Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IHD602 Assignment RVF1 HydraulicJump 20161011yim
Загружено:
AshafАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IHD602 Assignment RVF1 HydraulicJump 20161011yim
Загружено:
AshafАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Department of Irrigation and Hydraulics
Faculty of Engineering, Cairo University
IHD-602: Advanced Hydraulics
Fall 2016
Assignment RVF-1
Hydraulic Jumps
1) A free hydraulic jump occurs in an open channel with a 4 m wide rectangular crosssection. The depth and velocity at the toe of the hydraulic jump are 0.3 m and 8 m/s,
respectively. Do the following:
Determine the depth, velocity, and Froude number at the downstream end of the
jump.
Classify the jump based on Froude number at jump toe.
Determine the energy dissipation efficiency of the jump.
Estimate the length of the jump and roller.
Plot the time-averaged free surface profile for the jump.
Plot the maximum time-averaged velocity along the jump.
Plot the time-averaged velocity with depth at half the jump length from the toe.
Plot the cross-section average air concentration along the jump.
Determine the maximum air entrainment ratio for the jump and the location of this
ratio.
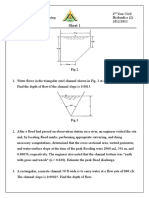
2) A hydraulic jump occurs in a trapezoidal channel having a bed width of 7.0 m and side
slopes of 1:1. The discharge in the channel is 25 m3/s. Construct the specific force
diagram, determine critical depth, and get the conjugate (sequent) depths for the
hydraulic jump given that the jump height is 1.0 m. Find also the head lost and rate of
energy dissipation.
3) Solve problem 6.17 from Subramanya (2009):
The Rihand dam in U.P., India, has a sloping apron stilling basin with a slope of 0.077. If
the depth for a flood flow of 64.0 m3/s per metre width is 1.93 m, estimate the sequent
depth, length of jump, and energy loss in the hydraulic jump.
4) Solve problem 6.22 from Subramanya (2009):
A circular culvert of 1.5-m diameter carries a discharge of 1.0 m3/s. The channel can be
assumed to be horizontal and frictionless. If the depth at the beginning of a hydraulic
jump occurring in this channel is 0.30 m, determine sequent depth.
5) Solve problem 6.31 from Subramanya (2009):
Water flows from under a sluice gate into a wide rectangular channel having a bed slope
of 10 cm/km. The gate opening is such that the discharge rate is 6.0 m3/s/metre width.
Determine whether a free hydraulic jump can occur and if so determine its sequent
depths when the depth at the vena contracta is (i) 0.50 m and (ii) 0.40 m. Assume
Mannings n = 0.015.
Oct 11, 2016
Page 1 of 2
Department of Irrigation and Hydraulics
Faculty of Engineering, Cairo University
IHD-602: Advanced Hydraulics
Fall 2016
6) Review the article by Ohtsu et al. (1999) then answer the following question:
A hydraulic jump occurs in an open channel of width 4 m. The hydraulic jump occurs
downstream of a vent of width 1.0 m and height 0.25 m. The tailwater depth is 1.2 m
and the discharge is 2 m3/s. Determine the following:
The flow pattern in the jump (I, II, or III).
The flow depth immediately downstream of the jump.
The type of the jump (steady asymmetric, periodic asymmetric, or symmetric).
Energy loss in the jump.
Length of jump.
This assignment is due by Tuesday, October 25.
Rules:
Submit your own work. Copying other students assignments is not allowed!
Plots should be produced using computer software; e.g., Microsoft Excel.
References:
Ohtsu, I., Y. Yasuda, and M. Ishikawa. 1999. Submerged Hydraulic Jumps below
Abrupt Expansions. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 125 (5): 492499.
Subramanya, K. 2009. Flow in Open Channels. Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Oct 11, 2016
Page 2 of 2
Вам также может понравиться
- Sheet 1Документ10 страницSheet 1lawanОценок пока нет
- Sheet 1Документ10 страницSheet 1lawanОценок пока нет
- Sheet 1Документ10 страницSheet 1lawanОценок пока нет
- Sheet 1Документ11 страницSheet 1lawanОценок пока нет
- Sheet No (6) Rapidly Varied Flow - Hydraulic JumpДокумент1 страницаSheet No (6) Rapidly Varied Flow - Hydraulic JumpDorry MagdyОценок пока нет
- Open Channel Flow and Hydraulic Similarity QuestionsДокумент16 страницOpen Channel Flow and Hydraulic Similarity QuestionsArun ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Application of Momentum PrincipleДокумент2 страницыApplication of Momentum PrincipleDawa TamangОценок пока нет
- Assignment RVF HJ 1Документ1 страницаAssignment RVF HJ 1Abdel Samie MuhyadinОценок пока нет
- Fluid Tute 3 Ce-T3 - Bce303 - Er. Sunil KR YadavДокумент2 страницыFluid Tute 3 Ce-T3 - Bce303 - Er. Sunil KR Yadavamansri035Оценок пока нет
- Examples On Hydraulic Jump PDFДокумент3 страницыExamples On Hydraulic Jump PDFSylvester WafulaОценок пока нет
- CvaДокумент2 страницыCvaZaid HadiОценок пока нет
- Rapidly Varied Flow (Hydraulic Jump) : Tutorial-6Документ1 страницаRapidly Varied Flow (Hydraulic Jump) : Tutorial-6arpit_089Оценок пока нет
- CE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question BankДокумент9 страницCE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question Banksankaran sОценок пока нет
- Mee 303 Homework 3Документ4 страницыMee 303 Homework 3Tomisin EniolaОценок пока нет
- PS3Документ2 страницыPS3Syrille Lubigan AlarconОценок пока нет
- Rapidly Varied Flow Tutorial ProblemsДокумент1 страницаRapidly Varied Flow Tutorial ProblemsfyqahОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics Model Exam QuestionsДокумент2 страницыHydraulics Model Exam QuestionsRamani RajОценок пока нет
- FM Question Bank PDFДокумент6 страницFM Question Bank PDFprabhumaluОценок пока нет
- Ii Mid FM&HMДокумент8 страницIi Mid FM&HMSrinivas RaghavanОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics 1 Assignment 2Документ1 страницаHydraulics 1 Assignment 2Sylvester WafulaОценок пока нет
- Uce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPДокумент8 страницUce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPkarthickaryanОценок пока нет
- CE6451-Fluid Mechanics and Machinery QBДокумент10 страницCE6451-Fluid Mechanics and Machinery QBVignesh DuraiОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinry-U2Документ3 страницыFluid Mechanics and Machinry-U2seaОценок пока нет
- Taller 2 - 2P-2020Документ1 страницаTaller 2 - 2P-2020Yoel LobeloОценок пока нет
- National University of Science and Technology: This Examination Paper Consists of 3 PagesДокумент3 страницыNational University of Science and Technology: This Examination Paper Consists of 3 PagesmbolaОценок пока нет
- CE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringДокумент9 страницCE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringSivarajSivaОценок пока нет
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsДокумент4 страницы9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- HydraulicsДокумент4 страницыHydraulicsHakdog GieОценок пока нет
- TCW3101200904 HydraulicsДокумент3 страницыTCW3101200904 HydraulicsTinashe Mazokera100% (1)
- 6Документ44 страницы6RAM NAIDU CHOPPAОценок пока нет
- Taller 1 - 2P - 2019Документ1 страницаTaller 1 - 2P - 2019Josman SalgadoОценок пока нет
- Mixed TopicДокумент105 страницMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Advanced Hydraulics Module 1: Key Concepts of Open Channel FlowДокумент4 страницыAdvanced Hydraulics Module 1: Key Concepts of Open Channel FlowRajendra Kore100% (1)
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsДокумент4 страницы9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Spring Semester 2014 Third Year Civil (Batch 2011-2012)Документ1 страницаSpring Semester 2014 Third Year Civil (Batch 2011-2012)Michael MillerОценок пока нет
- Sheet 3Документ4 страницыSheet 3Mohamed TallyОценок пока нет
- FlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFДокумент3 страницыFlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10Qs - 2023 PDFRamil EnsarОценок пока нет
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Документ2 страницыPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsОценок пока нет
- Numericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowДокумент7 страницNumericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowCristiano Omega RalteОценок пока нет
- CET203 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRAULICS, December 2020Документ3 страницыCET203 FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRAULICS, December 2020cedayan418Оценок пока нет
- Open Channel Flow WorksheetДокумент2 страницыOpen Channel Flow WorksheetMac KYОценок пока нет
- Practice Set 3Документ1 страницаPractice Set 3Sudhir KumarОценок пока нет
- UniMasr.com_75c3b940d42559236051914be1dcc630Документ26 страницUniMasr.com_75c3b940d42559236051914be1dcc630shefffОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics IVSemДокумент5 страницFluid Mechanics IVSemHimanshu BhardwajОценок пока нет
- Compre Hydraulics PSДокумент5 страницCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Test On Fluid MechanicsДокумент11 страницTest On Fluid MechanicsJonathan GreenОценок пока нет
- QuizДокумент6 страницQuizR SharmaОценок пока нет
- 14 MarksДокумент4 страницы14 MarksmohanОценок пока нет
- HHM Question Paper B.tech-IIДокумент2 страницыHHM Question Paper B.tech-IINizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryОценок пока нет
- Thermo - Hydrulic Turbine - Dimensional AnlysisДокумент17 страницThermo - Hydrulic Turbine - Dimensional AnlysisbachayadavОценок пока нет
- HYDRAULICДокумент5 страницHYDRAULICMuhammad Hazim Bin Ahmad FauziОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsДокумент7 страницFluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsPraveen SharmaОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery Question PaperДокумент7 страницHydraulics and Hydraulic Machinery Question PaperAlexdorwinaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Документ15 страницChapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Jerle ParondoОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment 4Документ2 страницыFluid Mechanics Assignment 4Rojan PradhanОценок пока нет
- Problems Open Channel FlowДокумент3 страницыProblems Open Channel Flow8986103t100% (1)
- Assignment 2Документ2 страницыAssignment 2mustefa kelilОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4 QuestionsДокумент2 страницыTutorial 4 QuestionsJiNx AngОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ9 страницBook 1AshafОценок пока нет
- Career Point IIT Physics Unit DimensionДокумент16 страницCareer Point IIT Physics Unit DimensionAbbhijit Roy50% (2)
- SRX BrochureДокумент10 страницSRX BrochureAshafОценок пока нет
- Open Channel FlowДокумент24 страницыOpen Channel FlowoscarjofkОценок пока нет
- HJ LengthДокумент5 страницHJ Lengthbhassan 2007Оценок пока нет
- Attributes and DialogsДокумент29 страницAttributes and DialogsErdenegombo MunkhbaatarОценок пока нет
- 10 1 1 124 9636 PDFДокумент11 страниц10 1 1 124 9636 PDFBrian FreemanОценок пока нет
- #### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0Документ9 страниц#### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0MARCOОценок пока нет
- DC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlДокумент5 страницDC Motor Dynamics Data Acquisition, Parameters Estimation and Implementation of Cascade ControlAlisson Magalhães Silva MagalhãesОценок пока нет
- 2014 mlc703 AssignmentДокумент6 страниц2014 mlc703 AssignmentToral ShahОценок пока нет
- Biology Mapping GuideДокумент28 страницBiology Mapping GuideGazar100% (1)
- Petty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForДокумент3 страницыPetty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForCrizhae OconОценок пока нет
- 4 Wheel ThunderДокумент9 страниц4 Wheel ThunderOlga Lucia Zapata SavaresseОценок пока нет
- RUJUKANДокумент3 страницыRUJUKANMaryTibanОценок пока нет
- всё необходимое для изучения английского языкаДокумент9 страницвсё необходимое для изучения английского языкаNikita Chernyak100% (1)
- Books of AccountsДокумент18 страницBooks of AccountsFrances Marie TemporalОценок пока нет
- Water Jet CuttingДокумент15 страницWater Jet CuttingDevendar YadavОценок пока нет
- JurnalДокумент9 страницJurnalClarisa Noveria Erika PutriОценок пока нет
- MODULE+4+ +Continuous+Probability+Distributions+2022+Документ41 страницаMODULE+4+ +Continuous+Probability+Distributions+2022+Hemis ResdОценок пока нет
- Chennai Metro Rail BoQ for Tunnel WorksДокумент6 страницChennai Metro Rail BoQ for Tunnel WorksDEBASIS BARMANОценок пока нет
- UAPPДокумент91 страницаUAPPMassimiliano de StellaОценок пока нет
- NLL - Elementary - Coursebook 2019 PDFДокумент24 страницыNLL - Elementary - Coursebook 2019 PDFgilmolto100% (1)
- Game Rules PDFДокумент12 страницGame Rules PDFEric WaddellОценок пока нет
- Liebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VДокумент2 страницыLiebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VsinoОценок пока нет
- Tech Data: Vultrex Production & Drilling CompoundsДокумент2 страницыTech Data: Vultrex Production & Drilling CompoundsJeremias UtreraОценок пока нет
- Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Документ182 страницыPhilippine Coastal Management Guidebook Series No. 8Carl100% (1)
- Survey Course OverviewДокумент3 страницыSurvey Course OverviewAnil MarsaniОценок пока нет
- Maverick Brochure SMLДокумент16 страницMaverick Brochure SMLmalaoui44Оценок пока нет
- LM1011 Global ReverseLogДокумент4 страницыLM1011 Global ReverseLogJustinus HerdianОценок пока нет
- 621F Ap4405ccgbДокумент8 страниц621F Ap4405ccgbAlwinОценок пока нет
- NAT Order of Operations 82Документ39 страницNAT Order of Operations 82Kike PadillaОценок пока нет
- Book Networks An Introduction by Mark NewmanДокумент394 страницыBook Networks An Introduction by Mark NewmanKhondokar Al MominОценок пока нет
- Nama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Документ3 страницыNama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Yetri MulizaОценок пока нет
- April 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesДокумент16 страницApril 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- TOGAF 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation GuideДокумент114 страницTOGAF 9 Foundation Part 1 Exam Preparation GuideRodrigo Maia100% (3)