Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
W41 Gas Laws Ex 3
Загружено:
Bid HassanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
W41 Gas Laws Ex 3
Загружено:
Bid HassanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
@cikgubid
Name of student: _________________________
Class:
Date:
Week:
Time:
Wednesday
12.10.16
41
(6.30 pm 9.30 pm)
Kipli Yassin Resources, Heritage Garden
Subject:
Topic:
1
2
3
PHYSICS, Form 4
4 HEAT
4.4 Gas Laws Exercise 3
The kinetic theory of gas is based on the following assumptions
The molecules in a gas move freely in random motion and possess kinetic energy.
The force of attraction between the molecules are negligible.
The collisions of the molecules with each other and with the walls of the container are elastic collisions.
Boyles Law
P1
V
That is PV = constant
Or P1V1 = P2V2
Small volume molecules hit wall more often, greater pressure
Relationship between pressure and volume
Boyles law states that for a fixed mass of gas, the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to its volume when the
temperature is kept constant.
Boyles law can be shown graphically as in Figure below:
P
(a) P inversely proportional to V
3
1/V
(b) P directly proportional to 1/V
The volume of an air bubble at the base of a sea of 50 m deep is 250cm 3. If the atmospheric pressure is 10m of water,
find the volume of the air bubble when it reaches the surface of the sea.
P2= 10m
PI =50m + 10m
V1=250cm3
P1V1 = P2V2
60m (250 x 10-6)m3 = 10m x V2
1.5 x 10-3 m3 = V2
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Physics Form 4
An air bubble of capacity 15 cm3 at a pressure of 320 cm Hg is released from the sea. Determine the volume of the
bubble when it reaches the surface of water, if the atmospheric pressure is 76 cm Hg. Assume that the temperature of
the water is constant. [Ans: 63 cm3]
A bicycle pump of length 40 cm has a uniform cross-sectional area. It contains air at atmospheric pressure. If
the piston is pushed down a distance of 17 cm to force air into a tyre, what is the resultant air pressure in the
pump? Assume that the temperature of the air is constant. [Patm = 1 atm] [Ans: 1.74 atm]
Figure 6
Figure 6(a) shows a glass tube closed at one end with a small quantity of mercury trapped inside. When the
tube is in a horizontal position, the length of air column at the closed end of the tube is 8 cm and the length of
the mercury column is 2 cm.
(a) What is the pressure of the air trapped inside the tube in a horizontal position?
(b) What is the length of the column of air trapped inside the tube, when the tube is in a vertical position as
shown in Figure 6(b)?
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Physics Form 4
Figure 7
A rod of tube with one end closed has a strip of mercury 3 cm long. When the tube is held vertically, the
length of air trapped is 8 cm as in Figure 7(a). Atmospheric pressure is taken as 76 cm Hg.
(a) Calculate the length, x of air which is trapped when the tube is placed horizontally as in Figure 7(b).
(b) Calculate the length, y of air trapped when the tube is inverted as shown in Figure 7(c).
A bubble of air with volume 4 cm3 is released from a submarine at the depth of 50 m. What will be the volume of the
bubble when it has risen to a depth of 14 m? [Atmospheric pressure = 10 m water]
An air bubble released by a diver has a volume of 6.0 cm3 at the depth of 5 m. What is the volume of the bubble at a
depth of 2 m? [Atmospheric pressure = 10 m water] [ Ans: 7.5 cm3]
10
Figure 10 shows trapped air inside a thin glass tube in three different positions. [P atm = 76 cm Hg]
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 10
Determine the value of x and y.
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Charless Law
Physics Form 4
VT
that is V = constant
T
Higher temperature, faster molecules, larger volume to keep the pressure consta
Relationship between volume and temperature
Lower temperature
Charles law states that for a fixed mass of gas, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to its absolute
temperature when its pressure is kept constant.
The temperature -2730C is the lowest possible temperature and is known as the absolute zero of temperature.
Fill the table below.
Temperature
Absolute zero
Ice point
Steam point
Unknown point
Kelvin Scale(K)
0
273
373
( + 273 )
Complete the diagram below.
-273
Celsius scale (0C)
-273
0
100
100
/0C
A syringe in a refrigerator contains 4.5 ml of air at 3 oC. When the syringe was taken out and placed in a room where
the temperature was 27oC, the air in it expands. Calculate the final volume of the air in the syringe. [ Ans: 5.0 ml]
The volume of a fixed mass of gas is 150 cm3 at 35oC. If the gas is heated at a constant pressure, what is the volume of
the gas when the temperature reaches 87oC?
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Physics Form 4
Figure below shows a glass tube containing some trapped air inside it. At 27 oC, the horizontal column of trapped air is
9 cm.
If the atmospheric pressure does not vary, how much is the horizontal column of air at a temperature of 45 oC.
[Ans: 9.54 cm3]
Pressures Law
PT
That is P = constant
T
Higher
temperature
molecules move
faster, greater
pressure
Relationship between
pressure and temperature
1
The pressure law states that for a fixed mass of gas, the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to its absolute
temperature when its volume is kept constant.
An iron cylinder gas has a pressure of 360 kPa when it is kept in a store at temperature 27 oC. What is the pressure of
the gas when the cylinder is moved outdoors where the temperature is 40 oC? [Ans: 375.6 kPa]
Before a journey from Kuching to Lundu, the air in a car tyre has a pressure of 200 kPa and a temperature of 27 oC.
After the journey, the air pressure in the tyre is 240 kPa. What is the temperature of the air in the tyre after the
journey? [Assume the volume of the tyre is constant] [ Ans: 87oC]
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Physics Form 4
The pressure of nitrogen gas in a light bulb is 60 kPa at 20 oC. Calculate the temperature of the gas when the pressure
inside the bulb rises to 90 kPa after the bulb is lighted up. [ Ans: 166.5oC]
A closed flask contains gas at a temperature of 95 oC and pressure of 152 kPa. If the temperature is reduced to 17 oC,
what is the new pressure of the gas? [Ans: 106 kPa]
A motorcycle tyre is found to possess a pressure of 3.2 atmospheric when it was tested in a garage at a temperature of
27oC. By assuming that the volume of the air in the tyre is fixed, what is the surrounding temperature if the tyre is
found to possess a pressure of 3.5 atmospheric? [ Ans: 55oC]
@cikgubid
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws, Exercise 3
@KYRHG
The product of pressure and volume of a fixed
mass of gas at constant temperature is
A a variable
B equal to one
C a constant
D negative
Absolute zero is the temperature at which gas
molecules theoretically
A occupy no volume at all
B move the fastest
C will read 273oC in temperature
D contain twice the number of molecules at
room temperature
Mercury freeze at 234 K. What is this temperature
in oC?
A. 39
C. 30
B. 12
D. 72
Which of the following statements about the gas
pressure is false?
A Gas molecules collide with each other to
produce gas pressure.
B Gas molecules move randomly at high speed.
C The collisions between the molecules
themselves and collisions between molecules
and wall of containers are elastic.
D Gas molecules always collide with the wall of
container to produce gas pressure.
When the gas in an enclosed container is heated at
fixed pressure, what will happen to the frequency
of collisions between the gas molecules?
A. It decreases.
B. It increases.
6
Physics Form 4
C. It remains constants.
When a fixed mass of gas expands slowly at fixed
temperature, which of the following quantities
increases?
A Kinetic energy of gas
B Average speed of gas
C Gas pressure
D Volume of gas
What will happen when a fixed mass of gas in an
enclosed container is compressed slowly without
any change in temperature?
A The gas pressure increases.
B The volume of gas remains constant.
C The kinetic energy of gas increases.
D The distance between gas molecules increases.
The volume of an air bubble at the base of a sea of
50 m deep is 200 cm3. If the atmospheric pressure
is 10 m of water, find the volume of the air bubble
when it reaches the surface of the sea.
A. 1000 cm3
C. 1250 cm3
3
B. 1200 cm
D. 1450 cm3
The volume of an air bubble is 5 mm3 when it is at
a depth of h cm below the water surface. Given
that its volume is 15 mm3 when it is at a depth of 2
m, find the value of h.
[Atmospheric pressure = 10 m of water]
A. 10
B. 15
C. 22
D. 26
10 A gas of volume 20 m3 at 37oC is heated until its
temperature becomes 87oC at constant pressure.
What is the increase in volume?
A. 3.2 m3
C. 7.2 m3
3
B. 5.2 m
D. 8.2 m3
11 The volume of a gas is 1 cm3 at 15oC. The gas is
heated at fixed pressure until the volume becomes
triple the initial volume. Calculate the final
temperature of the gas.
A. 325oC
C. 485oC
B. 442oC
D. 591oC
12 The air pressure in a container at 33oC is
1.4 10 5 Nm 2
. The container is heated until the
temperature is 55oC. What is the final air pressure
if the volume of the container is fixed?
1.30 10 5 Nm 2
A.
C.
5
1.50 10 Nm
B.
1.60 10 5 Nm 2
1.62 10 5 Nm 2
D.
13 The air pressure in one of the tyres of a car is 25
kPa at 27oC. After a long journey, the temperature
of the air in the tyre is 87oC. Find the air pressure
in the tyre now.
A. 27 kPa
C. 30 kPa
B. 29 kPa
D. 32 kPa
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
Physics Form 4
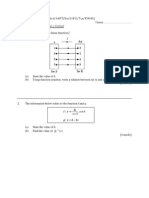
14 Diagram 14.1 and Diagram 14.2 shows two identical flasks being heated with different quantity of heat for 15
minutes.
Diagram 14.1
Diagram 14.2
(a) State the physical quantity represented by the difference of two mercury levels, X and Y.
(b) Why must the level of the mercury be fixed at X?
(c) Based on Diagram 14.1 and Diagram 14.2,
(i)
compare the difference of two mercury levels, h and H.
(ii)
compare the readings of the two thermometers,
(iii)
compare the amount of heat supplied for 15 minutes
W41, 4.4 Gas Laws
@KYRHG
(iv)
(d) (i)
(ii)
Physics Form 4
state the relationship between the heat supplied and the temperature.
Sketch a graph of air pressure against temperature in Kelvin.
State the relationship between the pressure and the temperature of air.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Nidek GYC-1000 Photocoagulator - Technical TrainingДокумент85 страницNidek GYC-1000 Photocoagulator - Technical TrainingAngela RoblesОценок пока нет
- 06 The Chlor-Alkali Industry PDFДокумент26 страниц06 The Chlor-Alkali Industry PDFpetrolorito100% (2)
- Supervision Manual As Guidance For Supervisory StaffДокумент20 страницSupervision Manual As Guidance For Supervisory StaffAxelОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1: Phase Equilibrium: Figure 1. Handwritten Sample CalculationДокумент13 страницProblem Set 1: Phase Equilibrium: Figure 1. Handwritten Sample CalculationJay SableОценок пока нет
- Nippon Steel Seamless CasingДокумент18 страницNippon Steel Seamless Casingjohndo3Оценок пока нет
- ASTM Casting MaterialsДокумент1 страницаASTM Casting Materialschy_81Оценок пока нет
- Revision AddMaths SPM 2010 12.11.10Документ2 страницыRevision AddMaths SPM 2010 12.11.10Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- Khodaie Et Al-ACI Spring 2016Документ13 страницKhodaie Et Al-ACI Spring 2016erosОценок пока нет
- W31 Coordinate Geometry SPM QuestionsДокумент7 страницW31 Coordinate Geometry SPM QuestionsBid HassanОценок пока нет
- Aws D1.1 - WPS - Smaw-Fcaw PDFДокумент1 страницаAws D1.1 - WPS - Smaw-Fcaw PDFBernathTurnipОценок пока нет
- Penetration Limits of Conventional Large Caliber Anti Tank - Kinetic Energy ProjectilesДокумент9 страницPenetration Limits of Conventional Large Caliber Anti Tank - Kinetic Energy ProjectilesSteve RothwellОценок пока нет
- W45 5.3 Total Internal Reflection Ex2Документ2 страницыW45 5.3 Total Internal Reflection Ex2Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- 4.4 Gas Laws: 1 Wednesday 40Документ5 страниц4.4 Gas Laws: 1 Wednesday 40Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- W44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionДокумент6 страницW44 5.3 Total Internal ReflectionBid HassanОценок пока нет
- 2.10 Work, Energy, Power & Efficiency Ms As Shown in The Figure BelowДокумент1 страница2.10 Work, Energy, Power & Efficiency Ms As Shown in The Figure BelowBid HassanОценок пока нет
- AddMaths Form 5 Revision P1Документ2 страницыAddMaths Form 5 Revision P1Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- Week 29 Revision ExerciseДокумент2 страницыWeek 29 Revision ExerciseBid HassanОценок пока нет
- Revision Addmaths Form 5 2016Документ5 страницRevision Addmaths Form 5 2016Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- AddMaths Test 1 Hour 40 MinsДокумент1 страницаAddMaths Test 1 Hour 40 MinsBid HassanОценок пока нет
- 2.12 Understanding ElasticityДокумент10 страниц2.12 Understanding ElasticityBid HassanОценок пока нет
- Revision ExerciseДокумент3 страницыRevision ExerciseBid HassanОценок пока нет
- W4 Revision 1Документ2 страницыW4 Revision 1Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- Revision 3 W11 TueДокумент2 страницыRevision 3 W11 TueBid HassanОценок пока нет
- Revision W32TueoДокумент2 страницыRevision W32TueoBid HassanОценок пока нет
- Answer All Questions.: Progressive Tes 1 30 MinutesДокумент1 страницаAnswer All Questions.: Progressive Tes 1 30 MinutesBid HassanОценок пока нет
- 3.1: Quadratic Functions & Its Graph (Fungsi Kuadratik & Grafnya)Документ1 страница3.1: Quadratic Functions & Its Graph (Fungsi Kuadratik & Grafnya)Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- AddMaths Revision Exercise SPM 2015Документ6 страницAddMaths Revision Exercise SPM 2015Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- Quadratic EquationsДокумент6 страницQuadratic EquationsCYОценок пока нет
- Revision Exercise (Chapter 1 - 7) Addmaths Form 4, W31: July 26, 2012Документ2 страницыRevision Exercise (Chapter 1 - 7) Addmaths Form 4, W31: July 26, 2012Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- CHP 8.2 Normal (Mon) W26Документ8 страницCHP 8.2 Normal (Mon) W26Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- CHP 8 Binomial Revision ExeДокумент2 страницыCHP 8 Binomial Revision ExeBid HassanОценок пока нет
- JEE Main 2023 31 January Shift 2Документ13 страницJEE Main 2023 31 January Shift 2barnwalk367Оценок пока нет
- KC WS+rock-H - DatasheetДокумент2 страницыKC WS+rock-H - DatasheetIoana PopescuОценок пока нет
- 2014 Van DijkДокумент77 страниц2014 Van DijkJungHyunParkОценок пока нет
- 60 - BS 13577 2007Документ12 страниц60 - BS 13577 2007mazos77Оценок пока нет
- Nureg CR 4513Документ193 страницыNureg CR 4513raelgfsОценок пока нет
- BELZONA 1111 Product Specification SheetДокумент2 страницыBELZONA 1111 Product Specification Sheetsibi_s_rajОценок пока нет
- 0 14 en PDFДокумент74 страницы0 14 en PDFPPMA IndonesiaОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 ClimateДокумент14 страницUnit 4 Climatebego docenciaОценок пока нет
- Thesis PagesДокумент68 страницThesis PagesarunОценок пока нет
- Slugging in A Flare HeaderДокумент34 страницыSlugging in A Flare Headercepong89Оценок пока нет
- (VCE Biology) 2007 Chemology Unit 1 Exam and SolutionsДокумент28 страниц(VCE Biology) 2007 Chemology Unit 1 Exam and SolutionsJustine LyОценок пока нет
- ExportДокумент686 страницExportRony JamesОценок пока нет
- Standard For Food Grade Salt PDFДокумент5 страницStandard For Food Grade Salt PDFMercyОценок пока нет
- Dr. Sapana Garg - 16-2-18Документ10 страницDr. Sapana Garg - 16-2-1816_dev5038Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Tables UpdatedДокумент50 страницThermodynamic Tables Updatedmiraabellaa247Оценок пока нет
- X X X A T: MECH 364 Assignment 2Документ9 страницX X X A T: MECH 364 Assignment 2Chandra SekarОценок пока нет
- CHEM-E2150 - 7 Surface Interactions Part 1van Der Waals ForcesДокумент41 страницаCHEM-E2150 - 7 Surface Interactions Part 1van Der Waals ForcesDikshit SynergyОценок пока нет
- Method Descriptions Screen Assay ME SCR21Документ2 страницыMethod Descriptions Screen Assay ME SCR21guanakhoОценок пока нет
- Structural Analysis Tutorial 7Документ5 страницStructural Analysis Tutorial 7pratyush mishraОценок пока нет
- HS-C0964SA3 / HS-C1264SA4 HS-C1865SA4 / HS-C2465SA1: FeaturesДокумент1 страницаHS-C0964SA3 / HS-C1264SA4 HS-C1865SA4 / HS-C2465SA1: FeaturesklseklseОценок пока нет