Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Translation
Загружено:
lolcakejam0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыBiochemistry
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документBiochemistry
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров2 страницыTranslation
Загружено:
lolcakejamBiochemistry
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
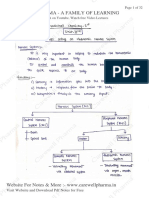
TRANSLATION
Components for translation
mRNA transmits info encoded in DNA
Eukaryotic
A 5UTR precedes the translation initiation
signal
Usually the 1st AUG sequence (initiation codon)
Prokaryotic
No capped
Polycistronic
More than 1 initiation codon
Ribosome positioning sequence at 10
nucleotides upstream of the AUG codon
UTR follows termination signal
tRNA is a bilingual translator molecule
Clover-leaf = secondary structure
L-shaped = tertiary structure
Codons in mRNA are 3-letter words
1:1 correspondence of bases to AA = permit
mRNA to encode only 4 diff. AA
2:1 correspondence of bases to AA = 16 AA
Multiple codons for a single amino AA
degeneracy
Start signal (AUG) = methionine signifies the
initial, amino terminal residue
UGA = termination (usual)
Mitochondrial termination = AGA, AGG
Stop signals = UAG, UAA, UGA
UGA codon = additional function of coding for
SELENOCYSTEINE
Seleocysteine-tRNA is synthesized from a
specific seryl-tRNA, a sec-inserion sequence, a
defined stem-loop structure in mRNA
o eEFSec & SBP2 (selenocysteine
insertion binding protein required for
its synthesis
Codon-Anticodon interactions permit reading of mRNA
anti-parallel
Codons are read in a sequenctial, nonoverlapping reading frame
Anticodon & AA-acceptor sites are at opposite
ends of L-shaped tRNA
o Bridges the gap between nucleotide
sequence of mRNA & site of protein
assembly on ribosome
Frequent anticodon nucleotide is inosinic acid
(I), hypoxanthine, which base pairs with U, C, A
o Wobble hypothesis = permits less
stringent base pairing between the 1st
position of anticodon and the
degenerate (3rd) position of codon
3codon
base
A
C
G
5 anticodon base
possible
U, I
G, I
C, U
A, G, I
Aminoacylation of tRNA activates AA for protein
synthesis
Two step process catalyze by aminoacyl-tRNA
synthetases (each is specific for single AA)
Aminoacyl-ester linkage is lower in energy
compared to aminoacyl-adenylate
Correct selection of both tRNA and AA by the
synthetase is therefore central to fidelity in
translation
Some AA are recognized by bulk (Try) o lack of
bulk (Gly) or by charges
Additional proofreading step increases
discrimination by many (not all) aminoacyl
synthethases
Each synthetase must also correctly recognize
one to several tRNA species that can carry the
same AA, while rejecting incorrect ones.
Ribosomes
Complex RNPs that is made up of 2 dissimilar
subunits, each contains RNA & many proteins
Large subunit sites of peptide bond formation
(peptidyl transferase) ad of elongation factor
binding (translocation domain) opposite site of
central protuberance
Stalk projects to right
Small subunit platform protrudes toward the
reader.
mRNA & tRNA interact in the decoding site, in a
cleft between platform & subunit body
the site of peptide bond formation is distant
from exit site and the growing peptide passes
through groove in ribosome to reach the exit
aminoacyl-tRNA is bound by the small subunit
an is oriented with the acceptor end near
peptidyl transferase
while translocation domain is near the
decoding site
tRNA is directional & collinear with mRNA
also 5-3
INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Requirements: (should be in proper orientation)
1) Small (40S) ribosomal subunit
2) mRNA
3) tRNA complex of amino-terminal
AA
4) followed by association of large
(60S) subunit now a completed
initiation complex
STEPS:
1) eIF2 binds to GTP & Met-tRNA
(initiator tRNA) forming TERNARY
COMPLEX
no other aminoacyl-tRNA
can replace initiation
specific Met-tRNA in this
step
8) GTP is hydrolyzed eIF5B-GTP is
released
9) Complete initiation complex is an
80S ribosome with mRNA &
initiator tRNA correctly positioned
to begin translation
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
Prokaryotes: fMet-tRNA
(formylated); recognized by
IF2
eIF3 binds to small subunit (40S)
surface blocking subunit
association with 60S
eIF3 = anti-association
factor
eIF6 = binds 60S subunit
(+) COMPLEX
eIF2-GTP
Met-tRNA
eIF3-40S
PRE-INITIATION COMPLEX
mRNA-eIF4F (cap-binding
complex)
eIF4A = RNA helicase;
unwinds secondary
structure in untranslated
leader sequence of mRNA
PAB (Poly A binding
protein) = loops the 3 end
of mRNA near to 5 cap
mRNA is scanned in 5 3 until
AUG is found
GTP is hydrolyzed via eIF5 eIF2GDP is released
Released eIF2-GDP interacts with
GNF eIF2B & GTP eIF2-GTP for
another round of initiation
Final step: binding of pre-initiation
complex by 60S subunit and
eIF5B-GTP
IRES (internal ribosomal entry sites) = common
in messengers that encode protein that protect
cells from stress, when the translation of most
mRNAs is REPRESSED
Prokaryotes fewer initiation factors
1) 30S-IF3 binds to either mRNA or
ternary complex (IF2 & fMet-tRNA,
GTP)
2) IF1 = also acts in formation of PIC
3) 50S binds to PIC
4) GTP is hydrolyzed release of
initiation factors
Prokaryotes rely more on
RNA-RNA interactions to
position mRNA
ELONGATION
Peptidyl transferase
Growing peptide to alpha-amino group of the
AA residue of the aminoacyl-tRNA
Efficiency & fidelity enhanced by NONribosomal EFs that use GTP
Up to 3 tRNA molecules are bound to specific
sites that span BOTH ribosomal subunits
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Non Linear PharmacokineticsДокумент33 страницыNon Linear PharmacokineticsClaudОценок пока нет
- FleaДокумент23 страницыFleaAAREEZ IMRAANОценок пока нет
- Stress 2Документ4 страницыStress 2le thi lan anhОценок пока нет
- Obesity Related Cognitive Impairment The Role of Endo - 2019 - Neurobiology ofДокумент18 страницObesity Related Cognitive Impairment The Role of Endo - 2019 - Neurobiology ofSabrina YenОценок пока нет
- Formulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediДокумент2 страницыFormulir Review Judul Skripsi 2019 (Update 28 Maret 2019) Kevin ThenediKevin ThenediОценок пока нет
- Medical ChemistryДокумент32 страницыMedical Chemistryabhishek kumar singhОценок пока нет
- I. Use of English (3.0 PTS) Part A: Choose The Correct Answer To Fill in The Blank. (1.5 PTS)Документ6 страницI. Use of English (3.0 PTS) Part A: Choose The Correct Answer To Fill in The Blank. (1.5 PTS)Rebecca DОценок пока нет
- CV Sample - PHDДокумент3 страницыCV Sample - PHDJuhi DeoraОценок пока нет
- Grade7 LifeScience NGSS 2016 PDFДокумент9 страницGrade7 LifeScience NGSS 2016 PDFJomar SolivaОценок пока нет
- VEGF and AngiogénesisДокумент7 страницVEGF and AngiogénesisMiranda YareliОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Revision Guide PDFДокумент40 страницCambridge International AS and A Level Biology Revision Guide PDFGirish Krishnan67% (3)
- Biomechanics of BoneДокумент27 страницBiomechanics of BoneJimmy ThomasОценок пока нет
- Nervous CoordinationДокумент36 страницNervous CoordinationOlamide AyindeОценок пока нет
- WasteДокумент49 страницWasteMirza ShahrezaОценок пока нет
- Cations and Anions in Fresh Fruit Juice by Fast Ion ChromatographyДокумент8 страницCations and Anions in Fresh Fruit Juice by Fast Ion ChromatographyAravinthОценок пока нет
- Acanthostega ReconstructionДокумент14 страницAcanthostega ReconstructionAndrew KirkОценок пока нет
- Zincogen NBFДокумент7 страницZincogen NBFcodesolutionroОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 14 - SkripsiДокумент5 страницJurnal 14 - SkripsiBagusSatriyaОценок пока нет
- After DefenseДокумент86 страницAfter DefenseTsega YeОценок пока нет
- Acceptability: ©WHO/Sergey VolkovДокумент26 страницAcceptability: ©WHO/Sergey VolkovBeatriz PatricioОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Lipid Profile Among Patients With Seborrheic DermatitisДокумент7 страницAssessment of Lipid Profile Among Patients With Seborrheic DermatitisAinun Aii NoorОценок пока нет
- Reading Explorer 4, Third Edition Additional Reading Practice Unit 1BДокумент29 страницReading Explorer 4, Third Edition Additional Reading Practice Unit 1B응애Оценок пока нет
- Science Olympiad Mock Test 1Документ8 страницScience Olympiad Mock Test 1vidhan tiwariОценок пока нет
- Myers AP 3e - Unit 3 - WatermarkДокумент78 страницMyers AP 3e - Unit 3 - WatermarkRahaf AftanОценок пока нет
- Plants and EnvironmentДокумент284 страницыPlants and EnvironmentYen LeОценок пока нет
- 12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesДокумент9 страниц12 Biology Notes Ch11 Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesAnkit YadavОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 2Документ5 страницLab Report 2Jessica TysonОценок пока нет
- Queen of Philippine Orchids - The Rare and Beautiful Waling-waling FlowerДокумент4 страницыQueen of Philippine Orchids - The Rare and Beautiful Waling-waling FlowerWendy BalaodОценок пока нет
- Vision IAS Environment Part 1Документ169 страницVision IAS Environment Part 1Anup ShindeОценок пока нет