Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Building Drainage
Загружено:
Tj TalhaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Building Drainage
Загружено:
Tj TalhaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
11/4/2016
Building House Drainage
Introduction
The residential plumbing system is often
taken for
granted, but it is an important part of the
structure.
A complete plumbing system provides an
adequate
supply of water and removes waste.
There are three principal parts:
1. Water supply system.
2. Water and waste removal system.
3. Plumbing fixtures.
11/4/2016
Typical Drainage System
Components of a residential drainage system
Water and Waste Removal
Used water and other wastes are carried to the
sanitary sewer or septic tank through the waste
removal system.
These pipes are isolated from the water supply system
and must be sized for sufficient capacity, have the
proper slope and venting, and have provisions for
cleanouts.
Typically it is practical to drain as many of the fixtures
as possible into a single main drain.
The drainage system is not under pressure and
depends on gravity to carry the waste to the sewer.
11/4/2016
Water and Waste Removal
A vertical drain pipe that collects
waste from one or more fixtures
is called a soil stack.
Soil stacks that drain water
closets are called main stacks.
Every house must have at least
one main stack, which is
generally 3" in diameter.
Each bathroom must have a main
stack.
Stacks that do not drain water
closets are called secondary
stacks.
Secondary stacks are 1-1/2"
diameter.
Water and Waste Removal
Fixtures are connected to the
stack using a branch main.
All stacks extend into
basement and empty into the
house drain.
All structures must have
at least one house drain,
but may have several.
The house drain becomes the
house sewer once it is outside
the house. The house sewer
empties into the city sanitary
sewer or private septic
system.
11/4/2016
Water and Waste Removal
Gases from the system
dissipate through the vent
stack12" above roof. The
vent stack provides an air inlet
for the drainage system to
operate properly
A trap is installed below each
fixture to prevent gases from
entering the house. The trap
is always filled with water.
Water closets have a built-in
trap.
Each stack requires a cleanout
at the base.
Traps
The trap most commonly used
with plumbing fixtures is the Ptrap. The P-trap gets its name
because of its general shape-that
of the letter P.
Traps are required because they
prevent sewer gases from
entering a building and causing
serious illness or death.
The term Trap Seal refers to the
water being held in the bent
portion of a fixture trap. The trap
seal forms a seal against the
passage of sewer gases through
the trap and into the building.
11/4/2016
Traps
Examples of P-Traps
House Drain
A house drain is the pipe that
receives all waste and water
discharged by the soil stacks
and waste lines.
This house drain is laid from a
point just outside the building
foundation wall where it
connects to the house sewer,
then through the wall, and
either along or under the
cellar floor to the point where
connection with the soil stack
is made.
Before laying this drain,
determine its overall length
and how much pitch to give it
so that it will drain as it
should.
11/4/2016
House Trap
Building (House) traps shall be
provided with a cleanout and a relief
vent or fresh air intake on the inlet
side of the trap.
Relief vents or fresh air intake shall be
carried above grade and shall be
terminated in a screened outlet
located outside the building.
The size of the relief vent or fresh aid
intake shall not be less than one-half
the diameter of the drain to which the
relief vent or air intake connects.
House Drains and House Traps
Building traps.
Building (house) traps shall be prohibited, except where local conditions necessitate such
traps.
Building traps shall be provided with a cleanout and a relief vent or fresh air intake on the
inlet side of the trap. The size of the relief vent or fresh air intake shall not be less than
one-half the diameter of the drain to which the relief vent or air intake connects. Such relief
vent or fresh air intake shall be carried above grade and shall be terminated in a screened
outlet located outside the building.
11/4/2016
Soil stacks and waste stacks
A soil stack is a vertical drain pipe that carries soil waste from sanitary units
(i.e. toilets).
A waste stack is any other vertical drain pipe that doesnt carry soil from a
sanitary fixture.
Cleanouts
A plumbing cleanout is a cleanout fitting with a removable
plug that is found in a roughed in waste system. It is
designed to help keep clear any type of debris that could
cause any type of stoppage in the water drain lines.
Cleanouts are usually placed at the connection point between
the sewer lines and the drain lines where the base is located
of a vertical stack and at all places were the pipe direction
changes at 90 degrees.
11/4/2016
Cleanouts
Cleanouts are required at base of all stacks.
Vents
To prevent the siphonage of a trap
seal in fixture traps and allow
gravity flow of drainage, you must
let atmospheric air from outside the
building into the piping system to
the outlet (or discharge) end of the
trap. The air is supplied through
pipes called VENTS. This air
provides pressure on the outlet end
of the seal equal to pressure on the
inlet end.
Since the air supplied by the vent to
the outlet end provides a pressure
equal to that at the inlet end of the
trap, the trap seal cannot escape
through siphonage.
All vent systems should be provided
with a main vent or vent stack and a
main soil and waste vent. A main
vent may be defined as the
principal artery of the venting
system, and vent branches may be
connected to the main vent and run
undiminished in size as directly as
possible from the building drain to
the open air above the roof.
11/4/2016
Vents
The term main soil and waste vent, or soil stack vent, refers to the portion of
the stack extending above the highest fixture branch. In the figure, this vent
extends through the roof. Actually, it is an extension of the main soil and waste
stack.
Vents
An INDIVIDUAL VENT is a vent
that connects the main vent with
the individual trap underneath or
behind a fixture
11/4/2016
Vents
A COMMON VENT vents two traps to
a single vent pipe.
The unit vent can be used when a pair
of lavatories are installed side by
side, as well as when they are hung
back to back on either side of a
partition
Plumbing Plans
The Plumbing Plan is a plan view that shows the complete
plumbing system.
The plumbing plan shows the location, size, and type of all
plumbing equipment.
The plumbing plan should include:
Waste lines and vent stacks.
Drain and plumbing fixture locations.
Size and type of pipe to be used.
A plumbing fixture schedule.
Symbols Legend.
General notes.
A plumbing plan is required for each floor of the house.
10
11/4/2016
Plumbing Symbols
Plumbing Fixture Schedule
11
11/4/2016
Plumbing Plan
12
Вам также может понравиться
- TCR 29 8 21Документ56 страницTCR 29 8 21Tj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Manpower ScheduleДокумент24 страницыManpower ScheduleTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- 1913 Mom Ext 16 021221Документ2 страницы1913 Mom Ext 16 021221Tj TalhaОценок пока нет
- PunchlistДокумент5 страницPunchlistTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- BOQ Finishing WorkДокумент26 страницBOQ Finishing WorkTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- HistogramДокумент1 страницаHistogramTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- ObservationsДокумент1 страницаObservationsTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- TCR-29!8!21-Activity Resource Assignments JawadДокумент52 страницыTCR-29!8!21-Activity Resource Assignments JawadTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- SBCA Form ZP-1 SubmissionДокумент2 страницыSBCA Form ZP-1 SubmissionTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- 211118-The Court Industrial Park ProposalДокумент71 страница211118-The Court Industrial Park ProposalTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- TCSS NomenclatureДокумент1 страницаTCSS NomenclatureTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Daily ReportДокумент2 страницыDaily ReportTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Plant Directory - Tcip ParkДокумент6 страницPlant Directory - Tcip ParkTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- 8 Story Residential BuildingДокумент9 страниц8 Story Residential BuildingTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- PB23BДокумент1 страницаPB23BSaad AmirОценок пока нет
- Installation Instructions GrasppДокумент9 страницInstallation Instructions GrasppCow SepurОценок пока нет
- Samsung PDFДокумент4 страницыSamsung PDFTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Asphalt Concrete Wearing Course RequirementsДокумент29 страницAsphalt Concrete Wearing Course RequirementsTj TalhaОценок пока нет
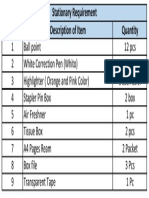
- Office stationary listДокумент1 страницаOffice stationary listTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Office stationary listДокумент1 страницаOffice stationary listTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- CENTRAL ORDNANCE DEPOT TENDER FOR ORDNANCE AND UN STORESДокумент11 страницCENTRAL ORDNANCE DEPOT TENDER FOR ORDNANCE AND UN STORESTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- MerchaДокумент6 страницMerchaTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- Tip 2Документ1 страницаTip 2Tj TalhaОценок пока нет
- List of Authorized Branches For Issuance of Fresh NotesДокумент18 страницList of Authorized Branches For Issuance of Fresh Notesfarrukhnawaz50% (2)
- Csi Etabs & Safe Manual: Part III: Model Analysis & Design of SlabsДокумент83 страницыCsi Etabs & Safe Manual: Part III: Model Analysis & Design of SlabsAnonymous LJ1v8KKОценок пока нет
- Lecture26 09Документ4 страницыLecture26 09lonkar.dinesh@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- Labour Productivity Chart in Uae PDFДокумент9 страницLabour Productivity Chart in Uae PDFTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- BS 6262 1982Документ88 страницBS 6262 1982Tj TalhaОценок пока нет
- ReadMeSAP2000v1700 PDFДокумент4 страницыReadMeSAP2000v1700 PDFTj TalhaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Lofa El240g1hsДокумент2 страницыLofa El240g1hsDouglas MОценок пока нет
- ATA24 Bombardier q400 Electrical PowerДокумент85 страницATA24 Bombardier q400 Electrical PowerAbiyot AderieОценок пока нет
- Product Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)Документ7 страницProduct Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)srmohapatra5086100% (1)
- ESP ButtonДокумент17 страницESP ButtonDamjan MilanovićОценок пока нет
- Flow Diagram SymbolsДокумент5 страницFlow Diagram SymbolshussainОценок пока нет
- Palm Oil MSDSДокумент5 страницPalm Oil MSDSCaliche Omn100% (1)
- Improving Packed Tower PerformanceДокумент3 страницыImproving Packed Tower PerformanceManish542Оценок пока нет
- 12 18 13polyaspartic Webinar CommercialДокумент48 страниц12 18 13polyaspartic Webinar CommercialAelya SanОценок пока нет
- Corrosion of Chrome PlatingДокумент37 страницCorrosion of Chrome PlatingdavideОценок пока нет
- Celda de Carga Tipo Z Sensortronics - 60050 (Molinos de Pasta)Документ1 страницаCelda de Carga Tipo Z Sensortronics - 60050 (Molinos de Pasta)Schiraldi BonillaОценок пока нет
- OMEGA AIR-Process and Sterile Filtration - EN - 950119Документ12 страницOMEGA AIR-Process and Sterile Filtration - EN - 950119Junaid AhmedОценок пока нет
- AP Chem Test - Chapter 10,11,13 - Gases, Solutions, Solids, Liquids, Inter Forces (2010-2011)Документ12 страницAP Chem Test - Chapter 10,11,13 - Gases, Solutions, Solids, Liquids, Inter Forces (2010-2011)dlloyd63050% (2)
- Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery ManualДокумент22 страницыValve Regulated Lead Acid Battery Manualevanelizan100% (1)
- Khushboo PriyambadaДокумент121 страницаKhushboo PriyambadanguyendaibkaОценок пока нет
- Latching Assignment PLC Ladder LogicДокумент4 страницыLatching Assignment PLC Ladder LogicsalonyОценок пока нет
- Dies and Inserts Catalog 2018Документ36 страницDies and Inserts Catalog 2018Ahmed MohamedОценок пока нет
- Jazeera Wood Elegance StainДокумент2 страницыJazeera Wood Elegance StainAhmad BougeisОценок пока нет
- S# Isin CFI Code (As Per New ISO) Security Name Security Symbol Sector Name Security Type StatusДокумент25 страницS# Isin CFI Code (As Per New ISO) Security Name Security Symbol Sector Name Security Type StatusahmedalishОценок пока нет
- Flexible grid coupling selection guideДокумент18 страницFlexible grid coupling selection guidechavico113Оценок пока нет
- Furniture Locksand CatchesДокумент15 страницFurniture Locksand CatchesNishant DeoОценок пока нет
- Ingersoll Rand Dryer O&M Manual 80442833-EnДокумент48 страницIngersoll Rand Dryer O&M Manual 80442833-EnBill BrighamОценок пока нет
- Precios y Cantidades de Recursos Requeridos Por TipoДокумент3 страницыPrecios y Cantidades de Recursos Requeridos Por TipoWilder Huaman MuñozОценок пока нет
- Vicks Humidifier V745a ManualДокумент5 страницVicks Humidifier V745a ManualOrly Genoune HenkinОценок пока нет
- IFR 101 ManualДокумент28 страницIFR 101 ManualsunhuynhОценок пока нет
- SDLG Wheel Loader LG958 Complete Appliance Service Manua1 PDFДокумент268 страницSDLG Wheel Loader LG958 Complete Appliance Service Manua1 PDFFrancisco Ferrer100% (1)
- A Comparative Investigation On The Effects of Nanocellulose From BacteriaДокумент13 страницA Comparative Investigation On The Effects of Nanocellulose From BacteriaPaloma GuardeziОценок пока нет
- Solcourse - Polythene DPM DatasheetДокумент2 страницыSolcourse - Polythene DPM DatasheetkibzeamОценок пока нет
- Method of Scaffolding WorksДокумент25 страницMethod of Scaffolding WorksFarrukh Javed100% (1)
- 6.3 - MCB & MCCBДокумент25 страниц6.3 - MCB & MCCBAnonymous qJXSQDSoE100% (2)
- Standard Specification For GB 700Документ12 страницStandard Specification For GB 700Ma'arif Nuzul AddibОценок пока нет