GP
ee) are in HP
(d) satlsfy c « 2b+ 3c=0
7. If the sum of the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + C = 0 is equal to the sum of the
squares of their reciprocals, then E:, !?_ and -be. are c a
in:
Cal arithmetic progression (b) geometric progression ec) harmonic progression
(d) anthmetico-geornerric progression
8. The number of the real solutions of the equation Xl - 3 J x I + 2 = 0 is :
(a) 2 _ ec) 1
(b) 4 (d) 3
9. The value of 'a' for which one root of the quadratic equation
Ca2 - Sa + 3) xl + (3a -1) x + 2= a is twice as large as the other, is ;
(a) 2/3 (b) -2/3
(c) 1/3 (d) -1/3
10. If A 0=[: . :] and A2 0= [~ :} then:
(a) a '" a2 + b2, ~:::: ab
(b) a =a2 + bZ, 13= 2ab (c) a "" a2 + b2, f3. '" 02 - b2 (d) ex = 2ab, 13 "" 02 + b2
11, A student is to answer 10 out of 13 questions in an examination such that he. must choose at least 4 from the first five questions. The number of choices. available to him is :
(a) 140 (c) 280
(b) 196 Cd) 346
12. The number of ways in which 6 men and 5 women can dine at a round table, if no two women are to. sit together, is given by : .
(a)6!x5! (b) 30
(c) 5!)(41 (d)7!.x5!
13. If 1, ro, ro2 .are the cube roots of unity, then :
1 ro" a/"
8= OJ" OJ2n 1
ro2n 1 w" is equal to : (a) 0
(c) CO
(b) 1 (d) (fJ2
14. If "C, denotes the number of combinations of n things taken r at a time, then the expression -c, + J + "C, -1 + 2 X ''C,equals :
(a) n+ -c, (b)" + -c, + 1
(e) n e- 'c, (d) , .... 'c, >- I
15. The number of integral terms in the expansion of (-,J3 + VsiS6 is :
(a) 32 (b) 33
(e) 34 (d) 35
16. If x is positive, the first negative term in the expansion of (1 + xi7.!s is :
(a) 7th term (b) 5th term
ee) 8th term (d) 6th term
17. The sum of the series
1 1 1 . I
1-2 - 2.:3 + T4 - ... upto 0) IS equa to:
(a) 210g< 2 (b) loge 2 - 1
(c) log. 2 (d) log. (~)
18. Let fex) be a polynomial function of second degree. If f(l) = f(-I)and a, b, care in AP, then f ' Cal. t ' (b) and t ee) are in :
(a) AI'
(b) GP
(c) HP
(d) arithmetico-geometric progression
19. If Xl' x2' X3 and Yl' Yz, Y3 are both in GP with the same common ratio, then [he points (Xl, Y!), (x2, h) and (X3., Y3):
(a) lie on a straight lint:
(b) lie on an ellipse
(c) lie on a circle
(d) are vertices of a triangle
20. The sum of the radii of inscribed and circumscribed circles for an II sided regular polygon of side a, is :
(a) a cot(~) (b) ~ cot (;)
(c) a cot (!:-) Cd) E. cot (.~-)
271 4 211
21. If in a triangle ABC
a cos2 (%) + e cos2 ( %) = '~J,
then the sides a, band c .
(a) are in AI' (b) arc in GP
(e) are in HP (d) satisfy a -I- b "'c
22. In a triangle ABC, medians AD' and BE are
drawn. If AD. '" 4, L DAB '" ~ and L. ABE '" .j , then the area of the 6 ABC is :
(a) 8/3 (b) 16/3
(e) 32/3 Cd) 64/3
23. The trigonometric equation sin -I x = 2 sin -i a, has a solution for:
(a) 1,.2 <I al < _I_
.. -J2
1 (c)jaj<"2
(b) all real values of a
1 (d)jaj;,;~· ~
J2
24. The upper 3/4th portion of a vertical pole subtends an angle tan -J 3/ Sat a point in the' horizontal
plane through its foot and at a distance 40 ill from the foot. A possible height of the vertical pole is :
(a) 20 m (b) 40 m
(e) 60 m Cd) 80 m
25, The real number x when added to its inverse gives the minimum value ofthe sum at x equals to:
(a) 2 (b) 1
(c) -} (d)-2
26. If f: R ~ R satisfies f( x + Y)= I(x) + fey),
~
for all x, Y ER and f(1) = 7> then E fer) is:
iI"~1
. Tn (a) 2
(c) 7n~n + 1)
27. If f(x) =- x", then the value of f '(1) reI) 1"'(1)
f(l) ~ ~ + -""""21 - """"3! + ...
(-1)" f "(1)
+ is:
Il!
(a) 2" (b) 2"-1
(c) 0 Cd) 1
28. Domain of definition of the function
[(x) '" -~ + 10gJO (xJ - x), is :
4-x
Cal '(1, 2)
(b) (-1, 0) v (1, 2) (c) (1, 2)u (2, m)
(d) (-1,0) v (1,2) v(2, 0))
[ 1 - tan (1)] [1 - sin x]
is:
[ 1 + tan (~) l[n - 2XJ3
29. lim
1 Cal .. c 8
(e) . .!... 32
(b) 0
(d) cc
log (3 + xl-log (3 - x)
30. If lim = k, the value
:<-,0 X
of k is: (a) 0 (e) 2/3
(b) -1/3 (d) -2/3
31. If f n (a), gl1 (a) exist and are not equal for some
n, Further if ita) "" g(a) = k and
lim !(a)g(x) ~ fla),- gea) f(x)+ gea) "" 4
r _,." g(x) - !(x) ,
then the value of k is equal to ;
(a) 4 (b) 2
(c) 1 Cd) 0
32. The function !(:x) = log ex + .~ x2 + 1), is ; (a) an even function
(b) an odd function
(c) a periodic function
(d) neither an even nor an odd function
33. If f(x)={xe~ [I;i ~~] ,x;t: Othen f(x) is:
o ; x=o
(a) continuous as well as differentiable for all x (b) continuous for all x but not differentiable at x=O
(c) neither differentiable nor continuous at x",O
(d) discontinuous everywhere
34.lf the function f(x) = 2x3 - 9axz + 12a2x + 1, where a > 0, attains its maximum and minimum at p and q respectively such that p2 '" q, th~fI. a
equals:
(a) 3 (b) 1
(c) 2 Cd) V2
35. If fey)= el, gey)= y;y > 0
and Fet) '" f~ fCt - y) g(y) dy, then: (a) Fer) = 1 -e-~(1 + t)
(b) FCc)'''' c/ - (1 + t)
(e)F(t)=tl
(d) F(t) = te"
36. If fea + b - x) = fex), then fa" x f(x) dx is equal to:
. a + b JO
(a) -2- a feb - x) dx
(b) a; b J: f(x)dx
b - a fO
(e) --y a f(x) dx
a + b JO
(d) ~ a f(a+ b+ x) dx
2
JX see2t dt
37. The value of lim 0 is :
r ->0 X sin x
(a) 3 (e) 1
(bJ 2 Cd) -1
38. The val ue of the in tegral I '" f ~ x(1 - x)" dx is :
1 (a) n + 1
1 1
(e) 11 'I' 1 - ,,+ 2
(b) _1_. n+2
(d) _. _1_ + _. _1_. n+l n+2
1 + 23 + 33 + .. + 113,
- lim - ---, ---IS:
nc-s cc n.JI
(a) lJ30 (b) 0
(e) 1/4 Cd) 1/5
40. Let :x rex) '" (es: X), x > O.
J4 3 ' 3
If _e"nr dx=F(k)-F(l),
1 X
then one of the possible values of k, is :
(a) 15 (b) 16
(c) 63 (d) 64
41. The area of the region bounded by the curves y = 1 x -]1 and y =,3 -I x] is :
(a) 2 sq unit (b) 3 sq unit
(c) 4 sq unit (d) 6 sq unit
42, Let f(x) be a function satisfying f '(x) '" f(x) with f(O) '" 1 and g(x} be a function that satisfies jex) + gex) = x '. Then the value of the
integral II: f(x) g(x) dx, is :
e2 5 e2 3
(a) e - 2 - ~ (b) e.+ 2' - 2.
~ 3 ; 5
ec) e - -2 ~ 2: (d) e + 2' + 2:
43, The degree and order of the differential equation of the family of all parabolas whose axis is x-axis, are respectively:
(a) 2, 1 (b) 1, 2
(c) 3,2 (d) 2,3
44. The solution of the differential equation
, -1 dy
(l+y2)+,(x~etan Y) dx =O,is:
-1 (a) ex - 2) = ke" Ian y
(b) 2 X et•n -I y '" e2 tan .. 1 y + /( (c) Xe,"n-1Y '" ran " y + k
(d) xe2 [an-1 Y = emn-! y + k
45. If the equation of the locus of a point equidistant from the points (aI' bJ land (a2, b2}is Cal - az) x + (hi - bz) Y + c = 0, then the value of'C'is:
1 2 2 22
(a) 2 Cal + bz - eli - hI)
2 2 2 2
(b) Q1 .- Q2 + hJ - b2
1 2 2 b2 2
(c) '2 Cal + a2 + I + b2)
Cd) Jat + ~2 -ai -bi
46. Locus of centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (acost,asint), (bsint,-bcost) and (1, 0), where t is a parameter, is :
(a) (3x _1)2 + (3yi == a2 - b2
(b) (3x -1/ + (3y)2 = a2 + b2
(c) (:3x + Ii + (3yi == a2 + b2
Cd) (3x+ Ii + (3yi == a2 - b2
47. (f the pair of straight lines Xl - 2p>.y - y2 = 0 and x2 - 2q>.y - y2 = 0 be such that each pair bisects the angle between the other pair, then:
(a) s=« (b)"p=- q
(c) pq == 1 -Cd) pq = - 1
48. A square of side a lies above the x-axis and has one vertex at the origin. The side passing through the origin makes an angle
a (0 < U < *) with _ the positive direction of
x-axis. The equation of its diagonal nor passing through the origin is :
(a) y (cos a -sin a)- x (sin a -cos a)=a (b) y (cos u + sin: 0:) + x (Sin a - cos 0.) '" a (c) y (cos a + sin a) + x (sin 0. + cos a) "" a (d) y (cos 0: + sin aJ+ x (cos a --sin o:)=a
49. If the two circles (x - Ii + (y - 3i = r2 and x2 + y2 - 8x + 2y + 8 == 0 intersect in two distinct points, then : (a) 2 <,. < 8
ec) ree2
(b) r < 2 (d) r » 2
50. The lines 2X - 3y == 5 and 3x - 4y = 7 are diameters of a circle having area as 154 sq unit. Then the equation of the circle is :
(a) x2 + y2 + 2x - 2y == 62
(b) x2 + y2 + 2x - 2y == 47
ec) x2 + y2 - 2x + 2y = 47
(d) x2 + y2 - 2x + 2y = 62
51. The normal at the point (btl, 2 btl) on a parabola meets the parabola again in the point (bd, 2bt 2)' then;
x2 y2
52. The foci of "the ellipse 16 + Il == 1 and the
2 2
hyperbola 1~4 - ~ 1 == ~5 coincide. Then the
value of b2 is :
(a) 1 Ce) 7
(b) 5 Cd) 9
53. A tetrahedron has vertices atO(O,"O,O), A(1, 2, 1), B (2, 1, 3) and C (-1, 1, 2). Then the angle between the faces OAB and ABCwill be :
(a) cos-1 G~J (b) cos-1 GD
ec) 300 (d) 900
54. The radius of the circle in which the sphere xl + y2 + z2 + 2x - 2y - 4z - 19 := 0 is cut by
the plane x + 2y + 2 z + 7 == 0 is ;
(a) 1 (b) 2 .
ee) 3 (d) 4
x-2 y-3 2-4
55. The lines -1- == -1- '" ~ and
x-I y-4 z-5
k- == -2- == -1- are coplanar if:
(a) k == 0 or -1 (b) b= 1 or-l
(e)k=Oor-3 (d)k=3or-3
56. The two lines x = ay + b, Z == cy + d and x = a' y + b', z == c' y + d' will be perpendicular, if and only if :
(a) aa' +bb' + cc' + 1 == 0 (b) acr' + bb' + cc' = 0
(e) (a.+ cr')(b + b')-+ (e+ c')= 0 (d) aa' + cc' + 1 = 0
57. The shortest distance from the
12x + 4y + 3z == 327 to the
xl + y2 + Z2 + 4x - 2y - 62:= 155 is :
4
(a) 26 . (b) 11 13
(e) 13 (d) 39
plane sphere
~8. Two systems-of rectangular axes have the same origin. If a .plane cuts. them at distances a, b, c and a' , b' , c' from the origin, then:
1:, 1 1 1 1 1
(a) - + -+ -+ -+ -+ -= 0
c? b2 c2 a,2 b'z e''2.
- 1 1 1· 1 1 1
(b) -+ --,- +-+ ---=0
a2 b2 c'- a,2 b,2 C,2
1 1 1 1 1 1
ee) - - - - - + - - - - - == 0
02 b~ c2 a,2 b,2 C,2
1.-i 1 111
(d) - + - + - - - - - - - == 0
a2 b2 c2 a,2· b,2 C,2
~ -.7 4-
59. a, D, C are three vectors, such
4- -.7 ~ 7 4- ~. -» a + D + C = U, I a 1 = 1, 1 b 1 "" 2. 1 C
-,)~ ~-» ~-».
then a. b + b- C + c- a IS equal to :
dlat
1= 3,
(a) 0 (c) 7
(b) -7 Cd) 1
-,) ---0> 4-
60. If u, v and ware three non-coplanar vectors,
~4~ 44--Jo~
then; u + v -w)· [(u - v) x( v -w)1 equals:
(a) 0
(b) tr·~ x ~
(c)ll~x1 (d)31t.~ x~
61. Consider points A, B, C and D with position
vectors 7 i - 4 j -I- 7 k. i - 6 J + 10 k.
-1-31+41.. and sl-1+sk respectively. Then ABCD is a :
(a) square
(b) rhombus
ec) rectangle
(d) parallelogram bur not a rhombus
62. The
and
vectors
~ ...... "... .......
AC = 5 i - 2 j + 4 k are- the sides of a triangle
ABC_ The length of the median through A is:
(a) .Jls (b) m
(c) 53 (d) ,[288
63. A particle acted -on by constant forces
4 i + 1 - 3 k and 3 i + 1 - k is displaced from the point! + 21 + 3k to the point si + 41 + k. The total work done by the forces is :
(a) 20 unit (0) 30 unit
(c) 40 unit (d) 50 unit
---+ ......... --)."...,'" -----) ............ ""
64. Let u = i + J. v ~ i - j and w '" i + 2 j + 3 k.
. If ~ is a unit vector such that \t. ~ =: 0 and
---+ ~ - ---+ -
v • n = 0, then 1 w- 11 ! is equal to :
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 Cd) 3
65. The median of a set of 9 distinct observations is 20.5. If each of the largest 4 observations of the set is increased by 2, then the median of the new set:
(a) is increased by 2 (b) is decreased by 2
(c) is two times the anginal median
(d) remains the same as that of the original set
66. ln an experiment with 15 observations on x, the following results were available
E Xl = 2830, L x = 170 .
One observation that was 20, was found to be. wrong and was replaced by the correct value 30. Then the corrected variance is :
(a) 78.00 (b) 188.66
(c) 177.33 Cd) 8.33
67. Five horses are in a race. Mr. A selects two of the horses at random and bets on them, The probability that Mr. A selected the winning horse, is :
(a) i
5
(c) ~. 5
(b) ~ 5
Cd) ~ 5
68. Events A, B, C arc mutually exclusive events
3x + 1 1- x
such that peA) '" -3-' PCB) '" -4- and
PCC) = 1 -22x . The set of possible values of x
are in the interval:
(a) [~, ~J
(e) [~, liJ
(b{1' ~]
(d)[O,1]
69. The mean and variance of a random variable X having a binomial distribution arc 4 and 2 respectively. then P(X '" 1) is :
1 1
(a) 32 (b) 16
1 1
(c) "8 Cd) 4
-Jo ~ --+ ---7
70. The resultant of forces P and Q is R. If Q is
~
doubled. then R is doubled. If the direction of
~ ---+
Q is reversed, then R is again doubled, then
p2 ;Q2: R2 is:
(a)3:1:1 (c) 1: 2: 3
(b)2:3:2 (d)2:3:1
71. Let Rl and R2 respectively be the maximum ranges up and down an inclined plane and R be the maximum range on the horizontal plane. Then R1, R, R 2 are in :
(a) arithrnetico-geometric progression (AGP) (b) AP
ec) GP
Cd) HP
-»
72. A couple is of moment G and the force forming
---+ ~
the couple is P. If P is turned through a right
angle. the moment of the couple thus formed is
~ 4-
H. If instead, the forces P is turned through an
angle u, then the moment of couple becomes :
-+ -~ 74. Two stones are projected from the top of a cliff
(a) G sin IX - H cos Ct h. metres high, with the same speed u so as to hit
...:; -+ [he ground at the same spot. I f one of the stones
(b) H cos C( + G sin (t is projected horizontally and the other is
-) -+ projected at an angle e to the horizontal, then
C c) G cos IX + H sin Ct tan e equals :
-) -+ f?; (b) 2g f~
(d) H sin (t - G cos Ct (a) .
73. Two panicles start simultaneously from the (c) 2hK- Cd) ufj;
same poim and move along two straight lines,
one with uniform velocity ti and the other from 75. A body travels a distance s in t seconds. It starts
...:; from rest.and ends at rest, In the first part ofthe
rest with uniform acceleration f. Let tt be the
angle between their directions of motion. The journey, it moves with constant acceleration f
relative velocity of the second panicle w.r.t. the and in the second part with constant
first is least after a time: retardation r. The value oft is given by:
(a) u sin a (b) f cos a (a) 25 (] +~) (b)~
1 1
f u -- + -
(d)uc9sa f r
(c) L/ sin C1. (d) ~2S (7 +;)
f (c) .j2s(j + r)
/MNSWERS
III. PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY
1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (a) 5. (d) 6. (a) 7. (a) 8. (d)
9. (e) 10. (b) 1l. (a) 12. ee) 13. (e) 14. (d) 15. (e) 16. (a)
17. (a) 18. (e) 19. (c)' 20. (b) 21. Ce) 22. Cd) 23. (d) 24. . (b)
25. ~d) 26. (a) 27. Cd)' 28. (c) 29. (e) 30. (b) 31. Cd) 32. (a)
33. (d) 34. ee) 35. (e) 36. (a) 37. (c) 38. (d) 39. (a) 40. (d)
4l. (c) 42. (a) 43. (d) 44. (a) 45. (b) 46: (a) 47. (a) 48. (b)
49. (b 50. (c) 51. ee) 52. Cd) 53. (b) 54. (d) 55 . (e) 56. (b)
57. (b) 58. (a) 59. ecl . 60. (a) 61. (d) 62. (b) 63. (e) 64. (a)
65. (a) 66. (b) 67. (a) 68. Cd) 69. (b) 70. (c) 71. (c) 72. (a)
73. (b) 74. (d) 75. (d) 76. (b) 77. (a) 78. eb) 79. (a) 80. (b)
81. (b) 82. (c), 83. Cd) 84. (d) 85. (b) 86. (e) 87. (a) 88. (b)
89. .(d) 90. (b) 91. ec) 92. (c) 93. ee) 94. (b) 95. ecl 96. (b)
97. (b) 98. ee) 99. (b) 100. Ce) 10l. (a) 102. eb) 103. ec) 104. (a)
105. ed) 106. (a) 107. (d) 108. (d) 109. (e) 110. (b) 111. (a) 112. (e)
113. Cd) 114. (b) 115. Cb) 116. Ce) . 111. (a) 118. (c) 119. (a) 120. (b)
121. (b) 12.2. (a) 123. (d) 124. (b) 125. (b) 126. (b) 127. (a) 128. (d)
129. (e) 130. (a) 131. (b) 132. (b) 133. (c) 134. (c) 135. (d) 136. (b)
137. (a) 138. (d) 139. (a) 140. (e) 141. (a) 142. (b) 143. (c) 144. (a)
145. (a) 146. (d) 147. (d) 148. (e) 149. (d) 150. . (e)
",,.. MATHEMATICS
1. (c) 2. (c) 3. (d) 4. (a) 5. (b) 6. ec) 7. (c) 8. (b)
9. (a) 10. eb) 11. (b) 12. (a) 13. (a) 14. (b) 15. (b) 16. (e)
17. (d) 18. (a) 19. (a) 20. (b) 21. (a) 22. ("') .23. (a) 24. (b)
25. (c) 26. (d) 27. (el 28. (d) 29. ee) 30. Cc) 31. (a) 32. (b)
33. (b) 34. (e) 35. (b) 36. (b) 37. (c) 38. (e) 39. Cd) 40. (d)
41. (c) 42. ee) 43. (b) 44. (b) 45. (a) 46. (b) 47. (d) 48. (d)
49. (a) 50. (e) 51. (a) 52. (c) 53. (a) 54. (c) 55. (e) 56 .. (d)
57. (c) 58. (d) 59. '(b) 60. (b) 61. C") 62. (e) 63. (e) 64. (d)
65. Cd) 66. (a) . 67. (d) 68. (a) 69. (a) 70. (b) 71. (d) 72. (c)
73. (d) 74. (d) 75. (d)
(x) No option is correct in question paper. HlNTS fI SOLUTIONS
1. When particle describes circular path in a magnetic field, its velocity is always perpendicular to the magnetic force.
~-4
Power P = F . v 0: Fv cos 9
Here, 0= 90°
But
P",O W
P=t
W =p·t
Hence, work done W=O
2. The force on a particle is y
. (everywhere)
z
So,
~ -4-+-+
F=q(E+vxB)
or
-+ -+ -+ F=Fe+Fm
:.1. = q"1 =-16 X 10-18 xl04 C-k) = 16 x 1O-1~ k
-+ J8 ~ ~
and F", '" - 16 x 10- (10 i x B j)
=,-16xl0-17 xB(+k) =-16xl0-17 Bli:
Since, particle wi!! continue to move along + x-axis, so resultant force is equal to O.
-4 ..,+
F.+F",=O
16 x 10-14 =16xlO-17 B
B = 16·:x 10-14 = 103 16 xl0-17
B = 103 .wb/m2
3. When magnet -is divided into two equal parts, the magnetic dipole moment
I M M' = pole strength x"2 = 2"
[pole strength remains same] Also, the mass of magnet becomes half i. e. ,
, m m=2
Moment of inertia of magnet mil
[= "12
4·
New moment of inertia
I' = 112 (-i-) Gf = 1r~28
[' .: 8
Now, T '" 2n ~(~B-)
TO = 2n ~(~:B) = 2rr (~~~2)
TO=?':' => TO 1
2 Y='2
W = MB (1 - cos 0)
W =MB (1 - cos 60°) W=MB
2
. MB=2W
Torque, T '" MB sin 600 ME.J3 2W.J3
=-2-=-2-
=w)3
5. Inside bar magnet, lines of force are from south to north.
6. At Curie temperature, a ferromagnetic substance transits into paramagnetic substance.
7. In stational)' position, spring balance reading = mg "" 49
In "" 49 = 5 kg 9.8
When lift moves downward. mg - T "" mG
Reading of balance .
T==mg-ma
== 5 (9.8- 5) = 5x 4.8 "'24.0N
mg
8.
Vu:;! V l E L
where, l == balance point
L = length of potentiometer wire I
or V = I E
V = 30 x E = 30. E
100 100
9. Germanium is semiconductor, whereas copper is conductor.
For conductors, R oc A t For semiconductors,
. 1
R oc-
At
Hence, when both are cooled, then resistance of copper decreases whereas that of germanium increases.
10. Some of the characteristics of an optical fibre are as follows :
(i) This works on the principle of total internal reflection.
(ii) It consists of core made up of
glass/silica/plastic with refractive index n1, which is surrounded by a glass or plastic cladding with refractive index nz(nz > nj)' The refractive index of cladding can be either changing abruptly or gradually changing (graded index fibre).
(iii) There is a very little transmission loss through optical fibres.
(iv) There is no interference from stray electric and magnetic fields to the signals through optical fibres.
11. Thermo-emf of thermocouple = 25j.l.V;oC.
Let 8 be the smallest temperature difference. Therefore, after connecting the thermocouple with the galvanometer, thermo-emf
E == (25IlV;oC) xiWC) = 258 x 10-6 V
Potential drop developed across the
galvanometer
== iR = 10,,5 X 40 = 4 X 10-4 V
4x10~4 '" 258x10-6'
12. According to Faraday's law of electrolysis, III =: zit
m~.!l. = zzn.
IIlcu zCu
0.13 32.5 mCn = 31.5
mcu =; 0.126 g
13. As we know that formula of velocity is 1
y=--_
)~Of'O
'y2 = _1_ == [LT ·-1 ]2 Il oEo
_1_=[eT-2]
Il OlOO .
14. Mass of disc (X), nlx == nR2tp
where, p '" density of material of disc
1 . 2 1 2 2
IX"'2.mxR =2.nR [pR
1 4 Ix == 2. 1lptR
Mass of disc (Y)
my'" 1l (4Ri % p == 4nR2tp
1 2 1 2 6 2
t, = 2. my (4R) == 2. 4nR tp·1 R
Iy == 327ttpR4 ... (ii)
... (i)
and
Iy 321ltpR4 T:" 1
x -1lptR4
2
= 64
.. Iy=64Ix
15. According to Kepler's law T 2 oc 1'3
52 a; 1'3
(f 'i cc(4rl prom Eqs. (i) and (ii)
25 1'3
(f'i = 641'3 T '= .J1600 '['=40h
... 0) ... (ii)
or
16. Angular momentum
L == [(f) ... (i)
Kinetic energy
K == ~ 10/ = ~ L(O [from Eq. (i)]
L= 2K
(j)
L'= 2(~1
20)
L' == !:_
4
Now;
18.
~ \V--)o
[Before decay]
v<---® @--)oU [After DecayJ Apply conservation of linear momentum. 0= 4u - 234v
4u
=> y = 234
The residual nucleus will recoil with a velocity
f 4u .
0234 unit.
Recoil speed of residual nucleus is 2~~'
Note : If they will ask the recoil velocity, then
. ,4u dt4U
answer remains same t.e., 234 an no - 234 as
the word recoil itself is signifying the direction of motion of residual nucleus.
19. Let at '0' there will be a collision. If smaller sphere moves x distance to reach at 0, then bigger sphere will move a distance of (9R - x).
5M
F"" GMxSM (12R - xi.
F G xSM
asrnolJ == M = (12R _ X)2
F GM
~ig == SM = (12R _ X)2
i 2' ==.!. G x SM t2 0
x == '2 a..~l"lIt 2 (i2R _ xi ... I
(9 R - x) ==.!.2 ~ig t2.!. GM 2 t2 ••• (ii)
2 (12R - x)
Thus, dividlngEq. (i) by Eq. (ii), we get
.. __ x_=s
9R -x
::::> x e= 4SR - 5x
=> 6x =: 45R
=> x=7.SR
20. The difference in the variation of resistance with temperature in metal and semiconductor is caused due to difference in the variation of the number of charge carriers with temperature.
21. v2 = u2 + :?as
0== (50 x l~r + 2a x 6
a =-16 m/s2
(a == retardation)
Again y2 ",u2 + 2as
(. 5)2 .
0"" ,100)(18 -16x2)(5
(100 x 5)2
S == 18 x18,x 32 == 24.1",24 ill
22. The ball will be at point P when it is at a height of 10 ill from the ground. So, we have to find the distance OP, wh ich can be calculated directly by considering it as a projectile on a levelled plane (OX).
torn/s
Ground
OP == R = ~2 sin 2.Q == 102 x sin (2 x300)
g 10
= lO-J3 == 5J3 2
= 8.66 m
23. To increase the range of ammeter we have to connect a small resistance in ___2_ A..L1iih '~ parallel (shunt), let its value ~
be R. 0.810
Apply KCL at junction to divide the current.
R
~
,~
lOA 1A 0.810,
Voltage across R = Voltage across ammeter.
~ 9R =0.81 xl
, => R == 0.:1 = 0.090
24. Planck's constant (11) == J - s[MI?r2] [T) [MLlrl]
Momentum (p) kg - m - 5-1
= [M][L][rl] ",(MLT-I]
25. Resultant force is zero, as three forces acting on the particle can be represented in magnitude . and direction by. three sides of a triangle in same order. Hence, by Newton's 2nd law
( ._} l
! 1 = 171 dd v ,particle velocity ("1) will be
I, t )
same.
26 [F' G·. I Charge enclosed
.. rom ,auss aw, --"----
. '1l
= Flux leaving the surface]
_g_ = <h - ~1
£0
q "" ($2 - ~) tio
27, Let R he the normal contact force by wall on the block.
R =ION 10N
Ii. = IV and f 70 ~R
~tR ~'w
= w = O.~ x 10 = 2 N
28. LeI coefficient of friction
be p, then retardation will be ~lg.
From equation of motion, v = u~· at
='> 0 ~ 6 - ~lg x 10
6
=- f1 = 100 = 0.06
29. Here B is implying A bur A is not implying B, as kinetic energy of a sysrem of particles is zero means speed of each and every particle is zero which sa ys tha t rnorne nturn of every particle is zero.
But statement A means linear momentum of a system of particles is zero, which may be true even if particles have equal and opposite momentums and hence, having non-zero 1m.
30. Mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends on distance between two coils and geometry of two coils.
31. Let acceleration of system (rope + block) is Q along the direction of applied force. Then
p
a= M + m
w
--:.a
M
Draw the FBD of block and rope as shown in figure.
_8
_8
m
T --fJlJJj!h!i(:i;'l::~:!Jf'Jf.,/jI(~'.'iii{!f'.:'iii'.1· • p
Where, T is the required parameter
For block T = Ma
MP T=--M+m
32. The arrangement is shown in figure.
Light s pri n 9 balance
M
Now, draw the free body diagram of the spring balances and block.
~1
BlOCky
Mg
Tl
For equilibrium of block, T] '" Mg where, 1'1 = Reading of 52
For equilibrium of 82, T2 "" 11 where, T 2 = Reading of 51
For equilibrium of St, T2 = T3
Hence. TI = T2 '" Mg
So, both scales read M kg.
33. Elastic energy stored in the wire is
U 1 . 1
= 2 stress x strain x vo urnc
1 F t.l
='2'1fxT"xAL
1
='2F Al
'" ~ x 200 x 1 X 10.-3"" 0.1 J
34. The escape velocity is independent of anglc of projection, hence, it will remain same i. e., 11'
km/s, .
35.
... (ii)
•.. (i)
Dividing Eq. 0) by CU), we have
.. ~~JM~ m
9 M 25 M+ m
=> 9M + 9m "" 25M
=> 16M =9m
m 16 -M=9
36. Heat cannot flow itself from a lower temperature to a body of higher temperature. This corresponds to' second law of thermodynamics.
37.
(given)
Hence,
38; T '" 21!-f[
Given,
AT 1 Al T='2T
jl"'21%
AT 1
T = '2 x21% '" 10.5%
39. The given equation of wave
y = 10-4 sin (600t - 2x ... -j) .. ,.(1)
Standard equation of wave
y",aSin (rot =kx + $) .. \(ii)
Now comparing Eqs, el) and (ii), we get,
(t) '" 600 and k ~ 2
. _ ro 600
velocity of wave", k '" 2 = 300 m/ s
40.e=_Ldi=_L (-2-2)
dt 0.05
(4)
8 =L 0.05
L '" 8 x ~.05 == 0.1 H
41. In an LC circuit the energy oscillates between inductor (i~ the magnetic field) and capacitor (in the electric field).
U t: max [Maximum energy stored in capacitor] Q2
2C
U B max [Maximum energy stored in ind uctor] Le
=__:Q_
2
where, To is the current at this time. For the given instant U!! '" U B
q2 LiZ 2C=Z
i .. f.,
From energy conservation
VE + VB = V E max'" U B max
=>
q2 Q2
2 2C' ~2C
q= Jz
42. The core of transformer is laminated to reduce energy loss due to eddy currents.
--)0 4- ---'t
43. .. t=orl<F
---'t ---'t ---'t ---'t---'t
t is perpendicular to both rand F, so r· t as
---'t---'t
well as F - t has to be zero.
44. Given: No Ie = 5000, N Ie = 1250 N = No e~x{ = No e-s).
Where '}~ is decay constant per min N l=No Ice--s}.
1250·= Nn A e-·s).
NoA = 5000 = 4 No le-Si• 1250
(5)" =0 4
5" = z log, 2 k= OAin 2
45. Since, 8 «-pardcles 40- -parucles and 213'particles are emitted, so new atomic number
Z'=Z~8x2+4)<1-2xl = 92-16 + 4 - 2
'" 92-14
=78
, 1 2
46. hf '" hfo + 2: mv
2 2hfl 2hfo
Hence, vI = -m - -TTl
2 2 2h
VI - V2 = - [fl - f2) m
47. Protons cannot be emitted by radioactive substances during their decay.
48. Resistance in the arms AC and BC are in series, A
3V
3(2 R'=3+3",6n Now R' and 3 n are in parallel,
R ",6x3=2"
.' 'q 6 + 3 H
Now, V=IR
3
I", 2'" 1.5 A
49. Aluminium is a metal, so when we insert an aluminium foil, equal and opposite charges appear on its two surfaces. Since, it is of negligible thickness, it will not. effect the capacitance.
Alternative : From the formula
C '" t::oA
d-t+.E__ K
=:> Here, K '" C1J and t ---)0 a
eoA EoA
So, C 0; ~-:O = --or ""Co
50. x = 4 (cos nt + sin ztr )
= ~ x../2 [cos ltt + sin TIt]
,..'2 .
x '" ill sin [ TIt + % ]
So , amplitude = 4.fi
51. At P due to shell, potential q
Vi ~-~- 4TI Co R
at P due to Q, potential
"
--d-
Q
V2 =---If
411 Co2
2Q 41l£oR
:. Net potential at P V"'\'J+V2
P UR/2 R Q
=_q-+~
4TIEoR 4TIEoR
2
52. W '" ~ CV2 '" ~ 2
1 (8 x 1O-18i
=- x ---
2 100 X 10-6
'" _!_ x 64 X 10-36 = 32 X 10-32 J 2 100 x 10-6
53. x = at 3, Y =~t 3
dx 2
V ",-=3a.t
-x: dt
v, = i '" 313t2 Resultant velocity
_---
/ 2 2
v=cv, + Vy
=~9a2t4 + 9132t4 =3t2~a2+~2
54. Given: P «T 3 ... (i)
In an adiabatic process
T Y pI -, y '" constant 1
T oc----
p(l-y)/y
T (yly-I) ocp
q
... (ii)
Comparing Eqs. (i) and (ii), We get
., _Y-=3
)'-1
31' - 3=y 2y= 3 c, 3 ~=Y=2:
55. Work does not characterise the thermodynamic state of matter, it is a path function giving only relationship between two quantities,
56. TJ '= 627 + 273 = 900 K
Q1 = 3x 106 cal
T2 = 27 + 273 = 300 K QJ Q2
., T; == '[2
57.
T2 300. 6
Q2 '" lj x QJ = 900 x 3 x 10
'" '1 x 106 cal Work done =Q1 - Ql
= 3 x 10 - Ix 106"" 2 X 106 cal :. 2 x 4.2 x 10C, J= S.4x 106 J
1 2 1 3 '22
WJ = 2 k x Xl :;:2 x 5 x 10 x (5 x 10-)
= 6.25 J
1 2
.W. ~, 2. k (XI + x::J
= ~ x 5 x 103 (5 x 10-2 + 5 x 10-2)2 <= 25 J
Net work done = Wz - WJ
'" 25- 6.25= 18.75 J
'" l8.75N-m
5&. The wire will vibrate with the same frequency as that of source. This can be considered as an example of forced vibration.
T = 10x9.8N'='98N, m = 9.8 x 10-3 kg/m
. 1 ~('r)'-
Frequency of wire f '" .;-_ --
2t m
1 19S-)
=0 2 x 1 'II 9.8 x 10-J
"" 50 Hz.
59. I,= 256 Hz
For tuning fork f" - Ii = ± 5, f2 <= frequency of piano
12 <= (256 + 5) Hz, or (256 - 5) Hz
When tension is increased, the beat frequency decreases to 2 beats/so
If we assume tha I the frequency of piano string is 261Hz, then on increasing tension, frequency, more than 261Hz. But it is given that beat frequency decreases to 2, therefore 26] is not possible.
Hence, 251 Hz i.e., 256-5 was the frequency of piano string before increasing rension.
60. At X= 0, kinetic energy is maximum and
, potential energy is minimum.
61. ~ kT == 7.7 x 10-14 J
T _ 2x 77x 1O,·H - 3 x 1.38 x 10-23 0: 3.7x 109 K
62. A;; ssCSI3:\ has larger size among the four atoms given, thus, electrons present in the outermost orbit will be away from the nucleus and the electrostatic force experienced by electrons due
to nucleus will be mnurnum, Therefore, the energy required to liberate electrons from outer orbit will be minimum in case of ssCS1J3.
64. Due to the reverse biasing the width of depletion region increases and current flowing through the diode is almost zero. And in this case electric field is almost zero at the middle of the depletion region.
213.6
65. E ~ - Z -;:;2 eV
For first excited state
E., = - 32 x 13.6
f. 4-
<=- 30.6 eV
Ionisation energy for first excited state of Li21 is 30.6 eV.
66. P <= constant
[lv",P
=>
t·: P = force x velocity] [": F '" Mal
Ma x v = P P VQ"'Jj
V x [::_~.] =!...
ds M
Iv., I ,I' P
v" dv = - ds
o uM
[Assuming at t = 0 it starts from rest, i.e., from s '" OJ
=>
, =>
=>
=> S <LC1n
67. Here, thrust force is responsible to accelerate
the rocket, so initial thrust of the blast = rna
'" 3.5 X 1.04 xlO = 3.5 x lOs J\i"
.68. Sustained interference is possible with coherent sources only.
69. Force on - ql
---j. 1 qq' 1 qq , , F == -- ___l__1_ i + -- ___l,-l [sin Oi - cos OJl
4:rrf{) b2 4Il£o a2 .
From above, x I component - q 1 F 12
of force is ~.
F == ___!h_ l q2+ q3 sin 0] . e
x 47t8o b2 a2 :
l l: F
F· q2 % in OJ: 13
.. ix: - + - sm' .
Xb2 02
v2 2
70. R =_ '" (220) P 1000
where, V and P are denoting rated voltage and power respectively
P = Va2pPlied = 110 x 110 x 1000
. . consumed R 220 x 220
=2S0W
71. Objective of compound microscope is a convex lens. Convex lens forms real and enlarged image when an object is placed between its focus and lens.
7
76. Hydrogen spectrum coloured radiation means visible radiation corresponds to Balmer series (nl == 2, 112 '" 3,4 ..... )
380 nm 780 nm visible
V!BGYOR I
CH --)- 2nd orbit
-----?
-------:)-
3rd line from the red end it means 5 -+ 2
77. ;., == _!!_ == 1.105 X 10-33 m mv
78. For s-electron, I == O.
3600 n=O--l
3= 3600 -1 I)
0= 90°
74. According to Newton's law of cooling
dQ ocA8
dt
But dQ a; (A Or (given) dt
73.
.. n = 1
75. Given: I' = 1+ 100% 1 = 21
Initial volume = final volume nr21 = 1tr,2 I'
,2 r21 2 I
r =r=' X2i
i.e.
r2 r,2=_
2
r 2/
R'==PA,==P-----;2 1(r
p·41
1t~
=4R
Thus,.. !ill = R' - R = 4R - R
=3R 3R
. % AR =.- x 100% = 300%
.. R,
79. Mass of one unit-cell (m) == volume x density == oj xd
3 Mz Mz
"'a x--· -=-.
No a3 No
58.5 x 4
m= g
6.02 x 1023
.. Number of unit cells in 1 g == _!_
m
6.02)( 1023 ._ 2.57 X 1021 58.5>( 4
80. Glass is a supercooled liquid, which forms a non-crystalline solid. The common lime-soda glass used for bottles and jars is a supercooled mixture of sodium and calcium silicates.
8·1. NH3·an inorganic solvent.
AgI is having much higher covalent characteristics iri comparison to AgCI.
82. AU physical and chemical properties of elements ate periodic function of atomic number- Modem periodic law.
83. C-atorns form covalently bonded plates (layers). Layers are bonded weakly together, that's Why one layer can slfde over other cause lubricacy. Cannot be melted easily as large number of atoms being bonded strongly in [he layer form big entity.
o
II
84. CH3 -C -CH- CH3
I 2 13 4
CH3 3-mcrhyl. butan-z-one
or 3"methyI2·bul'i\n(}[\e
o II
keto (-~C --:- ) functional group is given priority,
85. LiA!K4 reduces -CDDH to ~CHPH without affecting C = C bond.
86. In between two successive collision, no force is acting on the gas molecules, Resultantly it travels with uniform velocity during this interval, and hence, it moves along a straight line.
87. Cu, Ag, Au group of elements arc called coinage metals as these are used in minting coins.
88. C"HZ,,02 is general formula for open chain add and ester
Il == 3 C~H602
Acid
-0
II
CHsCHz -C-O-H
o 1\
Bster eHa -C-O-CH3
89. Alcohol has polar Ii which makes inter-molecular H-bonding possible. Bther is non polar hence no Hsbending. Lack of H -bonding in ether makes it more volatile than alcohol. .
90. Chiral compounds which have one chira! centre, All four atoms or groups attached to carbon are different
91. Alkaline earth metal salts are causing hardness:
Temporary hardness caused by soluble Ca and Mg hydrogen carbonates .. calcium and magnesium soluble sulphates and chlorides cause permanent hardness.
92. Molec~le Hybri.di~ Repulsion sation
S02 sp2 Ip - bp. bp - bp
Bond angle
119"
104.5°
OH2 sp' Ip - Ip, bp -Ip
bp-bp
SA:! Sp3 -do-
NH sp3 Ip - nfl, bp - bp
~ 90"
lOr
98. N02 and 03 both are having irregular geometry.
94. N3~ 7 + 3= 10 electrons
F~ 9 + 1 '" 10 electrons Na"" 11 -1 '" 10 electrons
Resonating (canonical) structu res of formate ion
96. In CO 2' C·atom is.sp-hybridised thus it has linear structure.
ln XeFz, Xe is sp3d hybridised with three lone-pairs of electrons on equatorial. position. This minimises repulsion hence it has also linear
structure.
Cr: [Ar] I tit J tit I tI f I
3d5 4S'
c-. [Ar) I tl t I tit It I
3d5 4sQ
_97.
(by first IP)
This is stable EC hence romlatiol' of Cr'" by second IP requites maximum enthalpy.
98.
6HQ", - \Ie
Takes place with decrease in number of mole or pressure hence lncrcase in pressure shifls eqnillbrium in COIWrlrd side.
Tokes place with evolution of bent or increase in remperaru rc lienee decrease in IC m peram re sh i fts I his equilibriumin forward
, side.
99. 2BC13+ 3H2 ----+ 2B + 6HCI
2 I 3 I 2m,,1 .
mo mo 21._6 g ~ 2 mol
21.6 g B '" 2 mol B'" 3 mol H2 PV = nRT
. V'" nRT =3x 0..0.821 x 273 672 L
.. P 1 -.
[NO 12 (1.2 x 1O-2P
100. K '" _~2 _
- c [NP 41 4.8 x 10-2
'" 3 X 10.-3 mol L-1 ior. AB2 ~ A2+ + 2 B-
- S 25
Ksp '" [A2" J [B-J2
== (5) C2SP '" 453 =4(lx1C-5i
'" 4 x1C"15
102. Ag+ + e- ~ Ag
965CC == C.IF'" 0..1 equivalent Ag = 0..1 mol Ag
'" 10.8 gAg
- EO 0.0.591 I Q
103. Eeen == <ell - --. ~ og rt ,
Cu 2+ + Zn -------7 Zn 2+ + Cu
~lM 1M
Q = [Z02+] =-~= 10. [Cu 2+] 0..1
E '" 1.10.- 0..0.591 log 10.
cell Z
= 1.10.- 0..0.295 = 1.0.705 V
104. t:-.T f '" molality x K J xi =o..2x1.85)(13
HX - -- H+ +X-1 Ct == 0..3
'" 0..4810 i = 1 + Ct '" 1.3
:.fp "'-0.48IQ~
105. Rate becomes xY times lfconcentration is made x times of a reactant giving /h order reaction.
Rate = k [At [Blm
Concentration of A is doubled hence x '" 2, y = n and rate becomes == Zn times
Concentration of B is halved, hence x '" 1/2 and
(l)m
y == m and rate becomes = 2. times
(l)m _
Net rate becomes = (2)n 2, times
'" {2t- m times
106. Let molarity ofBa(OH)2 '" M 1
. . Normality = 2 M I
Molarity ofHCI = 0.1 M = 0.1 N
NJ\.'t'=N2V2 2M 1 x 25 == 0.1 x 35 MJ =O.07M
107. t:.G'" "" - Wm~". Maximum work done by the system.
108.CHz=CH2 + H2 -------7 CH3 -CH3 AH "" (BE),.;ttanl' - (BE)",oduns
== 4 (BE)c_H + (BE)c=c + (BE)H_H ~[6(BE)c_H + {BE)c_d
=-I25kJ
109. Enthalpy change is state function and depends only on initial and final condition do not depend on path or interrnediares.
110. High pressure inside the cooker increases boiling point, thus heat consistently given is used up by food material instead in boiling and constant boiling evaporation.
Ill. Ideal solution b. H = 0 t:-.v= 0. [;A-A == FH -s= FA_B
112. (~n = k [NO]2 (02)
"'k(~~Or(n~z) (:) '" ~ (rtNoiCn02)
(:) ~ k ("(~;no,)
:8(~;)
113.
EO _ 2.303RT I . K
((!!1 - nF og eq
D. 295 = 0.0591 I K
. 2 og eq
logKeq = 10
K "" 1010
oq
114. An irreversible process => spontaneous process
= (dS)\IE (change in entropy) == + ve > 0 - = (dG)y. p (change in Gibbs free-energy)
-ve=><O
115. As temperature increases desorption increases.
Adsorbent + Adsorbate ~ Adsorbed state + 6E Adsorption is exothermic process (forward direction), desorption is endothermic process (Backward direction)
According to Le-Chatelier's principleincrease in temperature favours endothermic process,
116. k '" A e-E~/IIT
k ea Rate constant
A '" Pre-exponential, frequency factor EQ '" Activation energy
R = Gas constant
T = Temperature
117. More ~ vc value of EQ means larger reducing power.
H8. Proton affinity it means affinity for proton l.e., basiciry
NHrNitrogen has pair of electron to donate as well as higher tendency to donate due to lower electronegativiry. P is not suitable as that has larger size.
119. ZnO can react with acid and base both.
ZnO + 2HCl -----)0 ZnC12 + HP ZnO + 2NaOH ...._.. NazZnO 2 + HP 120. HgI2 + 2K 1 -------+ K2Hgl4
II . soluble
Hglz -------+ Hg + 12
121. ~HCl + -102 ~ Hp + Cl2
122. In Holmes signals of the ship mixture of CaC2 andCaJPz is used.
123. Fe26• [Ar] 3d6 4s2
Fe2t (24elccmms) ~[Ar] 3d6 4so
124. 2CrO~- + 2H+ ...._.. Cr20i- + Hp 125 .. K4[Ni(CN)4] --+ 4K+ + (Ni{CN)414- X + ( 4 x ~ 1) '" ~ 4 x~4=~4 x=o
126. The pair of electron present with nitrogen will not be available to be donated as W will consume that one.
127. CO(NH3)sci] Cl2 __,_ [Co(NH3 )5CI]2+ + 2CC
Ihree ions
2CI- + 2Ag+ ~ 2AgCI
free
2 mol 2 mol 2 mol
128. Due to lanthanide contraction there occurs net decrease in size. Only one 0.85 'A is smaller one.
-p -p ··U
129. ~~4Th ~ ~ ~tjx ---} ~~oy
130.C =Co Gr
Total lime 18 6
y =--,--_. =- '"
TIn 3
Co'" 256g
C ~ 256 (l)6 '" 256 4
(uudcccycdl ~ . - 2 64 =;. U
131. Factual
1 . 1 S""in·'
132. CaSO 4' 2: H.p + 12: H20 ~
Hardening
CaSO 4 . 2H20 CaSO 1 . 2H20
Gypsum Gypsum
(orthorhombtc) (monoclinic)
133.1 i< 10-8 M Hel solution Hp i5al50 present there which also undergoes self ionisation HP'~H+ +OH-
10,,7 M at 25"C
If it is taken simply even without co, I ion effect, higher concentration must be conx.-Iered which is 10-7 M but H<' from HC] decreases self ionization which further decrease self ionization, hence, [H'] from Hp.
Hence, net concentration must be smaller than lO-"1M
Hence, acidic
134. NH3, CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH
K, ..
(CH3 hNH + Hp .,..- eel'I:l)2 NI f2 + OH-
r effect maximum stabilization more Hsbond stability high, hence, most basic
K2 4
CHJNH2 + HP ...---" CH3NH3 + 01-1- K3·
NH~ + Hp ..----" NH; + OH-
KJ >K~ > K~
Hence, basicity order is
(CH3)2NH >CH3NH2 > NH3 PdlH2 135.CH2=CH-CHzCH3 ~
Butelle-l ii, pres:sllr~~
CH3 -C!i2 -CHz -CHJ
hUU~!lC
other reagents arc successful with polar double bonds.
·136. Solubilities of carbonates decreases down the group because latticeenergy decrease is almost constant while decrease in hydration energy happens sharply .. Finally difference of hydration energy and lattice energy decreases thus solubility decreases.
137, Prorona tion of -OB is t1rSL step. Conversion of poor leaving group (-01-1) into good leaving
+
group (-OI-I 2)'
138. Meta 1 oxides lying below I Ig in electrochemical series decompose to form metal.
ZnO, MgO, CuO ~) no effect
AgP~Ag+02
'"
AgNO 3 -)0 Ag20 ------t Ag + 0 ~
139. During thunderstorm, there is formation of NO which changes to NOz and ultimately to HN03 (add-rain).
O2
N2 + 02~ NO --> N02
1'{20
~ N20 S -----'---7- HNO 3 (pH < 7)
140. Partial hydrolysis of cellulose gives the disaccharide cellobiose (CI2H22011). Cellobiose resembles maltose (which on acid catalysed hydrolysis yields two molar equivalents of D-Glucose) in every respect except one : the configuration of its glycosidic linkage.
142. Calcined gypsum does not contain CaC03 (that's sulphate one).
143. Hydrogen bonding is involved molecular force in the DNA molecule.
Crick observed the
type of hydrogen bonding
purine-purine and
Watson and
purine-pyrimidine
(instead of
pyridine-pyridine)
144. ~::~ --> ~ ~-I
C-J © (i) NaOH,A
bond (iil HNOJ ,._ v II pr (A I)
O 7Jeowp .. s
reactive (iii) AgNO,
(benzylic)
(i) NaOII,!J.
(ii) i-1N03 --'---::....___". no ppt. (iii) AgN03
H"
145. C2HSNC + Hp ---)0 HCOOf:i + C2HsNHz FOfU\IC acid
C2HSNH2 + H+ ---)0 CzHsNHj
Salt
146. t.-. E = 0, in a cyclic process.
{!.I-=-!. when n is odd 1. fen) =; 2'
11 h .
- 2: ,wen 11 IS even
and f : N -;. I, where N is the set of natural. numbers and [ is the set of integers.
Let x, /e N and both are even.
Then f(x) = I(Y)
147.
NC + CHCI, + ale KOH ~~ CH3
p-toluidlne (a carbylamine reacrion.]
148. Nylon threads are made up of polyamide some
common are
°
II
Nylon 6 H2N -fCHzTsC-OH Monomer
o 0
II \I
-HN-fCH21sC-NH-fCHi1sC-NH-
o
II
Nylon 66 HO-C-fCH21.4COOH
and H2N -f CH2r m~ Co-polymer
o 0
II II
-HN-C-+CH274G-NH-fCH27G
o °
II II·
NH-C-fCHz"14G-
149. In neopenrane, all H are equivalents.
CH3 CH3
I hv I
H.,C -C-CH3 ~ H3C -C-CH.,Cl
J j . Clz' I L
CH3 CH;>
IS!!. Liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen are good fuel.
Again x, Y EN and both are odd.
Then
f(x) = f(y)
x-I y-l -2-"'-2 ~ x'=y
i. e., mapping is one-one.
Since each negative integer is an image of even natural number and positive integer is an image of odd natural number. So mapping is onto. Hence, mapping is one-one onto.
2. Key Idea : if ZI' Z 2 and Z3 are the VlJrtices of all equilaterai rrianglt. Then
:1. :1. :1.
ZI + 22 + z} '" ZlzZ ... z2z:l + z3z1 .
._. Origin, ~ and z2 are the vertices of an equilateral triangle, then
:1. :1.
21 + z2 '" ZjZZ
o=!> (zi + z2i =: 3z1zZ ••• (i)
Again 21' 22 are the roots of the equation z2+uz+b=O,
then ZI + 22 =' - a and ZlZ2 == b
Putting these values in Eq. (i), we have (- a)2=: 3b = a2 == 3b
3. Let Z = Ii ciO and (j) = 'i ei'~
~ Given
~ 'Pi = 1 ... (i)
11"
and arg (z) -- arg (0) = 2"
:=> (1- ~ = ~ ... (ii)
then Zft) "" IjC-iO. '2ei9 == 'lIz e ;(O-~)
From Eq. (i) and Eq. (ii), we get
Zti) = 1 Co.;"'2
1t . . 71
.. cos "2 - I Sin '2
Z~) '" - i
Note: We know that r (cos 0 + i sinO) '" r e'o
4.(1+i)X =[(l+i)(l+~)JX
1-1 (1-1)(1.+1)
=[(1 + i2~:] x ",[~~3.i.]X
1 - 1.2 2
==> o-~;r '" Cif ,,; 1 (given)
~ (if = (it",
where n is any positive integer,
;;;;:,. x =411
1, + abc = 0 :=> abc = - 1
Alternative Solution:
The vectors (1, Q, (?). (1, b, b<), (1, c. (2) me non
coplanar.
.. Their scalar triple product if. 0
I 1 a a2
i.e., I'} b b2 #-0
1. C c2
... (i)
1l is given that
1 + (1"1 i
1 + ~J~ \= 0 I .~ e~\
,
a a2 1 In (l2 a:1
b b2 I I/- b3
=> } +\b =0
c cL 1 C L c:l
c
la (12 i 1+ abel ~ a c? I
==> b b2 b 1/ =0
·c ,2 C ,2.
11 P 1
il a Q21 11 a aZ I
:=> ! ] b bZ!./_ abc 1 b b~ ~O
'1 c c~ i 11 c c21
- (1 + abc)i i a 2
(l .
o=!> b b2 ",0
1 c c:O
, ==> abc * -1. (using (i))
6. Key Idea: The s),stem of linear equations QIX + /)1)' -l- ctz::: 0
QZX + b?y '1' Czz = 0
and a3x + hi)' + C:)z '" 0
The system of linear equations has a non-zero solution, then
I} 2.a 01
]1.3b b=O 1 4c c]
J\pplyingRz -7 R2 -·R), H:{ -7 H:l-· /{l
\ I 2.a a I
o 3b-2a b-(.II=O
o 4e-2.a c-n,
0:::. (3b - 2u) (c - cr) - (4c - 2.a) (b - c) =0 0
==> 3be - :ib" -. 2a.c + 2a~ '" 4bc - 2ab - 4ac .~ 2a2
=> 4ac - 2ac = 4bc·· 2£1.b - 3h, + 3ab
=> 2ac = be + ab
On dividing by abc, weget
2 I J -il =0. + C
i. e., Cl, 11, c are in HP.
7. Key Idea: If 0:, l> be the roots of the equation axZ + bx + c + 0, then
b c
a + l> = ~ - and a~ = -.
a a
Given equation is
ax2 + bx + c == 0
Let a, !3 are the roots of this equation.
Then a + 13 == - £ and ap = .£
a a
1 1 0:2 + n2
Also a + t3 =; - + - = -."....;p:__
IX 2. 132 IX 2152
a + 13 = (0: + l3i- 2aP Calli
~ a+~=(o:;:r-;t3
~ (_ E_) = (-.bl a)2 _ 2._
a cia cia
~ _!!_ = (£)2 _ 2a
a c c
~ 2n = (£)2 +!!_
C C a
2n =!!. [£ +.£]
c c c a
2n b c 1)=c+(i
cab .
~- - -are mAP. a' b' c
abc . H
=> -'-'-barem P. c a
8. x2 - 31 x I + 2 == 0
If x » 0, then r x I = x therefore x2 - 3x + 2 = 0 ;:::) xl - 2x - x + 2 = 0 => x (x - 2) -1 (x - 2) = °
~ ex -1)(x - 2) = °
=> x =1,2
If x < 0, then I x I = - x therefore x2 + 3x + 2 == 0
;:::) x2 + 2x + x + 2 = 0 => x (x + 2)':" 1 ex + 2) = 0
;:::) (x + 1) (x + 2) = 0
;:::) x=-I,-2
Hence, four solutions are possible.
9. Key Idea : If 0. and 20: are the roots oj the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, then 2b2 == 9ac
Since one root of the quadratic equation Ca2-5a+3)x2+(3a-l)x+2=0 is twice as
large as the other, then
=:>
2(3a -Ii' = 2x9 (a2 - 5a+ 3)
=:> 9a2 - 6a + I == 9a2 - 45a + 27
=> 45a - 6a =; 27 - 1
26 2
;:::) a= 39 ="3
Alternate Solution
The given equation is
(a2 - 5a+ 3) Xl + (3a -1) x + 2= 0
Let a and 2a. are the roots of this equation, then a + 2a = _ (3a - 1)
(a2-5a+3)
3a '" _ (3a-I)
. Ca2 - Sa + 3)
2 0:'20.= 2--(a- 5£1+ 3)
2a 2 = ----;;__:2=---...._ (a2 - Sa + 3)
=> [ - (30 - 1)]2 2
2 3(~ _ 50+ 3). (a2 - Sa + 3)
(3a _1)2 1
9 (a2 - Sa. + 3l = (a2 - Sa + 3) (30 -Ii = 9 (a2 - 50.+ 3) 9a2 + 1 - 6a = 9a2 - 4Sa + 27 4Sa - 6a = 27 - 1
39a= 26
2
a="3
10. A = [b ~ J. A 2 = [~ ~ ]
and
=>
A2=A.A=[b ~J[b ~]
=> A2=[a2+b2 ab+ba] ba+ab b2+a2
_ [a2 + b2 2nb]
- 2ab a2+b2
=> [p ~J ==[ a~::2 a22:~2]
=> 0. = a2 + b2, 1'1 '" 2ab
11. The number of choices available to him = sc" x.8C6 + sc" X 6CS
51 . B! 51 8!
= 4!1! x 6!2!+ 5!0! x 5!3!
5 8"x7 . 8x'7x6
'" x -- + 1 x --::_;_.,....:.
2 3><2 .
=5><4x7+8x7
= 140 + 56 = 196
12. The number of ways to. sit men = 5!
and the number of ways to sit women = 6C 5 X 5!
Total number of ways '" 5! x 6CS x 5!
= 5! x 6 x 5! = 6! x 51
1 ron roln
13.8= ro" ro2/1 I
ro2n I roll = 1 (o?" -1) _ (J)"{ro211- roll!) + (J)211(roR _ 0(411) "" I (1 -1) - 0+ ro2n (e" .... o") '" a
14. Ker Idea: nCr + 1 + "Cr :: n+lC,+ I-
nc,+! + "C'_1 + 2"Cr
= ncr + 1 + "Cr + "Cr-1 + "Cr = 1l+1C,+1 + l1+lCr
= "ot-lee+}
15. (I' + l)th term of (..[3 + iifS)256
i.e., T, + 1 -= 256Cr (3pS6 - r)!2 (5t/~
Th . I if 256 - r d r \.. th e terms are integra ,,1 '-2-- an "8 are no ,
positive integer.
r = 0,8,16, 24,32, ... , 256 Hence total terms are 33.
16 .. : (r+ l)th term in the expansion of (1 + Xf7 (S
¥ (¥ - 1) '" (¥- r + ] ) x'
r!
Now this term will be negative, if the last factor in Nr, is the only one negative factor.
=:). 27 -r+ 1 <o=:) 32 <1'
5 5
=:) 6.4 < r :::> least value of r is 7.
Thus first negative term will be 8th. Alternate Solution
(1 + xP/5 = 1 + 27 x + 27 (27 -1) xl
5 5 5 2\ .
+ 27 (27 _ 1) (27 _ 2) x3
5 5 5 3!
+ 27 (27 -1) (27 _ 2) (27 _ 3) X4
S 5 5 5 4\
+ 2~ (2~ _1)(2; _ 2)(2~ _ 3)(2; _ 4) ~:
+ 2; e; _1)(2; _2)(2; -3)(~; -4)e; -5) ~~ + 2; (2; _} )(2; _ 2)e; _ 3)(2; _ 4) (2; _ 5)
x (2; _ 6) ;7! + ...
Here 2; _ 6 is negative i. e" 8th term is negative in the expansion of (1 + Xl7/S•
1 1 1 '
17.}.2 - 2-3 + 3.'4- ...
= (1 -.!) - (1. - .!.) + (.! - !) -
22334:'"
1 1 1
=1-2'2+ 2'3-2.'4+'"
=2[1-~+~-~+ ... ] -1
'" 210g (1 + 1)-1 '" 2 log 2 - log e "" log 4 - log e.
4 =Ioge
18. Let lex) == Ax2 + Bx + C
.. f(l) = A + B + C
and fC-l)=A-B+C
1(1)= f(-I)
= A+B+C=A-B+C
:::> 2B = 0
B=O l(x)=Ax2 +C
Now f' (x) = 2Ax
:. /,(a) = 2Aa, J'(b) = 2Ab, /'(e) = 2Ac Also a, b, C are in AP.
., 2Aa, 2Ab, 2Ac are in AP.
=:> f '(a), 1 '(b), f '(c) are inAP.
19. If xl> X2, Xl and Yv Y2' Y3 are in GP,
then let Xl = rx1> X3 = r2xI
and Y2 = ryl' Y3 = r2Yl
with common ratio r. then the points are
2 2
(Xl' Yl)' (1'Xj, 1)'1) and (r Xl' r Yl)'
I X Y 11 Xl y, 1
Now x~ .y~ 11 = rXJ 1)'1 1
x3 Y3 1 r2Xl rZYl 1
= X1Yl I ~ ; ill
r2 r2
'" X1YI (0) = 0
(Since two column: are identical) Thus these points lie on a straight line. Alternate Solution
Let XI = a=:> X2 == 111' and X3 = a,-2 and Y '" b =:> h =, br and Y 3 = b,-'2
Let the points are A(a, b), B(ar, br) and C(ar2, b?).
New slope of AB '" beer - 11)) '" !!. ar- a
ber2 - r) b
and slope of BC '= - 2 a
aCr - r)
slope of AB '" slope of BC => MJI BC
But B is a common point.
.. A, B and C are collinear.
i.e., the points (XI' Yl ),. (X2, Y2) and (x3' Y3) lie on a straight line ..
20. AB '" a
and In~AON,
ON .LAB AN=BN
·n AN tan - Oon ON
ON '" AN cot 2! == ~ cot 2:
11 2 11
and sin ~::: AN
11 OA
OA == AN cosec 2: == ~ cosec .::
11 2 11
Sum of the radii = ON + OA
a 'It a "It
== "2 cot 11 + "2 cosec n
=!![cos ~ + ~1 ]
2 . It .. '1{
Sin n Sin n.
'" ~[.l +.c: %] = ~[.~+2~in: 1]
Sin n sin ""2it cos 211
a "It
=2 cot 211
2C 2A 3b
.21. a cos 2: + c COS 2" = "2
=> a [~ (.~b C)] + C [ s (Sb~ a)] =3i
S [s - c + s - a] 3b
·b 2
2 s [2 S .. C - a] == 3b2 2 5 [a + b + C - C - a] '" 3b2 . (a + b +e) b '" 3h2
=>
=>
. a+b+c=3b 2b;"a+ c
i.e., a,b, c are in AP.
. C JS(S-C) A ~s(s-a)
Note: C05 2 = ... '---ab and cos "2" ~.
22. Given AD == 4 and BD= DC A
B ·D
In 6 ABG tan .:: = AG
, ·3 BG
BG '" AG cot ~
c
818 BG=-x-=---
3 J3 3.J3
B
1
"'2 xBG xAD
1 8 16
=-x--·x4=-· --
2 3.../3 3../3
Since, median divide a triangle into two triangles of equal area. Therefore
Area of t. ABC == 2 x area of 6 AVB
=2x~=~
3./3 3..[3
Area of !) ADB
23. Key Idea: The range of sin-l x is [ -~, ~l
We have sin -I. x = 2 sin -1. a
=> -.:: < sin " x <.::
2 -. - 2
- 2! < 2sin-l as'::
2- 2
- ~. < sin -J a < .!:
4 -. - 4
. (It) . 'It
Sill -"4 .,; a s Sin "4
1 1
--::;a$-
.J2 12
lal.s;2- ..f2
24. Given 92 ::: tan-1 ~
"R
cth
9, H
O~_. __ 40m ~A
3
tan 9:. "'"5
AC
In 6 AOC, tan Elt '" OA
1
""'h h
.±__ =-- 40 160
Infl .AOn,
A8 h
tan (81 + 92) '" OA '" 40
taneJ +tan92. h 1 .: tan ~ tan 92 '" 40
h 3
160 +"5 h
1 __ h ,,~ '" 40 160 5
S[h + 96] It
800 - 311 40
.=;:> 200 [h + 96) '"' 800h - 3112
~ 200h + 19200 "" 800h - 3h2
=> 3h2 - 600h + 19200 = 0
::::;> 112 - 200h + 6400 == 0
=;;. (h-160)(h-40)",,0
=> 11 = 1600rh =40
.. Height of the vertical pole == 40 m,
1 25. f(x) = x + - x
f'(X)=l-~\
Put f' (x) = 0 for maxima and minima 1
1--=0
x2
x=±l
f"(x)=~-
x3
At x'" 1, f" (x) 0= + ve
., f(x)will be minimum at x = 1. Value of f(x) at x == 1 is 2.
But at x = -1 value of f(x) "" - 2
Thus, f(x) attains minimum value at x = - 1.
"
26. L f(I-)~f(I)+ f(2) + f(3) + ... +/(n)
r- 0- I
= fel) + 2/(1) + 3f(l) + ... + 71/(1) (since fex + y) = fex) + I( y)) '" (1 + 2+ 3+ ... ~- n)f{l)
== n (n + . .!2. 7 = 7n Cn + 1)
2 2
27. f(x) = x" =:_, 1(1) = 1 f'(x)=nx,,-J =>1'(1)=71
r·cx)= Tt (n -1) X"··2=> f"el)", n (n -1)
rex)= 71 (71 -1)(n - 2) 2·1
rel)= n en -1)(71 - 2) 2·1
We have
1'(1) f"(I) 1"'(1) f(l)-I! + ---z-!-~+ ...
(-Irf"(l)
+--71-"--
= 1 _ ..:!.. :: Cn - 1) _ n Cn - 1 len - 2) +
I! + 2! 3! .
(-1)" n (Ii - l)(n - 2) 2.1
+ n!
'" (1-1)" == 0
28. -_. fex) = ~ + 10g1Q (Xl - x) 4-x
For domain of fex)
::::;> x3 - X > 0
=> x (x -1)(x + 1) > 0
-y-:yy;
-1 0 1
Region is (- 1, 0) u (I, ()(J)
and 4 - x2 ~ 0
::::;> x~± 2
Region is (- 00, - 2) u (-2, 2) u (2, OC) •
:. Common region is (-1, 0) v (1, 2) u (2, (0).
[ 1 - tan 1-] [1 - sin x]
29. lim
x-.~ [1+tan1][1t-2X]3
x = ~ - h as x ~ ~ h ~ 0
.2 2'
1 - tan (% -~) (1 _ cos h) lim
11 _,_ 0 (11: It)· (2 h):l
l+tan 4-"2
2 . 2 h , h Sin '2 = lim tan -2' 8h3
'._0
h [. h]2
'" lim !. tan 2 x Sin 2, x!
h->O 4 !! x 2 .~ 4
2 2
. 1 [tan~: [Sin ~12 1
'" I;l~ 32· -h- --11- 32
"2 "2
30. lim log (3 + x) - log (3 - x) =; k
x_,_o x
Let
Applying L' Hospital's rule
[3~X+3:XJ
1 = k
lim
x_,_o
Note: L' Hospital's rule can be applied only, if a fu nction is of the form of (g) form.
31. lim fea) g(x) - fea) - g(a) f(x) + g(a) = 4
x"".o g(x)- f(x) ..
Applying L' Hospital rule
lim f(a)g'(x)-g{a)f'(x)=4
x ..... a g'(x)- f'ex)
lim
k g'Cx)- kf '(x) = 4 s' (x) - f '(x)
x ..... 0
~ k=4
32. fex) = log (x +~)
~ f( - x) '" log (- x + ~ x2 + 1)
~ f(x) + it- x)", log ex + ~X2 + 1)
+ log (- x + ~ x2 + 1)
'" log (1)'" 0 Hence f(x) is an odd function.
Note: A function is said to be an even function, if (x) '" fe-x), Otherwise it is called an odd function.
33. Key Idea: Ajim.ction is continuous in an interval [a, b1 if it is. continuous at x = a and x = band each point of interval (a, b).
Continuity at x = 0
( I. 1)
f(O-O)= lim (O-h)e- t=hf+(-hl
h ..... O
= lim (-h)e-(~-T.) == lim (-h)=O
h40 h~O
f(O+O)", lim(O+h)e-(~+T.)
h~O
~ fCO - 0) = fCO) '" f(O + 0)
Therefore f(x) is continuous for all x. Differentiability at x '" 0
-n+ ~)
Rf' (0) = lim he - 0
h ..... O h - 0
= lim Lh = 0
h ..... O e
-n-t.)
Lf '(0) = lim (- h) e - 0
h~O (-h)-O
lim eO = 1
h ..... ·O
Rf '(O)~Lf '(0)
f(x) is not differentiable at x '" o. 34.': fex) =2x3 - 9ax2 + 12a2x + 1 f '(x) '" 6x2 - 18ax + 12a2
Put f' (x) = 0
6[x2 - 3ax + 2a2] = Q
x2 - 3ax + 202 = 0 x2 - 2ax - ax + 2a2 = 6 x ex - 2a) - a ex - 2a) = 0 ex - a) (x - 2a) '" 0
~ x = a, x = 2a
Now f "(x) '" 12x -18a
at x » c
f "(x)= 12a-18a=- 6a
:. fex) will be maximum at x = a i.e., p s= a ,
at x= 2a
f "(x) = 24a -18a = 6a ., f(x)wilI be minimum at x'" 2a i.e., q= 2a.
Givenl =q
~ a2=2a~a=2
35. F(t) = r; fCt - y) g(y) dy
= I;el-Y ·ydy =et, I;e-Y ydy = l [(-ye-Y)~ - I;l (-e-Y) dy] = el [(- te-t - 0) - (e-Y)~]
= et ( _ te-r _ (e-t _ eO)] ..
= l [ - te" - e-t + 1]
= [1 - e-r (1 + t)] i =et-(1+t)
36. Key Idea:
ex f(x)dx= I: (a + b-x)f(a+ b-x)dx
Let' I '" r: x fex) dx ... (i)
~ 1= I:ca+ b - x)f(a+ b- x)dx
=> 1= I:ca+ b-x)f(x)dx
[Since given f(a + b - x) == f(x)]
=> I = (a + b) r>ex) dx - I: x f(x) dx
~ I == (a + b) I: f(x) dx - I [using Eq. (i)]
~ 2I=(~+b)I>(x)dx
~ I=(a;b) I:f(X)dx
r" sec~ dt (0 ) ,
37. lim o. ~O fonn
,,-.0 xsmx
Applying L' Hospital's rule
sec2 x2. 2x
= lim .
x .... o X cos x + Sin X
Again applying L'Hospital's rule
,. 2x. 2 sec2 x2 . tan x2 • 2x + 2sec2 x2
; 1m --------~-----------------
x 40 - x sin x + cos x + cos x .
0+ 2sec2 0 =1
0+2cosO
38. I '" J; x (1 - xtdx Letl-x~z => -dx=dz
1 = r(l- a) z"( - dz) == J; 0. - z) z"dz
I [n .. , n+ 2]:
= I (z"-z",·I)dz =:: _z z_
o n+1 0+2
o
1 1
=n+l-0+2 39. Key Idea: lim ! £ (.:.)4 = r x4dx .
n ... "" n r",1 n 0
1 + 24 + 34 + ... + n4
lim
c: , lim ! £ (.:.)4
rI-." n ,;1 n
. 3
I· 1 I' 1; (r)
- 1m - x 1m --... -
n--)ll)!l n !1~-orJ n ,.=1 n
= r1 X4 ax _ lim 1. x II x3 dx
Jo n->",n. 0
=[ x:I -o=~
d eStn x
40. dxF(x)=---x-, x>o
On integrating both sides, we get eSlnx
F(x) == J x- dx ... (i)
Also [4 ~ estn ,,' dx = [4 3x2 • e'in ,,3 dx
I X I x3
= F(k) - F(l) Let Xl = z => 3x2 dx =:. dz 64 sfn.
:::} J _e _ dz » F(k) - Fo.)
I z
Using Eq. (i)
[F(Z)]:4 = F(k) - F(l) .
:::;. F(64) - F(l) = F(k) - F(1)
:::} k = 64
41. Y =1 x-II =={_:-/i, ~:~
and y = 3 _I x I == {3 + x, x < 0 3- x, x> 0
Solving y := x-I and y = 3 - x
:::;. :::;. :::} and
x-1=3-x 2x=4 x=2 y=3-2
y=1
AB2 = (2 -If + (1 - 0)2 = 1 + 1 =2
:::} AB=.J2
and Be2 = (0 - 2/ + (3 _1)2 = 4 + 4 = 8
Be = 2./2
Area of rectangle ABCD = ,AB x Be
=./2x2J2.
= 4 sq unit
42. Given f '(x) == f(x) and f(O) = 1
Then let f (x) =:. C
Also f(x) + g(x);;; x2
g(x)=x2 -c
Again
J; I(x) g(x) dx == J; c (x2 - c) dx
== f~ (x2C - e2x) dx
== J; >c dx - J; e2"dx =[x2C - J2xCdx]~ - ~[iX]b
== [x2ex - 2 (xC - C)]~ - .! (e2 _ eO)
.. 2
[ 2_x ... ......x ..,,_x. 1 1 2
= X to -~" + 0.: lo - 2. (e -1)
== [(x~ - 2x + 2) C]~ _l e2 + l 2 2
= [(l - 2 + 2) el - (0 - 0 + 2) eO] _ ~ e2 + ~ 1 -, 1
=[e-2]-2e~+"2
123
""e-"2e -"2
43. General equation of parabola whose axis is
y2 =4a(x+h)
On differentiating with respect to x
dy dy
2y dx = 4a :=) y dx = 2a
Again differentiating, we get.
y (dy)2 + Y d2y '" 0
dx dx2
This is a differential equation whose degree and. order are 1 and 2 respectively.
-1 . dv
44. (1 + y2) + ex - etan Y) dx. = 0
2 dx -I
.:::} (l + y ) - + x = enID Y
dy
dx 1 eLan-1 y
:=)-+ -- X=---
dy 1 + y2 1 + y2
I ~l .• dy
IF=e1pJY=e l+y2 =elan-Iy
Therefore required solution is
-1 -1 e",n-1 y
X_elan y = felan y ·---dy + kl 1 + y2
xe,an -1 Y
-1 1 2 -1
xetan y = _ e tan y + k]
2
2x e,an-J y = e2 tan--I y + k
45. Let Pea, ~) be the point which is equidistant to A(al, h:t) and Reaz, b2)·
PA=PB
:=) (a - ali + 03 - bJ l = (a - azl + 03- b1.l
=> 0.2 + at + 2a1 Ct + 131. + bf - ~bl
'" a 2 + a~ - 2aa2 + 132 + bi - ~b2
=> 2(a2 - al)a + 2(b2 - h:t)!3
+ (at + b:t2 - a~ - bi) '" 0
=> (a2 -ad a + (bz - b:t)!3
1 1. 2 2 2
+ "2 (al + bi - a2 - b2) = 0
Thus the equation of locus is
((1.2 - al)x+ (b1. - h:t)y
1 (2 1.2 2 b2) 0
+"2<li+"l-a2- 2 '"
But the given equation is
(a2 - al)x + (b2 - l1)y + coo 0
1 (2 b2 2 b2
C = -"2 a1 + 1 - (12 - 2)
1 2 b2 2 2
= "2 (a2 + 2 - a1 - bi)
Alternate solution
(aI' h:t land (a2, b2)satisfy the equation. So that
al (al -a2)+ bl (bl -b2)+ c=O (i)
and a2 (al - a2) + b2 (bl - b2) + c = 0 (ii)
On adding Eqs, (i) and (ii), weget
(al + a2)(al - a2) + (b: + b2)(b] - b2) + 2c = 0
:=) 2c = - [af - ~ + b? - b~]
1 2 ~ 2 2
=> c ="2 [a2 + b2 - al - bi]
46. Co-ordinates of the vertices of a triangle are (a cost, a sin t), (b sin t, - b cos t) and (1, 0). centroid is
and
a cos t + b sin t + 1
x"". 3
3x - 1 '" a cos t + b siri t
a sin t - b cos t + 0
y== 3
... (i)
~ 3y"'asint-'-bcost .,.(ii)
Squaring and adding Eqs, 0) and (ii), we get (3x - 1/ + (3yi
== (a cos t + b sin t)2 + (a sin t - b cos t l
(3x -1/ + (3)'i = a2 + b2
47. The given equation is x2 - 2pxy - y2 == 0 .
On comparing with
ax2 + 2hxy + by2 = O,we get
a = i, b = -1, 2h "" - 2p=> h ;0 - P Equation of the bisector of angles
Xl _),2 xy
a:=-b=T
.ry
2 2 X -y
1+1
-p
2 2 2xy
x -y =---
p
... (i)
But given equation of the bisector of angles is
x2 - 2qry - y2 = 0 ... (ii)
On comparing (i) and (ii), we get 2
-·=-2q =>pq=-l p
48. Line OA makes an angle u with x-axis and OA = a, then co-ordinates of A are (a cos a, asin a).
B {<H)OS {gO'" a:}, a sin(90',_ Ct))
A(acos a:, a sin a)
Also OB .L OA, then OB makes an angle (90Q + a )with x-axis, then co-ordlnatesof B are (a cos (900 + a), a sin (90" + 0;))
'" (- a sin (:t, a cos (1) Equation of the diagonal not passing through the origin is
- • a cos CI. - a sin u
(y-asmo;)"'----, - -- (x-acosct)
- asm 0; - a ccs 0;
, sin 0; - cos u
:::;. (y - a sm o ) == . . (x - a cos 0:)
smo:+cos(X.
::::) (sin 0: + cos 0:) (y - a sin a)
= (sin ct -cosa)(x-acosa)
:::;. (sin a -r- cos c.) y - a sin a (sin a + cos a)
==- (sin u - cos u) x -acos ct (sin .u - cos u) ::::) y (sin a + cos c ) -t- x (cos o - sin «)
=U sin 0; (sin u + cos ce)
- a cos u (sin u - cos u) ==- a [sin 2 a: + sin IX cos U
- cos ct sin ct + CO$2 o.] :. y(sin ct + CGS ct) + x (cosa - sin 0.) = a
49. Key Idea : Two circles of radii Ii. and '2 respectively intersect in two distinct points, if Ii. - 1'2 < CIC 2 < 1', + 1'2 .
The equation of first circle is
ex -ll + (y - 3l ==?Centre CI (1, 3) and radius 1', ==- r and equation of second circle is
x2 + y2 _ 8x + 2y + 8 '" 0
~_:_-~
CentreC2(4, - 1) and radius r, == ~42 + 12 - 8
==,/17 - 8", 3
Two circles in tersect in two distinct points, then
rl-r2.<CIC2<fl+r2
:::;. r- 3 < 1(4 -1/ + (-1 - 3)2 < I' + 3
::::) I' - 3 < ,)9 -+ 16 < I' + 3
~ 1'-3<5<r+3
=0> r-3<SandS<r+3
~ 1'< 8 and 2< I'
2<r<8
50. The equations of diameters of a circle are
2x-3y"'S ' . .,0)
and 3x - 4y '" 7 ... (ii)
On solving Eqs, (i) and (ii), we get
x = 1, y '" -1.
r, Co-ordrnates of centre are (1, -1) and area of the circle", 'ltr2
154,., 22?-
7
1"=7
Equation of the circle is
(x - 1/ + (y + II = 72
x2 _ 2x + 1 + y2 + 2y + 1. == 49 x2 + y2 ~ 2x + 2y == 47
51. Ker Idea : Equation 0/ normal a, a point (ae ,2at) on a porabola y2 = 4ax is
Y = - tx + 2ae + bt 3.
Equation of the normal at point (bl ~, 2 bt I) on parabola is
y =-[1 x+ 2bt1 + btr
It also passes through (be 22, 2bt 2), then
. 2bt2 =-tl· br/ + 2h!"j + btI3 2t2 - 2tl = - tj (t22 _tI2)
= -tl (t2 + t1)(t2 - tl)
=0> 2= - t) (t2 + [1)
2
::::) [2+tl=--
[1
2
::::) t2c:::-tj--
tl
Note:
1. If a normal drawn at a point tj on the parabola meets the parabola again at a point f2' then
2 .
t2 = - tr t;·
2_ Three normals can be drawn at a point on a parabola.
3. Foot of the normals drawn from a point are called conormal points.
. . x2 y2
52. Key Idea: The fOCI of al1 ellipse 2" + """2 = 1 are a b
_ .' •. x2 yl
(±a.e, 0) and foCi of a hyperbola a'2 - r: lore
(±a' e', 0).
Equation of the hyperbola
x2 y2 .
-------=1
Cs2r (~r
Eccentricity is given by
b,2 .: a'2 (e,2 -1)
81 = 144 ( ,2 -1)
25 25 e
,2 9 25
e .: 1 + 16 = 16
, 5
e.:-
4
Then, foci of a hyperbola are
( 12 5 )
(± a' e", 0) == ± 5 x 4' °
'" (± 3, 0)
Equation of the ellipse is x2 y2
16 + II == 1
Foci of an ellipse are (± ae, O) "" (± 4e, 0).
But given focus of ellipse and hyperbola coincide, then
4e=3 =;> e=~ Also b2 == a2 (1 - (2)
=16(I-l~)=I6-9=7
53. Vector perpendicular to face OAB '" iii y
B
A x
z
~ .-.)., ..... ..... "" ..... A .....
= OA x OB '" (1 + 2j + k) x (2i + j + 3k)
==(5i-J-3k)
Vector perpendicular to face ABC == ~
-4--1> AA A AAA
== AD xvAC'" (i - j + 2k) x (-2i - j + k)
== (i - 5) -3 k)
Since angle between faces equals angle between their normals. Therefore
5 x 1 + (- 1) x (- 5) + (- 3) >( (- 3)
=752 + (-Ii + (- 3/ JI2 + (- 5)2 + (-3l 5+5+9 19
55 J3s == 35
a= cos-J G~)
54. Equation of sphere is
x2 + y2 + Z2 + 2x - 2y - 4z - 19 '" 0 Centre of the sphere is (~ 1, 1, 2)
and radius =~(-li + (Ii + (2/.+ 19 =55=5
Equation of plane is
x + 2y + 2 z + 7 '" °
Length of the perpendicular from centre 0 on the plane is
ON",-Ix1+Ix2+2x2+7
. ~I2 + 22 + 22
'" 12=4
3
In ~ OEN, OEl '" ON2 + NE2
==> 52 = 42 + NB2
==> NB2 == 25 -16
==> NE2 '" 9
==> NB: 3
55. The lines
and
x-2 y-3 z-4 -I-=-I-:~
x-I y-4 z-5 -k- = -2- = -1-
.. ,(ii)
".(i)
are coplanar, if
Y2 - Y1Z2 -ZJ I
ml nJ '" 0
m2 n2
IlL i !kl=o
k 2 1
==> -1 (1 + 2k)-1 (1 + k2)+ 1 (2-k):O -2k - 1 - 1 - e + 2 - k = 0 _k2 - 3k '" 0
k '" 0 or - 3
56. Equa dons of the lines are x==ay+b, z=cy+d
x-b z-d
=r :» -c-=y
x-b y-O z-d -a-=-I-=-c-
x = a' y + b' , z = c' y + d'
x - b' z- d'
-0'- = y, -c'- == y
x - b' y - 0 z - d' ~=-I-=-c'-
... (i)
and
... {li)
~
Eqs, 0) and (ii) will be perpendicular to each other, if
1112 + m1m2 + nln2 == 0
=> aa' + 1 x 1 + c x c' = 0
=> aa' + cd + 1 = 0
57. Equations of sphere and plane are
? 2 2
x: + Y + z + 4x - 2y - 6z- 155 == 0
and 12x + 4y + 32 - 327 = O.
Centre of the sphere is (- 2, 1, 3) and radius of sphere
= ~4 + 1 + 9 + 155 == ../169 == 13
Lenght of the perpendicular from centre on the plane
=1- 2x12+ 1 x4+ 3x3-3271 .J144 + 16 + 9
=; j'-111~ 3271
;; 338 = 26 13
Shortest distance between the pi ane and sphere = 26 - radius of sphere
== 26 -13 = 13
58. Consider OX, OY, OZ and Ox, Oy,Oz are two system of rectangular axes.
Equation of the plane correspondmg to OX, OY, OZ as axes is
X y Z
a + b + c == 1 ... Ci)
Similarly. equation of the plane corresponding to Ox, Oy, Oz as axes is
.:! + y + .:.. = 1 C")
a' b' c' ... 11
Length of perpendicular from origin to Ci) and (ii) must be same,
. 1 1
L e .• r=:o====
. I a~ + bI2 + c~ J1_ + 1...2 + J....2
V 1 a,2 b' c'
59. ("it + 1i + 7.? = ("it + -s + ~). ("1 + "It + 7) ~ ("1+ "ff + -~y = I ~ 12 + l-S 12 + 1"112
+ 2 (it, -s + -g ,"1 + 7. . it) => 0=12+ 22+ 32+2C;t·-s +"'ff.~ + 1.1') => 2 ("1 ' -g + It . ~ + "'l . it ) '" - 14
~ -rl> ~ ~ --t--t
a . D + Ij . c + C ' a = -7
~ ~ ~. --t _. --t-)
60.(u + v -w)·[(u - v)x(v -w)]
--t --t --t --t --t -+ -) == (u + v - w)· [u x V - U x W
--t --t -'10 ~
~vxv+vxw]
~ -) --t -* --t --t ~ -+ -) + v . u x V - v· u xW + v· V xW
-\i.1t x~ +~:ti x~-~.7 xiZ
~ ~ ~_~ --t --t --t 4 -t == U . v xw - V . U xw - w· u xv
--t -+ --t == U· v xw
Since (it Ii ~ ] = [tl ti ~] '" [~ It ~ ] '" [~ ~ ~l
'" (w: ti w: I "" [w: ~ :w J = o
Note:
--t ~ ~
If u, v, ware coplanar vectors, then
--t --t--t
[u v w) =0
61. Given
---+ ............... ~ ...... ~ ....
OA=7i-4j+7k,OB=i-6j+lOk,
--t ~ ~ A ~ A" ~
OC== - i - 3j +.4k and OD '" Si - j + 5k
AB = ~(7 _1)2 + (- 4 + 6i + (7 - lOi
:= -../36+4-;9 := ..J49 =-7
Be:= JCl + Ii + (- 6 + 3)2 + (10 - 4i := J4 + 9 + 36 := J49 == 7
CD == ~ (- 1 - 5)2 + (- 3 + 1 i + (4 - 5)2 = . ./36+ 4+ 1 =.J4l
_ DA = Jes _7)2 + (-1 + 4)2 + (S-7l = J4 + 9 + 4 = J17
Thus no option is correct.
62. Let D is mid point of Be.
A
BL-----~D------~C
-,» -,»
~ AB.j·AC
:. AD '" 2
(3i + 4 k) + (Si - 2j + 4 k) 2
8i-2j+8k 4~ ~ 4k =--2--= l-J+
-,» -,» r:-----
:. Length of AD =1 ADI =v42 + (-ll + 42
= J16 + 1 + 16 = 53
63. Total force
-7 ~A (- A~A
F = (4 i -i- j - 3K) + (3 i + j - k)
=71 -l- 2J-4k
Displacement
-7 A AA A A A
d = (5i + +J + k)- (i + 2j + 3k)
;:(41+2)-21{)
-,» -,» Total work done = F . d
= Oi + 2)- 4k) - (41 + 23.- 21<) := 28 -f 4 + 8
'" 40 unit
-)0 A A_' A A -)0 A A A
64. u = i + j, v = i - j and w = i + 2 j + 3 «,
Ii is a unit vector such that
and
Therefore, n is perpendicular to both 11 and-,) But Ii, ~ lie in the X)' plane.
~ n is a unit vector along z-axis
'-* A
Hence, I w . n I = 3
65. Median of new set remains the same as thai of the original set.
66. Given N = 15
L Xl = 2830, LX == 170
One observation 20 was replaced by 30, then 1: Xl "" 2830 - 400 + 900 = 3330
I. x;; 170 - 20 + .30 = 180
Variance, c:/ == k ;~ - C::Nxf
= 3i~_Q - (\8~r
3330 ._ 15 x 144
= ---15·--- .. -
'" 3330 - 2160 =:U 70;= 78.0
15 15
67. The probability that Mr. A selected the loosing horse'" j: x 1 = ~
5 4 5
The probability that Mr. A selected the winning
horse", 1 - ~ =: ~ .
68.0 S; peA) $ 1, 0 S PCB) S; 1, 0 S P(C) S 1 and ° S peA) + PCB) + peC):S 1 3x + 1
0:::;· "3 -Sl
] 2
=> -~SXS;3
Osl-X<l . 4 -
and
-3:S;xSI
1 - 2x 0:::;-2-$1
1 1
=> -"2::;x:5"2
3x+l I-x 1-2x and a s -3- 'I, -4-' + ~ s; 1
o s ]3- 3x $12
1 13
=> 3:::;x::;'-3
From all these conditions
1 1
.i:« x <._
3"" -2
69. Key Idea: The meaJl arid variance of a random variable in binomial distribution are np a.nd npo
and
np = 4 and npq = 2
1 1
q'" 2' but P + q -=1;::;. P <= 2
1 nX2"'4:=on==8
We have, P ex::::. r)", "Crp' q"-r
8 (1)7 (1)1
P (X == 1) = C1 '2 - '2
= 8 x..!.. =1_",_!. _ 28 2S 32
70. Key Idea : Resultant force of two forces P and Q acting at an angle ct, is given by
R == ~p2 + Q2 + 2PQ cos a
If a is the angle between P and Q, then
R2 =p2 +Q2 + 2PQ cos n ... (i)
---) ---t
If Q is doubled, then R is doubled
:::> 4R 2 = p2 + 4Q2 + 4PQ cos a. ... (ii)
Since,
Again if the direction of Q is reversed, then It is again doubled
=:> 4R2 = p2 + (- Qi + 2P (-Q) cos ct
4Rz =p2 + Q2 -'2PQ cos a ... (iii)
Adding (i) and (iii)
'SR2=2p2+2Q2 C')
•. , IV
Multiplying by 2 in (iii) and adding (ii) 12R2 == 3P2 + 6Q2
:=0 4R2 =p2 + 2Q2 ... (v)
Subtracting (v) from (iv), we get
R2 = p2
Putting in (v)
4R2 =R2 + 2Q2
=:> 3R2 = 2Q2
p2 Q2 R2 2'''''3''''2
=- p2:Q2:R2=2:3:2
71. Since RI and Rz respectively be the maximum ranges up and down an inclined plane, then
u2
R = -,.--.....,..-,----
1 g(l + sin (3)'
Uz
R = --".-..,.......,,.,.
2 g(l - sin (3).'
U2
R=-,
g
No _!. - _!_ _ g(1 + sin )3) g(1 - sin P)
w'R + R - 2 + 2
1 2 U U
_ g[l + sin p + 1 - sin 13]
- u2
2g 2.
=~=R
1 1 2
=>-+-=-
RI R2. R
1 1 1 ,
=>R'R'RaremAP
1 2
=- Rj, R, Rz are in HI',
72. LetAB = d.
AM is the perpendicular distance from A to B. In/!"ABM,
",_N
sin 0= AM AB
AM == d sin 0 Moment of couple,
---) --,). ---)
G == p. AM == P d sin 0 ... (i)
---)
Where P is turned a right angle, then
Moment of couple,
---) ---) ---+
H = P . d sin (900 + 0) = P d cos e .. , (ii)
---)
When P is turned through an angle c, then
Moment of couple
-t
'" P - d sin ((I. + 0)
---)
'" p . d [sin Ct cos f) + cos a. sin 8]
---) ---)
'" (P . d cos fl) sin ct + (P . d sin f») COS'(l
-t -t
'" G cos a. -I- H sin a. [Using (i) and Cii)]
73. We have
R 2 = u2 + f 2(,2+ 2uft cos (1800 - ex) R2 = u2 + f2t2 - 2uf! cos a
2 2:1
V = ~ __ "!'_L~ __ :_~~.[t__c_~~ a.
Let
,
"
I
, , , ,
I
,
, , ,
dV 2
dt ::: 0 + 2/ t - 2ui cos a
d2V 2
-=2/:::+ ve
dt2
i. e., velocity will be least after a time.
dV 2
dt :: 0 '" 2f t - 2uf cos a
==> 2f2 t '" 2uf cos a
2ui cos a
==> t::-'-----'
2f2
u cos a
=:»:
74. When stone is projected horizontally, then u
R""ucosOxt A
and 11::: usin Oxt + ~t2 J
=:- R "" ut and h = 2. gt h
~ R =ut an_dt =f{ 1
=> R '" u pgh ... 0) q~, "'-~~-==-A-=--=--=----~-'
When stone is projected at an angle of e to the horizontal, then'
R=ucosflxt ... (ii)
1 2
and h '" - u sin e x t + 2. gr , ... (iii)
USing Eq, (I) in Eq. (ii), we get
u.J¥'=ucosext
t == c'.015 ,r..,. (2h 2gh
=:- cr Vg ... (iv)
u=o -f __ r ""='O
A v B
1.01 x, C x2--'---i and tJ + t2 == t
We have from A toC
)12 =u2 + 2fxl
v2 == 0 + 2fxl
and =>
)12
Xl "" 2/
)I"'U+ ft v", 0 + ftl V
tl =J
From C to B, )12 '" u2 + 2ft V,2 == v2, - 2rxi 0,=)12 - 2rx2
and v' = v - rt 2
=> O=v-Itz
On adding Eqs, (i) and (iii?
Xl + Xl = v; (} + ~)
2s 2 (1 1)
=V 1+-':
On adding Eqs. (il) and (iv)
=> tl+tZ=V(Y+n
=> t ==)1 (1 + n
t2 =v2 (j + ~r
... 0)
... (Ii)
... (iii)
... (iv)
... (v)
... (vi)
Вам также может понравиться
- Solved Papers 2003Документ15 страницSolved Papers 2003sourav singhОценок пока нет
- Aieee 2003Документ20 страницAieee 2003gunjan kadelОценок пока нет
- Paper I Physics QuestionsДокумент16 страницPaper I Physics QuestionsDipankar DeoriОценок пока нет
- Eamcet 2006Документ14 страницEamcet 2006Mohammed SalahuddinОценок пока нет
- Manipal UGET Medical 2012 Previous Year Paper With SolutionsДокумент32 страницыManipal UGET Medical 2012 Previous Year Paper With SolutionsYashwanth SrinivasaОценок пока нет
- Practice Test For NeetДокумент13 страницPractice Test For NeetMohammed Aftab AhmedОценок пока нет
- Carnot Cycle Maximum EfficiencyДокумент18 страницCarnot Cycle Maximum EfficiencyAlok ShawОценок пока нет
- AIEEE2003Документ45 страницAIEEE2003alabasmОценок пока нет
- 02 PhysicsДокумент14 страниц02 PhysicsSaikatSenguptaОценок пока нет
- Aieee 2002Документ32 страницыAieee 2002Mohit YadavОценок пока нет
- 27-12-18 - SR - IIT-IZ-CO SPARK - Jee-Main - SURPRISE TEST (GTM) - QP PDFДокумент13 страниц27-12-18 - SR - IIT-IZ-CO SPARK - Jee-Main - SURPRISE TEST (GTM) - QP PDFM jhansiОценок пока нет
- Aieee 2004.Документ52 страницыAieee 2004.NCERT SolutionsОценок пока нет
- 2755IIT JEE Physics Question Paper-1999Документ12 страниц2755IIT JEE Physics Question Paper-1999SARTHAK MISHRA X-E ROLL NO - 47Оценок пока нет
- AIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryДокумент36 страницAIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryDiyaОценок пока нет
- AIEEE 2002 Physics and Chemistry QuestionsДокумент18 страницAIEEE 2002 Physics and Chemistry QuestionsDeepa LakshmiОценок пока нет
- CG PET 2006 Question Paper: PhysicsДокумент24 страницыCG PET 2006 Question Paper: PhysicsRahul BadgujarОценок пока нет
- Aieee 2002 QДокумент18 страницAieee 2002 Qvishal kumarОценок пока нет
- JEE Main Sample PaperДокумент13 страницJEE Main Sample PaperAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Physics 4Документ5 страницPhysics 4gayathri444Оценок пока нет
- AIEEE Paper 2002 PDFДокумент18 страницAIEEE Paper 2002 PDFKiran Raj RОценок пока нет
- Jee Main Mock Test PaperДокумент52 страницыJee Main Mock Test PapermanojОценок пока нет
- Aipmt Paper 1999Документ32 страницыAipmt Paper 1999koushikОценок пока нет
- UNIT-3 Electrostatics Cet QuestionsДокумент7 страницUNIT-3 Electrostatics Cet QuestionsUMME HANIОценок пока нет
- Aieee 2002 QДокумент33 страницыAieee 2002 Qsiddharth1996Оценок пока нет
- EXERCISESДокумент33 страницыEXERCISESSandeep Chahal100% (1)
- Eklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1Документ58 страницEklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1arja keerthanaОценок пока нет
- Section - 1 Physics: T T M M N NДокумент5 страницSection - 1 Physics: T T M M N NmdaОценок пока нет
- Ele MCQ (Physics Questions)Документ8 страницEle MCQ (Physics Questions)Motivation TechnologyОценок пока нет
- IIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)Документ12 страницIIT JEE - Mains Model Test Paper - 1 (Physics, Chemistry, Maths)studysteps.in83% (6)
- Coulombs Charges and Field Multiple QuestionsДокумент9 страницCoulombs Charges and Field Multiple QuestionsjitenhrtОценок пока нет
- Ecat Entrance Test - 1: Physics Flt-1Документ9 страницEcat Entrance Test - 1: Physics Flt-1XXXОценок пока нет
- C022Документ17 страницC022FATHIMAОценок пока нет
- Harsh AДокумент10 страницHarsh AharshanauocОценок пока нет
- Jee Mains - 1Документ29 страницJee Mains - 1AbhijeetОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS MOCK TESTДокумент6 страницPHYSICS MOCK TESTManishKumarОценок пока нет
- (www.entrance-exam.net)-AIEEE Maths Sample Paper 7[]Документ20 страниц(www.entrance-exam.net)-AIEEE Maths Sample Paper 7[]Aditya RamОценок пока нет
- Physics 2017Документ32 страницыPhysics 2017milapdhruvcomputerworkОценок пока нет
- MFT Samp Questions PhysicsДокумент9 страницMFT Samp Questions PhysicsBerkan YilmazОценок пока нет
- IITians PACE AITS 1 2012 PAPER 1 With SolutionsДокумент28 страницIITians PACE AITS 1 2012 PAPER 1 With SolutionsHarishChandraОценок пока нет
- AIEEE 2003 Questions Papers PDFДокумент20 страницAIEEE 2003 Questions Papers PDFRemoОценок пока нет
- VITEEE Question Paper 2019 PDF DownloadДокумент52 страницыVITEEE Question Paper 2019 PDF Downloadchanti489Оценок пока нет
- Physics 2021Документ34 страницыPhysics 2021milapdhruvcomputerworkОценок пока нет
- Physics: (Mock Test-3) 1Документ7 страницPhysics: (Mock Test-3) 1Piyush khadatkarОценок пока нет
- 11th January 2019 (Second Shift)Документ35 страниц11th January 2019 (Second Shift)hermoine gawarОценок пока нет
- MCQ Questions - PHYДокумент17 страницMCQ Questions - PHYsanjayОценок пока нет
- Otp - 1 PDFДокумент5 страницOtp - 1 PDFBBA GОценок пока нет
- 11 PHY Set 2Документ5 страниц11 PHY Set 2dikshachoud44Оценок пока нет
- Full Length 3Документ35 страницFull Length 3rishikeshkallaОценок пока нет
- Iit Mains Exam Type Questions of Electrostatics PDFДокумент13 страницIit Mains Exam Type Questions of Electrostatics PDFRupinder Sidhu100% (2)
- 8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Документ7 страниц8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Abin VargheseОценок пока нет
- PCB_gujcet-28-03-2024Документ14 страницPCB_gujcet-28-03-2024Mayursinh rathodОценок пока нет
- PCM_gujcet-28-03-2024Документ14 страницPCM_gujcet-28-03-2024Mayursinh rathodОценок пока нет
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОт EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОценок пока нет
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (4)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3От EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- General KnowledgeДокумент44 страницыGeneral KnowledgeAnonymous ioNuZrgОценок пока нет
- WWW - Questionpaperz.in CDS Sample Paper 1Документ28 страницWWW - Questionpaperz.in CDS Sample Paper 1cdsaryaОценок пока нет
- Upsc Political ScienceДокумент56 страницUpsc Political ScienceraviОценок пока нет
- PhilosophyДокумент40 страницPhilosophyசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- StatisticsДокумент44 страницыStatisticsசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engg UpscДокумент44 страницыMechanical Engg UpscManikandan VijayanОценок пока нет
- SociologyДокумент40 страницSociologyசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- CDS (1) 09 Elementary MmathsДокумент32 страницыCDS (1) 09 Elementary MmathsNCERT SolutionsОценок пока нет
- ZoologyДокумент48 страницZoologyimdebarshiОценок пока нет
- Public AdminДокумент60 страницPublic Adminசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Philosphy XДокумент40 страницPhilosphy Xசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент46 страницPhysicsசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- MathematicsДокумент36 страницMathematicsசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Medical ScienceДокумент36 страницMedical Scienceசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Geology XДокумент40 страницGeology Xசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Indian History 09Документ40 страницIndian History 09poorv1235570Оценок пока нет
- GeologyДокумент40 страницGeologyசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Pre Qs. PaperДокумент48 страницPre Qs. PaperSidharth Singh AntilОценок пока нет
- Geography 09Документ48 страницGeography 09mrinalinisingh46Оценок пока нет
- Electrical EnggДокумент48 страницElectrical EnggNCERT SolutionsОценок пока нет
- ChemistryДокумент48 страницChemistryNiharika Satyadev JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Economics XДокумент42 страницыEconomics Xசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- AgricultureДокумент48 страницAgricultureNCERT SolutionsОценок пока нет
- CommerceДокумент56 страницCommerceசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- BotanyДокумент36 страницBotanyசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- AIEEE - 2009: SolutionДокумент17 страницAIEEE - 2009: SolutionAbhijeet ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Civil EnggДокумент54 страницыCivil Enggசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- Animal HusbandaryДокумент36 страницAnimal Husbandaryசுப.தமிழினியன்Оценок пока нет
- MathsДокумент14 страницMathsapi-3739396100% (1)
- Aieee 2008Документ26 страницAieee 2008NCERT SolutionsОценок пока нет
- Detail Pre-commissioning Procedure for Service Test of Plant Air UnitsДокумент31 страницаDetail Pre-commissioning Procedure for Service Test of Plant Air UnitsAnhTuấnPhanОценок пока нет
- Clock ReactionДокумент4 страницыClock ReactionTheyvan T-vanОценок пока нет
- Quarter 2 - Module 2: Consumer ChemistryДокумент30 страницQuarter 2 - Module 2: Consumer ChemistryBurn and Ashes100% (1)
- Kamias As Stain RemoverДокумент20 страницKamias As Stain RemoverTrisha Mae Tapawan100% (1)
- Powder Technology: 5+ 3 Jing Zhu, Yongcai Zhang, Li Shen, Jing Li, Liangliang Li, Fen Zhang, Ya ZhangДокумент15 страницPowder Technology: 5+ 3 Jing Zhu, Yongcai Zhang, Li Shen, Jing Li, Liangliang Li, Fen Zhang, Ya ZhangJerusa PachecoОценок пока нет
- 12 Chem Ch2 Colligativeproperties Asgmt2 HWДокумент3 страницы12 Chem Ch2 Colligativeproperties Asgmt2 HWAnisha GolaniОценок пока нет
- StarDesignPower CargillBeauty PresentationДокумент28 страницStarDesignPower CargillBeauty PresentationJames WuОценок пока нет
- SARA Method D4124Документ9 страницSARA Method D4124mahamuninaresh1Оценок пока нет
- Development of A Compounded Propofol Nanoemulsion Us 2023 International JourДокумент10 страницDevelopment of A Compounded Propofol Nanoemulsion Us 2023 International JourAndrade GuiОценок пока нет
- II PUC CHEMISTRY IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR SOLID STATEДокумент29 страницII PUC CHEMISTRY IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR SOLID STATEom sri sai enterprisesОценок пока нет
- CGCMSsolutionDataProject1Rtx 5 MS 2019ulyarti Sampel Minyak - QGDДокумент9 страницCGCMSsolutionDataProject1Rtx 5 MS 2019ulyarti Sampel Minyak - QGDDion FebyanОценок пока нет
- The Essential Boat Maintenance ManualДокумент290 страницThe Essential Boat Maintenance ManualAnantoly KoretskyОценок пока нет
- Discussion For Anion ExchangeДокумент2 страницыDiscussion For Anion ExchangeEzekielОценок пока нет
- Defix: Linacol MedicalДокумент2 страницыDefix: Linacol MedicalMohammed Al-YagoobОценок пока нет
- Approved Raw-Materials SuppliersДокумент4 страницыApproved Raw-Materials SuppliersDhanus KodiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test BankДокумент20 страницChemistry The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change Silberberg 5th Edition Test Bankanthonyramosscdkyoagqn100% (39)
- PT - Science 7 - Q1Документ2 страницыPT - Science 7 - Q1OmarieОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics 3.0 With PracticeДокумент92 страницыFluid Mechanics 3.0 With PracticeCosmic BrilliantОценок пока нет
- Uk Chemistry Olympiad Examiners Report 2017Документ4 страницыUk Chemistry Olympiad Examiners Report 2017JackieWilsonОценок пока нет
- Phenol Handwritten Notes by LMДокумент14 страницPhenol Handwritten Notes by LMpanchaldalshukh46Оценок пока нет
- Quiz 4 040142021 SolutionsДокумент2 страницыQuiz 4 040142021 SolutionsmoienОценок пока нет
- Masterkure 106 TdsДокумент2 страницыMasterkure 106 TdsEmre ErdoğanОценок пока нет
- General Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 5Документ43 страницыGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 2 - Module 5Leica Mariel100% (1)
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesДокумент8 страниц9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesNerminОценок пока нет
- Chem 11 Total Review With Answers Key UpdateДокумент28 страницChem 11 Total Review With Answers Key Updatemelissa.figueroamoralesОценок пока нет
- CFR Title 21 Food Additive RegulationsДокумент6 страницCFR Title 21 Food Additive RegulationsNgan SonledaОценок пока нет
- Revision Notes: Excretory OrgansДокумент4 страницыRevision Notes: Excretory Organskavitaruby1980Оценок пока нет
- Previous QuesionsДокумент39 страницPrevious Quesionshojibox903Оценок пока нет
- Br. Kade Postupak I Ime Preparata Konc. (%) Temp (°C) Miješanje Otopine Materijal Kade Br. Faze (Al I Fe) Vrijeme Obrade PH, ProvodljivostДокумент3 страницыBr. Kade Postupak I Ime Preparata Konc. (%) Temp (°C) Miješanje Otopine Materijal Kade Br. Faze (Al I Fe) Vrijeme Obrade PH, ProvodljivostBranko BrezecОценок пока нет
- To Cite This Version:: Clifford FongДокумент39 страницTo Cite This Version:: Clifford Fongnasir uddinОценок пока нет









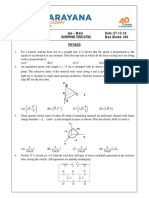























![(www.entrance-exam.net)-AIEEE Maths Sample Paper 7[]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/722125930/149x198/9e7c5c9714/1712850347?v=1)