Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
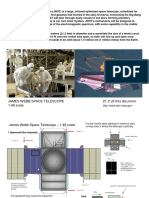
James Webb Space Telescope - 1 To 48 Scale Paper Model PDF
Загружено:
Hola PatagoniaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
James Webb Space Telescope - 1 To 48 Scale Paper Model PDF
Загружено:
Hola PatagoniaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a large, infrared-optimized space telescope, scheduled for
launch in 2014. JWST will find the first galaxies that formed in the early Universe, connecting the Big Bang
to our own Milky Way Galaxy. JWST will peer through dusty clouds to see stars forming planetary
systems, connecting the Milky Way to our own Solar System. JWST's instruments will be designed to
work primarily in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum, with some capability in the visible
range.
JWST will have a large mirror, 6.5 meters (21.3 feet) in diameter and a sunshield the size of a tennis court.
Both the mirror and sunshade won't fit onto the rocket fully open, so both will fold up and open once
JWST is in outer space. JWST will reside in an orbit about 1.5 million km (1 million miles) from the Earth.
JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE
1:48 scale
21.3 (6.5m) dia mirror
http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/
The star tracker takes sightings of reference stars
to keep track of where the telescope is pointing.
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
FOLD UP
1-Spacecraft Bus Assembly
STAR TRACKER
FOLD UP
MAIN BUS
STAR
TRACKER
STAR SENSORS
bond paper
ROLL
ROLL-THEN CUT
ONE SQUARE END
CYLINDER. CUT
REMAINDER IN HALF
AT 45 DEGREES
FOLD UP
DO NOT FOLD USE TO
ATTACH FORE/AFT
SUNSHIELD SUPPORT
BEAMS
FOLD UP
MOUNT TO BLUE SQUARE ON BUS
FOLD UP
ROLL
The spacecraft bus houses the equipment
that runs the satellite: keeping the
batteries charged; pointing the
telescope/spacecraft at the target
stars; etc.
HGA MOUNT
HGA
PRIMARY
REFLECTOR
SECONDARY
REFLECTOR
TRIPOD
BUS END
FOLD ARMS INTO
BEAMS, REINFORCE
ELBOW WITH ROLL
CUT
The high gain antenna is used to receive commands from,
and return the telescopes observations to, the Earth.
Copyright 2010: John Jogerst.
Not for commercial use.
For educational or personal use only.
DISH END
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
2-Solar Arrays
8-Secondary Mirror Assembly
AFT EDGE OF BUS AND AFT END OF SOLAR SHIELD
MOMENTUM FLAP
The momentum flap helps stabilize the
spacecraft. JWST is so precise that solar
pressure on the large sunshields can
actually rotate (slowly) the telescope, spoiling
its aim. The flap adjusts to counteract part of
this pressure to help keep the telescope view
steady.
Copyright 2010: John Jogerst. Not for commercial use.
For educational or personal use only.
The solar panel generates the power
that runs the satellite and the telescope
instruments.
SECONDARY MIRROR
SUPPORT STRUTS
2 OF 3
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#5 bottom aft end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
STAR SENSORS
Option: print on
bond paper
ROLL
ROLL-THEN CUT
ONE SQUARE END
CYLINDER. CUT
REMAINDER IN HALF
AT 45 DEGREES
The sunshields keep the satellite cool by
blocking the heat of the sun. This allows
the JWSTs infra-red telescope to see
and analyze very faint, distant objects.
Since the JWST sees in infra-red light
(heat), it must be kept very cold or the
heat from the spacecraft itself would
obscure its view.
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#5 bottom fore end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
STAR
TRACKER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#4 aft end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#4 fore end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#3 mid aft end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#3 mid fore end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#2 aft end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#2 fore end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#1 top aft end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope
1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
#1 top fore end
Master Pattern
PRINT THIS ON
PLAIN BOND PAPER
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
3-Sunshields
MOUNTING TABS
SPREADER BARS cut cross beam bars short to achieve angle of sunshade
The spreader bars hold the five sunshield layers apart
to increase their insulating effectiveness.
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
Do not bend black ears on end-used to attach to spreader bars.
4-Sunshield support beams trim ends if needed to butt
with spacecraft bus assembly
The sunshield support
beams are the bones that
hold the sunshields in
position. Folded for launch,
they unfold in space to
stretch out the sunshields.
AFT
AFT
FORE
The center support boom is the
backbone that connects the
satellite bus to the instruments
and telescope.
FORE
CROSSBEAM
5-Center
Support Boom
CROSSBEAM
6-Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM)
8-Secondary Mirror Assembly
SECONDARY MIRROR
SUPPORT STRUT
1 OF 3
IEC
The ISIM contains the telescopes science
instruments that will observe and analyze
distant objects. Instruments include:
Near InfraRed Camera (NIRCam),
Near InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec),
Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI),
and the Fine Guidance Sensor Tunable Filter Camera (FGS-TFI)
The support struts hold the secondary mirror precisely in position
to reflect light from the primary mirror to the science instruments.
They are folded for launch and unfold in space.
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
6-Integrated Science Instrument Module
INSTRUMENT SHIELD
7-Primary Mirror
The primary mirror collects infrared light for the science
instruments. A 6.5 meter (21 4) mirror makes JWST
the most powerful space telescope. JWST uses infrared light (heat) to see objects at the very edge of our
visible universe.
PRIMARY MIRROR
ISIM Electronics Compartment (IEC)
TOP
The IEC contains electronic equipment
that generates heat when operating,
so they must be isolated from the
Hubble Space Telescope
science instruments.
mirror to scale
MIRROR FRONT SURFACE
The JWST mirror is so large it must be folded to fit into its
launch rocket. The three mirror segment in the outer rows
are folded back for launch, then unfolded into precise
alignment once JWST is in space. The mirror segments are
held in place by an intricate truss the backplane.
MIRROR BACK SURFACE
These rows fold back for launch.
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
REVISED BACKPLANE - FRONT
For a detailed scratch-build, refer to pictures and
the JWST web site.
Backplane structure is truss of box beams.
Mirror mounts are welded, tube structures.
Outer column of 3 mirrors folds back for
launch.
Shield is thin sheet.
Secondary mirror support struts
mount to pads on backplane truss
behind shield.
The JWST backplane actually consists of a truss structure attached
to the ISIM (black rectangular shape on part); the mirror supports
(oval structures on part); thermal shields on the back of the mirror
supports and a shielding panel at the bottom that prevent heat from
the ISIM and IEC from reaching the mirrors. This part has been simplified
to make it easier to build.
For detailed primary mirror,
cut out dotted
circle and inset
the curved
mirror.
James Webb Space Telescope 1:48 scale
GLUE 2ND
REVISED BACKPLANE - BACK
For a detailed scratch-build, refer to pictures and
JWST web site.
Backplane structure is truss of box beams.
Protective covers over attachments.
8-Secondary Mirror Assembly
AFT OPTICS
CENTER ON
FACE OF MIRROR
The secondary mirror takes the light
focused by the primary mirror and
sends it back to the instruments
through the aft optics.
GLUE THIS FIRST
Вам также может понравиться
- The Strange, Icy World of PlutoДокумент11 страницThe Strange, Icy World of PlutoDiago AlbertoОценок пока нет
- Astronomy, Petabytes, and MySQLДокумент47 страницAstronomy, Petabytes, and MySQLOleksiy Kovyrin100% (4)
- Mars Polar Lander Deep Space 2 PresskitДокумент47 страницMars Polar Lander Deep Space 2 PresskitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Manned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969От EverandManned Mars Landing: Presentation to the Space Task Group - 1969Оценок пока нет
- Cyborg Glove ExcerptNick and Tesla's Super Cyborg Gadget Glove (Excerpt)Документ67 страницCyborg Glove ExcerptNick and Tesla's Super Cyborg Gadget Glove (Excerpt)Quirk BooksОценок пока нет
- Pleasures of the telescope: An Illustrated Guide for Amateur Astronomers and a Popular Description of the Chief Wonders of the Heavens for General ReadersОт EverandPleasures of the telescope: An Illustrated Guide for Amateur Astronomers and a Popular Description of the Chief Wonders of the Heavens for General ReadersОценок пока нет
- Orbital MechanicsДокумент28 страницOrbital MechanicsMartin Schweighart MoyaОценок пока нет
- Vistas in Astronomy: Volume 28От EverandVistas in Astronomy: Volume 28P. BeerОценок пока нет
- Voyager Fact SheetДокумент14 страницVoyager Fact SheetBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Pluto and Lowell Observatory: A History of Discovery at FlagstaffОт EverandPluto and Lowell Observatory: A History of Discovery at FlagstaffОценок пока нет
- Timed: Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and DynamicsДокумент20 страницTimed: Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and DynamicsBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Mission To Touch The Sun: Parker Solar Probe: Nandan A K 51 S3C1Документ33 страницыMission To Touch The Sun: Parker Solar Probe: Nandan A K 51 S3C1nandan akОценок пока нет
- Part 1: 3D Printing and Laser Cutting: Ultrascope Explorer SeriesДокумент39 страницPart 1: 3D Printing and Laser Cutting: Ultrascope Explorer Seriesca.lalamaОценок пока нет
- Spacelab An International Success StoryДокумент561 страницаSpacelab An International Success StoryBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Origins of NASA NamesДокумент242 страницыOrigins of NASA NamesdroberОценок пока нет
- The Unlikely Soviet Explorers That Beat America To The MoonДокумент3 страницыThe Unlikely Soviet Explorers That Beat America To The MoonKlaatu78Оценок пока нет
- Issue Vol. 10, 04 2012Документ163 страницыIssue Vol. 10, 04 2012Rogério CavalcanteОценок пока нет
- Lifting Titan's Veil: Exploring The Giant Moon of SaturnДокумент22 страницыLifting Titan's Veil: Exploring The Giant Moon of SaturnFer MontesinosОценок пока нет
- No. 134 - December 2008Документ68 страницNo. 134 - December 2008European Southern ObservatoryОценок пока нет
- Space Exploration HistoryДокумент53 страницыSpace Exploration HistoryRaajeswaran BaskaranОценок пока нет
- Media, NASA, and America's Quest For The Moon (Mediating American History)Документ1 страницаMedia, NASA, and America's Quest For The Moon (Mediating American History)Anonymous TYEW7pfОценок пока нет
- Major Activities in NASA Programs October 1, 1959 - March 31, 1960Документ192 страницыMajor Activities in NASA Programs October 1, 1959 - March 31, 1960Bob Andrepont100% (1)
- Design, Development and Testing Nitrous Oxide System of A Hybrid Rocket MotorДокумент36 страницDesign, Development and Testing Nitrous Oxide System of A Hybrid Rocket MotorMohamed TarmiziОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Apollo 8 Photography and Visual OperationДокумент350 страницAnalysis of Apollo 8 Photography and Visual OperationBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Significant Achievements in Space Astronomy 1958-1964Документ73 страницыSignificant Achievements in Space Astronomy 1958-1964Bob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- ESO/CERN Agreement Renewed: No. 2 - November 1974Документ6 страницESO/CERN Agreement Renewed: No. 2 - November 1974European Southern ObservatoryОценок пока нет
- Mars Quick FactsДокумент10 страницMars Quick FactsAviation/Space History Library100% (6)
- Into The Thermosphere The Atmosphere ExplorersДокумент171 страницаInto The Thermosphere The Atmosphere ExplorersBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- A Space Elevator For The Far Side of The MoonДокумент23 страницыA Space Elevator For The Far Side of The MoonMarshall EubanksОценок пока нет
- NASA Report Details 1962 Space and Aviation EventsДокумент374 страницыNASA Report Details 1962 Space and Aviation EventsunabombaОценок пока нет
- Arthur C Clarke - When The Twerms CameДокумент2 страницыArthur C Clarke - When The Twerms Camegosai83100% (1)
- NASA Space Shuttle STS-126 Press KitДокумент118 страницNASA Space Shuttle STS-126 Press KitOrion2015Оценок пока нет
- Astronomy - February 2019 USA PDFДокумент80 страницAstronomy - February 2019 USA PDFRaluca Roxana RujaОценок пока нет
- ESO Turns 40: CATHERINE CESARSKY, Director General of ESOДокумент60 страницESO Turns 40: CATHERINE CESARSKY, Director General of ESOEuropean Southern ObservatoryОценок пока нет
- Mercury-Atlas Mission No. 4-8A (Capsule 8A)Документ16 страницMercury-Atlas Mission No. 4-8A (Capsule 8A)Bob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- NASA Facts International Space Station Assembly Rev E June 1999Документ9 страницNASA Facts International Space Station Assembly Rev E June 1999Bob Andrepont100% (1)
- The Jovian Beet: Un H CC Mpli NTДокумент6 страницThe Jovian Beet: Un H CC Mpli NTBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Astronomy, Vol. 51.01 (January 2023)Документ64 страницыAstronomy, Vol. 51.01 (January 2023)georgetacaprarescuОценок пока нет
- Expedition 4 Press KitДокумент52 страницыExpedition 4 Press KitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Gps II ManualДокумент108 страницGps II ManualAlejandroguillermoОценок пока нет
- Science - Satrun Voyager 1981 PDFДокумент30 страницScience - Satrun Voyager 1981 PDFLuis Romero100% (2)
- Hubbles Legacy PDFДокумент240 страницHubbles Legacy PDFBogdan VladОценок пока нет
- NASA Facts The Press Site at KSC 2004Документ4 страницыNASA Facts The Press Site at KSC 2004Bob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Dreams, Hopes, Realities NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, The First Forty YearsДокумент236 страницDreams, Hopes, Realities NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, The First Forty YearsBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- NASA: 187392main Aresv Fact SheetДокумент4 страницыNASA: 187392main Aresv Fact SheetNASAdocumentsОценок пока нет
- Probing the Red Planet - A History of Mars MissionsДокумент35 страницProbing the Red Planet - A History of Mars MissionszackОценок пока нет
- Galaxy evolution in full colourДокумент7 страницGalaxy evolution in full colourParag MahajaniОценок пока нет
- Successful Completion of An Ambitious Project - A Midwinter Night's DreamДокумент40 страницSuccessful Completion of An Ambitious Project - A Midwinter Night's DreamEuropean Southern ObservatoryОценок пока нет
- Space Shuttle MissionsДокумент2 страницыSpace Shuttle MissionsAviation/Space History Library100% (1)
- M1 - Crab Nebula Globular ClusterДокумент110 страницM1 - Crab Nebula Globular ClusterPete_FPWОценок пока нет
- Where No Man Has Gone Before: A History of Apollo Lunar Exploration MissionsДокумент562 страницыWhere No Man Has Gone Before: A History of Apollo Lunar Exploration MissionsPeter AylwardОценок пока нет
- UK-6 Press KitДокумент16 страницUK-6 Press KitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Fltsatcom-B Press KitДокумент9 страницFltsatcom-B Press KitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Mars Pathfinder Landing Press KitДокумент44 страницыMars Pathfinder Landing Press KitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- The Eclipse ProjectДокумент178 страницThe Eclipse ProjectBob Andrepont50% (2)
- Pioneer IV Press KitДокумент19 страницPioneer IV Press KitBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- The Sensory Neuron As A Transformer: Permutation-Invariant Neural Networks For Reinforcement LearningДокумент17 страницThe Sensory Neuron As A Transformer: Permutation-Invariant Neural Networks For Reinforcement LearningHola PatagoniaОценок пока нет
- Active One Shot Learning 2016Документ8 страницActive One Shot Learning 2016Hola PatagoniaОценок пока нет
- 1606 02318Документ10 страниц1606 02318Hola PatagoniaОценок пока нет
- Research Tools For The Age of Digital Scholarship - Wiley PDFДокумент5 страницResearch Tools For The Age of Digital Scholarship - Wiley PDFHola PatagoniaОценок пока нет
- JWST Model 1-48scale Final-Parts PDFДокумент20 страницJWST Model 1-48scale Final-Parts PDFHola PatagoniaОценок пока нет