Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Staphylococcus: Gram Positive Cocci
Загружено:
lykaperiasИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Staphylococcus: Gram Positive Cocci
Загружено:
lykaperiasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
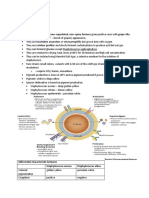
Staphylococcus and Micrococci
Gram Positive Cocci
Staphyloccus or Streptococcus
high content of peptidoglycan
Family Micrococcaceae
1. Staphylococcus human pathogen
2. Micrococcus rarely infectious
3. Planococcus marine env
4. Stomatococcus emerging rare oppor.
Staphylococcus
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Gram-positive arranged in tetrads or clusters
Facultative anaerobes
Medium-sized, raised creamy colonies on BAP
Catalase positive
Oxidase negative
Non-motile
Non-spore forming
Reduces nitrates to nitrites
Grows in 7.5 to 10% NaCl
BACITRACIN resistant
Can divided into two groups
S. aureus: coagulae POSITIVE
CoNS (Coagulase Negative Staph): S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, S.
hominis, S. hemolyticus and S. warneri
Staphylococcus
positive
Medium sized, raised, creamy
Tetrads or clusters
Mannitol Salt Agar: 7.5 to 10% NaCl
3.
Colistin-Nalidixic Acid (CNA)
BA + colistin and nalidixic acid which
are selective for gram positive
GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS
Catalase
BAP
Arrangement
2.
Streptococcus
negative
Pinpoint, flat, colorless
Pairs or chains
Ferments many CHO (lactic acid)
Resistant to drying, heat and NaCl
Generally sensitive to many antimicrobials. May produce resistance gene:
1.
2.
Culture
1.
Blood Agar Plate - medium convex, creamy and dome shaped, white to yellow
pigment.
3.
Beta-lactamase production plasmid control by transduction or conjugation
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Monobactams and cCrbapenems
inhibiting the cell wall systhesi
Methicillin: B-lactamase resistant
mecA Staphylococcal cassette chromosome
ccrA and ccrB catalyze precision excision of SCCmec
Insertion sites for plasmids and transposons
Vancomycin
MIC > 16 ug/mL
vanA from enterococci
Staphylococcus and Micrococci
Clinical Findings
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Carbuncle, furucle
Impetigo
Scalded skin syndrome
Food poisoining
TSS
Pneumonia
Bacteremia
Ostemyelitis
Staphylococcus aureus
BAP: medium to large colonies, creamy appearance, narrow zone of Beta-hemolysis
MSA yellow colonies
DNAse test + (clearing of the dye toluidine blue w/ HCl; turns PINK)
Coagulase + (bacterial colonies in saline + rabbit plasma
fibrin clots)
Antigenic Structures
1.
Teichoic acid P of glycerol and ribitol phosphate that provide rigidity
2.
3.
to the cell wall
Protein A adhesins that resist opsonization
Capsules inhibit phagocytosis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
1.
2.
Extracellular Enzymes & Toxin
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Coagulases convert fibrinogen to active fibrin
Staphylokinase dissolves fibrin clots
Lipase hydrolyzes fats
Hyaluronidase hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid
DNase degrades DNA
6.
7.
8.
9.
Exfoliatins hydrolyzes tissue (Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome)
Leukocidins lyse neutrophils and macrophages
Hemolysisn lyse RBCs
Enterotoxins
a. Staph related poisoning (A & B)
b. Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (F)
non-hemolytic on BAP
Positive growth on CAN
Coagulase NEG
DNase NEG
Susceptible to NOVOBIOCIN
Bacterial endocarditis
Nosocomial infections
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Coagulase NEG
DNase NEG
resistant to NOVOBIOCIN
Stomotococcus mucilaginosus
NEG growth in 7-5 to `0% NaCl
CAT POSITIVE weakly
Coagulase NEG
Staphylococcus and Micrococci
7-10% NaCl
+
+
Catalase
POS
POS
COAG
POS
neg
DNase
POST
neg
NOVOBIOCIN
S. auereus
S. epidermidis
S. saprophyticus
Stomotococcus
+
-
POS
Weakly +
neg
neg
neg
resistant
susceptible
mucilaginosus
General Characteristics:
Вам также может понравиться
- Staphylococcus: Made By: Shalini BishtДокумент70 страницStaphylococcus: Made By: Shalini BishtEduardo SalazarОценок пока нет
- Staphylococcus: Made By: Shalini BishtДокумент70 страницStaphylococcus: Made By: Shalini BishtEduardo SalazarОценок пока нет
- S. AureusДокумент39 страницS. AureusRajkishor YadavОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Gram Positive CocciДокумент9 страниц1.1 Gram Positive CocciJustine Mel Concepcion IlardeОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsДокумент15 страницGram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsKyle PicocОценок пока нет
- Week 3 - Topic 1 - Demonstration of Characteristics, Lab Diagnosis & Pathogenesis of StaphylococcusДокумент24 страницыWeek 3 - Topic 1 - Demonstration of Characteristics, Lab Diagnosis & Pathogenesis of StaphylococcusTayyaba TahiraОценок пока нет
- CB Part 3Документ76 страницCB Part 3Mohammad MambuayОценок пока нет
- Campylobacter PDFДокумент78 страницCampylobacter PDFKhushi PatelОценок пока нет
- Staphylococci & MicrococciДокумент52 страницыStaphylococci & Micrococcihoneylemon.coОценок пока нет
- Chapter15 StreptococciДокумент66 страницChapter15 StreptococciNursheda Abangon AzisОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Документ45 страницGram Positive Cocci Sem 1 1Charmaine Corpuz Granil100% (1)
- Anubhav Rai StaphylococcusДокумент34 страницыAnubhav Rai StaphylococcusHemant KumarОценок пока нет
- GRAM Positive CocciДокумент67 страницGRAM Positive CocciNoraine Princess TabangcoraОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент27 страницGram Positive Coccishekhar JhaОценок пока нет
- Staphylococcus Aureus: DR Surender Kaur Asst - Prof. GMCДокумент22 страницыStaphylococcus Aureus: DR Surender Kaur Asst - Prof. GMCkaursurenderОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual VMC 311 2016 PDFДокумент74 страницыLaboratory Manual VMC 311 2016 PDFrajkumar871992Оценок пока нет
- MICROBIOLOGYДокумент7 страницMICROBIOLOGYjiangОценок пока нет
- Campylobacter Jejuni (Microb Notes)Документ4 страницыCampylobacter Jejuni (Microb Notes)puteri90Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Bacteriology Finals 2.0: Gram Positive BaciliДокумент13 страницClinical Bacteriology Finals 2.0: Gram Positive BaciliEzra LonodОценок пока нет
- Structure of Bact P.E.2018Документ60 страницStructure of Bact P.E.2018Ludmila BuzurniiОценок пока нет
- Staphylococci and StreptococciДокумент40 страницStaphylococci and StreptococciAshwani Mathur, Ma-306100% (1)
- Food Poisoning - ANMДокумент19 страницFood Poisoning - ANMdesyОценок пока нет
- 2008 Block2 ReviewДокумент28 страниц2008 Block2 ReviewbellОценок пока нет
- STAPHYLOCOCCIДокумент26 страницSTAPHYLOCOCCIDaud Rehman KhanОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive & Negative CocciДокумент14 страницGram Positive & Negative Coccilanie_flores_3Оценок пока нет
- Family of StreptococcaceaeДокумент10 страницFamily of StreptococcaceaeLovely B. AlipatОценок пока нет
- S Aureus (Autosaved)Документ16 страницS Aureus (Autosaved)Pitua IvaanОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент6 страницGram Positive Coccitamiqua1Оценок пока нет
- Strepto ClassДокумент34 страницыStrepto ClassAbcdefg HijklОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive Cocci - Sem 1Документ45 страницGram Positive Cocci - Sem 1Charmaine Corpuz GranilОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics in PeadiatricsДокумент14 страницAntibiotics in PeadiatricsrisanaОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент140 страницGram Positive CocciBles Cy LagrimasОценок пока нет
- Finasls 1 Staph Strep PDFДокумент50 страницFinasls 1 Staph Strep PDFFrancis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Macrocytic AnemiasДокумент49 страницMacrocytic Anemiasdr_asr100% (1)
- ResourceДокумент5 страницResourcechindobr8Оценок пока нет
- Virus Bacteria Fungi Parasite Cell Diameter Nucleic Acid Type of Nucleus Ribosome Mitochondria Nature of Outer Surface Motility ReplicationДокумент11 страницVirus Bacteria Fungi Parasite Cell Diameter Nucleic Acid Type of Nucleus Ribosome Mitochondria Nature of Outer Surface Motility ReplicationDelvin Jan del RosarioОценок пока нет
- 40 Neisseria Moraxella CatarrhalisДокумент2 страницы40 Neisseria Moraxella CatarrhalisnicaОценок пока нет
- MDR Gram PДокумент69 страницMDR Gram Psaraabolghasemi1Оценок пока нет
- LJ MediaДокумент3 страницыLJ MediaJerry ThompsonОценок пока нет
- S. MutantДокумент15 страницS. MutantShahriar ShamimОценок пока нет
- 44 Chloramphenicol, Tetracyclines, Macrolides, ClindamycinДокумент77 страниц44 Chloramphenicol, Tetracyclines, Macrolides, ClindamycinNagu KopparapuОценок пока нет
- Group 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamДокумент11 страницGroup 2 - Bacte Lab. ExamAОценок пока нет
- BacteriologyДокумент107 страницBacteriologyVivek ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Lab 6Документ5 страницLab 6moodyОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент34 страницыGram Positive CocciMaria Cecilia Flores50% (2)
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsДокумент53 страницыStreptococcus Pneumoniae MbbsShyam MishraОценок пока нет
- Pyogenic Cocci Pyogenic Means " Pus Forming" Cocci Means "Spherical Bacteria"Документ14 страницPyogenic Cocci Pyogenic Means " Pus Forming" Cocci Means "Spherical Bacteria"Ab AbОценок пока нет
- VibrioДокумент20 страницVibrioDayana PrasanthОценок пока нет
- Micrococcaceae / Staphylococci: ConsiderationДокумент3 страницыMicrococcaceae / Staphylococci: ConsiderationleoОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive Cocci StaphylococciДокумент41 страницаGram Positive Cocci StaphylococciZainab ElgehaniОценок пока нет
- Chocolate AgarДокумент4 страницыChocolate AgarMaria Chacón CarbajalОценок пока нет
- Special MicrobiologyДокумент68 страницSpecial MicrobiologyrefuapalackyОценок пока нет
- Laporan BLJR Mandiri Tid 2Документ34 страницыLaporan BLJR Mandiri Tid 2budi setiawanОценок пока нет
- Gram Negative CocciДокумент53 страницыGram Negative CocciBles Cy LagrimasОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Antimicrobial DrugsДокумент7 страницUnit 8 Antimicrobial DrugsKathleen MontañoОценок пока нет
- L1 - StaphylococciДокумент35 страницL1 - Staphylococciyouservezeropurpose113Оценок пока нет
- Practical Medical Microbiology PHT382Документ22 страницыPractical Medical Microbiology PHT382mdsajidaaliОценок пока нет
- Gram Positive CocciДокумент21 страницаGram Positive CocciRedelle Mae Nini100% (2)
- Bacteriology LectureДокумент38 страницBacteriology LectureAisle Malibiran Paler100% (1)
- Project Documentation Part 2Документ42 страницыProject Documentation Part 2Lorena LanchoОценок пока нет
- Whitepaper Case Study Bell CanadaДокумент12 страницWhitepaper Case Study Bell CanadageehbeeОценок пока нет
- TP - RTT Calculation UMTSДокумент11 страницTP - RTT Calculation UMTSShahnawaz AnjumОценок пока нет
- SonarWiz OptionДокумент45 страницSonarWiz Optionmiko sjОценок пока нет
- Beginning CosmodynesДокумент2 страницыBeginning CosmodynesDilip KiningeОценок пока нет
- DKC Spoilers Arc 1 PDFДокумент139 страницDKC Spoilers Arc 1 PDFdysry100% (4)
- "View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter MenuДокумент89 страниц"View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter Menuelty TanОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Procedure: Preventive Mantenance of HT MotorДокумент5 страницMaintenance Procedure: Preventive Mantenance of HT Motorsanjay sharmaОценок пока нет
- Rigid Body Dynamics & RotationДокумент45 страницRigid Body Dynamics & RotationAshlesh Sonje100% (1)
- Philippine Navy Enlisted Rating Structure: Military Science (Ms-2)Документ10 страницPhilippine Navy Enlisted Rating Structure: Military Science (Ms-2)Kristine AquitОценок пока нет
- 12Документ11 страниц12ANK SHRINIVAASAN100% (1)
- Is - Iso-2631-2-2003Документ14 страницIs - Iso-2631-2-2003picottОценок пока нет
- HI98308 ManualДокумент2 страницыHI98308 ManualFùq Tất ỨqОценок пока нет
- Ergonomics For Product DesignДокумент45 страницErgonomics For Product DesignNORASHIKEN BINTI OTHMANОценок пока нет
- Cool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoДокумент51 страницаCool Doody Thesis by SlidesgoNadya HОценок пока нет
- Project Proposal Form (Edexcel) 2Документ3 страницыProject Proposal Form (Edexcel) 2Максим КарплюкОценок пока нет
- Thermo-Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Needle Punched Non-Woven Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer CompositesДокумент13 страницThermo-Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Needle Punched Non-Woven Banana Fiber Reinforced Polymer CompositesRajeshwaranОценок пока нет
- Heavy Metals - Environmental Contaminants and Their Occurrence in Different Types of MilkДокумент10 страницHeavy Metals - Environmental Contaminants and Their Occurrence in Different Types of MilkAdeel ZafarОценок пока нет
- Baby Bugatti b0.8 - TiledДокумент10 страницBaby Bugatti b0.8 - TiledDemetrios6Оценок пока нет
- Increase and Decrease WBC CountДокумент2 страницыIncrease and Decrease WBC CountLecture NotesОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: NEOPOR 2200Документ11 страницSafety Data Sheet: NEOPOR 2200Şerbuţă AlexandruОценок пока нет
- Heat TransferДокумент15 страницHeat Transferaddtadd6Оценок пока нет
- Spring 2019 Honors Forensic Science Final Exam Study GuideДокумент5 страницSpring 2019 Honors Forensic Science Final Exam Study Guideapi-260817414Оценок пока нет
- N304DN/15 JUL/RBR-TBT: - Not For Real World NavigationДокумент21 страницаN304DN/15 JUL/RBR-TBT: - Not For Real World NavigationFrancisco FortesОценок пока нет
- Oxy IQ OxigenoДокумент70 страницOxy IQ OxigenoDavidОценок пока нет
- Moral Principles: 3.1 ConscienceДокумент5 страницMoral Principles: 3.1 ConscienceMichelle Stormflower KohОценок пока нет
- Making Inferences 3Документ38 страницMaking Inferences 3JayieepearlОценок пока нет
- Smart Cities - A Case Study in Waste Monitoring and ManagementДокумент10 страницSmart Cities - A Case Study in Waste Monitoring and Managementfaris100% (1)
- NBME 2 Block 1-4Документ112 страницNBME 2 Block 1-4Daniel EspinosaОценок пока нет
- A.kishore Journal PaperДокумент34 страницыA.kishore Journal PaperA KishoreОценок пока нет