Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Gravitation Assignment For Lit Jee
Загружено:
Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Gravitation Assignment For Lit Jee
Загружено:
Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics Assignment Sheet
Topic (Gravitation)
1.
In figure a spherical body of mass M is a
distance a from one end of a uniform
rod of length L and mass m. What is the
force between them.
2.
Consider a homogenous ring of mass M and radius R. What gravitational attraction does it
exert on a particle of mass m located a distance x from the centre of the ring along its axis ?
R
3.
dx
A thin rod of mass M is bent in a arc of circle of radius R, which sustained an angle 2 at
the centre. What is its gravitational force on a particle of mass m at the centre of curvature.
M
4.
A spherical hollow is made in a lead sphere of radius R. Such that its surface touches the
outside surface of the lead sphere and passes through its centre. The mass of the sphere
before hollowing was M. With what gravitational force will the hollowed-out lead sphere
attract a small sphere of mass m, which lies at a distance d from the centre of the lead
sphere on the straight line connecting the centres of the sphere and of the hollow ?
5.
Find the potential energy of the system shown in figure.
m
Ring
6.
Two bodies of masses m1 and m2 are placed at a distance r apart. Show that the position
where the gravitational field due to them is zero, the potential is given by
V
7.
G
m1 m 2 2 m1m 2 .
r
A non-homogenous sphere of radius R has the following density variation
0
R
3R
3R
for r
rR
; 0 for
2
3
4
8
4
R R 5R
and 2R ?
What is the gravitational field due to the sphere at r , ,
4 2 6
0 for r R / 3 ;
Narayana IIT Academy : 15, Central Market, West Punjabi Bagh, N. Delhi-26 Ph.: 45062651 / 52 / 53
8.
Two uniform solid sphere of equal radii R,
R
R
but mass M and 4 M have a centre to centre
N
separation 6R, as shown in figure. The two
4M
M
spheres are held fixed. A projectile of mass
x
m is projected from the surface of the sphere
of mass M directly towards the centre of the
6R
second sphere. Obtain an expression for the minimum speed v of the projectile so that it
reaches the surface of the second sphere.
9.
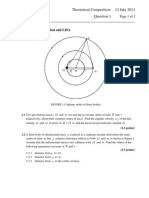
To what latitude does the syncoms coverage extend ?
10.
The largest and the shortest distance of the earth from the sun are r 1 and r2 respectively.
Calculate the distance from the sun when it is at perpendicular distance to the major axis of
the orbit drawn from sun.
11.
Two satellites S1 and S2 revolve round a planet in coplanar circular orbits in the same sense.
Their periods of revolution are 1h and 8h respectively. The radius of the orbit of S 1 is 104km.
When S2 is closest to S1 find (a) the speed of S 2 relative to S1 and (b) the angular speed of
S2 as observed by an astronaut in S1.
12.
Two masses m1 and m2 at an infinite distance from each other are initially at rest, start
interacting gravitationally. Find their velocity of approach when they are at a distance r apart.
13.
A planet moves around the sun along an ellipse so that its minimum distance from the sun is
equal to r and the maximum distance to R. Making use to Keplers laws, find its period of
revolution around the sun.
14.
An artificial satellite of the moon revolves in a circular orbit whose radius exceeds the radius
of the moon times. The process of motion the satellite experiences a slight resistance due
to cosmic dust. Assuming the resistance force to depend on the velocity of the satellite as
F v 2 , where is a constant, find how long the satellite will stay in orbit until it falls onto
the moons surface.
15.
The gravitational field in a region is given by Eg (5i 10j)N / kg . Calculate the work done
by an external agent in carrying a mass of 0.4 kg from point (0,0) to point (3,4) metre.
16.
A planet of mass m moves along an ellipse around the sun of mass M S, so that its maximum
and minimum distances from sun are r1 and r2 respectively. Find the angular momentum L of
this planet relative to the centre of sun.
17.
Three particles each of mass m, are situated at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side
length a. The only forces acting on the particles are their mutual gravitational forces. It is
desired that each particle moves in a circle while maintaining the original separation a. Find
the initial velocity that should be given to each particle and also the time period of the
circular motion.
18.
The mass of railway train is 100 metric tons. What will be its weight when it is (i) moving due
east (ii) moving due west along the equator at 72 km/h ? Radius of earth is 6400 km.
19.
A chord of length 64 m is used to connect a 100 kg astronaut spaceship whose mass is
much larger than that of the astronaut. Estimate the value of tension in the chord assuming
that the spaceship is orbiting near earths surface. Also assume that the spaceship and the
astronaut fall in a straight line from the earth centre. The radius of earth R = 6400 km.
Narayana IIT Academy : 15, Central Market, West Punjabi Bagh, N. Delhi-26 Ph.: 45062651 / 52 / 53
Narayana IIT Academy : 15, Central Market, West Punjabi Bagh, N. Delhi-26 Ph.: 45062651 / 52 / 53
Вам также может понравиться
- Gravitation-06-Subjective UnSolvedДокумент3 страницыGravitation-06-Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- GravitationДокумент7 страницGravitationRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- GravitationalДокумент8 страницGravitationalRathankar RaoОценок пока нет
- Sankalp - Phase Iv - Gra - 5Документ7 страницSankalp - Phase Iv - Gra - 5Harshit SinghОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Physics Gravitation Advanced AssignmentДокумент10 страницPhysics Gravitation Advanced AssignmentdxddxishxerxОценок пока нет
- Celestial Mechanics 2Документ3 страницыCelestial Mechanics 2Ranul JayawardenaОценок пока нет
- IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021: BY Referral CodeДокумент31 страницаIIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021: BY Referral CodeBishwadeep RoyОценок пока нет
- 11 AngularMomentumДокумент31 страница11 AngularMomentumaliswheeler12Оценок пока нет
- Universal GravitationДокумент46 страницUniversal GravitationNurulWardhani11Оценок пока нет
- LectureДокумент23 страницыLectureKenn SenadosОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 GravitationalДокумент3 страницыExercise 1 GravitationalfairusyfitriaОценок пока нет
- Gravitation (Irodove)Документ25 страницGravitation (Irodove)akhileshvv123Оценок пока нет
- Homework1 FIELDS 2013 2Документ2 страницыHomework1 FIELDS 2013 2GallinastutaОценок пока нет
- Gravitation: SynopsisДокумент7 страницGravitation: SynopsisWillSmithОценок пока нет
- Bansal Classes Gravitation Study MaterialДокумент16 страницBansal Classes Gravitation Study MaterialSahooashu60% (5)
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation (Physics)Документ43 страницыNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation (Physics)Maryanne100% (1)
- Gravitaion and Central ForceДокумент4 страницыGravitaion and Central ForceKrisnendu BiswasОценок пока нет
- IPhO2011 TH Q1Документ3 страницыIPhO2011 TH Q1Himansu MookherjeeОценок пока нет
- Gravitational V9SYFn3OFimPn3kmb2XYДокумент11 страницGravitational V9SYFn3OFimPn3kmb2XYAbhishek YadavОценок пока нет
- Wa0010.Документ3 страницыWa0010.BxkxnzixbОценок пока нет
- 09gravitation 144-162Документ11 страниц09gravitation 144-162KAMAL KANT KUSHWAHAОценок пока нет
- Physics Circle Gravitational LawsДокумент7 страницPhysics Circle Gravitational Lawsangaraagborkakoti99Оценок пока нет
- Universal Gravitation Multiple Choice-2012!06!13Документ8 страницUniversal Gravitation Multiple Choice-2012!06!13Michael CaiОценок пока нет
- Graviational Field and OrbitsДокумент51 страницаGraviational Field and OrbitsAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Usaaao Second Exam 2022 ProblemsДокумент6 страницUsaaao Second Exam 2022 ProblemsgirishmaharanaОценок пока нет
- Gravitation - Worksheet1706502953137Документ1 страницаGravitation - Worksheet1706502953137uvwx611Оценок пока нет
- Gravitation Class XIДокумент23 страницыGravitation Class XIKAMAL KANT KUSHWAHAОценок пока нет
- Winter AssignmentДокумент1 страницаWinter AssignmentTanishaОценок пока нет
- Assignment-Class: Xi Physics, Unit-6: (Gravitation)Документ1 страницаAssignment-Class: Xi Physics, Unit-6: (Gravitation)Neetu JainОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Artificial Satellites: Sunil Kumar SinghДокумент8 страницArtificial Satellites: Sunil Kumar SinghSarah AliОценок пока нет
- Unit 6Документ12 страницUnit 6sabirdxb107Оценок пока нет
- Gravitation HW KeyДокумент4 страницыGravitation HW KeyKatherine ZwienerОценок пока нет
- Circular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsДокумент1 страницаCircular Orbits Central Forces Mechanics ProblemsPerry EsguerraОценок пока нет
- Topic 6 Test 2022Документ15 страницTopic 6 Test 2022Ahmad OmarОценок пока нет
- Study Package: Subject: PHYSICS TopicДокумент7 страницStudy Package: Subject: PHYSICS Topicvishal110085Оценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Short theoretical questions on astronomy topicsДокумент3 страницыShort theoretical questions on astronomy topicscrimsonsnowОценок пока нет
- Class Xi Isc Gravitation AssignmentsДокумент2 страницыClass Xi Isc Gravitation Assignmentsanimalphysio1511Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 1-A2 Physics - AДокумент14 страницLesson 1-A2 Physics - ACheng WLОценок пока нет
- APhO Theoretical Problems (2000-2013)Документ107 страницAPhO Theoretical Problems (2000-2013)Science Olympiad Blog100% (7)
- HOTS GravitationДокумент3 страницыHOTS Gravitationmann123Оценок пока нет
- Gravitation AssignmentДокумент3 страницыGravitation AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- PHYS122 University of WaterlooДокумент174 страницыPHYS122 University of WaterlooEddy LiuОценок пока нет
- Ch11 SSMДокумент24 страницыCh11 SSMJuanca AbadОценок пока нет
- Nasa PI Day ProblemsДокумент21 страницаNasa PI Day ProblemsLKKОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4 - Mechanics 4 SolutionДокумент16 страницAssignment 4 - Mechanics 4 SolutionVincent haОценок пока нет
- Advanced HandoutДокумент8 страницAdvanced Handoutparthkalra1981Оценок пока нет
- SATELLITE COMMUNICATION GUIDEДокумент157 страницSATELLITE COMMUNICATION GUIDEShayaan PappathiОценок пока нет
- Gravitation Type 2 PART 1 of 3 ENGДокумент19 страницGravitation Type 2 PART 1 of 3 ENGRavi YadavОценок пока нет
- Acceleration Due To GravityДокумент3 страницыAcceleration Due To GravitySauri ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- New Hypothesis Models and Explanations of Physics Which May Unify Everything From Atom To Universe Amended 15Документ12 страницNew Hypothesis Models and Explanations of Physics Which May Unify Everything From Atom To Universe Amended 15Lucas XavierОценок пока нет
- Astronomy Olympiad Sample QuestionsДокумент3 страницыAstronomy Olympiad Sample QuestionsArnab ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Practice Astro 204 exam questionsДокумент2 страницыPractice Astro 204 exam questionsA.MОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- The Electrogravitic Theory of Celestial Motion and CosmologyОт EverandThe Electrogravitic Theory of Celestial Motion and CosmologyОценок пока нет
- SINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONДокумент5 страницSINGLE OPTION CORRECT ACCELERATIONShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones AdvancedДокумент8 страницAldehydes and Ketones AdvancedShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones KeyДокумент9 страницAldehydes and Ketones KeyShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones Key PointsДокумент3 страницыAldehydes and Ketones Key PointsShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones MainsДокумент8 страницAldehydes and Ketones MainsShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes and Ketones Key PointsДокумент3 страницыAldehydes and Ketones Key PointsShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Aldehydes & Ketones Advanced SolДокумент3 страницыAldehydes & Ketones Advanced SolShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Vector & KinematicsДокумент4 страницыVector & KinematicsShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Test On ErrorsДокумент5 страницTest On ErrorsShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Kinematics 2Документ8 страницKinematics 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Vector & Kinematics KeyДокумент3 страницыVector & Kinematics KeyShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- GT Questions 2Документ2 страницыGT Questions 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Kinematics 2Документ8 страницKinematics 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Kinematics 2Документ5 страницKinematics 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Kinematics 1 KeyДокумент5 страницKinematics 1 KeyShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Waves - 3Документ2 страницыWaves - 3Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Kinematics 1Документ6 страницKinematics 1Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Rotatory Motion - 3Документ4 страницыRotatory Motion - 3Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetism Mains Level Assignment For Iit JeeДокумент12 страницElectromagnetism Mains Level Assignment For Iit JeeShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Rotatory Motion 2Документ2 страницыRotatory Motion 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Rotatory Motion Concepts Explained in 30 QuestionsДокумент4 страницыRotatory Motion Concepts Explained in 30 QuestionsShiva Ram Prasad Pulagam100% (1)
- EmiДокумент27 страницEmiShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Review Sheet MagnetismДокумент3 страницыReview Sheet MagnetismShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- 24 - Assignment Sheet Gravitation - (AM+VBS) - Date - 5.12.2008Документ3 страницы24 - Assignment Sheet Gravitation - (AM+VBS) - Date - 5.12.2008Shiva Ram Prasad Pulagam100% (1)
- Waves 2Документ3 страницыWaves 2Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Waves 1Документ5 страницWaves 1Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Gravitation AssignmentДокумент3 страницыGravitation AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- 24 - Assignment Sheet Gravitation - (AM+VBS) - Date - 5.12.2008Документ3 страницы24 - Assignment Sheet Gravitation - (AM+VBS) - Date - 5.12.2008Shiva Ram Prasad Pulagam100% (1)
- Optics AssignmentДокумент9 страницOptics AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- CurrentДокумент2 страницыCurrentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamОценок пока нет
- Active and Passive Components: Kunal WakodeДокумент3 страницыActive and Passive Components: Kunal WakodeKunal WakodeОценок пока нет
- Rocket PropulsionДокумент41 страницаRocket PropulsionV DhinakaranОценок пока нет
- Bernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragДокумент4 страницыBernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragABHIJEETОценок пока нет
- DPP1Документ2 страницыDPP1Samarth SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Unidad III Termo IДокумент31 страницаUnidad III Termo IMusfirah AdeelОценок пока нет
- Radiation 1Документ37 страницRadiation 1guna sekaranОценок пока нет
- 2015 JC1 BT H2 PHY P1 Question SolutionДокумент11 страниц2015 JC1 BT H2 PHY P1 Question Solutionshakthee sivakumarОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент3 страницыPhysics ProjectChitwanRazdan100% (1)
- Understanding Basic Electronics and Resistor FundamentalsДокумент76 страницUnderstanding Basic Electronics and Resistor FundamentalsRaine LopezОценок пока нет
- HW 0225Документ8 страницHW 0225Sures RezОценок пока нет
- Electrical Panel Load Calculation 22 8 12Документ33 страницыElectrical Panel Load Calculation 22 8 12vicent johnОценок пока нет
- Test 06 Momentum 05dkДокумент4 страницыTest 06 Momentum 05dkraniel mandaingОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetismДокумент24 страницыNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetismDileep GОценок пока нет
- Upheaval Buckling Calculation 24Документ10 страницUpheaval Buckling Calculation 24Moustafa Fares100% (1)
- Mechanics Practice TestДокумент4 страницыMechanics Practice TestDemir GazetićОценок пока нет
- 0625 w11 QP 31Документ16 страниц0625 w11 QP 31shela26Оценок пока нет
- EE ReviewerДокумент13 страницEE ReviewerZZROTОценок пока нет
- High Temperature Gas Dynamics - Synopsis - Himanshu BanaitДокумент53 страницыHigh Temperature Gas Dynamics - Synopsis - Himanshu BanaitHimanshu BanaitОценок пока нет
- Boiler RatingsДокумент3 страницыBoiler RatingsAbbas AmirifardОценок пока нет
- How To Calculate The Size of Capacitor Bank - One by Zero ElectronicsДокумент14 страницHow To Calculate The Size of Capacitor Bank - One by Zero ElectronicsedyОценок пока нет
- A Micro-Method of Determining The Boiling Point ofДокумент8 страницA Micro-Method of Determining The Boiling Point ofDekace pohuwato100% (1)
- Circuit Breaker Tripping Due to FaultsДокумент124 страницыCircuit Breaker Tripping Due to FaultsRAJESHОценок пока нет
- Ohms Law Series Parallel Resistors PDFДокумент18 страницOhms Law Series Parallel Resistors PDFcrana10Оценок пока нет
- General Physics 2 Q3 M4Документ22 страницыGeneral Physics 2 Q3 M4Nyanko SorianoОценок пока нет
- Variacion de Temperatura en El Enfriamiento de Un MetalДокумент84 страницыVariacion de Temperatura en El Enfriamiento de Un MetalAndrés CaicedoОценок пока нет
- FN MKGGMS: Experiment 2.acceleration of GravityДокумент8 страницFN MKGGMS: Experiment 2.acceleration of GravityJessica RossОценок пока нет
- Physics Alternating Current and EMIДокумент14 страницPhysics Alternating Current and EMIPriyabrata PattanaikОценок пока нет
- Potier Reactance ExperimentДокумент5 страницPotier Reactance Experimentbt21eee122Оценок пока нет
- Experiment 4Документ5 страницExperiment 4dummy008Оценок пока нет