Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
PandasPythonForDataScience PDF
Загружено:
sonskusaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PandasPythonForDataScience PDF
Загружено:
sonskusaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet
Pandas Basics
Learn Python for Data Science Interactively at www.DataCamp.com
Asking For Help
Selection
Also see NumPy Arrays
Getting
>>> s['b']
Get one element
>>> df[1:]
Get subset of a DataFrame
-5
Pandas
The Pandas library is built on NumPy and provides easy-to-use
data structures and data analysis tools for the Python
programming language.
Dropping
>>> help(pd.Series.loc)
1
2
Country
India
Brazil
Capital
New Delhi
Braslia
Population
1303171035
207847528
By Position
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> df.iloc([0],[0])
'Belgium'
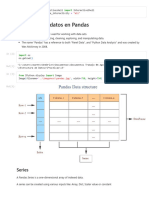
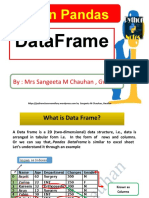
Pandas Data Structures
A
B -5
Index
>>> s = pd.Series([3, -5, 7, 4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
DataFrame
Columns
Index
Select single value by row &
column
'Belgium'
A one-dimensional labeled array
capable of holding any data type
Country
1
Belgium
India
Brazil
Capital
Brussels
Population
11190846
New Delhi 1303171035
Braslia
A two-dimensional labeled
data structure with columns
of potentially different types
207847528
>>> data = {'Country': ['Belgium', 'India', 'Brazil'],
'Capital': ['Brussels', 'New Delhi', 'Braslia'],
'Population': [11190846, 1303171035, 207847528]}
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(data,
columns=['Country', 'Capital', 'Population'])
'Belgium'
Select single value by row &
column labels
>>> df.at([0], ['Country'])
'Belgium'
By Label/Position
>>> df.ix[2]
Select single row of
subset of rows
>>> df.ix[:,'Capital']
Select a single column of
subset of columns
>>> df.ix[1,'Capital']
Select rows and columns
Country
Brazil
Capital
Braslia
Population 207847528
0
1
2
Brussels
New Delhi
Braslia
Boolean Indexing
Setting
Set index a of Series s to 6
Read and Write to Excel
>>> pd.read_excel('file.xlsx')
>>> pd.to_excel('dir/myDataFrame.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
Read multiple sheets from the same file
>>> xlsx = pd.ExcelFile('file.xls')
>>> df = pd.read_excel(xlsx, 'Sheet1')
df.shape
df.index
df.columns
df.info()
df.count()
(rows,columns)
Describe index
Describe DataFrame columns
Info on DataFrame
Number of non-NA values
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
df.sum()
df.cumsum()
df.min()/df.max()
df.idmin()/df.idmax()
df.describe()
df.mean()
df.median()
Sum of values
Cummulative sum of values
Minimum/maximum values
Minimum/Maximum index value
Summary statistics
Mean of values
Median of values
Applying Functions
>>> f = lambda x: x*2
>>> df.apply(f)
>>> df.applymap(f)
Apply function
Apply function element-wise
Internal Data Alignment
>>> s3 = pd.Series([7, -2, 3], index=['a', 'c', 'd'])
>>> s + s3
a
10.0
5.0
b
d
NaN
7.0
Arithmetic Operations with Fill Methods
I/O
>>> pd.read_csv('file.csv', header=None, nrows=5)
>>> pd.to_csv('myDataFrame.csv')
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
NA values are introduced in the indices that dont overlap:
>>> s[~(s > 1)]
Series s where value is not >1
>>> s[(s < -1) | (s > 2)]
s where value is <-1 or >2
>>> df[df['Population']>1200000000] Use filter to adjust DataFrame
Read and Write to CSV
Sort by row or column index
Sort a series by its values
Assign ranks to entries
Data Alignment
'New Delhi'
>>> s['a'] = 6
>>> df.sort_index(by='Country')
>>> s.order()
>>> df.rank()
Summary
By Label
>>> df.loc([0], ['Country'])
Sort & Rank
Basic Information
>>> df.iat([0],[0])
Series
Drop values from rows (axis=0)
>>> df.drop('Country', axis=1) Drop values from columns(axis=1)
Retrieving Series/DataFrame Information
Selecting, Boolean Indexing & Setting
Use the following import convention:
>>> s.drop(['a', 'c'])
Read and Write to SQL Query or Database Table
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>>
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///:memory:')
pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM my_table;", engine)
pd.read_sql_table('my_table', engine)
pd.read_sql_query("SELECT * FROM my_table;", engine)
read_sql()is a convenience wrapper around read_sql_table() and
read_sql_query()
>>> pd.to_sql('myDf', engine)
You can also do the internal data alignment yourself with
the help of the fill methods:
>>> s.add(s3, fill_value=0)
a
b
c
d
10.0
-5.0
5.0
7.0
>>> s.sub(s3, fill_value=2)
>>> s.div(s3, fill_value=4)
>>> s.mul(s3, fill_value=3)
DataCamp
Learn Python for Data Science Interactively
Вам также может понравиться
- Pandas Data Structures: SectionsДокумент13 страницPandas Data Structures: SectionsVinothkumar RadhakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Financial Analytics With PythonДокумент40 страницFinancial Analytics With PythonHarshit Singh100% (1)
- Assignment-1 (Python Pandas-Series Object and Data Frame: 1. Answer The FollowingДокумент8 страницAssignment-1 (Python Pandas-Series Object and Data Frame: 1. Answer The FollowingVaishnavi KesarwaniОценок пока нет
- Python Pandas MCQsДокумент7 страницPython Pandas MCQsYees BoojPaiОценок пока нет
- Data Wrangling With Python and PandasДокумент7 страницData Wrangling With Python and PandasCarlos Andrés PérezОценок пока нет
- Practical File PythonДокумент25 страницPractical File Pythonkaizenpro01Оценок пока нет
- 2 Python Data ProcessingДокумент66 страниц2 Python Data ProcessingShaifali Jain100% (2)
- IP Practices - IДокумент2 страницыIP Practices - Ivnitinkrishna18Оценок пока нет
- 12 IP Notes On SeriesДокумент5 страниц12 IP Notes On Serieslgarg2505Оценок пока нет
- Pip3 Install JupyterДокумент16 страницPip3 Install Jupyterblah blОценок пока нет
- Class Notes Class: XII Date: 17-04-2021 Subject: Informatics Practices Topic: Chapter-1Документ5 страницClass Notes Class: XII Date: 17-04-2021 Subject: Informatics Practices Topic: Chapter-1niranjana binuОценок пока нет
- Pandas DataframeДокумент48 страницPandas DataframeJames PrakashОценок пока нет
- Data Science - Unit IIДокумент173 страницыData Science - Unit IIDHEEVIKA SURESH100% (1)
- Practical Record 2 PYTHON AND SQL PROGRAMS - 2023Документ76 страницPractical Record 2 PYTHON AND SQL PROGRAMS - 2023isnprincipal2020Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet - PandasДокумент16 страницWorksheet - PandasDrishtiОценок пока нет
- IP TERM-1 Study Material (Session 2021-22)Документ84 страницыIP TERM-1 Study Material (Session 2021-22)AARTI BARWALОценок пока нет
- 12 SM IpДокумент180 страниц12 SM IpTechnical GamingОценок пока нет
- Ip Worksheet 3 - Q'SДокумент6 страницIp Worksheet 3 - Q'SShabin MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Intro To PandasДокумент7 страницIntro To PandasThe path to AllahОценок пока нет
- Lecture Material 3Документ7 страницLecture Material 32021me372Оценок пока нет
- Pragya FileДокумент31 страницаPragya FileArshpreet SinghОценок пока нет
- SBLC 1Документ23 страницыSBLC 1RajОценок пока нет
- Holidays Homework - 20231204 - 195647 - 0000Документ15 страницHolidays Homework - 20231204 - 195647 - 0000Arshpreet SinghОценок пока нет
- IP - Pandas 1 & 2 (Worksheet) Class 12Документ16 страницIP - Pandas 1 & 2 (Worksheet) Class 12WhiteОценок пока нет
- About R Language: InstallationДокумент7 страницAbout R Language: InstallationAditya DevОценок пока нет
- Saish IP ProjectДокумент16 страницSaish IP ProjectSaish ParkarОценок пока нет
- Practical File Part 1Документ17 страницPractical File Part 1Om Rane XII CОценок пока нет
- Programming With R: Lecture #4Документ34 страницыProgramming With R: Lecture #4Shubham PatidarОценок пока нет
- PandasДокумент16 страницPandasHoneyОценок пока нет
- Cleaning Data in Python: Pu!ing It All TogetherДокумент14 страницCleaning Data in Python: Pu!ing It All TogetherNourheneMbarekОценок пока нет
- 12 IpДокумент4 страницы12 IpMohit KarmakarОценок пока нет
- Pandas: ImportДокумент13 страницPandas: Importhello100% (1)
- Pandas DataFrame NotesДокумент6 страницPandas DataFrame NotesNhan Nguyen100% (1)
- XII - Informatics Practices (LAB MANUAL)Документ42 страницыXII - Informatics Practices (LAB MANUAL)ghun assudaniОценок пока нет
- Sesion 9Документ546 страницSesion 92marlenehh2003Оценок пока нет
- Journal 12Документ54 страницыJournal 12Be xОценок пока нет
- Final 1Документ38 страницFinal 1Mahil PawarОценок пока нет
- Class12 Pandas NotesДокумент23 страницыClass12 Pandas NotesMayank AhujaОценок пока нет
- Ip pb1 QP Ms Agra Set AДокумент17 страницIp pb1 QP Ms Agra Set AMayank MishraОценок пока нет
- This Study Resource WasДокумент5 страницThis Study Resource WasRayОценок пока нет
- Panel & MultiindexДокумент3 страницыPanel & Multiindexd38693402Оценок пока нет
- Numpy Basics Introduction ToДокумент35 страницNumpy Basics Introduction Topriyanka sharmaОценок пока нет
- Share IP XII Atom Bomb 2024 ExamДокумент35 страницShare IP XII Atom Bomb 2024 ExamMathematics PointОценок пока нет
- Using Python For Data Analysis - July 2018 - SlidesДокумент43 страницыUsing Python For Data Analysis - July 2018 - SlidesnicolepetrescuОценок пока нет
- Python Series DataFrames Commands Methods Properties Examples (2022-23) PDFДокумент16 страницPython Series DataFrames Commands Methods Properties Examples (2022-23) PDFSaniya Santhosh100% (1)
- Rec 11Документ49 страницRec 11Tamer SultanyОценок пока нет
- Time Series BasicsДокумент21 страницаTime Series BasicsChopra Shubham100% (1)
- Practical Record File XII Physics 22-23 FinalДокумент34 страницыPractical Record File XII Physics 22-23 FinalSUVODEEP SARKARОценок пока нет
- DataframepptuДокумент73 страницыDataframepptubrykymaОценок пока нет
- Pandas LibraryДокумент5 страницPandas LibrarynoneОценок пока нет
- Csc-322a (Week 11) Lab No 10Документ25 страницCsc-322a (Week 11) Lab No 10Osama AshrafОценок пока нет
- R Basics: Daniel StegmuellerДокумент14 страницR Basics: Daniel Stegmuellerblackdaisy13Оценок пока нет
- MohitДокумент19 страницMohitAyush GuptaОценок пока нет
- PandasДокумент16 страницPandaslalkrishna123Оценок пока нет
- Pandas: Computer Engineering Department Programming For Scientific Computing (Python) - CE0525Документ18 страницPandas: Computer Engineering Department Programming For Scientific Computing (Python) - CE0525KHUSH PATELОценок пока нет
- Block 1-Data Handling Using Pandas DataFrameДокумент17 страницBlock 1-Data Handling Using Pandas DataFrameBhaskar PVNОценок пока нет
- ArduinoprojectdraftДокумент6 страницArduinoprojectdraftapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Arduino-Adafruit GpsДокумент5 страницArduino-Adafruit Gpsapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- bmp180 Pressure Sensor Tutorial and ProjectДокумент29 страницbmp180 Pressure Sensor Tutorial and Projectapi-248437787100% (1)
- bmp180 Pressure Sensor TutorialДокумент14 страницbmp180 Pressure Sensor Tutorialapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Sharp FinalДокумент9 страницSharp Finalapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Isl 25129 RGB Sensor TutorialДокумент8 страницIsl 25129 RGB Sensor Tutorialapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Uv Final 2Документ10 страницUv Final 2api-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Sensor TestДокумент3 страницыSensor Testapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Uit Ultimate Gps Breakout v3 Tutorial For The Raspberry Pi 3Документ12 страницUit Ultimate Gps Breakout v3 Tutorial For The Raspberry Pi 3api-248437787Оценок пока нет
- 9 DofДокумент8 страниц9 Dofapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Hab 12-4 Pres - Mae V 1Документ11 страницHab 12-4 Pres - Mae V 1api-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Presentation Dec4Документ9 страницPresentation Dec4api-248437787Оценок пока нет
- Geiger Counter TutotialДокумент3 страницыGeiger Counter Tutotialapi-248437787Оценок пока нет
- hmc5883l Compass TutorialДокумент7 страницhmc5883l Compass Tutorialapi-248437787Оценок пока нет