Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
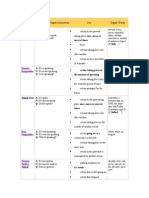
Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Present
Загружено:
gulzar72Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Present
Загружено:
gulzar72Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
tense
Simple Present
Affirmative/Negative/Question
A: He speaks.
N: He does not speak.
Q: Does he speak?
Present Progressive A: He is speaking.
N: He is not speaking.
Q: Is he speaking?
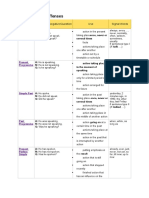
Simple Past
Past Progressive
Present Perfect
Simple
A: He spoke.
N: He did not speak.
Q: Did he speak?
A: He was speaking.
N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking?
A: He has spoken.
N: He has not spoken.
Q: Has he spoken?
Use
action in the present taking place once, never or several times
facts
actions taking place one after another
action set by a timetable or schedule
action taking place in the moment of speaking
action taking place only for a limited period of time
action arranged for the future
action in the past taking place once, never or several times
actions taking place one after another
action taking place in the middle of another action
action going on at a certain time in the past
actions taking place at the same time
action in the past that is interrupted by another action
putting emphasis on theresult
action that is still going on
action that stopped recently
Signal Words
always, every , never,
normally, often, seldom,
sometimes, usually
if sentences type I (If
I talk, )
at the moment, just, just
now, Listen!, Look!, now,
right now
yesterday, 2 minutes ago,
in 1990, the other day, last
Friday
if sentence type II (If
I talked, )
when, while, as long as
already, ever, just, never,
not yet, so far, till now, up
to now
finished action that has an influence on the present
action that has taken place once, never or several times before the
moment of speaking
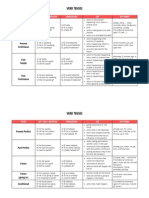
Present Perfect
Progressive
Past Perfect Simple
Past Perfect
Progressive
Future I Simple
Future I Simple
(going to)
A: He has been speaking.
N: He has not been speaking.
Q: Has he been speaking?
A: He had spoken.
N: He had not spoken.
Q: Had he spoken?
A: He had been speaking.
N: He had not been speaking.
Q: Had he been speaking?
A: He will speak.
N: He will not speak.
Q: Will he speak?
A: He is going to speak.
N: He is not going to speak.
Q: Is he going to speak?
putting emphasis on thecourse or duration (not the result)
action that recently stopped or is still going on
finished action that influenced the present
action taking place before a certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive
putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration)
action taking place before a certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple
putting emphasis on theduration or course of an action
action in the future that cannot be influenced
spontaneous decision
assumption with regard to the future
decision made for the future
conclusion with regard to the future
all day, for 4 years, since
1993, how long?, the
whole week
already, just, never, not
yet, once, until that day
if sentence type III (If
I had talked, )
for, since, the whole day,
all day
in a year, next ,
tomorrow
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask
her, she will helpyou.)
assumption: I think,
probably, perhaps
in one year, next week,
tomorrow
Future I Progressive A: He will be speaking.
N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking?
action that is going on at a certain time in the future
action that is sure to happen in the near future
action that will be finishedat a certain time in the future
Future II Simple
A: He will have spoken.
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken?
Future II
Progressive
A: He will have been speaking.
N: He will not have been
speaking.
Q: Will he have been speaking?
action taking place before a certain time in the future
in one year, next week,
tomorrow
by Monday, in a week
for , the last couple of
hours, all day long
putting emphasis on thecourse of an action
Conditional I Simple
A: He would speak.
N: He would not speak.
Q: Would he speak?
action that might take place
Conditional I
Progressive
A: He would be speaking.
N: He would not be speaking.
Q: Would he be speaking?
action that might take place
putting emphasis on thecourse / duration of the action
Conditional II
Simple
A: He would have spoken.
N: He would not have spoken.
Q: Would he have spoken?
action that might have taken place in the past
Conditional II
Progressive
A: He would have been
speaking.
N: He would not have been
speaking.
Q: Would he have been
speaking?
action that might have taken place in the past
puts emphasis on thecourse / duration of the action
if sentences type II
(If I were you, I would
go home.)
if sentences type III
(If I had seen that, Iwould
have helped.)
Вам также может понравиться
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentMariana PasatОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentPavlina HaralampievaОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент4 страницыTensesZandaОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Документ3 страницыSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент3 страницыTable of English TensesGonzalo AstorgaОценок пока нет
- TenseДокумент3 страницыTenseKiki MulqiahОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент4 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент6 страницTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'Оценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент4 страницыTable of English TensesKashif WakeelОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент2 страницыTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- Table TensesДокумент4 страницыTable TensesmariminniОценок пока нет
- TenseДокумент3 страницыTenseMădălina RădulescuОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndrea Paredes GuerreroОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент5 страницTable of English TensesMaria CristianОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaОценок пока нет
- English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыEnglish Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAndreaОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент3 страницыTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент5 страницTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798Оценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент4 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaОценок пока нет
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsДокумент4 страницыTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент3 страницыTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент3 страницыTable of English Tensesiuliana13Оценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaОценок пока нет
- English TensesДокумент2 страницыEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLyana LorenzaОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012Оценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент5 страницTable of English TenseskaterynavelОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleДокумент4 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsДокумент4 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsAdriana MuresanОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentДокумент3 страницыTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21Оценок пока нет
- Timpuri LeДокумент3 страницыTimpuri LemadybyaОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент4 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000Оценок пока нет
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesДокумент5 страницVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент4 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsОценок пока нет
- English Tenses SummaryДокумент2 страницыEnglish Tenses SummaryRedi BylekОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentДокумент1 страницаTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses MeliaДокумент19 страницTable of English Tenses MeliaMelia Kusuma WardaniОценок пока нет
- English TensesДокумент4 страницыEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoОценок пока нет
- Table of English TensesДокумент4 страницыTable of English Tensesdieba105Оценок пока нет
- 1BACH - Verb TensesДокумент3 страницы1BACH - Verb TensesEnrique FerreroОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент18 страницTensesNora Mestiri100% (1)
- All TensesДокумент3 страницыAll TenseskarenОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент5 страницTensesGanesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsДокумент2 страницыTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/ USE Signal WordsradivojerОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: TalkedДокумент4 страницыSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Документ2 страницыSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13Оценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент1 страницаTensesNucă EvelinaОценок пока нет
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question: (Going To)Документ9 страницTense Affirmative/Negative/Question: (Going To)Sure ManОценок пока нет
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент1 страницаSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialОценок пока нет
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsДокумент3 страницыTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102Оценок пока нет
- Tenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal WordsДокумент2 страницыTenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal WordssfiedlercОценок пока нет
- Table of English Tenses: Simple PresentДокумент3 страницыTable of English Tenses: Simple PresentSofiene GuedriОценок пока нет
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3От EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Оценок пока нет
- Hospitals Bupa 2019Документ26 страницHospitals Bupa 2019gulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Split 18.10.17Документ19 страницSplit 18.10.17gulzar72Оценок пока нет
- The Lean WayДокумент2 страницыThe Lean Waygulzar72Оценок пока нет
- 10 Lessons We Can Learn From Mahatma GandhiДокумент7 страниц10 Lessons We Can Learn From Mahatma Gandhigulzar72Оценок пока нет
- New Text DocumentДокумент4 страницыNew Text Documentgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- 1000 Verbs in QuranДокумент183 страницы1000 Verbs in Qurangulzar72Оценок пока нет
- The Zen of ResultsДокумент17 страницThe Zen of ResultsTracey DeeОценок пока нет
- Personal Productivity QuotesДокумент16 страницPersonal Productivity Quotesgulzar72100% (1)
- Personal Development QuotesДокумент20 страницPersonal Development Quotesgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Learning Styles - Concrete, Abstract, Random, and SequentialДокумент3 страницыLearning Styles - Concrete, Abstract, Random, and Sequentialgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- 25 Inspirational MoviesДокумент6 страниц25 Inspirational Moviesgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Morning Questions - Use The Power of Questions To Change Your Life PDFДокумент2 страницыMorning Questions - Use The Power of Questions To Change Your Life PDFgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Personal Development QuotesДокумент20 страницPersonal Development Quotesgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Anthony Robbins Challenges PDFДокумент31 страницаAnthony Robbins Challenges PDFgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Increment Salary 02102016Документ1 страницаIncrement Salary 02102016gulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Weekly Behaviour ReportДокумент1 страницаWeekly Behaviour Reportgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Tajweed RulesДокумент6 страницTajweed Rulesgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Akbar IncrementДокумент1 страницаAkbar Incrementgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Well Know English IdiomsДокумент1 страницаWell Know English Idiomsgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Kiran Police CaseДокумент15 страницKiran Police Casegulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Gulzar Exit Re EntryДокумент1 страницаGulzar Exit Re Entrygulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Kiran Police CaseДокумент15 страницKiran Police Casegulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Awesome GoodДокумент8 страницAwesome Goodgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- When To Use CommaДокумент1 страницаWhen To Use Commagulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Yoga StarterДокумент1 страницаYoga Startergulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Akbar IncrementДокумент1 страницаAkbar Incrementgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- 58 Habits For Children To KnowДокумент2 страницы58 Habits For Children To Knowgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Your Personal Brand - Top ValuesДокумент1 страницаYour Personal Brand - Top Valuesgulzar72Оценок пока нет
- Motion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsДокумент27 страницMotion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsRahul RajОценок пока нет
- Conductivity MeterДокумент59 страницConductivity MeterMuhammad AzeemОценок пока нет
- Ruahsur Vangin Basket-Ball Court Lungrem ChimДокумент4 страницыRuahsur Vangin Basket-Ball Court Lungrem ChimchanmariansОценок пока нет
- Undertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Документ3 страницыUndertaking:-: Prime Membership Application Form (Fill With All Capital Letters)Anuj ManglaОценок пока нет
- Matthew DeCossas SuitДокумент31 страницаMatthew DeCossas SuitJeff NowakОценок пока нет
- Animal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseДокумент11 страницAnimal Welfare in Bangladesh and The Role of Obhoyaronno CaseZarin Tanjim WoyshorjoОценок пока нет
- Christianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONДокумент64 страницыChristianity and Mental Health WEB VERSIONWorld Religion NewsОценок пока нет
- QTP Common FunctionsДокумент55 страницQTP Common FunctionsAnkur TiwariОценок пока нет
- Thomas Noochan Pokemon Review Final DraftДокумент6 страницThomas Noochan Pokemon Review Final Draftapi-608717016Оценок пока нет
- Volvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsДокумент3 страницыVolvo D16 Engine Family: SpecificationsJicheng PiaoОценок пока нет
- Morocco Top ScientistsДокумент358 страницMorocco Top Scientistsa.drioicheОценок пока нет
- Lesson 73 Creating Problems Involving The Volume of A Rectangular PrismДокумент17 страницLesson 73 Creating Problems Involving The Volume of A Rectangular PrismJessy James CardinalОценок пока нет
- TN Vision 2023 PDFДокумент68 страницTN Vision 2023 PDFRajanbabu100% (1)
- Crime Scene Drawing January Incident 10501-10600Документ100 страницCrime Scene Drawing January Incident 10501-10600columbinefamilyrequest100% (2)
- Steven SheaДокумент1 страницаSteven Sheaapi-345674935Оценок пока нет
- APA CitationsДокумент9 страницAPA CitationsIslamОценок пока нет
- Government by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesДокумент122 страницыGovernment by Algorithm - Artificial Intelligence in Federal Administrative AgenciesRone Eleandro dos SantosОценок пока нет
- Student Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenДокумент2 страницыStudent Worksheet Task 1 - Long Reading: Fanny Blankers-KoenDANIELA SIMONELLIОценок пока нет
- Faiths of Eberron PDFДокумент2 страницыFaiths of Eberron PDFCarrieОценок пока нет
- Session Guide - Ramil BellenДокумент6 страницSession Guide - Ramil BellenRamilОценок пока нет
- Fry 2016Документ27 страницFry 2016Shahid RashidОценок пока нет
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Документ106 страницDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Mai PhanОценок пока нет
- Churches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFДокумент2 страницыChurches That Have Left RCCG 0722 PDFKadiri JohnОценок пока нет
- ICONS+Character+Creator+2007+v0 73Документ214 страницICONS+Character+Creator+2007+v0 73C.M. LewisОценок пока нет
- KBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race ScheduleДокумент2 страницыKBC Autumn Regatta 2023 Saturday Race SchedulezainОценок пока нет
- Veritas CloudPoint Administrator's GuideДокумент294 страницыVeritas CloudPoint Administrator's Guidebalamurali_aОценок пока нет
- Immediate Life Support PDFДокумент128 страницImmediate Life Support PDFShilin-Kamalei Llewelyn100% (2)
- Rele A Gas BuchholtsДокумент18 страницRele A Gas BuchholtsMarco GiraldoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Control SystemДокумент9 страницIntroduction To Control SystemAbdulhakam Abubakar YusufОценок пока нет
- Water and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceДокумент18 страницWater and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceJoyce Marian BelonguelОценок пока нет