Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ieatc Spv3.Part.06.Inter As - Mpls
Загружено:
Umair AlamОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ieatc Spv3.Part.06.Inter As - Mpls
Загружено:
Umair AlamАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Service Provider CCIE
Advanced Technologies Class
Inter-AS MPLS
http://www.InternetworkExpert.com
Inter-AS MPLS Overview
MPLS VPNs can span multiple providers
Geographically diverse sites
Redundancy requirements
Inter-AS considerations
How much control does each SP want
How do SPs want to exchange routing information?
Label exchange required?
LDP/TDP typically not feasible
RSVP would require (n*(n-1)/2)
BGP offers alternative
Copyright www.INE.com
Inter-AS MPLS Designs
Option 1 / Option A
Back-to-Back VRF Exchange
Option 2 / Option B
VPNv4 BGP Exchange
Option 3 / Option C
Multihop VPNv4 BGP Exchange
Copyright www.INE.com
Inter-AS MPLS Designs
Back-to-Back VRF Exchange (Option 1)
SPs use one link per VRF needed
SP1 treats SP2 like another customer site
PE-CE routing (really PE-PE routing)
No label exchange, IPv4 packets only
Copyright www.INE.com
Inter-AS MPLS Designs
VPNv4 BGP Exchange (Option 2)
Connected SP PEs peer VPNv4 BGP
VPNv4 exchanges labels
LSP end-to-end
Copyright www.INE.com
Inter-AS MPLS Designs
Multihop VPNv4 BGP Exchange (Option 3)
Non-connected SP PEs peer VPNv4 BGP
IPv4 BGP exchanges labels at SP edge
Implies SPs must share internal routing
information
Copyright www.INE.com
Back-to-Back VRF Exchange
Pros
SPs do not need to exchange internal routing information
SPs control own VRF import & export policies
Route distinguishers and route targets locally significant
Simple configuration
Treated just like any other VPN site
Cons
Requires PE-PE IGP protocol
PE to PE routers must have all VRFs configured locally
Must maintain VPNv4 peerings with all internal PEs
Must maintain VRF routing tables
Copyright www.INE.com
VPNv4 BGP Exchange
Considerations
Route-target filtering on edge by default
no bgp default route-target filter
LSP is end to end
QoS considerations
Pros
SPs do not need to exchange IGP routes
IPv4 BGP typically already running between border routers
Cons
PE to PE routers must have all VPNv4 information
Must maintain VPNv4 peerings with all internal PEs (or with internal
VPNv4 route reflectors)
Copyright www.INE.com
Multihop VPNv4 BGP Exchange
Considerations
PE routers must have IGP route for remote PE routers to
Allow transport for VPNv4 session
Allow building of IGP transport label
LSP is end to end
PE to PE routers exchange labels via IPv4 BGP
Route reflection and next-hop processing
Pros
VPNv4 information only exchanged between devices with that VRF
VPN PE routers need not run BGP with anyone else
Cons
SPs must exchange internal routing info
Internal addressing may not be routable
Possibly exposes core routers to Internet
Copyright www.INE.com
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Project Manager Usually Follows Different Leadership Styles As Listed BelowДокумент24 страницыThe Project Manager Usually Follows Different Leadership Styles As Listed BelowUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- Day 15 - Scope Schedule Cost QuestionsДокумент14 страницDay 15 - Scope Schedule Cost QuestionsUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- PMPДокумент23 страницыPMPUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- F5 2 BIP OS SetupUtility1Документ3 страницыF5 2 BIP OS SetupUtility1Umair AlamОценок пока нет
- 06 June 2015 SFP Qty DcalДокумент47 страниц06 June 2015 SFP Qty DcalUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- VRF-Aware IPsec Using Crypto Maps and Custom FVRFДокумент4 страницыVRF-Aware IPsec Using Crypto Maps and Custom FVRFUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- Data Center Implementation Roadmap: Sacs PAS Cpgs Prcs Epgs Iptv MCS Vms - Vss Aodbs RMS Evids BRS Cuss I2BsДокумент1 страницаData Center Implementation Roadmap: Sacs PAS Cpgs Prcs Epgs Iptv MCS Vms - Vss Aodbs RMS Evids BRS Cuss I2BsUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- EEm Sol From Forum KangДокумент1 страницаEEm Sol From Forum KangUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MDS and Storage Area Networks (SAN) : © 2009 Cisco Systems - CAEДокумент43 страницыIntroduction To MDS and Storage Area Networks (SAN) : © 2009 Cisco Systems - CAEUmair AlamОценок пока нет
- Coffee Talk F5 Solution For Microsoft Exchange 2010 Updated2011aprilДокумент19 страницCoffee Talk F5 Solution For Microsoft Exchange 2010 Updated2011aprilUmair AlamОценок пока нет
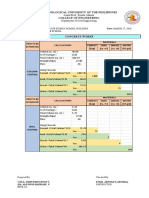
- 2 Concrete Works CompuДокумент14 страниц2 Concrete Works CompuALFONSO RAPHAEL SIAОценок пока нет
- MM SoftwareДокумент12 страницMM SoftwareRais RizalОценок пока нет
- OFBS Enrollment Form v.2Документ2 страницыOFBS Enrollment Form v.2Abrera ReubenОценок пока нет
- Manual Teclado Ligthsys - RiscoДокумент32 страницыManual Teclado Ligthsys - RiscoLuis Oliver Neciosup VasquezОценок пока нет
- What Is A StartupДокумент3 страницыWhat Is A StartupArun SoniОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Control Valves - Instrumentation ToolsДокумент13 страницDifferent Types of Control Valves - Instrumentation Toolsprabhanshu241991Оценок пока нет
- Certificado Apc Iso 14001-2004 PDFДокумент4 страницыCertificado Apc Iso 14001-2004 PDFMao MartinОценок пока нет
- Zero Trust NetworkingДокумент10 страницZero Trust NetworkingFaris AL HashmiОценок пока нет
- Best Practices For Vsphere (ESX 4) Service Console Partitions - VM - ETCДокумент14 страницBest Practices For Vsphere (ESX 4) Service Console Partitions - VM - ETCKritchatach WanichanonОценок пока нет
- Multi-Crop HarvesterДокумент6 страницMulti-Crop HarvesterErwinОценок пока нет
- KeyboardДокумент8 страницKeyboardaltawanmudzharОценок пока нет
- Microwave - Pathloss IV TrainingДокумент3 страницыMicrowave - Pathloss IV TrainingbantunnaОценок пока нет
- Configuring SNMP On ProteusДокумент12 страницConfiguring SNMP On ProteusAijaz MirzaОценок пока нет
- Sounder Beacons Specification - 240Документ4 страницыSounder Beacons Specification - 240ABDUL GHAFOORОценок пока нет
- Prob CДокумент4 страницыProb CnozetsubounolifeОценок пока нет
- Grades of Reinforcing SteelДокумент15 страницGrades of Reinforcing Steelshuckss taloОценок пока нет
- LSA Architecure TipsДокумент33 страницыLSA Architecure TipsDavid LewisОценок пока нет
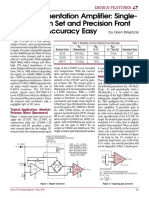
- LT1168 0500 MagДокумент2 страницыLT1168 0500 MagBillyОценок пока нет
- LS Retail Training Manual Version 4.2Документ170 страницLS Retail Training Manual Version 4.2MOHAMMED AARIFОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals V3F18: The LWD Is Adjusted With The User Interface. AdjustmentДокумент1 страницаFundamentals V3F18: The LWD Is Adjusted With The User Interface. AdjustmentOsman ElmaradnyОценок пока нет
- Cybot Baseboard LCD SchematicДокумент6 страницCybot Baseboard LCD Schematicapi-584352705Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic ArmourДокумент7 страницElectromagnetic ArmourLissete VergaraОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar 785c 789c Off Highway Trucks Service TrainingДокумент20 страницCaterpillar 785c 789c Off Highway Trucks Service Trainingjames100% (45)
- Q2 Electronics Module 5Документ34 страницыQ2 Electronics Module 5Roniese MamaedОценок пока нет
- Ekta Prajapati Resume PDFДокумент2 страницыEkta Prajapati Resume PDFghanapathy ramОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical Big Fish Career StoriesДокумент53 страницыGeotechnical Big Fish Career Storieskrainaoz2011Оценок пока нет
- Resistron: Operating InstructionsДокумент51 страницаResistron: Operating Instructions16_45_2013_gabri0% (1)
- 5S Implementation Copy 1 AutoRecoveredДокумент8 страниц5S Implementation Copy 1 AutoRecoveredChristian BarrientosОценок пока нет
- Q1 Module 7 - Topic7Документ2 страницыQ1 Module 7 - Topic7Kristel Ann MontianoОценок пока нет
- MDCS en 2022Документ8 страницMDCS en 2022ZaharОценок пока нет