Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Meiosis Kerlin
Загружено:
api-2930012170 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров1 страницаОригинальное название
meiosis kerlin
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
1K просмотров1 страницаMeiosis Kerlin
Загружено:
api-293001217Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
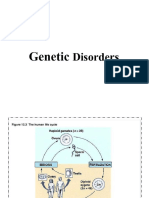
Mitosis And Meiosis Project
Meiosis VS. Mitosis
Paragraph
By; Kerlin Paulino
Nondisjunction
Crossing Over
The failure of homologous chromosomes
or sister chromatids to separate properly
during cell division.
Spermatozoon And Ovum
The exchange of genes
between homologous
chromosomes, resulting in a
mixture of parental
characteristics in offspring.
Fertilization
Random Assortment
The number of chromosomes is
halved from the parent cell
Haploid
2n
The action or process of fertilizing an egg,
female animal, or plant, involving the
fusion of male and female gametes to
form a zygote.
Genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes
by the passage according to the laws of probability of
one of each diploid pair of homologous chromosomes
into each gamete independently of each other pair.
Liver Cell
Mutation
The number of chromosomes
remain the same as parent cell
Diploid
n
Permanent alteration of the nucleotide sequence
of the genome of an organism, virus, or
extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements.
What is down syndrome? You may
ask yourself and over curiosity
questions. Down syndrome is a
chromosomal disorder caused by an
error in cell division that results in an
extra 21st chromosome. The condition
leads to impairments in both cognitive
ability and physical growth that range
from mild to moderate developmental
disabilities.Screening tests, such as
an ultrasound or a blood test during
your first or second trimester. These
can help show if the developing baby
(fetus) is at risk for Down syndrome.
But these tests sometimes give
false-positive or false-negative results.
Diagnostic tests, such as chorionic
villus sampling or amniocentesis.A few
of the common physical traits of
Down syndrome are: low muscle
tone, small stature, an upward slant to
the eyes, and a single deep crease
across the center of the palm. Every
person with Down syndrome is a
unique individual and may possess
these characteristics to different
degrees or not at all.People who
inherit an unbalanced translocation
involving chromosome 21 may have
extra genetic material from
chromosome 21, which causes Down
syndrome. Like trisomy 21, mosaic
Down syndrome is not inherited. It
occurs as a random event during cell
division early in fetal development
Вам также может понравиться
- SCIENCES GENE REPORT JskaДокумент4 страницыSCIENCES GENE REPORT Jskaheart louvОценок пока нет
- Research Report - Down SyndromeДокумент2 страницыResearch Report - Down SyndromeDestroyahОценок пока нет
- Genetic DisordersДокумент36 страницGenetic Disordersqurat-ul-ain.sonОценок пока нет
- Biology Investigatory ProjectДокумент17 страницBiology Investigatory ProjectAnmol Dhungel100% (6)
- Genetic DisordersДокумент37 страницGenetic DisordersAmalia Solehah (Nim: 2048201110145)Оценок пока нет
- Assessment and Care of The Newborn With Down Syndrome: Rachel Ranweiler, MS, NNPДокумент8 страницAssessment and Care of The Newborn With Down Syndrome: Rachel Ranweiler, MS, NNPRuxandra CretuОценок пока нет
- What Is Down Syndrome What Causes Down SyndromeДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Down Syndrome What Causes Down Syndromeapi-243322010Оценок пока нет
- 4 The Nursing Role in Genetic Assessment and CounsellingДокумент97 страниц4 The Nursing Role in Genetic Assessment and CounsellingBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatОценок пока нет
- Nurse As An Art - OmdДокумент67 страницNurse As An Art - OmdJozarine Chelsea LopezОценок пока нет
- Genetic DisorderДокумент13 страницGenetic DisorderLucreatia RynjahОценок пока нет
- Mutation:: Down's Syndrome, Klinefelter's Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome. Cri-Du-Chat SyndromeДокумент7 страницMutation:: Down's Syndrome, Klinefelter's Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome. Cri-Du-Chat SyndromeGj Salvador Tuballa IIОценок пока нет
- Glossary of Genetic Terms For PatientsДокумент6 страницGlossary of Genetic Terms For Patientssnowy45.rmОценок пока нет
- Chromosomal Aberrations: Advances in Chromosomal AnalysisДокумент4 страницыChromosomal Aberrations: Advances in Chromosomal AnalysisSyed Shah HussainОценок пока нет
- Case Study On Down Syndrome: Amera C. MalacoДокумент26 страницCase Study On Down Syndrome: Amera C. MalacoBajunaid MalacoОценок пока нет
- Karyotyping Learning OutcomesДокумент3 страницыKaryotyping Learning OutcomesALOIZA BELLE LAVI�AОценок пока нет
- Genetic TestingДокумент18 страницGenetic Testingneha100% (1)
- Biology Genetics Disorder By: Group A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5Документ21 страницаBiology Genetics Disorder By: Group A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5JawadОценок пока нет
- Mutation: Chromosome AbnormalitiesДокумент3 страницыMutation: Chromosome AbnormalitiesJulie marie PalmaОценок пока нет
- Group2 Prof Ed 2 ReportДокумент72 страницыGroup2 Prof Ed 2 ReportPrincess GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Biology Investigatory ProjectДокумент10 страницBiology Investigatory Projectmohd faizzОценок пока нет
- Genodermatoses: General ConsiderationsДокумент21 страницаGenodermatoses: General ConsiderationsCyd Buenaflor-MadayagОценок пока нет
- What Is Down Syndrome?: English Village, Gulan Street, Erbil, Kurdistan Region of IraqДокумент10 страницWhat Is Down Syndrome?: English Village, Gulan Street, Erbil, Kurdistan Region of IraqclubsanatateОценок пока нет
- Module 9 GeneticsДокумент11 страницModule 9 GeneticsCelest KnightwalkerОценок пока нет
- The Influence of Heredity and Environment On Human DevelopmentДокумент48 страницThe Influence of Heredity and Environment On Human DevelopmentShahrul FadreenОценок пока нет
- Chromosomal AbberationsДокумент33 страницыChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaОценок пока нет
- Down SyndromeДокумент3 страницыDown SyndromeMargie Ballesteros Manzano100% (1)
- Chapter 3Документ9 страницChapter 3Rae Ann FeguracionОценок пока нет
- Genetic DisordersДокумент17 страницGenetic DisordersNgz Krystle ChukwudifuОценок пока нет
- Epidemiology: Down Syndrome, or Down's Syndrome (Primarily in The United Kingdom)Документ9 страницEpidemiology: Down Syndrome, or Down's Syndrome (Primarily in The United Kingdom)anupa_joyОценок пока нет
- Heredity: Inheritance and VariationДокумент30 страницHeredity: Inheritance and VariationgermaineabeciaОценок пока нет
- Gene Therapy ReportДокумент3 страницыGene Therapy ReportAngela CubillaОценок пока нет
- Genetic Disorders Occur When A Mutation Affects Your GenesДокумент4 страницыGenetic Disorders Occur When A Mutation Affects Your GenesMiledysОценок пока нет
- Genetic - Down SyndromeДокумент11 страницGenetic - Down Syndromelightning proОценок пока нет
- Biology ProjectXIIДокумент28 страницBiology ProjectXIISayantan DasОценок пока нет
- Down Syndrom4Документ3 страницыDown Syndrom4api-346355246Оценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент45 страницUntitledMary Grace SunioОценок пока нет
- Mendelian Disorders Class 12Документ22 страницыMendelian Disorders Class 12Harith KumarОценок пока нет
- Homework # 1Документ5 страницHomework # 1Gladys VigiliaОценок пока нет
- Genetic Disorders IIIДокумент42 страницыGenetic Disorders IIIBahzad AkramОценок пока нет
- Genetics 23 24Документ75 страницGenetics 23 24Marlon CanilangОценок пока нет
- Prominent Ears (Common Atresia-Closure/fused) : What Is Down Syndrome?Документ4 страницыProminent Ears (Common Atresia-Closure/fused) : What Is Down Syndrome?TRUE FAITH YUQUIMPOОценок пока нет
- Los Genes y Los Cromosomas: LIC. Q.F.B. Blanco Vega Karla Gabriela Alumno: Lozano Gómez FranciscoДокумент5 страницLos Genes y Los Cromosomas: LIC. Q.F.B. Blanco Vega Karla Gabriela Alumno: Lozano Gómez FranciscoFrancisco Lozano GómezОценок пока нет
- Chromosomal Disorders SimpleДокумент8 страницChromosomal Disorders SimpleSadia KanwalОценок пока нет
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesДокумент61 страницаChromosomal AbnormalitiesManisanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Methods of Human GeneticsДокумент81 страницаMethods of Human Geneticsfae-ar_raziОценок пока нет
- Chromosomal Abnormalities (I I) 6 SDK 2013Документ63 страницыChromosomal Abnormalities (I I) 6 SDK 2013Edward WinchesterrОценок пока нет
- Patterns: OF InheritanceДокумент45 страницPatterns: OF InheritanceMary Grace SunioОценок пока нет
- SYNDROMEДокумент4 страницыSYNDROMEDavid AbadianoОценок пока нет
- Down SyndromeДокумент2 страницыDown SyndromeKakoy ZenarosaОценок пока нет
- Bio 1Документ3 страницыBio 1James TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Ày Ày Ày Ày Ày Ày ÀyДокумент9 страницÀy Ày Ày Ày Ày Ày Àyfelicen24Оценок пока нет
- 7 Down SyndromeДокумент5 страниц7 Down SyndromeAdnan RezaОценок пока нет
- NCMДокумент56 страницNCMPatrick Perreras Dela CuadraОценок пока нет
- PBL 2 Mosaic Down SyndromeДокумент8 страницPBL 2 Mosaic Down Syndromedeladestianiaji2490Оценок пока нет
- Midterm Reviewer, Dev PsychДокумент10 страницMidterm Reviewer, Dev PsychkatОценок пока нет
- DNA Mutations and Genetic DiseasesДокумент3 страницыDNA Mutations and Genetic DiseasesPramudith Liyanage0% (1)
- Ana 231 Chromosome AnomaliesДокумент28 страницAna 231 Chromosome AnomaliesAmadi CedarОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 - Chromosomal MutationsДокумент25 страницLesson 4 - Chromosomal MutationsSherwin YenogacioОценок пока нет
- Mosaic Down SyndromeДокумент4 страницыMosaic Down SyndromerositaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1-4 ReviewДокумент2 страницыUnit 1-4 Reviewapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mitosis and Meiosis Poster Rubric 2Документ1 страницаMitosis and Meiosis Poster Rubric 2api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mutations WorksheetДокумент3 страницыMutations Worksheetapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- MutationsДокумент7 страницMutationsapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Cell Transport Webquest 2Документ4 страницыCell Transport Webquest 2api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1-4 Re-Test Study GuideДокумент3 страницыUnit 1-4 Re-Test Study Guideapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- MutationsДокумент7 страницMutationsapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mod 3 4 5 Study GuideДокумент1 страницаMod 3 4 5 Study Guideapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Carbon Cycle PPT Notes-1Документ14 страницCarbon Cycle PPT Notes-1api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mod 4Документ10 страницMod 4api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Entire ModuleДокумент12 страницModule 4 - Entire Moduleapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Nitrogen Cycle ppt-1Документ14 страницNitrogen Cycle ppt-1api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mod 3-5 TrackerДокумент2 страницыMod 3-5 Trackerapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Eoc Review PacketДокумент12 страницEoc Review Packetapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Module 10 Day 4Документ8 страницModule 10 Day 4api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Plant Adaptation Project - RubricsДокумент2 страницыPlant Adaptation Project - Rubricsapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Jeopardy Eoc Bio ReviewДокумент106 страницJeopardy Eoc Bio Reviewapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Eoc BiologyДокумент116 страницEoc Biologyapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Genetics WebquestДокумент3 страницыGenetics Webquestapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Practice Questions With AnswersДокумент137 страницPractice Questions With Answersapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mod 11 Day 1Документ12 страницMod 11 Day 1api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Evolution Days 2 and 3Документ14 страницEvolution Days 2 and 3api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Module 10 Day 5Документ10 страницModule 10 Day 5api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Evolutionday 1Документ20 страницEvolutionday 1api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Module 8 Genetics Day 1Документ16 страницModule 8 Genetics Day 1api-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Module 5 CombinedДокумент16 страницUnit 2 Module 5 Combinedapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Sponge Bob Genetics PracticeДокумент3 страницыSponge Bob Genetics Practiceapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Genetis Practice Bunny GeneticsДокумент3 страницыGenetis Practice Bunny Geneticsapi-293001217Оценок пока нет
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis PracticeДокумент3 страницыMitosis Vs Meiosis Practiceapi-293001217Оценок пока нет