Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lesson 4 Nonverbal Symbols Functions
Загружено:
Idate PatrickОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson 4 Nonverbal Symbols Functions
Загружено:
Idate PatrickАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson 4 Symbol Systems: Nonverbal
Symbols
Nonverbal Symbols
Neither spoken nor written
Do not include words
Include vocal elements and visual
elements
Functions of Nonverbal Symbols
Simply repeat the message of verbal
symbols
Complements the verbal symbol by
clarifying or explaining
Serve as a means of accent
Substitute for the message
Contradict with verbal symbols
Two Types of Nonverbal Symbols
1. VOCAL ELEMENTS
Articulation - formation of discrete speech
sounds
*To have the correct production of sounds, we
should start with the organs of speech.
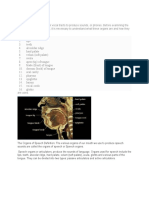
ORGANS OF SPEECH
Articulators - movable organs of the vocal tract
which is involved in articulation
Example: Tongue and lower lip
Points of Articulation - parts of the vocal tract
which cannot move but which are involved in
articulation
Example: Teeth
Other parts of the vocal tract include the
following:
Resonance Chamber - where the quality of the
vocal sound is modified
Pharynx
o Part of the vocal tract that connects
the larynx with the oral cavity
o Acts as resonance chamber for
vocal sound produced in larynx
Oral Cavity
Nasal Cavity
Voice - produced by vibrations of the vocal cords
Consonants - speech sound caused by
stoppage or hindrance of the voiced or voiceless
breath
Classifications of Consonants
1. Voicing
2. Point of Articulation
3. Manner of Articulation
Voicing - may be voiced or voiceless
Voiced the vocal folds are set in
vibration by the outgoing breath stream.
Voiceless the vocal folds do not vibrate,
and the resultant sound is composed
exclusively of the noise of friction.
Point of Articulation - tells where the sound
is produced
1. Bilabials produced with the lower lip or
against the upper lip (p, b)
2. Labio-dentals produced with the lower lip
near the upper teeth (f, v)
3. Interdentals produced with tongue tip
between the upper and lower teeth, but
not touching them
4. Alveolars produced with the tip of the
tongue near the alveolar ridge (t, d, n, s, z,
l)
5. Alveo-palatals produced with the front of
the tongue near the hard palate
6. Retroflex produced with the tip of the
tongue going upward and backward
towards the hard palate (r)
7. Prepalatal produced with the dorsum or
upper surface of the tongue near velum
(y)
8. Velars produced with the back of the
tongue against the velum (k, g)
9. Glottal produced with the narrowing of
the glottis so that the air passing through
causes friction but not sufficient vibration
to produce voice (h)
Manner of Articulation - tells how the sound
is produced
1. Stops produced by closing and opening
the mouth with an explosion (p, b, t, d, k,
g)
2. Nasals produced by the explosion of the
vocalized breath stream through the nose
(m,n)
3. Fricatives produced by forcing the air in
a continuous stream through a restricted
passage way (f, v, s, z, h)
4. Affricates produced when the
articulatory mechanism combines the
movements for the stop and fricative so
rapidly that two sounds are heard as a
single unit
5. Semi vowels produced by a smooth but
marked and rapid movement of the
articulators during the production of the
sound (w, y, r)
6. Lateral produced with the tip of the
tongue pressed lightly against the upper
teeth (l)
Voiceless Aspirated Stops / p, t, k /
A sound is aspirated when
accompanied by a strong puff of air
Vowels
- represent voice modified in various ways
by the shape of the oral cavity
shape is determined largely by the
position of the lips and that of the tongue
Classifications of Vowels
1. Section of the tongue
2. Height of the tongue
3. Shape of the lips
4. Articulatory muscle quality
Section of the tongue
a. Front Vowels- front of the tongue is
higher than the other parts of the tongue
b. Central Vowels- neither the front nor the
back of the tongue is raised
c. Back Vowels- back of the tongue is
higher than the other parts of the tongue
Height of the tongue
a. High Vowels- part of the tongue is raised
at a relatively high level
b. Lower-high Vowels- part of the tongue is
raised at a relatively lower-high level
c. Mid Vowels- part of the tongue is raised
at a relatively middle level
d. Low Vowels- part of the tongue is kept
low
Shape of the Lips
a. Rounded Vowels- both upper and lower
lops are so positioned that they may form
a circular or somewhat circular opening
b. Unrounded Vowels- both upper and
lower lips are not so positioned as to form
a circular opening
Articulatory muscle quality
a. Tense Vowels- muscles of the tongue and
neck are taut
b. Lax Vowels- muscles of the tongue and
neck are relaxed
ORAL INTERPRETATION
Paralanguage
Refers to those extra linguistic elements
such as voice quality, pitch, volume, rate
of speech that exist alongside the formal
language structure
Goes beyond words
Voice Quality - sound of the voice
Pitch - highness or lowness of a voice
Volume - loudness or softness of a voice
Rate - how fast or slowly a person talks
The Use of Focus in Oral Interpretation
(offstage focus)
1. Open Focus - directly to the audience
Example: Narration, asides
2. Closed Focus - directly to the defined
characters
Example: Dialogues, dramatic monologues
3. Inner-closed Focus - towards, but not
directly to the audience
Example: Soliloquies
4. Semi-closed Focus - ideally towards the
back-wall
Example: Address to muses, god,
inanimate object or absent person
2. VISUAL ELEMENTS
Kinesics
- Communicating through our looks and
gestures
- Coined by Ray L. Birdwhistell
o Facial Expression
o Hand Gesture
o Head Movement
o Posture
o Facial Expression and Gesture
Oculesics
- study of how eyes and eye movements
can communicate
Proxemics
- study of how people use space and
distance for purposes of communication
- coined by Edward T. Hall
Haptics
- expressing a tremendous range of feeling
through touching
Chronemics
- study of time in communication
Objectics
- display of ornaments, jewelry, glasses, and
other artifacts that have communicative
potential
Environmental Factors
how physical environments reveal the
characteristics of the owner of the place
and affect ones way of communication
Physical Appearance
- communicating through a persons
clothing
Вам также может понравиться
- Symbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Документ24 страницыSymbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Phonetic AДокумент28 страницPhonetic ANina BandalacОценок пока нет
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageДокумент7 страницSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaОценок пока нет
- Phonetics: Branch of Linguistic Which Studies The Characteristic of Speech SoundДокумент21 страницаPhonetics: Branch of Linguistic Which Studies The Characteristic of Speech SoundJian Patricia MontelavaОценок пока нет
- ÔN-TẬP-PHONETICSДокумент53 страницыÔN-TẬP-PHONETICSChau Nhat ThanhОценок пока нет
- Vowels AutosavedДокумент16 страницVowels AutosavedsangamitraachuОценок пока нет
- Phonology1 1Документ24 страницыPhonology1 1Mark Aldwin LopezОценок пока нет
- Speech and Theater ExamДокумент22 страницыSpeech and Theater ExamCres Jules ArdoОценок пока нет
- English: PhoneticsДокумент19 страницEnglish: PhoneticsdhruvОценок пока нет
- Phonology and Speech Sounds ExplainedДокумент24 страницыPhonology and Speech Sounds ExplainedAllene Salili HoncadaОценок пока нет
- Inglese modulo teoricoДокумент48 страницInglese modulo teoricoChiara D'AgostinoОценок пока нет
- Final Test PhonologyДокумент10 страницFinal Test Phonologynuha lathifahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsДокумент15 страницChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroОценок пока нет
- Session II Phonology Presentation-D SnowdenДокумент10 страницSession II Phonology Presentation-D Snowdenapi-218621193Оценок пока нет
- TP 1Документ4 страницыTP 1bereniceОценок пока нет
- Sound ClassificationДокумент13 страницSound Classificationjagodasielska99Оценок пока нет
- PhoneticsДокумент4 страницыPhoneticsnhutduynguyen31Оценок пока нет
- Meeting 2 PhonologyДокумент17 страницMeeting 2 Phonologydidik prihanantoОценок пока нет
- A Course in Phonetics by Peter Ladefoged PDFДокумент15 страницA Course in Phonetics by Peter Ladefoged PDFPralay SutradharОценок пока нет
- Introduction and Production of Speech SoundДокумент31 страницаIntroduction and Production of Speech SoundNguyệt MaiОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Phonetics and PhonologyДокумент10 страницIntroduction to Phonetics and PhonologyJo O ConnorОценок пока нет
- Lecture1 PDFДокумент2 страницыLecture1 PDFPhD LIVEОценок пока нет
- English Phonetic and Phonology RiassuntiДокумент29 страницEnglish Phonetic and Phonology RiassuntiArab NoreddineОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6. Phonetics: The Sounds of LanguageДокумент42 страницыLecture 6. Phonetics: The Sounds of Languageсымбат дуйсенОценок пока нет
- Speech OrgansДокумент5 страницSpeech OrgansprivateceeОценок пока нет
- Phonetics IДокумент40 страницPhonetics Iサイ-ドさんОценок пока нет
- Speech Organ, Vowel Diphtong, ConsonantsДокумент27 страницSpeech Organ, Vowel Diphtong, ConsonantsWan Mohd Izzat100% (1)
- Topic 2 PhoneticsДокумент25 страницTopic 2 PhoneticsRoger TerminatorОценок пока нет
- PhoneticsДокумент9 страницPhoneticsNguyễn Đình ĐạtОценок пока нет
- Phonetics & Spoken EnglishДокумент12 страницPhonetics & Spoken EnglishCharanjit SinghОценок пока нет
- English Phonetics:: The Sounds of English LanguageДокумент27 страницEnglish Phonetics:: The Sounds of English LanguageNguyễn Thanh Thảo NguyênОценок пока нет
- Human Speech OrgansДокумент5 страницHuman Speech OrgansLouise anasthasya altheaОценок пока нет
- Master of Arts in Education Major in English The Speech OrgansДокумент7 страницMaster of Arts in Education Major in English The Speech OrgansMicka Mercado Dimaano100% (2)
- SPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONДокумент9 страницSPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONEka MelyanaОценок пока нет
- NAAVДокумент20 страницNAAVd.duongnguyen1901Оценок пока нет
- Phonetics: The Sounds of Language Instructor: Faisal JahangeerДокумент24 страницыPhonetics: The Sounds of Language Instructor: Faisal JahangeerFaisal JahangeerОценок пока нет
- Organs of SpeechДокумент5 страницOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- Phonetics Chapter 1 Module 2Документ33 страницыPhonetics Chapter 1 Module 2Queenie CaraleОценок пока нет
- Speech Organs: Phonetic Organs & Their MechanismДокумент9 страницSpeech Organs: Phonetic Organs & Their MechanismMohan KalawateОценок пока нет
- Phonetics and PhonologyДокумент2 страницыPhonetics and PhonologyHồ Như QuỳnhОценок пока нет
- Speech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozДокумент55 страницSpeech Consideration IN COMPLETE Dentures: by Ekramul Haque Under The Guidance of DR Shaista AfrozPremshith CpОценок пока нет
- Phonetics branches and vowel articulationДокумент48 страницPhonetics branches and vowel articulationЕвгения ХвостенкоОценок пока нет
- Session 1Документ20 страницSession 1sergio lizzanoОценок пока нет
- The Speech OrgannnДокумент13 страницThe Speech OrgannnMicka Mercado DimaanoОценок пока нет
- Uas Alrino Ode MasimuДокумент10 страницUas Alrino Ode MasimuArif FlouncxОценок пока нет
- The Representation of Speech SoundsДокумент4 страницыThe Representation of Speech SoundsJuwita AnggreliaОценок пока нет
- Phonetics Phonology Full NotesДокумент24 страницыPhonetics Phonology Full NotesMuralitharan Nagalingam100% (3)
- Speech and Theater ArtsДокумент14 страницSpeech and Theater ArtsRussel Yamit100% (1)
- Organs of SpeechДокумент5 страницOrgans of SpeechMohd Shahrin BasniОценок пока нет
- Understanding The Concepts of Phonology PDFДокумент7 страницUnderstanding The Concepts of Phonology PDFAdrienne Dave MojicaОценок пока нет
- Phonetics and PhonologyДокумент34 страницыPhonetics and PhonologyArianna BОценок пока нет
- PhoneticsДокумент37 страницPhoneticsTejaswani RОценок пока нет
- Manner of Articulation: Speech OrganДокумент7 страницManner of Articulation: Speech OrganLipak gmailОценок пока нет
- thae mechanic of speechДокумент6 страницthae mechanic of speechCyril Kaye DolorzoОценок пока нет
- Phonetics Report 1-10-15Документ47 страницPhonetics Report 1-10-15Maria Victoria PadroОценок пока нет
- Language ReviewДокумент32 страницыLanguage ReviewMary Quincy MarilaoОценок пока нет
- Paper Group 5 - GA 1Документ3 страницыPaper Group 5 - GA 1idayanti830Оценок пока нет
- Segmental-based English Phonetics: Vowels and ConsonantsДокумент3 страницыSegmental-based English Phonetics: Vowels and ConsonantsSarah KhadijahОценок пока нет
- Articulatory PhoneticsДокумент3 страницыArticulatory PhoneticszelindaaОценок пока нет
- Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Calculus and Engineering FormulasДокумент5 страницAlgebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Calculus and Engineering FormulasIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Essentials of Modern Business Statistics (7e) : Anderson, Sweeney, Williams, Camm, CochranДокумент57 страницEssentials of Modern Business Statistics (7e) : Anderson, Sweeney, Williams, Camm, CochranIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Correl TechniquesДокумент5 страницCorrel TechniquesIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Quiz 4 - GicaleДокумент2 страницыQuiz 4 - GicaleIdate Patrick100% (2)
- Law1101 Chapter 2Документ5 страницLaw1101 Chapter 2Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Law1101 Chapter 2Документ14 страницLaw1101 Chapter 2Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Law1101 Chapter 2Документ14 страницLaw1101 Chapter 2Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- 6 01Документ25 страниц6 01Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- John Locke The Labor Theory of Value: Karen VaughnДокумент16 страницJohn Locke The Labor Theory of Value: Karen VaughnIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- CHAP1!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Документ8 страницCHAP1!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- RES100 4 ProblemДокумент1 страницаRES100 4 ProblemIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Courses To TakeДокумент2 страницыCourses To TakeIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- A B C D: Toilet ToiletДокумент1 страницаA B C D: Toilet ToiletIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Student Assistant ShipДокумент1 страницаStudent Assistant ShipIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- DebateДокумент15 страницDebateIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- GmosДокумент2 страницыGmosIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- From Sieve No. 4 Trial 1:: Sample ComputationДокумент3 страницыFrom Sieve No. 4 Trial 1:: Sample ComputationIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Cook ThesisДокумент100 страницCook ThesisTasmaqОценок пока нет
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: School of Civil, Environmental and Geological EngineeringДокумент1 страницаMapúa Institute of Technology: School of Civil, Environmental and Geological EngineeringIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- CE121F FieldWork1Документ6 страницCE121F FieldWork1Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- ENG 12 Listening Quiz - ENG12 - .Документ5 страницENG 12 Listening Quiz - ENG12 - .Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- 1 Fluid-Properties Tutorial-Solution PDFДокумент15 страниц1 Fluid-Properties Tutorial-Solution PDFIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Ms. Ma. Cecilia OrtizДокумент1 страницаMs. Ma. Cecilia OrtizIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Letter To My Fellow PauliniansДокумент1 страницаLetter To My Fellow PauliniansIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- CE140-1P Homework 1Документ11 страницCE140-1P Homework 1Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- CE140-1P - Lab Report Front PageДокумент1 страницаCE140-1P - Lab Report Front PageIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- CE120 0F FieldWork#1Документ5 страницCE120 0F FieldWork#1Idate PatrickОценок пока нет
- VolcanoДокумент1 страницаVolcanoIdate PatrickОценок пока нет
- Cels102-Chapter 1Документ10 страницCels102-Chapter 1Lemuel ClausОценок пока нет
- Effective Language in Public SpeakingДокумент3 страницыEffective Language in Public SpeakingOanny Oanaa100% (1)
- Forensic Language AnalysisДокумент6 страницForensic Language AnalysisSaraОценок пока нет
- EF3e Elem Filetest 12 AnswerkeyДокумент6 страницEF3e Elem Filetest 12 AnswerkeyYvette Hannali Aparicio SalazarОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Phonetic ScienceДокумент49 страницIntroduction To Phonetic ScienceMonMaОценок пока нет
- Assessing SpeakingДокумент4 страницыAssessing SpeakingLightman_2004Оценок пока нет
- Oral Comm. Module 4 Lesson 15Документ22 страницыOral Comm. Module 4 Lesson 15Nicole Bingayen100% (1)
- ENGLISH 1 Introduction To Linguistics Revised 23Документ41 страницаENGLISH 1 Introduction To Linguistics Revised 23Ricca Joy ArmillaОценок пока нет
- Types of Speech StylesДокумент40 страницTypes of Speech StylesChrisBaruelОценок пока нет
- 2 - Q2 SHS Oral Comm Module 2Документ21 страница2 - Q2 SHS Oral Comm Module 2Bryan BarreraОценок пока нет
- Medical Psychology Pidruch PDFДокумент144 страницыMedical Psychology Pidruch PDFRaavanОценок пока нет
- Oral Communication 2 Quarter Exam SCORE: 49/50Документ14 страницOral Communication 2 Quarter Exam SCORE: 49/50Selena MoradaОценок пока нет
- Maryland ESL Content StandardsДокумент88 страницMaryland ESL Content StandardsmadmaxpsuОценок пока нет
- Developing Speaking SkillsДокумент4 страницыDeveloping Speaking SkillsKyla Mariz Layones RecioОценок пока нет
- Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Technical University BFAD CurriculumДокумент200 страницDr. APJ Abdul Kalam Technical University BFAD CurriculumUPIDR FacultyОценок пока нет
- CALALPДокумент28 страницCALALPangela's world of funОценок пока нет
- Все семинары по стилистикеДокумент52 страницыВсе семинары по стилистикеviktoria ozОценок пока нет
- O'Grady 1 IntroducciónДокумент12 страницO'Grady 1 IntroducciónAlfonso telloОценок пока нет
- John Flowerdew ch1 ResumenДокумент5 страницJohn Flowerdew ch1 ResumenHoracio Sebastian LeguizaОценок пока нет
- JIC - Dubbing or Subtitling InterculturalismДокумент8 страницJIC - Dubbing or Subtitling InterculturalismDavidForloyoОценок пока нет
- English Solved QP 2022 BNUДокумент32 страницыEnglish Solved QP 2022 BNUDEVARAJA GUTTEDARОценок пока нет
- Miy 011Документ8 страницMiy 011GabbiОценок пока нет
- Test 01 Test 02: G.C.E. (O/L) Support Seminar - 2016 English Language Answer Guide - Paper IДокумент7 страницTest 01 Test 02: G.C.E. (O/L) Support Seminar - 2016 English Language Answer Guide - Paper IJaroos MohamedОценок пока нет
- Stages of language acquisitionДокумент4 страницыStages of language acquisitionJess ArceoОценок пока нет
- Types of Speeches and Rules for Effective Public SpeakingДокумент2 страницыTypes of Speeches and Rules for Effective Public SpeakingNikkieIrisAlbañoNovesОценок пока нет
- Module 5 Activities AkolДокумент7 страницModule 5 Activities AkolMa. Lorena AkolОценок пока нет
- Teach Speaking Skills with Accuracy & FluencyДокумент3 страницыTeach Speaking Skills with Accuracy & FluencyNana Liyana100% (3)
- Public Speaking-Debate and Argumentation SyllabusДокумент7 страницPublic Speaking-Debate and Argumentation Syllabusapi-324165021Оценок пока нет
- Edited G9 Slem Q1 W7Документ10 страницEdited G9 Slem Q1 W7Aventurado, Elijah Samuel V.Оценок пока нет
- Connected Speech FeaturesДокумент45 страницConnected Speech FeaturesTayyab Ijaz100% (2)