Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biology Vocabulary Revision
Загружено:
ddddddffdfdfАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biology Vocabulary Revision
Загружено:
ddddddffdfdfАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
Biology(chapter1-9)
Glossary
Chapter1 Classification
classification()
Kingdom
phylum( phyla)
class
order
family
Genus( genera)
specie
['kidm]
['failm]
[kl:s]
[:d]
['fmili]
['spi:i]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
prokaryotes
protoctists
fungi( fungus)
plants
animals
[pru'kriut]
n.
[fga]
[pl:nt]
['niml]
n.
n.
n.
arthropods
nematodes
annelids
molluscs
vertebrates
[:rpd]
['nemtud]
['nelidz]
['mlsk]
['v:tbrt, -,bret]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
fish
birds
mamals
reptiles
amphibians
[fi]
[b:d]
['mml]
['reptail]
[m'fbi:n]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
['di:ns]
characteristic
Mrs Gren
Movement
Reproduction
Sensitivity
Key definitions
An action by an organism or part of an organism causing a
change position or place.
The process that make more of the same kind of organism
The ability to detect or sense changes in the environment and
to make responses.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
Growth
Respiration
Excretion
Nutrition
A permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in
cell number or cell size or both.
The chemical reactions that break down nutrients molecules
in living cells to release energy
Removal from organisms of toxic materials,the waste producs
of metabolism(chemical reactions in cells including
respiration) and substances in excess of requirement.
The taking in of nutrients which are organic substances and
mineral ions, containing raw materials or energy for growth
and tissue repair,absorbing and assimilating them.
Chapter2 Cells
Apparatus
microscope
light microscope
electron microscope
photomicrograph
['maikrskup]
n.
n.
n.
n.,
Cell structure
celll wall
cell membrane
cytoplasm
vacuole
chloroplast
nucleus
mitochondrion
organelle
tissue
organ
All plant cells are surrounded by a cell wall made mainly of
cellulose. Give cells strength, help to protect and support
them. Fully permeable.
Controls the entrance and exit of substances, made of protein
and fat. Partially permeable.
A clear jelly which is nearly all water, containing many
substances dissolved in it, especially protein. Many metabolic
reactions take place.
Plant cellls have large vacuoles,which contain a solution of
sugars and other substances, called cell sap(). Animal
cells have much smaller vacules,which contain food or water.
Plant cells have chloroplasts. Thety Contain the green
pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight for
phtosythesis. Chloroplasts contain starch grains made by
phtosythesis.
Controls the activities of cells. Contains chromosomes(
)where inherit information stores.
A place where the respiration occurs
[,:g'nel]
['tisju:]
[':n]
n.
n.
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
organ system
organism
[':nizm]
n.
n.,
Chapeter3 Movement in and out of cells
diffusion
osmosis
active transport
diffuse
osmose
concentration gradient
concentrated
dilute
swell(swolled,swollen)
shrink(shrunk,shrunk)
turgid
plasmolysed
shrivel
stretch
carrier protein
The net movement of molecules from a region of high
concentration to a region of low concentration down a
concentration gradient as a result of their random
movement.
The diffusion of water molecules from a region of their
high concentration to a region of their low concentration,
throngh partially permeable.
The movement of ions in or out of a cell through the cell
membrane, from a region of their lower concentration to a
region of their higher concentration against a
concentration gradient, using energy (ATP)released during
respiration.
[di'fju:s]
vt. & vi.(), ()
['zmus]
v.()
n.
['knsntretd]
adj.
[dai'lju:t]
adj. ()
[swel]
vt. & vi.,
[rik]
vt. & vi.
['t:dd]
adj.
['plzmulaiz]
adj.()
[rvl]
v.
[stret]
vt. & vi.;
n.
Chapter4 The chemicals of life
metabolism
carbohydrate
monosaccharide(simple sugar)
glucose
disaccaride(complex sugar)
sucrose
maltose
polysaccharide
starch
cellulose
glycogen
[m'tb,lzm]
[,k:bu'haidreit]
[,mnu'skraid]
['glu:,ks]
[dai'skraid]
['sju:krus]
['m:ltus]
[pli'skraid]
[st:t]
['selj,ls, -,lz]
['laikuden]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.,
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
Plants: get glucose via photosythesis. transport sucrose.Store starch.
Animals: get glucose from food, store glycogen.
fat
lipid
fatty acid
glycerol
[ft]
[lpd, lapd]
n.,
n.
n.
-,rl, n.,
['gls,r:l,
-,rl]
['d,ps 'tisju: ]
['pruti:n]
adipose tissue
protein
ammino acid
n.
n.
n.
experiments
grind
tile
reagent(reactant)
product
Benedicts solution(contains
blue copper salts
emulsion
globule
iodine solution
[raind]
[tail]
[ri:'ednt]
['prdkt]
['bendkts]
vt. & vi.
n.,
n.,
n.
n.
['mln]
['lbju:l]
n.,
n.
n.
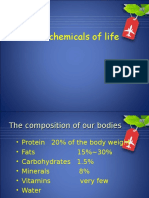
Carbohydrates, fats and proteins
carbohydrates
Elements they contain
C,H,O
Smaller molecules of monosacharrides
which they are made
fats
C,H,O
fatty acids
and
glycerol
Solubility in water
Sugars are soluble insoluble
Why organisms need Easily
availble Storage of
them
energy(15KJ/g)
energy(39
KJ/g),mak
ing
cell
membrane
s
proteins
C,H,O,N
amino acids
some are soloble
Making
cells,antibodies,enzymes,
haemoglobin and many
other
substances;also
used for energy
Chapter5 Enzymes
catalyst
['ktlst]
enzyme
['enzam]
n., a subtance that speed
up a chemical reaction and is not
changed by the reaction.
n. proteins that function as
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
activate
speed upaccelerate
break down
['ktiveit]
biological catalysts
vt., ,
v.
v.
The name of enzymes
carbohydrase
[k:buhaidreis]
maltase
sucrase
lactase
amylase
catalase
phosphorylase
protease
lipase
pectinase
['m:lteis]
['su:kreis]
['lkteis]
['m,leis]
['ktleis]
['fsfri,leis]
['prutieis]
['laipeis,'lipeis]
['pektineis]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.,
n.
n.
n.
n.
Structure and properties of enzymes
lock and key theory
dent
active site
substrate
slot
denature
optimum
optimum
temperature/pH
specific
[dent]
['sb,stret]
[slt]
[di:'neit]
['ptimm]
[spi'sifik]
n.
n.,
n.
n.,
vt.;
vt.
adj.;
The temperature/ph at which an
enzyme works fastest.
adj.,
Chapter6 Plant nutrition
photsynthesis
[,ft'snss]
n.
photosynthesize
[,futu'sinisaiz] v.
cabon dioxide + water sunlight glucose + oxygen
chlorophyll
Leaves
lamina
vein
midrib
petiole
vascular bundles
['lmin]
[vein]
['midrib]
['petiul]
n.
n.
n.()
n.,
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
cuticle
['kju:tkl]
upper epidermis
[,ep'd:ms]
palisade layer
spongy layer
[,pl'sed]
['spndi:]
mesophyll layer
stoma( stomata)
['mesfil]
['stum]
guard cell
xylem
['zailem]
lignin
phloem
['linin]
['fluem]
sieve plate
companion cell
n.() stop
water evaporating from the leaf.
n. no chlorophyll. Protect the
inner layers
n. most photosynthesis
n. some photosynthesis. Have
large air space
n.
n. oxygen and carbon dioxide
move in or out by diffusion through
stomata
n. control the stomata open
or close
n. carry water upward,dead
cells,helps to support plants. No end
wall
n.
n. carry sugars downward.
Has end wall
n.
n. () has nucleus
Investigation
destarch
control
flammable
alcho
beaker
rubber bung
test tube
Bunsen burner
limiting factor
[di'st:t]
[kn'trul]
['flmbl]
['lk,hl]
['bi:k]
['rb b]
['bnsn 'b:n ]
v.
n.
adj.,
n.;
n.
n.
n.
n.
n. something present in the
environment in such short supply that
it restrict life process.
Chapter7 Animal nutrition
diet
vitamin
fibre
mineral
peristalsis
stimulate
contract
['dait]
['vitmin]
['faib]
['minrl]
[,peri'stlsis]
['stimjuleit]
[kn'trkt]
n.
n.
n.()
n.
n.
vt.;
vt. & vi.;
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
relax
constipation
constipate
cholesterol
obesity
starvation
malnutrition
kwashiorkor
single
proteinSCP
mycoprotein
food additive
flavoring
colouring
presevative
emulsifier
[ri'lks]
[,knst'pen]
['knstipeit]
[k'lestrl]
['bi:sti:]
[st: 'ven]
['mlnju'trin]
[,kw:i':k:]
vt. & vi. ()
n.
v.
n.
n.;
n.,
n. not eating a balanced diet
n., caused
by a lack of protein in diet
n.
[,maiku'pruti:n]
n.
n.
n. ,
n.
n.
n.
cell
['fleivri]
['klr]
[pri'z:vtiv]
[i'mls,fa]
The processes of animals dealing with food
ingestion
[in'destn]
digestion
[dai'destn]
absorption
[b's:pn,
-'z:p-]
egestion
[i'destn]
assimilation
['sim'lein]
n. taking the substances(e.g
food,drink) into the body through
mouth
n. The break-down of
large,insoluble food molecules into
small,water-soluble molecules using
mechanical and chemical processes
n. the movement of digested
food molecules through the wall of
the intestine into the blood or lymph.
n. the passing out of food that
has not been digested ,as faeces
,through the anus.
The movement of digested food
molecules into the cells of body
where they are used,becoming part
of the body
Digestion
digest
mechanical digestion
chemical digestion
[dai'dest]
[mi'knikl]
['kemikl]
vt. & vi.
n.
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
tooth( teeth)
crown
root
[tu:]
[kraun]
[ru:t]
n.,
n. the part can be seen of teeth
n. the part embedded( ) in the
gum
n. very
hard, can be dissolved by acids.
n. hard, like bone, has chanels
in it which contain living cytoplasm
n. contains nerves and blood
vessels
n.
enamel
[i'nml]
dentine
['denti:n]
pulp cavity
[plp 'kviti]
gum
[m]
cement
[si'ment]
jawbone
incisor
['d:,bn]
[n'saz]
canine
['kenan]
premolar
molar
wisdom teeth
milk teeth
(deciduous teeth)
['pri:'mul]
['mul]
['wizdm]
n. large teeth towards the back of
n. the mouth. Used for chewing food
[d'sdu:s]
have.These start to grow at the age of 2430months, most children have 20 teeth
permanent teeth
['p:mnnt]
plaque
tartar
[plk]
['t:t]
n., most people have all
their 32 permanent teeth by about 17
years of age.
n. causes tooth decay()
n. cannot remove by brushing
alimentary canal
tongue
saliva
[li'mentri
k'nl]
[t]
[s'lav]
salivary duct
salivary gland
oesophagus
small intestin
[dkt]
[lnd]
['sfgs]
[n'testn]
n. cover the root, has fibres
growing out of it which is attach the
tooth to jawbone.
n.
n.
sharp-edged,chisel-shaped
teeth at the front of the mouth. Used
for bitting off pieces of food.
n. more pointed teeth at the
either side of incisors.
n.
n. ; the first set of teeth people
n.
n. mixes the food with saliva
n. , a mixture of
water,mucus and amylase
n. carry saliva to the mouth
n. produce saliva
n.,
n. between stomach and the
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
duodenum
ileum
large intestine
colon
rectum
caecum
appendix
anus
liver
[,dju(:)u'di:nm]
['ilim]
hepatic
bile
bile salts
[h'ptk]
[bal]
['kuln]
['rektm]
['si:km]
['pendiks]
['eins]
['liv]
bile pigment
bile duct
gall bladder
pancreas
pancreatic duct
pancreatic juice
[g:l 'bld]
['pkri:s]
stomach
gastric juice
['stmk]
['gstrk]
pepsin
rennin
['pepsn]
['renin]
hydrochloric acid
sphincter
['sfikt]
bolus of food
chyme
['buls]
[kaim]
villus( villi)
['vils]
colon. About 5m long. Quite narrow.
n.
n.
n.
n
n.
n.
n.
n.
n. Make bile. Convert excess
glucose to glycogen to store. Deal
with execess amino acids. Break
down toxins.
adj.
n. no enzymes
n. break up the large drops of
fats fat into very small ones.
n. produced by liver while it
breaks
down
old
RBC.NO
USEexcrete in faeces.
n. bile flows to the duodenum
through bile duct
n. stores bile
n., produce pancreatic juice
n.
n. contains amylase,trypsin,
lipase, sodium hydrogencarbonate.
n. has strong, muscular walls.
n. contains pepsin, rennin and
hydrochloric acid
n. a protease
n. only in stomach
of young mammals
n. provides proper environment
for enzymes(optimum pH2), kills
bacterial and viruses.
n. relaxes to let food pass into
the stoma
n.
n.(
)
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
goblet cell
mucus
lacteal
['gblt]
['mju:ks]
['lktil]
deamination
urea
faeces
[di:,mi'nein]
['jri:]
['fi:si:z]
n. secrete() mucus
n.
n. absorb fatty acids and
glycerol
n.
n.,
n.
Chapter8 Transport
blood circulatory system
blood vessels
heart
[h:t]
double circulatory system
oxygenated blood
deoxygenated blood
['ksidneitid]
n.
n.
n., pump the blood around the
body
n. the blood travels
through the heart twice on one
complete journey around the body.
n.
n.
Structure of heart
cardiac muscle
chamber
atrium atria
right atrium
['k:di:,k]
['teimb]
['eitrim]
left atrium
ventricle
['ventrikl]
right ventricle
left ventricle
septum
valve
['septm]
[vlv]
tricuspid valve
bicuspid valve
atrioventricular valve
semilunar valve
aorta
[trai'kspid]
[bai'kspid]
[,eitriuven'trikjul]
['semi'lju:n]
[e':t]
n.
n.
n.
n. receive the blood from the
vena cava.
n. receive the blood from the
pulmonary vein.
n. much thicher,more muscular
walls than atria.
n. pumps the blood to the
pulmonary artery which takes it to the
lungs
n. pumps the aorta,which takes
the blood around the body. Much
thicker cardiac muscles.
n.
n. stop blood flowing from
ventricles to atria.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
vena cava
( venae cavae)
coronary artery
[vi:n 'keiv]
n.
['k:r,neri:, 'kr-]
pulmonary vein
pulmonary artery
['plm,neri:, 'pl-]
n. supply blood to the heart
muscles
n. carry arterial blood
n. carry venous blood
heart attack
cardiac arrest
coronary heart disease
pacemaker
diastole
systole
n.
['peismeik]
[dai'stli]
['sistli]
n.
n.
n.,
n.
Blood vessels
artery
vein
[':tri]
[vein]
n. thick elastic wall, small lumen
n. thin wall, large lumen, has valves
stopping blood flowing backwards.blood is
kept moving in the veins by the contraction of
muscles around them
capillary
['kp,leri:]
pulse
sphygmomanometer
[pls]
[,sfimum'nmit
]
thrombosis
[rm'busis]
pulmonary embolism ['emblizm]
carotid artery
jugular vein
subclavian artery
hepatic vein
hepatic portal vein
hepatic artery
renal artery
renal vein
mesenteric artery
iliac artery
iliac vein
[k'rtid]
['djul]
['sb'kleivin]
['ri:nl]
[mesen'terik]
['ilik]
n. ; take
nutrients,oxygen and other materials to
the whole body, and take away their
waste materials. One cell thick
n.
n.,
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n. brings blood from the
digestive system to the liver
n. supplis liver with oxygen
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
blood
red blood cell
haemoglobin
platelet
[,hi:mu'lubin]
['pleitlit]
fibrinogen
[fai'brindn]
plasma
white blood cell
phagocyte
['plzm]
lymphocyte
antibody
['lmf,sat]
['nt,bdi:]
antigen
['ntdn]
pathogen
['pd()n]
mitosis
[mi'tusis]
['fusait]
immune response
immunosupressant
tissue fluid
lymph
[lmf]
n.
carry oxygen. no nucleus,
biconcave discs---large surface area.
n. a protein,contains iron
n. small fragment of cells,no
nucleus,made in red bone marrow,helps
blood clot.
n. the chemicals released by
the platelets and the damaged tissues set
off a chain of reactions,which cause the
fibrinogen to change into fibrin.
n.
n.
n. engulf and destroy the
pathogens and any of our own cells that
are damaged or worn out. Has lobed
nuclei.
n. produce antibodies
n. specific,like enzymes.1)alert
phagocytes to the presence of the
pathogen.2)antibodies may start off a
series of reactions producing enzymes to
digest pathogens.
n. any substance (as a toxin or
enzyme) that stimulates the production of
antibodies
n. , disease-causing bacteria
and viruses
n. cell division in which the
nucleus divides into nuclei containing the
same number of chromosomes
n. []
n.
n. the fluid formed that plasma
and white blood cells leaked out of blood
capillaries. It supplies cells with all their
requirements and carries away the waste
products. It also keeps the compositions
and temperature of blood constant.
n. ( ) the tissue fluid that is
conveyed to the lymphatic vessels.
Vocabulary revision before final exams!
lymph node
[nud]
n., contain large numbers
of white cells.
Chapter9 respiration
respiration
[,resp'ren]
n. the chemical reactions tant break
down nutrient molecules in living cells to
release energy.
aerobic repiration
[e'rbk]
n.
glucose + oxygen
carbon dioxide + water
anaerobic respiration
n.
glucose
alcohol + carbon dioxide
germinate
['d:m,net]
vt. & vi.()
ferment
[f'ment ]
vt. & vi.()
fermentation
[,f:mn'ten] n.
yeast
[ji:st]
n.
brew
[bru:]
vt. & vi.,
brewing
n.
Breathing system
lung
tracheawindpipe
bronchus( bronchi)
bronchiole
alveolus( alveoli)
diaphram
[l]
[tr'ki:]
['brks]
['brkiul]
[l'vils]
['daifrm]
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
n.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- IGCSE Biology Chapter4 The Chemicals of LifeДокумент24 страницыIGCSE Biology Chapter4 The Chemicals of Lifeddddddffdfdf75% (4)
- IGCSE Chemistry Organic ChemistryДокумент31 страницаIGCSE Chemistry Organic ChemistryddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Revision Quiz Macromolecules and Movement Into and Out of CellsДокумент2 страницыIGCSE Biology Revision Quiz Macromolecules and Movement Into and Out of CellsddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsДокумент6 страницNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Igcse 1 PDFДокумент35 страницChemistry Igcse 1 PDFRohit MITTALОценок пока нет
- 03 Movement in and Out of CellsДокумент5 страниц03 Movement in and Out of CellsddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент60 страницOrganic ChemistryddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry - Chapter 15.1 AlcoholsДокумент16 страницIGCSE Chemistry - Chapter 15.1 AlcoholsddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- 2016 Specimen Paper 5Документ10 страниц2016 Specimen Paper 5ddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- GorgДокумент87 страницGorgddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Chapter2 WordsДокумент1 страницаIGCSE Biology Chapter2 WordsddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- 2016 Specimen Paper 1 PDFДокумент16 страниц2016 Specimen Paper 1 PDFBioScMentor-1Оценок пока нет
- Times 40mins: ScoreДокумент4 страницыTimes 40mins: ScoreddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Ess Chem Unit 5 AnswersДокумент3 страницыEss Chem Unit 5 AnswersddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus in Index Card (A6) FormatДокумент44 страницыIGCSE Chemistry Syllabus in Index Card (A6) FormatddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Amount of SubstanceДокумент15 страницAmount of SubstanceddddddffdfdfОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- 41 Assignment Worksheets For SchoolДокумент26 страниц41 Assignment Worksheets For Schoolsoinarana456Оценок пока нет
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 8 (Bai 13)Документ4 страницыBai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 8 (Bai 13)nguyenanhmaiОценок пока нет
- ReliabilityДокумент5 страницReliabilityArmajaya Fajar SuhardimanОценок пока нет
- Drug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForДокумент7 страницDrug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForRafika DitaОценок пока нет
- Dri InternshipДокумент38 страницDri InternshipGuruprasad Sanga100% (3)
- Brief RESUME EmailДокумент4 страницыBrief RESUME Emailranjit_kadalg2011Оценок пока нет
- ALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85Документ15 страницALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85PОценок пока нет
- Solo ParentsДокумент1 страницаSolo ParentsOZ CincoОценок пока нет
- A Comprehensive Review of Cementitious Grouts - Composition, Properties, Requirements and Advanced PerformanceДокумент16 страницA Comprehensive Review of Cementitious Grouts - Composition, Properties, Requirements and Advanced PerformanceiporrasОценок пока нет
- Reading Practice 6Документ5 страницReading Practice 6Âu DươngОценок пока нет
- Wisconsin Humane Society To Acquire Kenosha's Safe Harbor Humane Society - Press ReleaseДокумент3 страницыWisconsin Humane Society To Acquire Kenosha's Safe Harbor Humane Society - Press ReleaseTMJ4 NewsОценок пока нет
- TraceGains Inspection Day FDA Audit ChecklistДокумент2 страницыTraceGains Inspection Day FDA Audit Checklistdrs_mdu48Оценок пока нет
- SanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological TestingДокумент67 страницSanMilan Inigo Cycling Physiology and Physiological Testingjesus.clemente.90Оценок пока нет
- Review - Practical Accounting 1Документ2 страницыReview - Practical Accounting 1Kath LeynesОценок пока нет
- Congenital Flexural Deformity in CalfДокумент6 страницCongenital Flexural Deformity in CalfBibek SutradharОценок пока нет
- Ventricular Septal DefectДокумент8 страницVentricular Septal DefectWidelmark FarrelОценок пока нет
- Rooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusДокумент9 страницRooftop Rain Water Harvesting in An Educational CampusAkshay BoratiОценок пока нет
- 10 2005 Dec QДокумент6 страниц10 2005 Dec Qspinster40% (1)
- PPR Soft Copy Ayurvedic OkДокумент168 страницPPR Soft Copy Ayurvedic OkKetan KathaneОценок пока нет
- Starkville Dispatch Eedition 9-10-20Документ12 страницStarkville Dispatch Eedition 9-10-20The DispatchОценок пока нет
- Neurocisticercosis PDFДокумент7 страницNeurocisticercosis PDFFiorella Alexandra HRОценок пока нет
- Transfer and Business Taxation SyllabusДокумент5 страницTransfer and Business Taxation SyllabusamqqndeahdgeОценок пока нет
- NORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For HearingДокумент146 страницNORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For Hearingcaod1712100% (1)
- Republic Act No. 10389Документ5 страницRepublic Act No. 10389Marge RoseteОценок пока нет
- Riber 6-s1 SP s17-097 336-344Документ9 страницRiber 6-s1 SP s17-097 336-344ᎷᏒ'ᏴᎬᎪᏚᎢ ᎷᏒ'ᏴᎬᎪᏚᎢОценок пока нет
- Phardose Lab Prep 19 30Документ4 страницыPhardose Lab Prep 19 30POMPEYO BARROGAОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Xi: Short Questions and 20% Long QuestionsДокумент3 страницыChemistry Xi: Short Questions and 20% Long QuestionsSyed Nabeel HassanОценок пока нет
- PolydactylyДокумент43 страницыPolydactylyWara Samsarga GedeОценок пока нет
- Eric Koech CV - Docx..bakДокумент7 страницEric Koech CV - Docx..bakPeter Osundwa KitekiОценок пока нет
- Bisleri Water Industry: Project ReportДокумент53 страницыBisleri Water Industry: Project ReportJohn CarterОценок пока нет