Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MCAT Chem
Загружено:
Hyeon Soh0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров2 страницыThis document discusses the properties of ideal gases and gas laws. It explains that ideal gases exhibit no intermolecular forces, elastic collisions between molecules, and the relationship between pressure, volume, moles, and temperature can be described using the ideal gas law. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as mean free path, Boltzmann's distribution, and how real gases differ from ideal gases due to intermolecular forces.
Исходное описание:
MCAT chem notes
Оригинальное название
MCAT chem
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses the properties of ideal gases and gas laws. It explains that ideal gases exhibit no intermolecular forces, elastic collisions between molecules, and the relationship between pressure, volume, moles, and temperature can be described using the ideal gas law. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as mean free path, Boltzmann's distribution, and how real gases differ from ideal gases due to intermolecular forces.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров2 страницыMCAT Chem
Загружено:
Hyeon SohThis document discusses the properties of ideal gases and gas laws. It explains that ideal gases exhibit no intermolecular forces, elastic collisions between molecules, and the relationship between pressure, volume, moles, and temperature can be described using the ideal gas law. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as mean free path, Boltzmann's distribution, and how real gases differ from ideal gases due to intermolecular forces.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
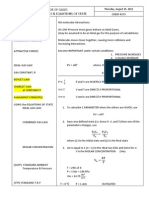
Gas Law
Ideal Gas Properties
- Low pressure (increase distance = decrease interaction)
- High Temperature (have enough energy to overcome intermolecular forces)
- No intermolecular forces
- All collisions are elastic
Concepts
Macroscopic
Pressure (P)
Volume (V)
Moles (n)
Temperature (T)
Microscopic
Collision frequency & force
Mean free path
Molecules
Average Kinetic Energy
Mass of gas X Matter for Pressure
- Lighter gas has faster speed (greater frequency) but smaller collision force
Boltzmanns Distribution
- Increasing temperature less steep
Real vs. Ideal gas
Pideal = Pobserved + a (n2 / V2)
Videal = Vcontainer - nb
a = attraction coefficient (a = - when particles repel) intermolecular force
nb = volume the molecules occupy ideal gas X occupy volume
Common Mistake
-
X converting C to K
Вам также может понравиться
- Lecture 2Документ21 страницаLecture 2Joe ParkОценок пока нет
- Module 3Документ3 страницыModule 3Tamoya Shirley100% (1)
- Lecture 12Документ5 страницLecture 12saadi yusufОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент8 страницKinetic Theory of GasesGupta GuptaОценок пока нет
- State Variables: X X X XДокумент16 страницState Variables: X X X XSaikumar PОценок пока нет
- Thermal Physics EquationsДокумент6 страницThermal Physics EquationsThanh NgânОценок пока нет
- Molecular View of Gases: Kinetic TheoryДокумент7 страницMolecular View of Gases: Kinetic TheorySarah FeyОценок пока нет
- Physics Ch3 NotesДокумент4 страницыPhysics Ch3 NotesAli GorganiОценок пока нет
- Generalization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Документ27 страницGeneralization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Husnil KhatimahОценок пока нет
- Gas LawДокумент1 страницаGas LawshennaabegailtanОценок пока нет
- Physics Topic 3 Study GuideДокумент5 страницPhysics Topic 3 Study GuideSai 0235Оценок пока нет
- Thermal 4 Kinetic Molecular TheoryДокумент15 страницThermal 4 Kinetic Molecular TheoryOmaru NimagaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9: ChemistryДокумент16 страницChapter 9: ChemistrytausmanОценок пока нет
- Physical Chemistry 01 2015 1stДокумент33 страницыPhysical Chemistry 01 2015 1stAzkha AvicenaОценок пока нет
- H2 Physics Formulae and Definitions: MeasurementДокумент7 страницH2 Physics Formulae and Definitions: MeasurementChong Yi AnОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент15 страницKinetic Theory of GasesNicholas OwОценок пока нет
- Gaseous State: Ideal GasesДокумент13 страницGaseous State: Ideal GasesM.S.A. Mobashwer HossenОценок пока нет
- No Definite Shape and Volume: Science (1) GasesДокумент2 страницыNo Definite Shape and Volume: Science (1) GasesAllen KateОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of Gases ExplainedДокумент22 страницыKinetic Theory of Gases ExplainedMegis HefrindhaОценок пока нет
- Chem1031 Study Notes For UNSWДокумент37 страницChem1031 Study Notes For UNSWOliverОценок пока нет
- Properties of Gases EquationsДокумент33 страницыProperties of Gases EquationsSdОценок пока нет
- Thermal Properties of Matter and Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент5 страницThermal Properties of Matter and Kinetic Theory of GasesAmmar ZaminОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes on Temperature, Thermal Equilibrium, and the Microscopic Model of an Ideal GasДокумент5 страницLecture Notes on Temperature, Thermal Equilibrium, and the Microscopic Model of an Ideal GasDonald Ng Jer YiОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Course: Termodinamika Dan Fisika Statistik - FIS62113Документ121 страницаIntroduction To The Course: Termodinamika Dan Fisika Statistik - FIS62113rahmadani fitrianaОценок пока нет
- Ideal Gas Law and Laws of ThermodynamicsДокумент9 страницIdeal Gas Law and Laws of ThermodynamicsVAN STEVEN SANTOSОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18: Thermal Properties of Matter: Topics For DiscussionДокумент21 страницаChapter 18: Thermal Properties of Matter: Topics For DiscussionAndrew MerrillОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент29 страницThermodynamicsCherry ObiasОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics NotesДокумент13 страницThermodynamics NotesParas ThakurОценок пока нет
- Physics of Fusion Power: Lecture 1: The Basics Lecturer: B.F.McmillanДокумент28 страницPhysics of Fusion Power: Lecture 1: The Basics Lecturer: B.F.McmillanArmagaddonОценок пока нет
- 11 Ideal GasesДокумент47 страниц11 Ideal Gaseslc1999227Оценок пока нет
- States of MatterДокумент14 страницStates of MatterSiya ChiniahОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент6 страницKinetic Theory of GasesNicholas OwОценок пока нет
- Chem 1302 Midterm ReviewДокумент9 страницChem 1302 Midterm ReviewSaddi MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 Study MaterialДокумент33 страницыClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 Study MaterialmeghaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Gases After-Lecture-NoteДокумент30 страницChapter 9 Gases After-Lecture-NoteElvis ChanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1: Thermodynamics: CHEM 452: Physical Chemistry For BiochemistsДокумент14 страницLecture 1: Thermodynamics: CHEM 452: Physical Chemistry For BiochemistsmoienОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics GlossaryДокумент1 страницаThermodynamics GlossaryzugoelfinitoОценок пока нет
- Actual Molecular Mass Empirical Molecular Mass: Che 102 Chemistry For Engineers ReviewДокумент8 страницActual Molecular Mass Empirical Molecular Mass: Che 102 Chemistry For Engineers ReviewTariq Ceniza RasulОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics LiteДокумент75 страницThermodynamics LiteAliakbar RiyazОценок пока нет
- Page 1 of 26: Masterton, W.L., Et. Al. Principles and Reactions: Chemistry For Engineering Students, Philippine Ed. 2016Документ26 страницPage 1 of 26: Masterton, W.L., Et. Al. Principles and Reactions: Chemistry For Engineering Students, Philippine Ed. 2016The Hamster VoyageОценок пока нет
- Thermal Properties of MatterДокумент12 страницThermal Properties of MatterSarah MontoyaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Gas LawsДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide Gas LawsAdamОценок пока нет
- Lecture35 PDFДокумент19 страницLecture35 PDFAveenОценок пока нет
- Phy Formula ListДокумент2 страницыPhy Formula ListtingsengОценок пока нет
- Physics 1220/1320 Thermodynamics and Electromagnetism Key ConceptsДокумент23 страницыPhysics 1220/1320 Thermodynamics and Electromagnetism Key ConceptsbeckerinskiОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of Gases - 152 - DownloadДокумент24 страницыKinetic Theory of Gases - 152 - DownloadIfiok UsoroОценок пока нет
- Phys NotesДокумент6 страницPhys NotesFelice TanОценок пока нет
- Gas LawДокумент7 страницGas LawCATHERINE BAGUIOROОценок пока нет
- Bab 1 Gas Ideal Dan NyataДокумент64 страницыBab 1 Gas Ideal Dan NyataVincent PradjinataОценок пока нет
- Properties of Gases (Report)Документ19 страницProperties of Gases (Report)Rex LapisОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasessДокумент9 страницKinetic Theory of GasessTchierry S PurhooaОценок пока нет
- Ideal GasДокумент10 страницIdeal GasОлжас ТыныштыкОценок пока нет
- States of Matter Course OutlineДокумент40 страницStates of Matter Course OutlinedevoydouglasОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws and Kinetic TheoryДокумент14 страницGas Laws and Kinetic Theorybrianouko25Оценок пока нет
- Bab I Gas Ideal Dan Nyata 2009 - 2010Документ64 страницыBab I Gas Ideal Dan Nyata 2009 - 2010Kezia IreneОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Molecular Theory: Based On The Idea That Particles ofДокумент11 страницKinetic Molecular Theory: Based On The Idea That Particles ofnpazОценок пока нет
- Survey of Physical Chemistry Notes - ReviewДокумент3 страницыSurvey of Physical Chemistry Notes - ReviewJp2133Оценок пока нет
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 1B: Harmonic Oscillators, & ThermodynamicsОт EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 1B: Harmonic Oscillators, & ThermodynamicsОценок пока нет
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsОт EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Full Length Aamc 1Документ5 страницFull Length Aamc 1Hyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ11 страницAssignment 4Hyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Orgo 1 SyllbusДокумент3 страницыOrgo 1 SyllbusHyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Bio SyllabusДокумент6 страницBio SyllabusHyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Name "Dave": End - Quote Find Start - QuoteДокумент3 страницыName "Dave": End - Quote Find Start - QuoteHyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Week 1Документ2 страницыWeek 1Hyeon SohОценок пока нет
- Logical Reasoning TipsДокумент1 страницаLogical Reasoning TipsHyeon SohОценок пока нет