Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Relative Density Test on Granular Soils
Загружено:
MazharYasinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Relative Density Test on Granular Soils
Загружено:
MazharYasinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
EXPERIMENT#2
PERFORMANCE OF RELATIVE DENSITY TEST ON
GRANULAR SOILS
ASTM D4254, ASTM D4253
OBJECTIVES
To find relative density of the granular soils by maximum and minimum void
ratios.
Applications of relative density to geotechnical projects involving cohesion-less
soil.
Relative density and percent compaction are commonly used for evaluating the
state of compactness of a given soil mass. The engineering properties, such as
shear strength, compressibility, and permeability, of a given soil depend on the
level of compaction.
RELATED THEORY
This experiment is performed to determine the relative density of cohesion less, free
draining soils using a vibrating table.
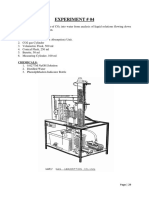
Schematic Drawing of a Typical Mold Assembly
The University of Lahore
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
RELATIVE DENSITY
Relative density or density index is the ratio of the difference between the void ratios
of a cohesion less soil in its loosest state and existing natural state to the difference
between its void ratio in the loosest and densest states.
The relative density of a soil is the ratio, expressed as a percentage
R =
R
e
e
100
(
(
)
)
Where
emax is the void ratio corresponding to the loosest density ( d min) of soil.
emin is the void ratio corresponding to the maximum density ( d max) soil.
ef is the void ratio corresponding to field density ( d f) of soil.
RELATIVE COMPACTION
Relative compaction is the percentage ratio of the field density to the maximum density
Relative compaction =
( )
VOID RATIO
Void ratio is the ratio between volumes of voids to the volume of soil solids.
It is denoted by e.
=
e=
MOULD SIZE SELECTION
Maximum size of
Mass of
soil particle
Soil (Kg)
Placement Device
Mould Volume
Surcharge
Weight (Kg)
3 (75mm)
34
Shower or Big scoop
0.5 ft3
86.2
1.5 (38mm)
34
Scoop
0.5ft3
86.2
0.75 (19mm)
34
Scoop
0.1 ft3
25.9
0.375 (9.5mm)
34
Funnel with spout
diameter of 1
0.1 ft3
25.9
0.187 (4.75mm)
34
Funnel with spout
diameter of 0.5
0.1 ft3
25.9
The University of Lahore
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
PROCEDURE
Take sample of cohesion less soil in its loosest form.
Check the maximum size of the soil particle and accordingly select the mould
and placement device.
Weigh the empty mould.
Measure the dimensions of empty mould.
Place the soil in mould with the help of a funnel and level the top surface with
the help of the spatula.
Weigh the Mould when fill with soil.
Now take the mould and place it on the vibrating table and fix it.
Note initial height with the help of dial gage (height of sample in loosest state).
Put 25 Kg weight on the plate and clamp the whole instrument.
Now start the vibrating table at amplitude of 60Hz frequency for 8 minutes.
Measure the height of the compacted soil sample after compaction with the help
of the dial gage.
Calculate d min and d max
d min =
d max =
Calculate e max and e min.
The University of Lahore
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
PRECAUTIONS
Funnel, through which the soil is to be placed, should be 0.5 to 1 above the
soil surface and there should be no contact between the lower-end of the funnel
with the soil surface.
The vibrating table should be operated at specified frequency conforming to
ASTM.
This experiment is applicable for soils containing up to 15% fine particles
(Passing #200) provided that the material is cohesion less and free draining.
Maximum particle size for this experiment is 3 (75mm).
OBSERVATIONS & CALCULATIONS
Diameter of Mould=d= 15.2 cm
Height of Mould=H=15.2 cm
Weight of Mould=
3.878 kg
Weight of Mould + Sand=
Weight of Sand=
Decreased Height
=
2.67
=8.234
kg
=8.234 3.878 = 4.356 kg
=12.7 cm
=1
= 1.72
Volume of sand when Mould is full=V=(
=
15.2
15.2
4
=2758.167 cm (Volume of loose soil)
The University of Lahore
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
Minimum dry density
=
=
W
V (in loose state)
4.356 1000
2758.167
= 1.579
Volume of Mould after compaction
15.2
12.7 = 2304.521 cm
4
=
Maximum dry density
W
V (in compacted state)
4.356 1000
2304.521
= 1.890 gmcm
Minimum void ratio
=
=
2.67 1
1 = 0.69
1.579
Maximum void ratio
=
2.67 1
1 = 0.41
1.890
Field void ratio
2.67 1
1 = 0.55
1.72
The University of Lahore
Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering
September 28, 2016
Relative density
100
=
=
0.69 0.55
100
0.69 0.41
= 49.63%
Relative compaction
=
=
100
1.72
100
1.890
= 91.00%
REFERENCE
ASTM D4253
Standard Test Methods for Maximum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils Using a
Vibratory Table
ASTM D4254
Standard Test Methods for Minimum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils and
Calculation of Relative Density
COMMENTS
It is generally recognized that either relative density or percent compaction is a good
indicator of the state of compactness of a given soil mass. However, the engineering
properties, such as strength, compressibility, and permeability of a given soil,
compacted by various methods to a given state of compactness can vary considerably.
Therefore, considerable engineering judgment must be used in relating the
engineering properties of soil to the state of compactness
In our case we get Relative density 49.63% and the relative compaction is 91%
The University of Lahore
10
Вам также может понравиться
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Soil Mechanics TestsДокумент9 страницSoil Mechanics TestsAfifah FauziОценок пока нет
- Standard Proctor Test ResultsДокумент4 страницыStandard Proctor Test Resultsmira asyafОценок пока нет
- Permiability Test Aim of The ExperimentДокумент7 страницPermiability Test Aim of The ExperimentArif AzizanОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics PowerpointДокумент239 страницSoil Mechanics PowerpointEdcel Angelo TomasОценок пока нет
- Material LaboratoryДокумент14 страницMaterial LaboratoryAnonymous tLXKwTОценок пока нет
- Field Density Lab ReportДокумент21 страницаField Density Lab ReportAnonymous DR3NznОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Foundation EngineeringДокумент39 страницLab Manual Foundation Engineeringartiraha100% (1)
- Design A Distillation Column With A Total Condenser and Partial Re Boiler For The Following SeparationДокумент41 страницаDesign A Distillation Column With A Total Condenser and Partial Re Boiler For The Following SeparationSihanu Subasingha100% (1)
- CBR (California Bearing Ratio) Test: 1. ObjectiveДокумент7 страницCBR (California Bearing Ratio) Test: 1. Objectivesdfsdf100% (1)
- Archimedes' PrincipleДокумент11 страницArchimedes' Principle1818dave100% (1)
- Thermal Composites FINALДокумент27 страницThermal Composites FINALTristan Joshua AlbaОценок пока нет
- Workability Test (Slump Test) Lab ReportДокумент10 страницWorkability Test (Slump Test) Lab ReportMAC DARREL MICHAEL MAC DARREL MICHAELОценок пока нет
- LINE SIZING CRITERIA PHILOSOPHY - Petroleum Corner PDFДокумент16 страницLINE SIZING CRITERIA PHILOSOPHY - Petroleum Corner PDFChowdhury FatemaОценок пока нет
- Water Cement Ratio (Gate60 Short Notes)Документ4 страницыWater Cement Ratio (Gate60 Short Notes)akash rathodОценок пока нет
- C6- Standard Consistency Cement PasteДокумент4 страницыC6- Standard Consistency Cement PasteMuhamad FarhanОценок пока нет
- Use of Non-Biodegradable Plastics in Flexible Pavement ConstructionДокумент74 страницыUse of Non-Biodegradable Plastics in Flexible Pavement ConstructionWaleed Bin YousufОценок пока нет
- CO2 Absorption ExperimentДокумент6 страницCO2 Absorption ExperimentRiazОценок пока нет
- Cube TestДокумент10 страницCube Testridhuanzainal100% (1)
- Falling Heat Permeability TestДокумент10 страницFalling Heat Permeability TestAiryn UyienОценок пока нет
- Data Analysis For Constant Head Permeability TestДокумент3 страницыData Analysis For Constant Head Permeability TestJackyu TeeОценок пока нет
- Atterberg LimitsДокумент8 страницAtterberg LimitsrbhavishОценок пока нет
- Report Silt Test For SandДокумент10 страницReport Silt Test For SandZanne Rose100% (1)
- Namibia University of Science and Technology: School of Engineering Bachelor of Engineering: Civil EngineeringДокумент6 страницNamibia University of Science and Technology: School of Engineering Bachelor of Engineering: Civil EngineeringHi270693Оценок пока нет
- CT Lab ManualДокумент26 страницCT Lab ManualJagathChandraОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Lab RecordДокумент55 страницSoil Mechanics Lab RecordshubhamОценок пока нет
- Constant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualДокумент3 страницыConstant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualmmОценок пока нет
- What Is The Difference Between Standard Proctor Test and Modified Proctor Test.Документ7 страницWhat Is The Difference Between Standard Proctor Test and Modified Proctor Test.Asif RajaОценок пока нет
- Standard oedometer and triaxial shear testsДокумент8 страницStandard oedometer and triaxial shear testsHiro Cerce Wilhelm ALDEN Abareta TonioОценок пока нет
- Ductility Test PDFДокумент4 страницыDuctility Test PDFAshishJamadarОценок пока нет
- Steel Lab ReportДокумент14 страницSteel Lab ReportDavid StamenovОценок пока нет
- Aggregate Testing Standards and LimitsДокумент4 страницыAggregate Testing Standards and LimitsAshadi HamdanОценок пока нет
- Curved BeamsДокумент2 страницыCurved Beamsivan bolañosОценок пока нет
- AGGREGATE Shape TESTSДокумент7 страницAGGREGATE Shape TESTSBernard KitosiОценок пока нет
- CE3A03 Consolidation Test Lab InstructionsДокумент5 страницCE3A03 Consolidation Test Lab InstructionsfostbarrОценок пока нет
- Overall Steve Edwards Vice President of Marketing at Ditten Hoefer SДокумент1 страницаOverall Steve Edwards Vice President of Marketing at Ditten Hoefer SAmit PandeyОценок пока нет
- School of Civil Engineering: A Project Report On Traffic Volume CountДокумент20 страницSchool of Civil Engineering: A Project Report On Traffic Volume Countsai vandan100% (1)
- Consolidation Lab Report: Integrity StatementДокумент19 страницConsolidation Lab Report: Integrity StatementAsad HafudhОценок пока нет
- Traffic SimulationДокумент32 страницыTraffic SimulationkarthikeanОценок пока нет
- 1.4 Manual On Project HydrologyДокумент28 страниц1.4 Manual On Project HydrologyPRABHUTIRUPURОценок пока нет
- Cube TestДокумент15 страницCube TestFAHIEMAH ZAHRA YAAKUBОценок пока нет
- 3 Constant HeadДокумент12 страниц3 Constant HeadWHfamilyОценок пока нет
- California Bearing RatioДокумент2 страницыCalifornia Bearing RatioKavi RamsagerОценок пока нет
- Soil Report 1Документ3 страницыSoil Report 1Akkash RaviОценок пока нет
- Lab 6: Specific Gravity of Sand and SoilДокумент16 страницLab 6: Specific Gravity of Sand and Soiljads docallosОценок пока нет
- Plastic Limit ReportДокумент7 страницPlastic Limit ReportAngelo John R. JavinezОценок пока нет
- Unconfined Compression TestДокумент11 страницUnconfined Compression TestAmiruddin JSОценок пока нет
- 2 Ss Unconfined Compression TestДокумент10 страниц2 Ss Unconfined Compression TestIqi IqahОценок пока нет
- Angularity Number SOPДокумент5 страницAngularity Number SOPSolankiОценок пока нет
- Liquid Limit and Plastic Limit Tests - Lab ExperimentsДокумент8 страницLiquid Limit and Plastic Limit Tests - Lab ExperimentsbilalОценок пока нет
- Determine Center of Pressure Using Hydrostatic ForceДокумент3 страницыDetermine Center of Pressure Using Hydrostatic ForceTemoteo L Pupa IIIОценок пока нет
- Density, Water Absorption & Compressive Strength of a BrickДокумент1 страницаDensity, Water Absorption & Compressive Strength of a BrickWan AzamОценок пока нет
- Penetration Test Lab ReportДокумент6 страницPenetration Test Lab ReportbawanlavaОценок пока нет
- Specific Gravity of Bitumen.Документ3 страницыSpecific Gravity of Bitumen.Bhaskar Pratim Das71% (7)
- Unconfined Compression Tests PDFДокумент6 страницUnconfined Compression Tests PDFHansen A JamesОценок пока нет
- Liquid and Plastic LimitДокумент13 страницLiquid and Plastic LimitDariusAngelitoОценок пока нет
- Impact of JetДокумент13 страницImpact of JetUmmi SurayaОценок пока нет
- StudentДокумент7 страницStudentKartik AryanОценок пока нет
- 04 Grain Size DistributionДокумент6 страниц04 Grain Size DistributionChristine Joy Casas AgquizОценок пока нет
- Discharge Through An Orifice: ME419 Fluid Mechanics LabДокумент13 страницDischarge Through An Orifice: ME419 Fluid Mechanics LabMansor MajbriОценок пока нет
- Silt ContentДокумент2 страницыSilt ContentBhupesh MulikОценок пока нет
- To Determine Specific Gravity of Solids by Pycnometer MethodДокумент3 страницыTo Determine Specific Gravity of Solids by Pycnometer MethodRahul KumarОценок пока нет
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985От EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Relative Density or Density Index of Sand (Is-2720-Part-15)Документ3 страницыDetermination of Relative Density or Density Index of Sand (Is-2720-Part-15)muhammad iqbalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 (Week 11) - DrRAДокумент38 страницChapter 4 (Week 11) - DrRAMUHAMMAD ZUHAIR NORAZLIОценок пока нет
- Construction Project StakeholdersДокумент19 страницConstruction Project StakeholdersMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- SBR LatexДокумент2 страницыSBR LatexMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Const.P. 2 2011Документ42 страницыConst.P. 2 2011MazharYasinОценок пока нет
- "Dear Students, Due Dates For Fall-2018 Semester Fee Are Mentioned BelowДокумент1 страница"Dear Students, Due Dates For Fall-2018 Semester Fee Are Mentioned BelowAlauddin Ahmad KHAN KHANОценок пока нет
- Construction and Building MaterialsДокумент9 страницConstruction and Building MaterialsMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Drawing Lecture-1Документ28 страницDrawing Lecture-1MazharYasinОценок пока нет
- GGBFSДокумент2 страницыGGBFSMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Citation 222245843Документ36 страницCitation 222245843MazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Burned Clay Pozzolana-Used PDFДокумент9 страницBurned Clay Pozzolana-Used PDFMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Light Weight ConcreteДокумент23 страницыLight Weight ConcreteMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- 3Документ4 страницы3MazharYasinОценок пока нет
- HOT WEATHER CONCRETING TIPSДокумент6 страницHOT WEATHER CONCRETING TIPSMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- CM 425 - Properties of Fresh Concrete PDFДокумент14 страницCM 425 - Properties of Fresh Concrete PDFTran Huynh NamОценок пока нет
- Cement: The Binding Building MaterialДокумент12 страницCement: The Binding Building MaterialMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Public Notice CE 2019 English PDFДокумент1 страницаPublic Notice CE 2019 English PDFMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Uol HRD EdifДокумент1 страницаUol HRD EdifMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Citation 222245843Документ1 страницаCitation 222245843MazharYasinОценок пока нет
- PlanДокумент1 страницаPlanMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Untitled MapДокумент1 страницаUntitled MapMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 10: To Determine The Effect of Rate of Loading On The Compressive Strength of P.C.C Cube and CylinderДокумент3 страницыExperiment No. 10: To Determine The Effect of Rate of Loading On The Compressive Strength of P.C.C Cube and CylinderMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Structurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceДокумент1 страницаStructurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Table: Assembled Joint Masses Joint Masssource U1 U2 U3 R1 R2 R3 CenterxДокумент80 страницTable: Assembled Joint Masses Joint Masssource U1 U2 U3 R1 R2 R3 CenterxMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Public Notice CE 2019 EnglishДокумент4 страницыPublic Notice CE 2019 EnglishMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Slab DesignДокумент78 страницSlab DesignMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Brick BondsДокумент4 страницыBrick BondsMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- ReactionsДокумент2 страницыReactionsMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Structurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceДокумент1 страницаStructurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Structurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceДокумент1 страницаStructurepoint - Spcolumn V5.50 (TM) - 1869762670 Day Trial License. Locking Code: 4-31D37. User: Mazhar Yasin, MsceMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- SP ColumnДокумент2 страницыSP ColumnMazharYasinОценок пока нет
- Control Valve SizingДокумент5 страницControl Valve SizingMostafa SharafОценок пока нет
- DURACON CONCRETE DENSIFIER HARDENS & DENSIFIES SURFACESДокумент2 страницыDURACON CONCRETE DENSIFIER HARDENS & DENSIFIES SURFACEStejas_tОценок пока нет
- Density Lab GuideДокумент7 страницDensity Lab Guideyesha arlertОценок пока нет
- Characterization of Malaysia Sand For Possible Use As ProppantДокумент9 страницCharacterization of Malaysia Sand For Possible Use As ProppantRafaelMauricioSepulvedaRuizОценок пока нет
- The Land Ethic - Aldo LeopoldДокумент21 страницаThe Land Ethic - Aldo LeopoldJuris MendozaОценок пока нет
- Pomegranate Aril Handling and Friction Characteristics by MaturityДокумент14 страницPomegranate Aril Handling and Friction Characteristics by MaturityAzslanОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics Individual Assignment IДокумент5 страницHydraulics Individual Assignment Ikibrom fishaОценок пока нет
- RP - 16.6 Methods and Equipment For Calibration of Variable Area Meters (Rotameters) PDFДокумент18 страницRP - 16.6 Methods and Equipment For Calibration of Variable Area Meters (Rotameters) PDFmilecsaОценок пока нет
- Cabbage Cold Storage Design and Cooling Time CalculationДокумент11 страницCabbage Cold Storage Design and Cooling Time Calculationrey mondОценок пока нет
- Symp00 Paper19Документ18 страницSymp00 Paper19anon-282063Оценок пока нет
- 10-Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Flow Meters PDFДокумент10 страниц10-Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Flow Meters PDFxjaf01Оценок пока нет
- Solid Propellant Rocket Nozzle ErosionДокумент27 страницSolid Propellant Rocket Nozzle ErosionThota Sri K Haritha100% (1)
- A Comparative Study of Silicon Surface Passivation Using Ethanolic Iodine and Bromine SolutionsДокумент5 страницA Comparative Study of Silicon Surface Passivation Using Ethanolic Iodine and Bromine Solutionsbib123456789huОценок пока нет
- Development of Nusselt Number Correlation Using Dimensional Analysis For Plate Heat Exchanger With A Carboxymethyl Cellulose SolutionДокумент9 страницDevelopment of Nusselt Number Correlation Using Dimensional Analysis For Plate Heat Exchanger With A Carboxymethyl Cellulose SolutionnghiОценок пока нет
- Overpressure generation by load transfer following shale framework weakeningДокумент15 страницOverpressure generation by load transfer following shale framework weakeningLok Bahadur RanaОценок пока нет
- Civil Lab 1Документ10 страницCivil Lab 1Zain Ul AbidinОценок пока нет
- Methods For Estimating Petrophysical Parameters From Well Logs in Tight Oil Reservoirs: A Case StudyДокумент8 страницMethods For Estimating Petrophysical Parameters From Well Logs in Tight Oil Reservoirs: A Case StudyVinod KumarОценок пока нет
- 18CV33 NewДокумент102 страницы18CV33 NewAkon JoshОценок пока нет
- ALS Geochemistry Service Schedule 2013 - USDДокумент44 страницыALS Geochemistry Service Schedule 2013 - USDlarv00970% (1)
- 5560 English PDFДокумент11 страниц5560 English PDFdonyaОценок пока нет
- Sysdrill v3.0 Release NotesДокумент39 страницSysdrill v3.0 Release NotescodigocarnetОценок пока нет
- Apparant DensityДокумент2 страницыApparant Densityaman anandОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 OscillationsДокумент24 страницыNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 Oscillationsaniruddha deshpandeОценок пока нет
- Material Stream: VAP: ConditionsДокумент13 страницMaterial Stream: VAP: ConditionsSuleman AhmadОценок пока нет
- Aashto T 224 2012Документ6 страницAashto T 224 2012Jose LuisОценок пока нет