Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Example 21
Загружено:
RamosPeter0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров2 страницыdfgdfg
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документdfgdfg
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
5 просмотров2 страницыExample 21
Загружено:
RamosPeterdfgdfg
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
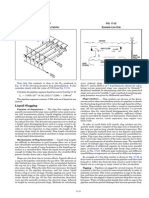
EXAMPLE 22.
2
Select drainage and vent piping sizes for the plumbing in an office
building for
which the fixtures are shown in Fig. 22.30.
SOLUTION
Selected dfu values from Table 22.2 are applied to each section of
the piping and totaled for each branch and stack, as well as for the building
drain and the building sewer. Individual fixture branches should not be less
than the size indicated in Table 22.3 for the minimum size of trap for each
fixture. An example of a fixture-unit summary and sample sizes of individual
branches that connect into a typical branch of the mens toilet group on any
floor are shown in the following table.
Table 22.3 indicates that a 3-in. (76-mm) horizontal fixture branch
is inadequate for the mens toilet group because this size pipe will handle
only 20 dfu. Therefore, a 4-in. (102-mm) pipe is selected (also a wise
minimum choice whenever water closets are served). Its capacity of 160 dfu
will be more than enough for the 36 fixture units needed here. The same
table shows that the soil stack diameter can be 4 in. (102 mm), and it is run
thus for its entire height. Its capacity of 90 dfu per story (or interval) is
sufficient for the 64 dfu that connect in at each T-Y connection. For three
branch intervals, this size stack will carry 240 dfu (this example requires 3
x64 =192 dfu); for its entire height, it will carry 500 dfu (this example
requires 5 x64= 320 dfu).
The vent stack must serve up to 338 dfu, with a 4-in. (102-mm)
soil stack, and with a maximum 70-ft (21.3-m) developed length. From Table
22.4, a 3-in. (76-mm) vent serving 540 dfu has a maximum developed length
of 150 ft (45.7 m), well over the minimum requirements. All vent stack
diameters will increase to 4 in. (102 mm) as they pass through the roof.
According to Table 22.5, the building drain and the building
sewer, at a pitch of in./ft (2.1%), should carry at least a total of 350 dfu. A
5-in. (127-mm) building drain or building sewer has a capacity of 480 dfu.
Although opinions may vary about the relative merits of
continuous or circuit venting, either system, properly designed, will
effectively prevent the siphoning of traps and relieve air pressures that could
cause foul gases to bubble through the traps into the occupied space.
Another system (Section 22.5c), especially suitable for high-rise buildings,
eliminates the the vent stack completely with equal
effectiveness.
Вам также может понравиться
- Drainagesystemslecturei 091022013358 Phpapp02Документ62 страницыDrainagesystemslecturei 091022013358 Phpapp02Abdul Raoof100% (1)
- Sanitary Drainage and Vent System Design ExampleДокумент16 страницSanitary Drainage and Vent System Design ExampleJessa Mae Evangelio PeruchoОценок пока нет
- TDP 504 - Duct Design Level 1 Fundamentals - QuizДокумент3 страницыTDP 504 - Duct Design Level 1 Fundamentals - QuizSuthi Sae DanОценок пока нет
- How To Properly Size Box PlenumsДокумент5 страницHow To Properly Size Box PlenumsAnwar Syed100% (3)
- Pipe Laying SlopeДокумент4 страницыPipe Laying SlopeAnbuОценок пока нет
- Water Mist System Design GuideДокумент6 страницWater Mist System Design Guidejun005100% (1)
- Exhaust Calculation BookletДокумент22 страницыExhaust Calculation BookletFaquruddin AliОценок пока нет
- PRICE - Air Distribution GuideДокумент5 страницPRICE - Air Distribution Guidenvenkat.narayan100% (1)
- AC Duct Design PDFДокумент6 страницAC Duct Design PDFkumar123rajuОценок пока нет
- Ibr BookДокумент33 страницыIbr BookRaja JayachandranОценок пока нет
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design PreparedДокумент6 страницShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design PreparedEmebu SamuelОценок пока нет
- بتول ماجد سعيد (التقرير النهائي)Документ20 страницبتول ماجد سعيد (التقرير النهائي)Batool MagedОценок пока нет
- Bs 6700 Pipe SizingДокумент20 страницBs 6700 Pipe SizingVelan SivasakthiОценок пока нет
- Deciding Width of A Pipe RackДокумент2 страницыDeciding Width of A Pipe RackSomnath LahaОценок пока нет
- PIPE SIZING CALCULATIONSДокумент17 страницPIPE SIZING CALCULATIONSJaykumar100% (6)
- Hydraulic Calculation Procedures for Automatic Sprinkler SystemsДокумент8 страницHydraulic Calculation Procedures for Automatic Sprinkler Systemsahmad adnanОценок пока нет
- Heating and Cooling Load CalculationДокумент7 страницHeating and Cooling Load Calculationirsalan_shahidОценок пока нет
- Design Criteria for Hunter Soil and Waste SystemsДокумент25 страницDesign Criteria for Hunter Soil and Waste SystemsfayasОценок пока нет
- Automatic Sprinkler Layout and DesignДокумент3 страницыAutomatic Sprinkler Layout and DesignMarc Danielle G Josue IIОценок пока нет
- Abu Dhabi-Sewerage Pipe Theories and CalculationДокумент19 страницAbu Dhabi-Sewerage Pipe Theories and CalculationPatel KalingaОценок пока нет
- Block 10 Module 2Документ18 страницBlock 10 Module 2Sandra FerrellОценок пока нет
- Appendix BДокумент2 страницыAppendix BjonongocoОценок пока нет
- Duct Design - Equal Friction MethodДокумент35 страницDuct Design - Equal Friction MethodAdhitya DarmadiОценок пока нет
- Design Guide: Hunter Rainwater SystemsДокумент5 страницDesign Guide: Hunter Rainwater SystemsTransgulfОценок пока нет
- Design Air Conditioning DuctsДокумент20 страницDesign Air Conditioning Ductsteo1285Оценок пока нет
- Design of Air Conditioning Ducts: LessonДокумент20 страницDesign of Air Conditioning Ducts: LessonAkhileshkumar PandeyОценок пока нет
- 3.1.4 Rainwater Disposal Systems Design: (A) Thermal MovementДокумент13 страниц3.1.4 Rainwater Disposal Systems Design: (A) Thermal MovementnvikkiОценок пока нет
- Appendices: Recommended Rules For Sizing The Water Supply SystemДокумент21 страницаAppendices: Recommended Rules For Sizing The Water Supply Systemrex tanongОценок пока нет
- DuctworkДокумент12 страницDuctworkNiong David100% (1)
- Duct RsesДокумент18 страницDuct RsesSameer AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Slug Catcher SizingДокумент8 страницSlug Catcher Sizingporchfroggy100% (1)
- Errata: This Errata Corrects Editorial Errors in The 44th Edition of API 5LДокумент5 страницErrata: This Errata Corrects Editorial Errors in The 44th Edition of API 5LChetan B KapadiaОценок пока нет
- Fike - Water Mist Design Machinery SpacesДокумент6 страницFike - Water Mist Design Machinery SpacesminiongskyОценок пока нет
- Compressed Air Distribution SystemsДокумент5 страницCompressed Air Distribution SystemsVarrit VejpongsaОценок пока нет
- 18-Duct DesignДокумент6 страниц18-Duct Designpryor.lamarioОценок пока нет
- Differential Head Flowmeters (Usbr - Gov) (ISO-5167 Stolz Equation) .HTMLДокумент7 страницDifferential Head Flowmeters (Usbr - Gov) (ISO-5167 Stolz Equation) .HTMLempanadaОценок пока нет
- Enterrado-Manual Caesar II 2011Документ22 страницыEnterrado-Manual Caesar II 2011FSAAVEDRAF100% (1)
- Steam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversОт EverandSteam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Mathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsОт EverandMathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsRoderick MelnikОценок пока нет
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionОт EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionОценок пока нет
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshОт EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshОценок пока нет
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsОт Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168От EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168Оценок пока нет
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceОт EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Industrial Process Plant Construction Estimating and Man-Hour AnalysisОт EverandIndustrial Process Plant Construction Estimating and Man-Hour AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Updates On Palay, Rice and Corn Prices, September 2018 (Week 2) PDFДокумент3 страницыUpdates On Palay, Rice and Corn Prices, September 2018 (Week 2) PDFRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Rice Quality enДокумент22 страницыRice Quality enKerr Ann CamposОценок пока нет
- RTRFBNKJ, K LK KLGBVДокумент1 страницаRTRFBNKJ, K LK KLGBVRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Eng Econ SlidesДокумент34 страницыEng Econ Slidesاحمد عمر حديدОценок пока нет
- Piping ComparisonДокумент1 страницаPiping ComparisonDenstar Ricardo SilalahiОценок пока нет
- Formwork PDFДокумент27 страницFormwork PDFKandarp Rajyaguru100% (1)
- ARDES 7 Urban Spaces 2Документ21 страницаARDES 7 Urban Spaces 2RamosPeterОценок пока нет
- 11th National Convention On Statistics (NCS) : EDSA Shangri-La Hotel October 4-5, 2010Документ27 страниц11th National Convention On Statistics (NCS) : EDSA Shangri-La Hotel October 4-5, 2010RamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Housing Policies ItДокумент29 страницHousing Policies ItRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- 2007 Design GuideДокумент337 страниц2007 Design GuideNapol T. TanОценок пока нет
- Rebar TolerancesДокумент4 страницыRebar Tolerancesjade5704Оценок пока нет
- Thesis Program Evaluation Form: I II Goals FactsДокумент1 страницаThesis Program Evaluation Form: I II Goals FactsRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Estimating Bill of MaterialsДокумент7 страницEstimating Bill of MaterialsBethelОценок пока нет
- Whether Individual or ContinuousДокумент2 страницыWhether Individual or ContinuousRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- WaterlineДокумент4 страницыWaterlineRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Key Messages CHB V1.1Документ3 страницыKey Messages CHB V1.1Josh AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Thermal ExpansionДокумент18 страницThermal ExpansionRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Visitor SurveyДокумент6 страницVisitor SurveyvarunbandiОценок пока нет
- Outline For ReportДокумент2 страницыOutline For ReportRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- s1481 ApayaoДокумент201 страницаs1481 ApayaoRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Curtain WallДокумент49 страницCurtain WallDaniel ReynoldsОценок пока нет
- Arki Design Survey ApayaoДокумент11 страницArki Design Survey ApayaoAngel Mendez RoaringОценок пока нет
- FASIA Entry Basketball 2014lastДокумент1 страницаFASIA Entry Basketball 2014lastRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Minimum Plumbing FacilitiesДокумент4 страницыMinimum Plumbing FacilitiesRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Ilocos Norte 24Документ5 страницIlocos Norte 24RamosPeter100% (1)
- Windtech BrochureДокумент16 страницWindtech BrochureCharly ValadezОценок пока нет
- Housing Unit Space PlanningДокумент5 страницHousing Unit Space PlanningRamosPeterОценок пока нет
- Price Monitoring in Public Markets in Metro Manila As of June 6, 2014Документ1 страницаPrice Monitoring in Public Markets in Metro Manila As of June 6, 2014RamosPeterОценок пока нет