Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Phys 102 Recitation Problem Set 1: Chapter 21
Загружено:
AhmetОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Phys 102 Recitation Problem Set 1: Chapter 21
Загружено:
AhmetАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Phys 102 Recitation Problem Set 1: Chapter 21
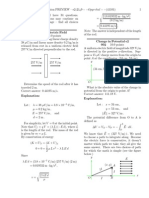
Ch. 21 Pr.13: Three charged particles are placed at the corners of an equilateral
triangle of side 1.2 m (Figure on the right). Calculate the magnitude and direction
of the net force on each charge due to the other two.
Ch. 21 Pr. 35: Determine the direction and magnitude of the electric field at the point P in figure below.
The charges are separated by a distance 2a, and point P
is a distance x from the midpoint between the two
charges. Express your answer in terms of Q, x, a, k.
Ch. 21 Pr. 48: Determine the direction and magnitude of
the electric field at the point P in figure below. The two
charges are separated by a distance 2a. Point P is on the
perpendicular bisector of the line joining the charges, a
distance x from the midpoint between them. Express your
answers in terms of Q, x, a, k.
Ch. 21 Pr. 53: A thin rod of length l carries a total charge Q
distributed uniformly along its length (See the figure below).
Determine the electric field along the axis of the rod starting at
one end - that is, find () for 0.
Phys 102 Recitation Problem Set 1: Chapter 21 Solutions
Ch. 21 Pr.13 Solution:
The forces on each charge lie along a line connecting the charges. Let the
variable d represent the length of a side of the triangle. Since the triangle is
equilateral, each angle is 60o. First calculate the magnitude of each individual
force.
F12 k
Q1Q2
d2
8.988 109 N m 2 C2
F13
7.0 10 C 8.0 10 C
6
1.20 m 2
F23
0.3495 N
F13 k
Q1Q3
d
8.988 109 N m 2 C2
Q1
Q2
F21
7.0 10 C 6.0 10 C
6
F12
Q3
F32
F31
1.20 m 2
0.2622 N
F23 k
Q2Q3
d2
8.988 109 N m 2 C2
8.0 10 C 6.0 10 C 0.2996 N F
6
1.20 m
32
Now calculate the net force on each charge and the direction of that net force, using components.
F1 x F12 x F13 x 0.3495 N cos 60o 0.2622 N cos 60o 4.365 102 N
F1 y F12 y F13 y 0.3495 N sin 60o 0.2622 N sin 60o 5.297 101 N
1 tan 1
F1 F12x F12y 0.53 N
F1 y
F1 x
tan 1
5.297 101 N
265
4.365 102 N
F2 x F21 x F23 x 0.3495 N cos 60o 0.2996 N 1.249 10 1 N
F2 y F21 y F23 y 0.3495 N sin 60o 0 3.027 10 1 N
2 tan 1
F2 F22x F22y 0.33 N
F2 y
F2 x
tan 1
3.027 101 N
1.249 101 N
112
F3 x F31 x F32 x 0.2622 N cos 60o 0.2996 N 1.685 101 N
F3 y F31 y F32 y 0.2622 N sin 60o 0 2.271 10 1 N
3 tan
F3 F F 0.26 N
2
3x
2
3y
F3 y
F3 x
tan
2.271 101 N
1.685 101 N
53
Ch. 21 Pr. 35 Solution:
Choose the rightward direction to be positive. Then the field due to +Q will be positive, and the field due
to Q will be negative.
Ek
x a
x a
1
4kQxa
2
2
x a x a
2
2 2
x a
kQ
The negative sign means the field points to the left .
Q
Ch. 21 Pr. 48 Solution:
From the diagram, we see that the x components of the
two fields will cancel each other at the point P. Thus
the net electric field will be in the negative y-direction,
x
a
E Q
EQ
and will be twice the y-component of either electric field vector.
kQ
Enet 2 E sin 2 2
sin
x a2
2kQ
a
2
1/ 2
2
x a x2 a2
2kQa
a2
3/ 2
in the negative y direction
Ch. 21 Pr. 53 Solution:
Choose a differential element of the rod dx a distance x from the origin, as shown in the diagram. The
Q
charge on that differential element is dq dx. The variable x is treated as positive, so that the field
due to this differential element is dE
dq
4 0 x x
dx
4 0
x x
. Integrate along the rod to find
the total field.
E dE
0
dx
4 0
x x
Q
4 0 x x
Q
4 0
dx
x x
0
1
Q 1
1
4 0 x x 0 4 0 x x
Q
Вам также может понравиться
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterОт EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterОценок пока нет
- CH 22Документ21 страницаCH 22lololololol22100% (1)
- UNIT EdittedДокумент76 страницUNIT EdittedNatalieCmFОценок пока нет
- CH 22 FДокумент21 страницаCH 22 FaklothОценок пока нет
- hw8 SolnsДокумент9 страницhw8 SolnsJennyОценок пока нет
- Electric Force & Electric FieldsДокумент13 страницElectric Force & Electric FieldsDesejo SozinandoОценок пока нет
- Electricity Homework SolutionsДокумент34 страницыElectricity Homework SolutionsDascaliuc Daniel0% (1)
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Документ7 страниц3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedОценок пока нет
- Quest Electrostatics 4 KeyДокумент5 страницQuest Electrostatics 4 KeyCarlos OrtizОценок пока нет
- C16 Electrostatic Student1Документ81 страницаC16 Electrostatic Student1Faris Izzuddin RoslinОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 SolutionsДокумент9 страницHomework 1 SolutionsmohdaficationОценок пока нет
- HW4 SolutionsДокумент15 страницHW4 Solutionsellie<3100% (3)
- 07 08 I FinalДокумент9 страниц07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedОценок пока нет
- Quest Electrostatics 1 KeyДокумент6 страницQuest Electrostatics 1 KeyCarlos OrtizОценок пока нет
- Exam 1 SolutionДокумент15 страницExam 1 SolutionNassir AlnamahОценок пока нет
- Ch16 h1 ProblemsДокумент4 страницыCh16 h1 ProblemsshaangakharОценок пока нет
- Quest Electrostatics 2 KeyДокумент6 страницQuest Electrostatics 2 KeyCarlos OrtizОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - ElectrostaticsДокумент33 страницыUnit 3 - Electrostaticsshinichi_kesian6117Оценок пока нет
- Y Q A A: Exam 1 SolutionДокумент9 страницY Q A A: Exam 1 SolutionCHRISTOPHER TEBIT SEMBIОценок пока нет
- Answers For Pre Test 1Документ4 страницыAnswers For Pre Test 1madbooks444Оценок пока нет
- Lecturer Tutorial Sp025 20212022Документ135 страницLecturer Tutorial Sp025 20212022faris zainuddinОценок пока нет
- Homework Solutions AllДокумент125 страницHomework Solutions AllokaysurepassОценок пока нет
- Ch1 Electric Force and FieldДокумент101 страницаCh1 Electric Force and FieldshahrulОценок пока нет
- The E Field and Voltage-SolutionsДокумент6 страницThe E Field and Voltage-SolutionsRosalinaОценок пока нет
- Quest Review 4 Electric Force, Magnetic Fields KEYДокумент16 страницQuest Review 4 Electric Force, Magnetic Fields KEYJ PОценок пока нет
- Chapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedДокумент98 страницChapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyОценок пока нет
- 07 08 II ms1Документ5 страниц07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedОценок пока нет
- HW2 SolutionsДокумент10 страницHW2 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- Phys102 Old Exam Problems Ch21-22Документ2 страницыPhys102 Old Exam Problems Ch21-22Reeja MathewОценок пока нет
- Review For Exam#1Документ5 страницReview For Exam#1sharathОценок пока нет
- HW 1 ProblemsДокумент4 страницыHW 1 ProblemsBorisRibicОценок пока нет
- p240w12 Mid1-2Документ14 страницp240w12 Mid1-2shlaeaОценок пока нет
- Solution1 PDFДокумент22 страницыSolution1 PDFewwiekimmieОценок пока нет
- Midterm 1 - TurnerДокумент7 страницMidterm 1 - TurnerAli Abbas SheriffОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Scalar and Vector PDFДокумент22 страницыChapter 2 - Scalar and Vector PDFhakimОценок пока нет
- Electrostatic For MurniДокумент55 страницElectrostatic For MurniAnonymous RMXuPuОценок пока нет
- Exam 1 SolutionsДокумент9 страницExam 1 Solutionsellie<3Оценок пока нет
- Welcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandДокумент20 страницWelcome To Electromagnetism: Ed CopelandDimitris ToubisОценок пока нет
- Stiffness MethodДокумент62 страницыStiffness MethodArviSan0% (1)
- Sample Problems: 112-Topic 1: Electric Forces & Electric FieldsДокумент4 страницыSample Problems: 112-Topic 1: Electric Forces & Electric FieldsChristine Cayosa CahayagОценок пока нет
- Physics 21 SolutionsДокумент92 страницыPhysics 21 SolutionsOğuzhan Odbay100% (1)
- Physic Electronic Exercise (With Ans)Документ5 страницPhysic Electronic Exercise (With Ans)Nor Shafiza JazaruddinОценок пока нет
- IIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsДокумент9 страницIIT-JEE Paper 1 SolutionsSrinivasulu KonetiОценок пока нет
- Midterm 01 Physics 2 UTДокумент8 страницMidterm 01 Physics 2 UTJonathan OrОценок пока нет
- Practice FinalДокумент26 страницPractice Finalchaseutd123Оценок пока нет
- Part Test 10Документ79 страницPart Test 10Srinivasarao SrinuОценок пока нет
- 10d-Electrostatics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSДокумент15 страниц10d-Electrostatics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSzeustamОценок пока нет
- E2 121 09-PreviewДокумент14 страницE2 121 09-PreviewTremendous JohnsonОценок пока нет
- ElectrostaticsДокумент9 страницElectrostaticsapi-283216587Оценок пока нет
- Part I: Problems: (3 Points) Q F F A AДокумент6 страницPart I: Problems: (3 Points) Q F F A AMahmoud FariedОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - Modern PhysicsДокумент23 страницыModule 5 - Modern PhysicsANGELO NINO ALVARADOОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Документ20 страницGrade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Priyanka KanaОценок пока нет
- Electric Potential: Answers To QuestionsДокумент26 страницElectric Potential: Answers To QuestionsgaferoprОценок пока нет
- Part 1 - Physics: L B A G 2Документ7 страницPart 1 - Physics: L B A G 2bindaaz301Оценок пока нет
- Chap23 10Документ10 страницChap23 10litrakhanОценок пока нет
- E&m 1-ProblemsДокумент2 страницыE&m 1-ProblemsdicksquadОценок пока нет
- 21Документ37 страниц21황선영Оценок пока нет
- Electric Field Ring of Charge & DiskДокумент30 страницElectric Field Ring of Charge & DiskAhsan Fazal QureshiОценок пока нет
- ME436s19h4-2 Mar 2019Документ1 страницаME436s19h4-2 Mar 2019AhmetОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5shhshsДокумент3 страницыAssignment 5shhshsAhmetОценок пока нет
- Artificial Intelligence and Ethics An Exercise in The Moral ImaginationДокумент10 страницArtificial Intelligence and Ethics An Exercise in The Moral ImaginationAhmetОценок пока нет
- Recitation Ch4Документ10 страницRecitation Ch4AhmetОценок пока нет
- Math 122, Solution Set No. 1: 1 Chapter 1.1 Problem 16Документ91 страницаMath 122, Solution Set No. 1: 1 Chapter 1.1 Problem 16homanho2021Оценок пока нет
- 03 Introduction To Quantum Entanglement PDFДокумент16 страниц03 Introduction To Quantum Entanglement PDFsaiphysics143Оценок пока нет
- The Fourth Political Theory by Alexander DuginДокумент1 страницаThe Fourth Political Theory by Alexander DuginBalconyОценок пока нет
- Homework 8Документ5 страницHomework 8Ale GomezОценок пока нет
- AFEM Ch02 PDFДокумент13 страницAFEM Ch02 PDFAnonymous f3iGLjxОценок пока нет
- Question Bank On Atomic Structure-2Документ7 страницQuestion Bank On Atomic Structure-2Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- Test - Atomic Theory Scientists - QuizletДокумент12 страницTest - Atomic Theory Scientists - QuizletjdОценок пока нет
- Special Relativity: Einstein Messes With Space and TimeДокумент18 страницSpecial Relativity: Einstein Messes With Space and TimeKýñg ButlerОценок пока нет
- Geometric Algebras For Euclidean Geometry: Charles GunnДокумент25 страницGeometric Algebras For Euclidean Geometry: Charles GunnZow NiakОценок пока нет
- This Dialogue Is For Number 1Документ2 страницыThis Dialogue Is For Number 1EnyAkustyaОценок пока нет
- On Lorentzian Concircular Structure Manifolds Satidfying Certain ConditionsДокумент7 страницOn Lorentzian Concircular Structure Manifolds Satidfying Certain ConditionsSunil YadavОценок пока нет
- Colloidal Quantum Dots As Platforms For Quantum InformationДокумент48 страницColloidal Quantum Dots As Platforms For Quantum InformationDanielОценок пока нет
- Kirchhoff-Love Plate Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент12 страницKirchhoff-Love Plate Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaV ARUL RAJОценок пока нет
- 2d Transformation PDFДокумент17 страниц2d Transformation PDFNamit JainОценок пока нет
- DPP 05Документ4 страницыDPP 05urmomОценок пока нет
- Types of MatricesДокумент8 страницTypes of Matricesمعتصم الكاملОценок пока нет
- Exact Solution of Von Karman EqДокумент5 страницExact Solution of Von Karman EqsyedmuhammadtariqueОценок пока нет
- Matrices DeterminantsДокумент3 страницыMatrices DeterminantsSUDHANSHU PANWARОценок пока нет
- Fitting Helices To Data by Total Least Squares by Yves NievergeltДокумент12 страницFitting Helices To Data by Total Least Squares by Yves NievergeltSylvain Doval JankowiakОценок пока нет
- 14Документ6 страниц14MEOW41Оценок пока нет
- Newton's Laws of GravityДокумент21 страницаNewton's Laws of GravityVal Anthony Villarin BalagonОценок пока нет
- Dynamics - Rigid Body DynamicsДокумент20 страницDynamics - Rigid Body DynamicsFelipe López GarduzaОценок пока нет
- The Four-Frequency of Light: Ds DX DXДокумент6 страницThe Four-Frequency of Light: Ds DX DXweylguyОценок пока нет
- Exercises With Detailed Solutions On Functional Analysis and Spectral Theory (Sheet 1)Документ50 страницExercises With Detailed Solutions On Functional Analysis and Spectral Theory (Sheet 1)Cristhian Paúl Neyra SalvadorОценок пока нет
- 15 Atom HidrogenДокумент42 страницы15 Atom HidrogenRahajengОценок пока нет
- Relativistic Velocity Addition Law Derived From A Machine Gun Analogy and Time Dilation OnlyДокумент6 страницRelativistic Velocity Addition Law Derived From A Machine Gun Analogy and Time Dilation OnlyErmias MesfinОценок пока нет
- Max-Von-Laue-1911-Artigo-On The Dynamics of The Theory of Relativity - Wikisource, The Free Online LibraryДокумент12 страницMax-Von-Laue-1911-Artigo-On The Dynamics of The Theory of Relativity - Wikisource, The Free Online Libraryroberto-martinsОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Physical Chemistry Practical and Intuitive - Hota, S - 2018 - Springer Singapore, Singapore - Anna's ArchiveДокумент704 страницыMathematical Physical Chemistry Practical and Intuitive - Hota, S - 2018 - Springer Singapore, Singapore - Anna's Archiveadrian.hodorОценок пока нет
- A Students Guide To EntropyДокумент4 страницыA Students Guide To EntropyJohn Hernan Diaz ForeroОценок пока нет
- Maaz Raja MCQs 1st Year MathДокумент3 страницыMaaz Raja MCQs 1st Year MathRaja MaazОценок пока нет