Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Astronomy Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
Shahid Yousaf100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
1K просмотров2 страницыkjkljkjlk kljjhljkjlj jhkjh
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документkjkljkjlk kljjhljkjlj jhkjh
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
1K просмотров2 страницыAstronomy Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
Shahid Yousafkjkljkjlk kljjhljkjlj jhkjh
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Astronomy Cheat Sheet Name: _______________________ Final Exam Date: _____
Rotation When an object spins on its axis.
Day How long it takes for an object rotate one time on its
axis.
Revolution When an object moves around another object
AKA: Orbit.
Year How long it takes for an object to revolve one time
around another object.
Keplers 2nd Law The closer an object is to the sun, the
faster it appears to move. The further an object is from the
sun, the slower it appears to move.
Our sun is composed mainly of
hydrogen, helium and carbon.
Tides are caused my the
gravitation pull between the
Moon and Earth.
A high tide occurs daily and
is when water levels are
increased.
A low tide occurs daily and
is when water levels are
decreased.
A neap tides is when the
tides hardly change at all.
These occur during Quarter
Moon phases.
A spring tide is when the
tides are extremely high
and extremely low. These
occur during Full and New
Moon phases.
Seasons are caused by
the angle at which the
Sun hits a certain
location at a certain
time of the year.
Sun
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Pluto is no longer
considered to be a
planet because its orbit
was discovered to cross
with Neptunes orbit
and Plutos mass does
not greatly exceed the
mass of the other
objects in its orbit.
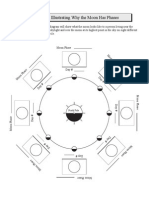
Creating a Moon-Phase Diagram:
1.
Locate the Sun.
2.
The phase closest to the sun is the New Moon. Color it completely
dark.
3.
Go directly across from the New Moon and label the Full Moon. This
phase should be left totally light.
4.
Go back to your New Moon. Move one step counter-clock-wise.
5.
This is the Waxing Crescent. Draw a small thumbnail of light and keep
the light pointing towards the sun always.
6.
Go straight across from that Moon and draw the Waning Crescent.
7.
Then the Quarter Moons.
8.
Then the Gibbous Moons.
9.
Remember: Keep the light pointing towards the Sun at all times.
10. All Waxing Moons (light increasing) are to the left of the Sun.
11. All Waning Moons (light decreasing) are to the right of the Sun.
Reflecting: Large and bounce light from the space object off of a set
of mirrors to magnify the image.
Refracting: Smaller and bend the light from the space object through
a set of lenses to magnify the image.
Amount of Time Studied: ______hr _____ mins
Parent/Guardian Signature: _________________
Confidence Level:
L 1 . 2 . 3 4 5 . J
Asteroids are very large rocky, metallic bodies that
orbit the Sun.
Meteors are small rocky bodies that orbit the Sun.
Meteorites are meteors that have fallen to Earth.
A star is a self-luminous body, consisting of a mass of gas
that holds its own gravity.
The Life-Cycle of a Sun-Like Star: They begin as a
nebular with gas and gravity. Then the mass forms a globule
in the middle. Due to gravity the globule collapses and
forms a spiraling disk of gas and dust. Then it forms a
protostar with protoplanets. Then they become an active
stay with young planets. Then it becomes a solar system
with the star in the middle. Then the sun-like star forms a
red supergiant, then a planetary nebula, then a white dwarf
and finally a black dwarf.
We are located in the Milky Way galaxy which is a spiral
(shape) galaxy, The Milky Way is located in the Local group
which is within the Virgo supercluster. Our closest
neighboring galaxy is called Andromeda.
The Big Bang Theory: The Universe began as an extremely
dense, single point. Due to high amounts of density, it
became unstable and exploded. The Universe is constantly
expanding with every second.
How Do We Know? Scientist use light signals from
telescopes to measure how objects in the universe move.
We understand that objects are moving way from us
because of Red Shift (longer wavelengths and lower
frequencies). If objects were moving towards us, there
would be Blue Shift (shorter wavelengths and higher
frequencies).
Spiral
Irregular
Elliptical
Вам также может понравиться
- Astronomy PDFДокумент6 страницAstronomy PDFJuan OchoaОценок пока нет
- 21st Century Astronomy PDFДокумент768 страниц21st Century Astronomy PDFCristinaGonzález100% (14)
- Astronomy & AstrophysicsДокумент381 страницаAstronomy & AstrophysicsRajiv Sinha100% (30)
- (Isaac Asimov's Library of The Universe 21st Century) Isaac Asimov - The Moon-Prometheus Books (2003) PDFДокумент36 страниц(Isaac Asimov's Library of The Universe 21st Century) Isaac Asimov - The Moon-Prometheus Books (2003) PDFCamila Bastos100% (1)
- Modem Astronomy - Startling FactsДокумент184 страницыModem Astronomy - Startling FactsRiaz Ur Rehman Khalid100% (6)
- Explore the Universe and Solar System FormationДокумент44 страницыExplore the Universe and Solar System FormationCristina Maquinto100% (1)
- Watermelon Mint Whipped Sugar Scrub - Humblebee & MeДокумент27 страницWatermelon Mint Whipped Sugar Scrub - Humblebee & MeShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- All About Space Book of The Solar System - 2014Документ180 страницAll About Space Book of The Solar System - 2014leonbeti100% (3)
- 01 Lal Kitab Concept - Rin Pitri KundaliДокумент4 страницы01 Lal Kitab Concept - Rin Pitri Kundalisorena0842100% (1)
- Astronomy PDFДокумент29 страницAstronomy PDFVaibhav PandeyОценок пока нет
- What Is AstronomyДокумент34 страницыWhat Is AstronomyShahrul Razi100% (1)
- Earthsci Lesson 3&4Документ4 страницыEarthsci Lesson 3&4Dalope CstrОценок пока нет
- Exoplanets: Worlds beyond Our Solar SystemОт EverandExoplanets: Worlds beyond Our Solar SystemРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Origin of The UniverseДокумент44 страницыOrigin of The UniverseLuis PazОценок пока нет
- Sun DiagramДокумент2 страницыSun DiagramAngel SolivanОценок пока нет
- Astronomy FormulaeДокумент36 страницAstronomy Formulaeescherer1099100% (3)
- Summary Notes - Topic 8 Astrophysics - Edexcel Physics IGCSEДокумент3 страницыSummary Notes - Topic 8 Astrophysics - Edexcel Physics IGCSEFahimDayhanОценок пока нет
- The Importance of Photo Type & Risk Assessment - Pastiche TrainingДокумент7 страницThe Importance of Photo Type & Risk Assessment - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- The Martian Enigmas - A Closer LookДокумент187 страницThe Martian Enigmas - A Closer LookMaiman Lato100% (1)
- Dermatological, Cosmeceutical and Corneotherapy DifferencesДокумент5 страницDermatological, Cosmeceutical and Corneotherapy DifferencesShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Understanding Dermal Pigmentation - Pastiche TrainingДокумент6 страницUnderstanding Dermal Pigmentation - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 The Beginning of The Universe PDFДокумент39 страницLesson 1 The Beginning of The Universe PDFZhayne Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Quiz AnswersДокумент12 страницQuiz AnswersChuah Chong YangОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Powerpoint CHP 1Документ18 страницAstronomy Powerpoint CHP 1emailtotesttestОценок пока нет
- Abraham Ibn Ezra - The Beginning of Wisdom VIIIДокумент7 страницAbraham Ibn Ezra - The Beginning of Wisdom VIIIElvira Dubois100% (2)
- Input 1 Formation of UniverseДокумент29 страницInput 1 Formation of UniverseMyko JayeОценок пока нет
- The Solar SystemДокумент10 страницThe Solar Systemrosana f.rodriguezОценок пока нет
- Elementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsОт EverandElementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Created By-: Sheikh Khalilur RahmanДокумент23 страницыCreated By-: Sheikh Khalilur RahmanKiron SheiqОценок пока нет
- Internal Heat of The EarthДокумент2 страницыInternal Heat of The EarthANNA BABONОценок пока нет
- Theories of The UniverseДокумент30 страницTheories of The Universetatskopling100% (1)
- Working With Dispositors PDFДокумент5 страницWorking With Dispositors PDFnicholehuntsmanОценок пока нет
- Explore the vast Universe with the Big Bang TheoryДокумент74 страницыExplore the vast Universe with the Big Bang TheorySofia Nuñez100% (1)
- Universe: Presented By: Faeza Shams Muneeba ZafarДокумент29 страницUniverse: Presented By: Faeza Shams Muneeba ZafarhelperforeuОценок пока нет
- Our Dynamic Planet - Earth and Life - Book 2, Part 1 PDFДокумент192 страницыOur Dynamic Planet - Earth and Life - Book 2, Part 1 PDFwrongplanet67Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 27: Motion in The UniverseДокумент11 страницChapter 27: Motion in The UniverseSadman SlenderОценок пока нет
- 1373588326Документ35 страниц1373588326Fareed ShahwaniОценок пока нет
- Space Physics NotesДокумент5 страницSpace Physics NotesjisungserbiaОценок пока нет
- Space PhysicsNotesДокумент44 страницыSpace PhysicsNotesthethmusan.2007Оценок пока нет
- Science ReviewerДокумент11 страницScience ReviewerZoe BeatrizОценок пока нет
- Solar SystemДокумент64 страницыSolar SystemSharif MalekzadaОценок пока нет
- Solar System Members-1Документ35 страницSolar System Members-1Joyae ChavezОценок пока нет
- Beyond Our Solar System: Honors Earth ScienceДокумент22 страницыBeyond Our Solar System: Honors Earth Scienceapi-27481415Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ44 страницыLecture 1SunilKumar DОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 Space PhysicsДокумент19 страницUnit 6 Space PhysicsCloud WtafОценок пока нет
- Lecture # 1 GSAДокумент26 страницLecture # 1 GSAMalaham Pari KhanОценок пока нет
- Powerpoint Assignment 1 Edu 210Документ10 страницPowerpoint Assignment 1 Edu 210api-242428404Оценок пока нет
- Detecting Planets Around Distant StarsДокумент41 страницаDetecting Planets Around Distant StarsadammendozaОценок пока нет
- Astronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers: What Is Science?Документ20 страницAstronomy 1143 Final Exam Review Answers: What Is Science?samsul bahriОценок пока нет
- Physics &cosmosДокумент29 страницPhysics &cosmosNorhaima TacorangaОценок пока нет
- Geography CompilationДокумент35 страницGeography CompilationDanish MohammedОценок пока нет
- Constituents and StructuresДокумент18 страницConstituents and StructuresHassan BareachОценок пока нет
- The Big Bang Theory Explains How the Universe FormedДокумент36 страницThe Big Bang Theory Explains How the Universe Formedeyren fallorОценок пока нет
- Earth MotionsДокумент59 страницEarth MotionsJanmari FajardoОценок пока нет
- TitkeДокумент16 страницTitkeZahid ShahОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Study Guide AnswersДокумент2 страницыAstronomy Study Guide Answersapi-240689882Оценок пока нет
- Earth's Place in the UniverseДокумент28 страницEarth's Place in the UniverseJemarjo SalandananОценок пока нет
- The Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!Документ36 страницThe Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!RamОценок пока нет
- Universe Physics IGCSEДокумент23 страницыUniverse Physics IGCSEaribahamjad8129Оценок пока нет
- Q1 UniverseДокумент36 страницQ1 UniverseKevin Francis Echon MagaoayОценок пока нет
- The Birth of Astronomical Studies: - Astronomy - Study of All Matter and Energy in The UniverseДокумент65 страницThe Birth of Astronomical Studies: - Astronomy - Study of All Matter and Energy in The UniverseLJ Valdez100% (1)
- SupernovaДокумент2 страницыSupernovaveena bhatОценок пока нет
- Explore the UniverseДокумент12 страницExplore the UniverseRaquelОценок пока нет
- 02 - 03 - Geology - Origin of The Universe and Solar System PDFДокумент34 страницы02 - 03 - Geology - Origin of The Universe and Solar System PDFSebastian Guzman67% (3)
- G8 Q4 UniverseДокумент37 страницG8 Q4 UniverseLocal ClownОценок пока нет
- Class 01 Geography as a Discipline 1687309987Документ94 страницыClass 01 Geography as a Discipline 1687309987pandeyji8055Оценок пока нет
- Motion in The Universe: F M M) /DДокумент5 страницMotion in The Universe: F M M) /DMaisha FОценок пока нет
- The Big Bang TheoryДокумент13 страницThe Big Bang TheoryHilary YvonneОценок пока нет
- Universe Lesson 1 1Документ34 страницыUniverse Lesson 1 1Joanna RollanОценок пока нет
- The Universe: by Praveen Kumar ReddyДокумент49 страницThe Universe: by Praveen Kumar Reddypraveen111102Оценок пока нет
- Origin of the Universe ExplainedДокумент234 страницыOrigin of the Universe ExplainedMohsin AbbasОценок пока нет
- 6.1 Earth & The Solar SystemДокумент27 страниц6.1 Earth & The Solar SystemHakim AbbasОценок пока нет
- Universe and Solar System: Rhenn B. Songco, RN, LPTДокумент26 страницUniverse and Solar System: Rhenn B. Songco, RN, LPTRhenn SongcoОценок пока нет
- Earth ScienceДокумент22 страницыEarth ScienceKaireen OzОценок пока нет
- White Clay MSDS SummaryДокумент5 страницWhite Clay MSDS SummaryShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Vitamins E & A and The Skin - Virtual BeautyДокумент2 страницыVitamins E & A and The Skin - Virtual BeautyShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Ageing Skins, Comedones and Other Keratolytic Disorders - Pastiche TrainingДокумент4 страницыAgeing Skins, Comedones and Other Keratolytic Disorders - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Acid Mantle pH BalanceДокумент2 страницыAcid Mantle pH BalanceShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Pigmentation - Melanosome Transfer To Keratinocyte - Pastiche TrainingДокумент3 страницыPigmentation - Melanosome Transfer To Keratinocyte - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- The Importance of Genetics in Skin Analysis - Virtual BeautyДокумент3 страницыThe Importance of Genetics in Skin Analysis - Virtual BeautyShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Vitamin E For Skin Maintenance & Protection - Virtual BeautyДокумент2 страницыVitamin E For Skin Maintenance & Protection - Virtual BeautyShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Why Say No To Emulsifiers - Virtual BeautyДокумент4 страницыWhy Say No To Emulsifiers - Virtual BeautyShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- The Wound Healing Process - Virtual BeautyДокумент3 страницыThe Wound Healing Process - Virtual BeautyShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Skin Treatments in Summer - Pastiche TrainingДокумент5 страницSkin Treatments in Summer - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- The Three R's of Corneotherapy - Pastiche TrainingДокумент3 страницыThe Three R's of Corneotherapy - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Epidermal Turnover - The 30 Day Myth - Pastiche TrainingДокумент4 страницыEpidermal Turnover - The 30 Day Myth - Pastiche TrainingShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Acai Seed PowderДокумент1 страницаTechnical Data Sheet: Acai Seed PowderShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: White ClayДокумент1 страницаTechnical Data Sheet: White ClayShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Malpighia Punicifolia LДокумент2 страницыTechnical Data Sheet: Malpighia Punicifolia LShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Sheet: Organic Acai PowderДокумент2 страницыTechnical Data Sheet: Organic Acai PowderShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Vanilla Jasmine BalmДокумент1 страницаVanilla Jasmine BalmShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Guide Formulation - UV-curing transparent primerДокумент1 страницаGuide Formulation - UV-curing transparent primerShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Vaseline Healthy White Sun+Pollution Protection SPF 24 Pa++ Ingredients (Explained)Документ14 страницVaseline Healthy White Sun+Pollution Protection SPF 24 Pa++ Ingredients (Explained)Shahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Watermelon Mint Hand & Body Lotion - Humblebee & MeДокумент22 страницыWatermelon Mint Hand & Body Lotion - Humblebee & MeShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Urtekram Anti-Pollution Cellulite Scrub Ingredients (Explained)Документ14 страницUrtekram Anti-Pollution Cellulite Scrub Ingredients (Explained)Shahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Ultra Mild Color Protection Shampoo (2C-LV, 160NC, LMB, LipidC, PSM D9)Документ1 страницаUltra Mild Color Protection Shampoo (2C-LV, 160NC, LMB, LipidC, PSM D9)Shahid YousafОценок пока нет
- MakingCosmetics Inc. water-resistant cream (w/o) formula and methodДокумент1 страницаMakingCosmetics Inc. water-resistant cream (w/o) formula and methodsilvia7villa.saОценок пока нет
- Vanilla Oatmeal Whipped Body ButterДокумент1 страницаVanilla Oatmeal Whipped Body ButterShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Waterless Beauty Balm: Ingredients Bolded Below Supplied by Formulator Sample ShopДокумент1 страницаWaterless Beauty Balm: Ingredients Bolded Below Supplied by Formulator Sample ShopShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- Probiotic Water Jelly Formulation: Trade Name INCI Name % VendorДокумент2 страницыProbiotic Water Jelly Formulation: Trade Name INCI Name % VendorShahid YousafОценок пока нет
- UNINDRA Soal Ujian Akhir Paket 2 Semester Genap Tahun Akademik 2020/2021Документ2 страницыUNINDRA Soal Ujian Akhir Paket 2 Semester Genap Tahun Akademik 2020/2021Derall SantosoОценок пока нет
- Pop-Up Diagram Illustrating Why The Moon Has PhasesДокумент1 страницаPop-Up Diagram Illustrating Why The Moon Has PhasesJilbabku IbadahkuОценок пока нет
- North: Magaram Rasi-Sahra Rasi (Earth Sign) Female House of SaturnДокумент1 страницаNorth: Magaram Rasi-Sahra Rasi (Earth Sign) Female House of SaturnStar WindowsОценок пока нет
- Pemetaan Stakeholder Terkait Wog: Tugas Iii Agenda Iii Maulani Pradiana, S.SiДокумент49 страницPemetaan Stakeholder Terkait Wog: Tugas Iii Agenda Iii Maulani Pradiana, S.Simaulanis93Оценок пока нет
- English Question Bank-3Документ9 страницEnglish Question Bank-3sonaliОценок пока нет
- Thiruvalluvar University: 229-Sri Bharathi Women'S Arts & Science College, Kunnathur-ArniДокумент10 страницThiruvalluvar University: 229-Sri Bharathi Women'S Arts & Science College, Kunnathur-ArniGopinathan MОценок пока нет
- Science Q2 Week 5 ModuleДокумент10 страницScience Q2 Week 5 ModuleMACAINAG, AngelicaОценок пока нет
- Social Studies Teachers Guide Grade 7 - 3 UnitsДокумент58 страницSocial Studies Teachers Guide Grade 7 - 3 UnitsNatiОценок пока нет
- Vedic Match Making Report: Birth DetailsДокумент7 страницVedic Match Making Report: Birth DetailsfuckscribdsuckmydickОценок пока нет
- Welcome To The 20's by SlidesgoДокумент50 страницWelcome To The 20's by SlidesgoAllison Villagomez MuñozОценок пока нет
- Grade III SSC L 1 Hello Universe - CДокумент4 страницыGrade III SSC L 1 Hello Universe - CDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYОценок пока нет
- Astrology Quiz 17Документ4 страницыAstrology Quiz 17Jatinder SandhuОценок пока нет
- Misa Review Asteroids in The Asteroid BeltДокумент4 страницыMisa Review Asteroids in The Asteroid Beltpayton littleОценок пока нет
- Planetary Glyph MeaningsДокумент2 страницыPlanetary Glyph MeaningseyeoftaurusОценок пока нет
- Ancient and Modern AstronomersДокумент20 страницAncient and Modern AstronomersYovany PerezОценок пока нет
- All About VolcanoesДокумент35 страницAll About VolcanoesDaSh KОценок пока нет
- Organic Food Pitch Deck by SlidesgoДокумент50 страницOrganic Food Pitch Deck by SlidesgoMarta RibeiroОценок пока нет
- Search For Extraterrestrial Life - John MillamДокумент41 страницаSearch For Extraterrestrial Life - John MillamhobbylijmОценок пока нет
- Solarsystem Crossword2Документ1 страницаSolarsystem Crossword2Tisha Nair ടിഷ നായര്Оценок пока нет