Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CORD PROLAPSE GUIDE
Загружено:
Usman Ali AkbarИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CORD PROLAPSE GUIDE
Загружено:
Usman Ali AkbarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
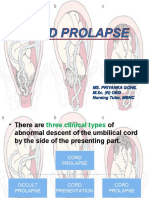
CORD PROLAPSE
There are three clinical types of decent of Cord
A. Occult prolapseThe cord is placed by the side of the presenting part and is not felt
by fingers on internal examination
B. Cord presentationThe cord has slipped below the presenting part and is felt lying in
the intact bag
of membranes
C. Cord prolapseThe cord is lying inside or outside the vagina following rupture of
membranes
Incidence of Cord Prolapse : 1:500 Deliveries
Risk Factors :
Maternal
- Pelvic tumors ( Fibroids )
- Narrow Pelvis
- Premature rupture of membranes,
- Grand multiparity (more than 5
pregnancies)
- Multiple Pregnancies
Fetal Causes
Prematurity
Mal Presentation
Breech Presentation
Transverse Lie
Multiple Pregnancy
Polyhydrominos
Placenta Previa
Large Baby
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made clinically by seeing the cord at introitus or feeling it.
Perinataly : Abnormal Fetal Heart sounds due to compression of umbilical vein between
the presenting part and the pelvis
Management :
Once prolapse of the cord has occurred urgent action is needed.
Immediate pelvic examination is to be done to find dilatation and effacement of
cervix:
- To relieve pressure on the cord.
- To find out if the foetus is alive or dead, strength of pulsations of the cord. Repeated
cord palpation for pulsation also induces spasm hence, listening to foetal heart is a
better alternative.
- To expedite delivery, if alive.
- To await spontaneous delivery if dead and the pelvis and presentation are favourable.
In cord prolapse:
First look for:
- viability of the foetus
- maturity of the foetus
- associated complicating factors
- dilatation of the cervix.
If the Foetus is Alive
Immediate vaginal delivery not possible or contraindicated
First aid is to minimise pressure on cord as long as the patient can be transferred or
prepared for
assisted delivery. Give oxygen to the mother:
- To lift the presenting part off the cord by the gloved fingers into the vagina and keep
there till definitive treatment can be done. Amnioinfusion may be done in an attempt to
decrease pressure on umbilical cord.
- Keep the patient in exaggerated elevated Sims position with pillow under the
buttocks.
- The end of bed may be elevated. High Trendelenburg and knee-chest position
traditionally mentioned is very tiring and irksome to the patient but may be tried
Definitive treatment
- Caesarean section when the baby is sufficiently mature enough to survive and the
cervix is not fully dilated.
If Foetus Dead
Labour is allowed to continue awaiting spontaneous delivery. Sometimes destructive
operation may be required.
Prognosis :
The foetal prognosis depends on the following factors:
Duration of cord compression : If longer than 10 minutes it will cause
cerebral damage , If around 20 minutes Fetal death.
- Status of membranescord presentation (membranes intact) has 100 per cent
survival rate for thefoetus, if diagnosed in time.
- Foetal reserve IUGR
- Stage of labour : The risk is less when the cord is prolapsed in the second stage
(30%) than when it prolapses in the first stage (70%).
- Foetal presentationThe dangers are greater in vertex than breech presentation.
Maternal :
Maternal morbidityis also increased as a consequence of operative delivery with
associated risk of anaesthesia, blood transfusion, infection and the direct trauma of
instruments
Вам также может понравиться
- Ukraine Baby FactoriesДокумент14 страницUkraine Baby Factories3adrianОценок пока нет
- Organophosphate Poisoning Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentДокумент23 страницыOrganophosphate Poisoning Signs, Symptoms, and TreatmentUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Angelica New PRC Cases FormattedДокумент7 страницAngelica New PRC Cases FormattedDino CamposОценок пока нет
- Antepartum HaemorrhageДокумент18 страницAntepartum HaemorrhageOjambo Flavia100% (1)
- Final Exam - QuestionДокумент3 страницыFinal Exam - QuestionMark ElbenОценок пока нет
- Rhesus Iso ImmunizationДокумент12 страницRhesus Iso Immunizationapi-3705046Оценок пока нет
- Importance of structured teaching on gestational hypertensionДокумент18 страницImportance of structured teaching on gestational hypertensionمالك مناصرةОценок пока нет
- Abortion PP TДокумент42 страницыAbortion PP TDivya ToppoОценок пока нет
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanДокумент5 страницPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩОценок пока нет
- Impaired Physical MobilityДокумент2 страницыImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranОценок пока нет
- NCP AnxietyДокумент6 страницNCP AnxietyRaijenne VersolaОценок пока нет
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedДокумент5 страницAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangОценок пока нет
- Discharge PlanДокумент1 страницаDischarge PlanglocelОценок пока нет
- Code Green Introduction Reviewer - RedДокумент4 страницыCode Green Introduction Reviewer - RedJamieОценок пока нет
- Student Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыStudent Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanMussaib MushtaqОценок пока нет
- Physical Exam - AppendectomyДокумент8 страницPhysical Exam - Appendectomyirish felixОценок пока нет
- DDSTДокумент61 страницаDDSTji payОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitДокумент9 страницNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitYesha Mae MartinОценок пока нет
- Course Unit 13 Ethical Issues Related To Technology in The Delivery of Health CareДокумент3 страницыCourse Unit 13 Ethical Issues Related To Technology in The Delivery of Health Carerising starОценок пока нет
- Case Pres Ncps FinalДокумент13 страницCase Pres Ncps FinalMariejoy YadaoОценок пока нет
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingДокумент2 страницыNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingShyla ManguiatОценок пока нет
- Activity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Документ5 страницActivity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Cameron De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Family Nursing Care Plan G4 BSN2 4 DonДокумент31 страницаFamily Nursing Care Plan G4 BSN2 4 DonStuart BlackОценок пока нет
- Nutrition for pregnant and lactating womenДокумент3 страницыNutrition for pregnant and lactating womenmo'niqueОценок пока нет
- NSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestДокумент2 страницыNSO - Adam's Forward Bend TestMaha AmilОценок пока нет
- Cu 4Документ3 страницыCu 4Paul SahagunОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDrug StudyJeremiah M. MascariñasОценок пока нет
- NCP RiskДокумент2 страницыNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan Healthy PregnancyДокумент7 страницTeaching Plan Healthy PregnancyKyedae ShymkoОценок пока нет
- Postpartum Physical Assessment ParametersДокумент5 страницPostpartum Physical Assessment ParametersKathrina CraveОценок пока нет
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPДокумент3 страницыImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliОценок пока нет
- NCP EsrdДокумент2 страницыNCP EsrdAziil LiizaОценок пока нет
- Cleft Lip and Palate CareДокумент11 страницCleft Lip and Palate CareEvangeline Anne MacanasОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk InfectionДокумент1 страницаNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Uremic SyndromeДокумент11 страницNursing Care of Uremic Syndromeyoedha_banditozz50% (2)
- Drug TabulationДокумент6 страницDrug TabulationRosemarie Canete Delarita100% (1)
- NCPДокумент9 страницNCPLeolene Grace BautistaОценок пока нет
- Course Task Nursing DiagnosisДокумент2 страницыCourse Task Nursing DiagnosisKyla Eunice RiveraОценок пока нет
- Abc NCPДокумент3 страницыAbc NCPKL AstudilloОценок пока нет
- Casepres NCPДокумент6 страницCasepres NCPdencio1992Оценок пока нет
- APOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasДокумент3 страницыAPOLONIO, JC - Natural Theory - Thomas AquinasJustin ApolonioОценок пока нет
- Week 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Документ7 страницWeek 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Jollan Marie BuenvenidaОценок пока нет
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsДокумент8 страницPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPДокумент7 страницIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoОценок пока нет
- Kawasaki DiseaseДокумент7 страницKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaОценок пока нет
- NCP For Rapid Shallow BreathingДокумент1 страницаNCP For Rapid Shallow Breathingbamboo2dОценок пока нет
- Medical Management For PneumoniaДокумент2 страницыMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- ER equipments & drugsДокумент3 страницыER equipments & drugsApple LlanesОценок пока нет
- Understanding Biopsy ProcedureДокумент5 страницUnderstanding Biopsy ProcedureDan HizonОценок пока нет
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsДокумент6 страницNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Malaria PosterДокумент1 страницаMalaria PosterTommaso ForzaОценок пока нет
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialДокумент10 страницInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayОценок пока нет
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Документ6 страницDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityДокумент1 страницаDrug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityHera Pamela Buelis BatoyОценок пока нет
- How to treat and prevent breast engorgementДокумент1 страницаHow to treat and prevent breast engorgementkurniaОценок пока нет
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETДокумент6 страницComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoОценок пока нет
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideДокумент2 страницыRectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideMariah Jane TaladuaОценок пока нет
- Abbreviations For Nursing StudentsДокумент7 страницAbbreviations For Nursing StudentssodiwoОценок пока нет
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Документ3 страницыElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliОценок пока нет
- NBS BrochureДокумент2 страницыNBS BrochureMichael Jordan De VeraОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент4 страницыNCPapi-3728995Оценок пока нет
- Santos Family - Prob IDДокумент3 страницыSantos Family - Prob IDchubachenes100% (2)
- Spina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningoceleДокумент1 страницаSpina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningocelesmilingstarsОценок пока нет
- AmbroxolДокумент1 страницаAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaОценок пока нет
- Group 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityДокумент4 страницыGroup 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityJuliaОценок пока нет
- Cord ProlapseДокумент11 страницCord ProlapseWilliams Emmanuel AdeyeyeОценок пока нет
- Cordprolapse 190701165943Документ28 страницCordprolapse 190701165943DrPreeti Thakur ChouhanОценок пока нет
- CRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX PathwayДокумент1 страницаCRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX PathwayUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachДокумент3 страницыChronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Polycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsДокумент1 страницаPolycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Chronic Renal Failure Long CaseДокумент2 страницыChronic Renal Failure Long CaseUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Nephrotic SyndromeДокумент2 страницыNephrotic SyndromeUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- CRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX Pathway - AdjДокумент1 страницаCRF Wtih Fluid Overload MX Pathway - AdjUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Renal Tubular Acidosis SummaryДокумент1 страницаRenal Tubular Acidosis SummaryUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Renal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjДокумент1 страницаRenal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Obstructive Airway Diseases ExplainedДокумент53 страницыObstructive Airway Diseases ExplainedUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisДокумент3 страницыUrinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Dialysis Treatment Options: Peritoneal Dialysis vs HemodialysisДокумент2 страницыDialysis Treatment Options: Peritoneal Dialysis vs HemodialysisUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Renal TransplantДокумент2 страницыRenal TransplantUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionДокумент9 страницGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Recurrent Nausea Andor VomitingДокумент8 страницRecurrent Nausea Andor VomitingUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- King Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Документ40 страницKing Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Usman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Ibs Presentation PDFДокумент18 страницIbs Presentation PDFUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- GRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)Документ1 страницаGRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)Usman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionДокумент9 страницGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Clinical Calendar 2016-2018Документ3 страницыClinical Calendar 2016-2018NickОценок пока нет
- Anaemia in PregnancyДокумент13 страницAnaemia in PregnancyUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Anaemia in PregnancyДокумент13 страницAnaemia in PregnancyUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Foreign Visiting Student Medical Status Form PDFДокумент1 страницаForeign Visiting Student Medical Status Form PDFUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- TSMEntry 2Документ1 страницаTSMEntry 2Usman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- IBS Pathophysiology & ManagementДокумент18 страницIBS Pathophysiology & ManagementUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Recurrent VomitingДокумент16 страницRecurrent VomitingUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Subject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THДокумент1 страницаSubject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- Diseases of The StomachДокумент17 страницDiseases of The StomachUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- When Hope DiesДокумент2 страницыWhen Hope DiesUsman Ali AkbarОценок пока нет
- 730 2113 1 PBДокумент7 страниц730 2113 1 PBFitrahMyatunОценок пока нет
- Maternal Factors and Preeclampsia IncidenceДокумент9 страницMaternal Factors and Preeclampsia Incidenceayu maulinaОценок пока нет
- Karakteristik Ibu Dan Post Natal Treatment (PNT) Berhubungan Dengan Terjadinya Postpartum Blues Ibu NifasДокумент7 страницKarakteristik Ibu Dan Post Natal Treatment (PNT) Berhubungan Dengan Terjadinya Postpartum Blues Ibu NifasNoeng AzZahОценок пока нет
- Factors Linked to Perineal Lacerations in ChildbirthДокумент9 страницFactors Linked to Perineal Lacerations in ChildbirthProfesi CatharinaОценок пока нет
- Ob-Gyn Practice Changers: Folic Acid, Omega-3s, Pre-eclampsia ManagementДокумент57 страницOb-Gyn Practice Changers: Folic Acid, Omega-3s, Pre-eclampsia ManagementVirginia AbalosОценок пока нет
- UG Log Book KMC ManipalДокумент3 страницыUG Log Book KMC Manipaldipanjan bhatacharjeeОценок пока нет
- Care of Mother, Child, Family and Population Group At-Risk or With ProblemsДокумент52 страницыCare of Mother, Child, Family and Population Group At-Risk or With ProblemsMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- Abdominal Palpation & Examination in Pregnancy 5.0 PDFДокумент11 страницAbdominal Palpation & Examination in Pregnancy 5.0 PDFPalaniswami Palaniswami100% (1)
- Teen Pregnancy: A Problem and an OpportunityДокумент13 страницTeen Pregnancy: A Problem and an OpportunitycokdebagusОценок пока нет
- Thyrotoxicosis in Patients With Hydatid MoleДокумент10 страницThyrotoxicosis in Patients With Hydatid MoleBaskarazrОценок пока нет
- Surrogate Mother (Negative Side)Документ16 страницSurrogate Mother (Negative Side)Theo DapamedeОценок пока нет
- Fetal Growth Restriction - ACOG 2019Документ23 страницыFetal Growth Restriction - ACOG 2019Adhitya Yudha MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Etiologies and Risk Factors of Placental Abruption.402Документ1 страницаEtiologies and Risk Factors of Placental Abruption.402Sohaib AliОценок пока нет
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesДокумент13 страницEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseДокумент6 страницUmbilical Cord ProlapseCeth BeltranОценок пока нет
- OBII - 16 Postterm Pregnancy - PDF Version 1Документ6 страницOBII - 16 Postterm Pregnancy - PDF Version 1Felina CabadingОценок пока нет
- Doh MCNДокумент14 страницDoh MCNCbrc CebuОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Placenta PreviaДокумент9 страницJurnal Placenta Previasheva25Оценок пока нет
- Cesarean Section (C-Section)Документ23 страницыCesarean Section (C-Section)Andreychi KalabaОценок пока нет
- Twins Identical and FraternalДокумент3 страницыTwins Identical and Fraternalteju2812Оценок пока нет
- Cord Prolapse: Case ReportДокумент37 страницCord Prolapse: Case ReportMica CumigadОценок пока нет
- Malpositions and MalpresentationsДокумент30 страницMalpositions and Malpresentationsiqra HassanОценок пока нет
- Fatima's admission interview for uterine contractionsДокумент2 страницыFatima's admission interview for uterine contractionsPUTRI AYU PRIHATINIОценок пока нет