Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pes Inv As 27b
Загружено:
api-336208398Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pes Inv As 27b
Загружено:
api-336208398Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
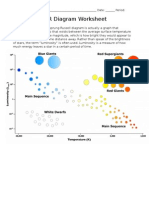
Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
Investigation
27B
27B Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
How can we use an H-R diagram to know where a star is in its life cycle?
Just like humans, stars go through a life cycle. Over the course of their lives, stars
change in ways that make each stage different and recognizable. A useful way to
organize this information is in a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, also called an H-R
diagram. In this investigation, you will learn how to identify stars of different types and
ages using the information in an H-R diagram.
The H-R diagram
Making observations
Materials
None
required
For astronomers, a graph that displays a stars luminosity on the y-axis and its surface
temperature on the x-axis sets up an extremely useful diagram called a Hertzsprung-Russell,
or H-R diagram. In 1910 Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell discovered that when
all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By
examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the
groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than
completely different types of stars. Just as infants, adolescents and adults are in different
stages of the human life cycle, main sequence, red giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs are
stars in different stages of the life cycle of stars.
a.
Describe the qualities and the location of white dwarf stars based on the H-R diagram.
Investigation
27B
Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
b.
Describe the qualities and the location of supergiant stars based on the H-R diagram.
c.
Describe the qualities and the location of main sequence stars based on the H-R diagram.
d. Describe the qualities and the location of red giant stars based on the H-R diagram.
Graphing star data
Table 1 contains data concerning the luminosity and surface temperature of 12 stars. Plot each
stars data on the grid and label each star (AL) on Table 2.
Table 1: Luminosity and surface temperature data
Name
Luminosity
Surface temperature
(C)
A Proxima Centauri
0.0017
3,100
B Rigel
66,000
11,000
C Sirius A
25.4
9,500
D Sirius B
0.026
25,000
350
3,600
65,000
3,200
250
4,700
135,000
3,300
E Aldebaran
F
Antares
G Arcturus
H Betelgeuse
I
Procyon A
6,200
Procyon B
0.0005
7,500
800
16,000
0.013
12,000
K Pi Andromedae A
L
40 Eridani B
Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
Investigation
27B
Table 2: Star data graph
Examining your graph
Compare your graph of star data to the H-R diagram from part 1. Look for groupings on your
graph that are similar to the H-R diagram and answer the following questions.
a.
Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with main sequence stars?
b. Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with supergiant stars?
c.
Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with red giant stars?
Investigation
27B
Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
d. Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with white dwarf stars?
Can you identify which group a star will fit into just by looking at its temperature alone?
Its luminosity alone? Explain your answer.
e.
Groupings on the H-R diagram and the life cycle of stars
Even though a star is not alive, it goes through a life cycle similar to living things. The
groups that appear in different sections of the H-R diagram are in different phases of their life
cycle.
a.
In what part of their life cycle are main sequence stars; beginning, middle, or end, or
some combination of those stages?
b.
What characteristics are common to main sequence stars?
c.
How are red giant and supergiant stars similar? How are they different? Include how
each one fits into the life cycle in some part your answer.
d. In what part of their life cycle are white dwarf stars; beginning, middle, or end, or some
combination of those stages?
Star Life Cycle and the H-R Diagram
Investigation
27B
e. What characteristics make white dwarf stars different from main sequence stars?
f.
What is the difference between a white dwarf star and a red giant star?
g.
Where is the Sun located on the H-R diagram and what group is it in?
h. Where would a Black Hole be located on an H-R diagram?
Вам также может понравиться
- HR Diagram Worksheet - NewДокумент4 страницыHR Diagram Worksheet - NewDon Amaru Sarma0% (2)
- Stars and Galaxies Virtual LabДокумент2 страницыStars and Galaxies Virtual Labapi-2608174140% (2)
- HR Diagram WorksheetДокумент2 страницыHR Diagram WorksheetImash ShanelkaОценок пока нет
- Project Hindsight - The Treatise On The Bright Fixed StarsДокумент63 страницыProject Hindsight - The Treatise On The Bright Fixed StarsBoris Zaslichko100% (1)
- Babylonian Part TwoДокумент106 страницBabylonian Part TwoPetr Radek100% (2)
- Classification of StarsДокумент3 страницыClassification of StarsJOSHUA CABIGAYAN100% (1)
- Classifying StarsДокумент6 страницClassifying StarsOde AsminОценок пока нет
- Horizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13th Edition Seeds Test BankДокумент25 страницHorizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13th Edition Seeds Test Bankkhondvarletrycth100% (25)
- HR DiagramДокумент8 страницHR DiagramSanchari BiswasОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5: 1. Sol: The 10 MДокумент5 страницAssignment 5: 1. Sol: The 10 Msrijanapple5Оценок пока нет
- Lab 6Документ5 страницLab 6Hunter GrossОценок пока нет
- HR Diagram - Student Guide: Background InformationДокумент11 страницHR Diagram - Student Guide: Background Informationsantiago floresОценок пока нет
- Aperture Photometry Obtaining and Analysing A H-R Diagram of M38 v2.0Документ14 страницAperture Photometry Obtaining and Analysing A H-R Diagram of M38 v2.0Arturo RuizОценок пока нет
- Classifying Stars The Hertzsprung Russell DiagramДокумент4 страницыClassifying Stars The Hertzsprung Russell DiagramcedricОценок пока нет
- HR Diagram - Student Guide: Background InformationДокумент9 страницHR Diagram - Student Guide: Background Informationsantiago floresОценок пока нет
- Stars in A BoxДокумент3 страницыStars in A BoxGergana SlavchevaОценок пока нет
- Stars in A Box: Background ScienceДокумент3 страницыStars in A Box: Background ScienceGergana SlavchevaОценок пока нет
- Question About Constellation Yr 5Документ6 страницQuestion About Constellation Yr 5Jc JoliatiОценок пока нет
- Astro2 2Nd Edition Seeds Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент35 страницAstro2 2Nd Edition Seeds Test Bank Full Chapter PDFregina.blackstock219100% (14)
- Tut39 HR DiagrammДокумент8 страницTut39 HR DiagrammViruTripathiОценок пока нет
- Cosmology Summary PT 2 2023Документ12 страницCosmology Summary PT 2 2023mxq88557Оценок пока нет
- Stellar Evolution Objectives SheetДокумент3 страницыStellar Evolution Objectives Sheetncl12142Оценок пока нет
- Soal OSK Astronomi 2011 EnglishДокумент9 страницSoal OSK Astronomi 2011 EnglishRicky PurnamaОценок пока нет
- Stellar Atmospheres HR PDFДокумент39 страницStellar Atmospheres HR PDFaggieОценок пока нет
- The Classification of Stellar SpectraДокумент39 страницThe Classification of Stellar SpectrahijibijiОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of StarsДокумент1 страницаCharacteristics of StarsNorel JanОценок пока нет
- Yellow Dwarf StarsДокумент4 страницыYellow Dwarf StarsAlmira Josefina BernardillaОценок пока нет
- Main Sequence: For The Racehorse, SeeДокумент13 страницMain Sequence: For The Racehorse, SeeDhaval MistryОценок пока нет
- Reading Passage 3: ConstellationДокумент4 страницыReading Passage 3: ConstellationYou Make My DayОценок пока нет
- Study GuideДокумент1 страницаStudy Guideapi-270695019Оценок пока нет
- PHY3 AJune 2006Документ1 страницаPHY3 AJune 2006api-3726022Оценок пока нет
- Lectures On Stellar Statistics by Charlier, Carl Vilhelm LudvigДокумент48 страницLectures On Stellar Statistics by Charlier, Carl Vilhelm LudvigGutenberg.orgОценок пока нет
- Stars and Stellar ClassificationДокумент8 страницStars and Stellar ClassificationsandragerouОценок пока нет
- Gcse WorksheetДокумент6 страницGcse WorksheetmaralОценок пока нет
- HWork 2Документ8 страницHWork 2Thomas ChouОценок пока нет
- H-R Diagram-1Документ9 страницH-R Diagram-1Joneryll Blessing Huliganga PaclarinОценок пока нет
- Stars and Classification Objectives SheetДокумент3 страницыStars and Classification Objectives Sheetncl12142Оценок пока нет
- Soal Astronomi 2014 Tingkat KabupatenДокумент5 страницSoal Astronomi 2014 Tingkat KabupatenRusdi SudarmanОценок пока нет
- HR Diagrams of Star Clusters: Student ManualДокумент20 страницHR Diagrams of Star Clusters: Student ManualOdin BorsonОценок пока нет
- HW 1Документ2 страницыHW 1Nilesh BarangeОценок пока нет
- Star Finder and IdentifierДокумент8 страницStar Finder and IdentifierSandunMigaraОценок пока нет
- Constellation and Equatorial SystemДокумент30 страницConstellation and Equatorial System吴振安Оценок пока нет
- Sci Astro 7.FAQДокумент11 страницSci Astro 7.FAQPantsik GrifoiОценок пока нет
- THE AND: Fixed Stars Constellations AstrologyДокумент258 страницTHE AND: Fixed Stars Constellations AstrologyВукашин Б Васић100% (1)
- Star Tales - Chinese ConstellationsДокумент2 страницыStar Tales - Chinese ConstellationsKart01Оценок пока нет
- Bohr's Star ModelДокумент4 страницыBohr's Star ModelShreyansh RaiОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet "The Sun and Stars": I. Objective/SДокумент3 страницыActivity Sheet "The Sun and Stars": I. Objective/SJan IceОценок пока нет
- Activity 5Документ5 страницActivity 5ARNOLD ARANOCOОценок пока нет
- FinalexamstudyДокумент24 страницыFinalexamstudyapi-339881021Оценок пока нет
- ApJS 2016-1Документ9 страницApJS 2016-1Hamael AbdulrazzaqОценок пока нет
- HR Diagrams AnsДокумент4 страницыHR Diagrams AnsMuhammad AsgharОценок пока нет
- Lplan9 22to9 26Документ3 страницыLplan9 22to9 26api-265304668Оценок пока нет
- Rudra History Hindu Astronomy Ephemeris 0903.1778v1Документ34 страницыRudra History Hindu Astronomy Ephemeris 0903.1778v1roberto-martinsОценок пока нет
- Stars Assessment DDДокумент5 страницStars Assessment DDapi-272838630Оценок пока нет
- Classification of Stellar SpectraДокумент25 страницClassification of Stellar Spectralittleitaly5Оценок пока нет
- HR Diagrams of Star Clusters: Student ManualДокумент20 страницHR Diagrams of Star Clusters: Student ManualPablo SaliОценок пока нет
- St. Joseph Astronomy Olympiad 2015 (Junior)Документ3 страницыSt. Joseph Astronomy Olympiad 2015 (Junior)Science Olympiad Blog100% (1)
- Important PDFДокумент107 страницImportant PDF5b00014fОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 1Документ4 страницыLesson Plan 1api-336208398Оценок пока нет
- Y 10 SciencelessonplanДокумент4 страницыY 10 Sciencelessonplanapi-336208398Оценок пока нет
- 2016 Lesson Plan 8 September Year 10 ScienceДокумент4 страницы2016 Lesson Plan 8 September Year 10 Scienceapi-336208398Оценок пока нет
- H-R Diagram09Документ1 страницаH-R Diagram09api-336208398Оценок пока нет
- Life Cycle of Stars Worksheet2Документ6 страницLife Cycle of Stars Worksheet2Zhiyong Huang0% (1)
- Stellarium User Guide-0.20.0-1 PDFДокумент380 страницStellarium User Guide-0.20.0-1 PDFJhon Francísco Hernández JiménezОценок пока нет
- The Night Sky Month by Month - Gater, Will.,Sparrow, GilesДокумент130 страницThe Night Sky Month by Month - Gater, Will.,Sparrow, GilesAline FaОценок пока нет
- MUL GU4.AN - NA Sipa - Zi.An - Na Šu - Gi Zubi or Gam3 Maš - Tab.Ba (.Gal.G Al - LulДокумент8 страницMUL GU4.AN - NA Sipa - Zi.An - Na Šu - Gi Zubi or Gam3 Maš - Tab.Ba (.Gal.G Al - LulRatsonMagenОценок пока нет
- 130 Stars NaksatrasДокумент8 страниц130 Stars NaksatrasComputershastriNoproblem100% (1)
- Nautical Almanac 2013Документ2 страницыNautical Almanac 2013waihtetОценок пока нет
- Top 100 Deep Sky ObjectsДокумент2 страницыTop 100 Deep Sky Objectsmcgg3Оценок пока нет
- Open Star ClusterДокумент15 страницOpen Star ClusterBainty Kaur ChughОценок пока нет
- Explain The Importance of Constellation To HumansДокумент18 страницExplain The Importance of Constellation To HumansSmiley DeSmillingОценок пока нет
- Important Fixed Stars LARGE TABLE and ARДокумент35 страницImportant Fixed Stars LARGE TABLE and ARjivaneto100% (2)
- Pamintul o Minune A CreatieiДокумент5 страницPamintul o Minune A CreatieivictorspanciocОценок пока нет
- Proxima CentauriДокумент14 страницProxima CentaurihurlyhutyoОценок пока нет
- Stars and ConstellationДокумент20 страницStars and ConstellationKim Zairyl FernandezОценок пока нет
- Science Form3 Chapter 9Документ4 страницыScience Form3 Chapter 9Sya Myra40% (5)
- SAS 2012 ProceedingsДокумент246 страницSAS 2012 Proceedingsmanuales1000Оценок пока нет
- Gravitational Collapse of Double Trios:Saiph (Kappa Orion)Документ64 страницыGravitational Collapse of Double Trios:Saiph (Kappa Orion)Drabrajib Hazarika100% (1)
- Aries Constellation PaperДокумент10 страницAries Constellation Paperapi-355409774Оценок пока нет
- Spectroscopic Atlas 2 0 EnglishДокумент124 страницыSpectroscopic Atlas 2 0 Englishspj_uhОценок пока нет
- Star Formation and EvolutionДокумент42 страницыStar Formation and EvolutionNiño Omar GedorioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Soal USM 2011Документ12 страницChapter 3 - Soal USM 2011Dio Putra WicaksonoОценок пока нет
- That Shapes Look Familiar!Документ32 страницыThat Shapes Look Familiar!Bernadeth DaracanОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Lesson 1Документ5 страницAstronomy Lesson 1Kristin WilsonОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Black Body QPДокумент11 страницEdexcel Black Body QPMehrabОценок пока нет
- ConstellationsДокумент16 страницConstellationsKhalid RedzaОценок пока нет
- NGC IC CatalogueДокумент3 страницыNGC IC CataloguerayaduqsОценок пока нет
- Piscis Austrinus The Southern Fish Piscis Notius Viento Del SurДокумент2 страницыPiscis Austrinus The Southern Fish Piscis Notius Viento Del Surceh ram100% (1)
- Saptarshi PDFДокумент15 страницSaptarshi PDFViriato SouzaОценок пока нет
- StarsGalaxies PDFДокумент2 страницыStarsGalaxies PDFAltinОценок пока нет
- Super Stargazer Guide BookДокумент8 страницSuper Stargazer Guide Bookarivalagan13Оценок пока нет