Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MSA Work Instruction
Загружено:
azadsingh1Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MSA Work Instruction
Загружено:
azadsingh1Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Work Instruction for Conducting R&R
1.0
Purpose: -
This Work instruction is intended to draw guidelines for conducting, analyzing and providing the criteria for
acceptance of measure system analysis. Also to understand the variability caused by the measuring system in
comparison with process variation.
2.0
Scope: -
All Measuring systems / equipments / instruments used for measuring characteristics directly influence the
product quality and have potential influence in acceptance of product.
3.0
Definitions
(1)
Repeatability :Repeatability is the variation in measurements obtained with one measurement
instrument when used several times by an appraiser while measuring the identical characteristic on
the same part.
(2)
Reproducibility: Reproducibility is the variation in the average of the measurements made by
different appraisers using the same measuring instrument when measuring the identical characteristic
on the same part.
(For more details please refer Measurement System Analysis MSA Reference Manual sanctioned by the
Chrysler/Ford/General Motors in line with the requirements of QS 9000.)
4.0
Pre requisites before conducting a MSA Study: -
4.1
Environment
All aspect of environment should be similar to the usage condition and kept constant while collecting data.
4.2
Selection of Measuring Equipment
Measuring equipment must have a discrimination that allows at least one-tenth of the expected process
variation of the characteristic to be read directly.
4.3
Selection of part
Parts selected for R&R study must represent the complete process variation.
4.4
Selection of Appraiser Operator
The appraiser chosen should be selected from those who normally operate / use the measuring system.
4.5
Marking serial number on part
Serial number should be marked on each part considered for the study. The measurement s should be made
in random order to ensure that any drift or changes that could occur will be spread randomly throughout the
study. The appraiser should be unaware of which numbered part is being checked in order to avoid any
possible knowledge bias. However person conducting the study should know which numbered part is being
checked and record the data accordingly.
Work Instruction for Conducting R&R
4.6
Selection of number of appraiser, samples and trials
Number of appraiser, samples and trials are based on the nature of process, sample profile, and the criticality
of the characteristic. It depends also on the time of inspection.
Generally for a short-term study, with one trial, number of samples are taken between 5 to 10, number of
appraiser are minimum 2 or more. For long-term study number of trails increases to minimum 3. For
attribute type of characteristic, number of samples should be minimum 10.
5.0
5.1
5.2
5.3
5.4
5.5
How to conduct the Study
Obtain the sample, which represents the actual or expected range of variations.
Refer the appraiser as A, B and C and number the parts 1 through 10 so that the numbers are
not visible to the appraiser.
Calibrate the gauge if this is a part of normal gauging procedure.
Sequence of taking measurement by appraiser A, B or C, one by one or by one appraiser all
samples and then next appraiser, can be decided based on the feasibility and availability of apprasier.
The data will be recorded on the format as per annexure 1.
The person who is conducting the study should record observation.
6.0
Analysis
The Average and range method is a mathematical method, which will provide and estimate of both
repeatability and reproducibility for a measurement system. Unlike to the Range method, this will allow the
measurement system to be decomposed into two separate components, repeatability and reproducibility, but
not their interaction.
The ANOVA method can be used to determine this interaction between gauge and appraiser. However, both
the average and range method and ANOVA method will provide information concerning the cause of
measurement system or gauge error.
For example, if repeatability is large compared to reproducibility, the reasons may be:
1)
The instrument needs maintenance.
2)
The gauge should be designed to be more rigid.
3)
The claming or location for gauging to be improved.
4)
There is excessive with in part variation
If reproducibility is large compared to repeatability, the reasons may be:
1)
The appraiser needs to be better trained in how to use and read the gauge instrument.
2)
Calibration on the gauge dial is not clear.
3)
A fixture of some sort may be needed to help the appraiser use the gauge more consistently.
7.0
Acceptance criteria
Guidelines for acceptance of gauge repeatability and reproducibility (% R & R) are:
Under 10% error the measurement system is acceptable.
10% to 30% error may be acceptable based upon importance of application, cost of gauge, cost
of repair, etc.
Over 30% error Measurement system needs improvement. Make every effort to identify the
problem and have them corrected.
8.0
Records
8.1 A list mentioning the current status of all measurements systems will be maintained.
8.2 A frequency sheet for all studies will be maintained.
8.3 A log of all studies will be maintained.
8.4 Individual measurement system report sheet will be maintained to address the improvement for each
measurement system.
Please refer annexure 2 and 3 for the formats of all above record sheets.
Вам также может понравиться
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationОт EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationОценок пока нет
- MSA ProcedureДокумент3 страницыMSA ProcedureAnkur0% (1)
- Measurement System AnalysisДокумент42 страницыMeasurement System Analysisazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- SPC MSA GuidelinesДокумент28 страницSPC MSA Guidelinesbill100% (2)
- MSA Training PPT 14-07-2020 PDFДокумент125 страницMSA Training PPT 14-07-2020 PDFLAKSHYA MITTAL100% (4)
- Procedure: Measurement System Analysis ExecutionДокумент1 страницаProcedure: Measurement System Analysis Executionaslam100% (1)
- MsaДокумент7 страницMsaGobi PSОценок пока нет
- Wi SPCДокумент4 страницыWi SPCSujeet Kumar100% (1)
- Quality Manual: Subject: Procedure For PFMEAДокумент3 страницыQuality Manual: Subject: Procedure For PFMEAPk Nimiwal100% (3)
- Red Bin Analysis ProcedureДокумент4 страницыRed Bin Analysis ProcedureVenkatesan92% (12)
- Manufacturing Process AuditДокумент1 страницаManufacturing Process AuditSachin Kumbhar100% (1)
- Checklist of Documentation For IATF 16949 - 2016Документ11 страницChecklist of Documentation For IATF 16949 - 2016Deepak kumarОценок пока нет
- Training in MSA PQ Systems Training Material PDFДокумент109 страницTraining in MSA PQ Systems Training Material PDFsaby aroraОценок пока нет
- System Audit RequirementДокумент37 страницSystem Audit Requirementavinashbatra171% (7)
- Control Plan TrainingДокумент20 страницControl Plan TrainingGAURAV SHARMAОценок пока нет
- Reverse FMEAДокумент27 страницReverse FMEAJobs Steve100% (2)
- MSAДокумент66 страницMSAGowri Krishna Chikkala100% (3)
- Statistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4Документ1 страницаStatistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4sa_arunkumarОценок пока нет
- Question Paper For MSA: Magnifico Training and Consulting ServicesДокумент2 страницыQuestion Paper For MSA: Magnifico Training and Consulting ServicesRajesh SahasrabuddheОценок пока нет
- Supplier APQP Training SupplementДокумент78 страницSupplier APQP Training SupplementjcperezОценок пока нет
- ApqpДокумент72 страницыApqpsaby aroraОценок пока нет
- Control Plan AIAGДокумент1 страницаControl Plan AIAGAhmad Firdaus100% (1)
- 4M Change Management For Supplier - TennecoДокумент1 страница4M Change Management For Supplier - TennecoOBSC PerfectionОценок пока нет
- CD6 Prototype Control PlanДокумент3 страницыCD6 Prototype Control Planmpedraza-1Оценок пока нет
- Special Characteristics PDFДокумент11 страницSpecial Characteristics PDFKristof MCОценок пока нет
- Attribute MSA TrainingДокумент21 страницаAttribute MSA TrainingDisha ShahОценок пока нет
- Red Bin Analysis FormatДокумент1 страницаRed Bin Analysis FormatPRABHAT RANJAN100% (1)
- Product Audit Check SheetДокумент3 страницыProduct Audit Check SheetLakshmanan Venkatesan100% (8)
- Msa (NDC)Документ7 страницMsa (NDC)rkshpanchalОценок пока нет
- SPC Course MaterialДокумент118 страницSPC Course MaterialKrunal Pandya100% (1)
- Acceptence Criteria - IMTEДокумент15 страницAcceptence Criteria - IMTEnedunchi83% (6)
- PFMEA AuditingДокумент18 страницPFMEA AuditingelevendotОценок пока нет
- Iso Iatf Quality System Manual PDFДокумент53 страницыIso Iatf Quality System Manual PDFKrishnamoorthyОценок пока нет
- 11.process Turtile DiagramДокумент20 страниц11.process Turtile DiagrammuthuselvanОценок пока нет
- 4.statistical Process ContorlДокумент47 страниц4.statistical Process ContorlMinhajul Haque SarkarОценок пока нет
- T2 VSA With RequirementДокумент8 страницT2 VSA With RequirementSandeep K Malhotra100% (3)
- SPC ProcedureДокумент5 страницSPC ProcedureKrunal Pandya100% (1)
- Poison Cake Test: Standard Operating ProcedureДокумент1 страницаPoison Cake Test: Standard Operating ProcedureGirdhar Sahu100% (3)
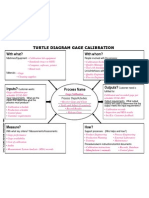
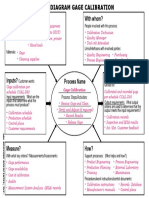
- Turtle Diagram (Calibration)Документ1 страницаTurtle Diagram (Calibration)semaphore689% (9)
- SPC TrainingДокумент80 страницSPC TrainingRubelio JaimesОценок пока нет
- Questions Process Audit: P2. Project ManagementДокумент11 страницQuestions Process Audit: P2. Project ManagementR JОценок пока нет
- GM 1927 36 Group C Elements BIQSДокумент52 страницыGM 1927 36 Group C Elements BIQSVanessa GurrolaОценок пока нет
- Turtle Diagram (Calibration)Документ1 страницаTurtle Diagram (Calibration)DL100% (1)
- W.I - Abnormal SituationДокумент1 страницаW.I - Abnormal Situation25april100% (2)
- Abnormal Handling Module (English Version)Документ15 страницAbnormal Handling Module (English Version)Mukesh Sharma Akshu67% (3)
- Required Documents For IATF - 16949Документ5 страницRequired Documents For IATF - 16949Rajesh Sahasrabuddhe0% (1)
- APQP FormsДокумент23 страницыAPQP FormsJOECOOL670% (1)
- Questoes Core ToolsДокумент2 страницыQuestoes Core ToolsMàrcia Neruda69% (13)
- PFMEA - MachiningДокумент14 страницPFMEA - Machiningmani317100% (1)
- Sample FMEA - MachiningДокумент20 страницSample FMEA - MachiningHemantОценок пока нет
- Operator Observance SheetДокумент5 страницOperator Observance SheetEr Avinash Kumar100% (2)
- Automotive Quality Management System Manual: Century Metal Recycling LimitedДокумент7 страницAutomotive Quality Management System Manual: Century Metal Recycling LimitedsunilОценок пока нет
- Sampling PlanДокумент2 страницыSampling PlanAbhay KarandeОценок пока нет
- AIAG-VDA PFMEA Template For Activity - (Delegate)Документ38 страницAIAG-VDA PFMEA Template For Activity - (Delegate)nadia_naaz90Оценок пока нет
- PFMEA and Control Plan Linkage ExamplesДокумент5 страницPFMEA and Control Plan Linkage Exampleslittlekheong100% (1)
- IATF 16949 2016 Gap ToolДокумент353 страницыIATF 16949 2016 Gap ToolOziel Cardenas33% (6)
- FMEA - 5th Edition FORMATДокумент2 страницыFMEA - 5th Edition FORMATManu100% (2)
- MSIL Audit Cheklist 16Документ22 страницыMSIL Audit Cheklist 16Pravin Balasaheb GunjalОценок пока нет
- Poison Test ProcedureДокумент2 страницыPoison Test Procedureprashanth92% (13)
- MSA PresentationДокумент37 страницMSA Presentationelifexp100% (1)
- Hourly Report of Tata - Disc: Part: Tata Shift:-DATEДокумент5 страницHourly Report of Tata - Disc: Part: Tata Shift:-DATEazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- 7,-Qad-28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74-100Документ1 страница7,-Qad-28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74-100azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Sheet Process: Technical Data ModificationДокумент1 страницаSheet Process: Technical Data Modificationazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Pdi 05 01.2015 Qad 28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74 100Документ1 страницаPdi 05 01.2015 Qad 28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74 100azad100% (1)
- Sheet Process: Technical Data ModificationДокумент1 страницаSheet Process: Technical Data Modificationazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Pdi 05 01.2015 Qad 28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74 100Документ1 страницаPdi 05 01.2015 Qad 28sample Inspection Report Mach. 74 100azad100% (1)
- 8654Документ43 страницы8654azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Cost Machine Shop-April 2015Документ18 страницCost Machine Shop-April 2015azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Oee Machineshop March15Документ8 страницOee Machineshop March15azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Cost-Machine Shop Mar-15 (Ram-Assy)Документ7 страницCost-Machine Shop Mar-15 (Ram-Assy)azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Copy of Crank Shaft Cycle TimeДокумент1 страницаCopy of Crank Shaft Cycle Timeazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Eat Right For Your Blood TypeДокумент5 страницEat Right For Your Blood Typekingcobra00791% (58)
- Item Code: Minimum Inventory in Store/monthДокумент1 страницаItem Code: Minimum Inventory in Store/monthazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Injection Molding GuideДокумент33 страницыInjection Molding Guidethangkhungpro0% (1)
- PQCS Welding ProcessДокумент22 страницыPQCS Welding Processazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Non-Conformity Report & Corrective Action: Description of Non-ConformanceДокумент1 страницаNon-Conformity Report & Corrective Action: Description of Non-Conformanceazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Pqcs SampleДокумент3 страницыPqcs Sampleazadsingh1100% (1)
- Process ChartДокумент1 страницаProcess Chartazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Aluminum Foundry TechniqueДокумент51 страницаAluminum Foundry Techniqueazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Projet ReportДокумент4 страницыProjet Reportazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Power MillДокумент158 страницPower Millazadsingh1100% (3)
- Happy Steels (P) LTD.: Qualification CriteriaДокумент2 страницыHappy Steels (P) LTD.: Qualification Criteriaazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Trident Auto ProfileДокумент17 страницTrident Auto Profileazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- PreДокумент3 страницыPreazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- FMEA1Документ25 страницFMEA1azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Supplier: Parveen Enterprises Customer - MEDICAMEN Biotech Limited Quotation - PE-01Документ2 страницыSupplier: Parveen Enterprises Customer - MEDICAMEN Biotech Limited Quotation - PE-01azadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Excels Keyboard Shortcuts: Menu Equivalent Comments AllДокумент5 страницExcels Keyboard Shortcuts: Menu Equivalent Comments Allazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- Age CharacterCalculationДокумент1 страницаAge CharacterCalculationAnonymous gwldee5Оценок пока нет
- Part Submission WarrantДокумент2 страницыPart Submission Warrantazadsingh1100% (1)
- Presstool Design Tutorial - MisumiДокумент166 страницPresstool Design Tutorial - Misumiazadsingh1Оценок пока нет
- GD&T Versus Geometrical Product Spec PDFДокумент14 страницGD&T Versus Geometrical Product Spec PDFHusen Taufiq100% (2)
- Stat ResearchДокумент12 страницStat ResearchMylady RamosОценок пока нет
- Training and Development in HALДокумент58 страницTraining and Development in HALyoganthmurthy100% (1)
- Vertical Integration and Economic Performance On Managerial Capability FrameworkДокумент14 страницVertical Integration and Economic Performance On Managerial Capability FrameworkAcademic JournalОценок пока нет
- Om CH-4Документ48 страницOm CH-4Tesfaye KebedeОценок пока нет
- Q1 PR2 Las Week 1 2 Sy22 23Документ17 страницQ1 PR2 Las Week 1 2 Sy22 23Mikka Ella Joy G. JaingaОценок пока нет
- Paper 6 Vol. 9 No - 1, 2016Документ12 страницPaper 6 Vol. 9 No - 1, 2016SANGAMESWARAN U 19MBR089Оценок пока нет
- 103Документ9 страниц103ieom2012Оценок пока нет
- Coordinate Systems KenyaДокумент3 страницыCoordinate Systems Kenyakaiguara100% (1)
- Compendium OF Research MethodsДокумент9 страницCompendium OF Research MethodsTarusengaОценок пока нет
- Management Quiz 4Документ3 страницыManagement Quiz 4Kevin JeremyОценок пока нет
- 4.designfor AASHTO 1997Документ18 страниц4.designfor AASHTO 1997Aku PalsuОценок пока нет
- PracressssssssДокумент39 страницPracressssssssAhdelyn ValenciaОценок пока нет
- EVAOverviewДокумент10 страницEVAOverviewchandar70Оценок пока нет
- Vito LIUZZI Introduction Statistics IC1Документ15 страницVito LIUZZI Introduction Statistics IC1Khaja MoinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5Lourene Jauod- GuanzonОценок пока нет
- Korean Film DomДокумент6 страницKorean Film DomRobert Frio86% (7)
- Vibroacoustic Fluid-Structure Interaction With FEMДокумент29 страницVibroacoustic Fluid-Structure Interaction With FEMYegor LuchenkovОценок пока нет
- Schroder and Kobbernagel News Repertoires 2016Документ26 страницSchroder and Kobbernagel News Repertoires 2016MilanaОценок пока нет
- 5.2 Nonprobability SamplingДокумент4 страницы5.2 Nonprobability SamplingKyle CayabanОценок пока нет
- Latest - MBA (Assignment)Документ21 страницаLatest - MBA (Assignment)auvanesОценок пока нет
- Rajasthani LanguageДокумент16 страницRajasthani LanguageDESSHОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 - Decline Curve AnalysisДокумент41 страницаLecture 4 - Decline Curve Analysisgeber39Оценок пока нет
- Which Statistical Tests To UseДокумент1 страницаWhich Statistical Tests To UsePam FajardoОценок пока нет
- Buckling ReportДокумент16 страницBuckling ReportAin Sherin100% (3)
- Sex Differences Attachment 2011-Del Giudice-193-214Документ22 страницыSex Differences Attachment 2011-Del Giudice-193-214Ruben IrvingОценок пока нет
- AP Psych-Unit 2 PowerPointДокумент82 страницыAP Psych-Unit 2 PowerPointAkansha JhaОценок пока нет
- The Influence of Social Networks On Consumer Behavior: Veronija NolcheskaДокумент13 страницThe Influence of Social Networks On Consumer Behavior: Veronija NolcheskaوردةالديرةОценок пока нет
- Red Label Tea: Group 4Документ9 страницRed Label Tea: Group 4shruti100% (2)
- Research Process Notes PDFДокумент18 страницResearch Process Notes PDFCLAUDINE MUGABEKAZIОценок пока нет