Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
As Physics Unit 2 Summary Edexcel
Загружено:
Mohamed Al SharkawyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
As Physics Unit 2 Summary Edexcel
Загружено:
Mohamed Al SharkawyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Potential
difference
- amount
of energy
transferred per
unit of charge
Potential
difference
- Volts (V)
Current - the
rate of flow
of charge
Charge (Q) Coulombs (C)
Current (I) Amperes (A)
Resistivity the amount
of resistance
given from a
unit volume of
a substance
Charge property of
matter upon
which electric
force acts
Resistance
(R) - Ohms ?
Symbols
and Units
Resistance
- opposition
to the flow
of charge
Definitions
Types
Waves
Standing
(two waves
with equal
frequency and
wavelength
moving in
opposing
directions
across the
same medium
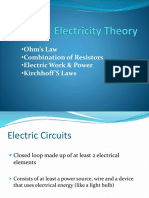
Electricity
Unit 2
Laws
Kirchoff's
Junction
Law - at a
junction, the
sum of the two
split currents
will total the
sum of the
input current
Equations
Voltage =
Work/Charge
Power =
Voltage
x Current
Ohms Law Given that the
temperature
and other
physical
properties
remain
constant,
the current
through a wire
is proportional
to the potential
difference
across its ends
Kirchoff's Loop
Law - the sum
of the potential
difference
across every
component
of a circuit
totals to the
sum of the
input voltage
of the cell
Вам также может понравиться
- EdexcelASPhysics RevisionGuide9781846905957 Pg26to41Документ16 страницEdexcelASPhysics RevisionGuide9781846905957 Pg26to41Ai Ling Lee100% (1)
- Physics Unit 3B PDFДокумент7 страницPhysics Unit 3B PDFZubanaОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 4Документ13 страницPhysics Unit 4ua785100% (1)
- h2 Physics DefinitionsДокумент7 страницh2 Physics DefinitionsSyed Osama HussainОценок пока нет
- IAL A2 Physics Note (Specification)Документ71 страницаIAL A2 Physics Note (Specification)SajitRahman100% (2)
- Unit 1 Physics On The Go NotesДокумент6 страницUnit 1 Physics On The Go NotesLoure Shakke80% (5)
- Unit 2 Revision ChecklistДокумент5 страницUnit 2 Revision ChecklistShafkat Sakeebur Rahman100% (2)
- Unit 1 Revision ChecklistДокумент4 страницыUnit 1 Revision ChecklistShafkat Sakeebur Rahman100% (3)
- Edexcel A2 Physics Notes Unit 5, Topic: Thermal Energy.Документ2 страницыEdexcel A2 Physics Notes Unit 5, Topic: Thermal Energy.Siddiqui80% (5)
- Physics Unit 1 MechanicsДокумент49 страницPhysics Unit 1 Mechanicsamir hamza100% (1)
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankОт EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankОценок пока нет
- IAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student SheetДокумент3 страницыIAS Physics SB1 Practs CP1 Student Sheethussain azizОценок пока нет
- Paper 7 Notes - FinalДокумент7 страницPaper 7 Notes - FinalUlee Abdul RaufОценок пока нет
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelДокумент6 страницSummary Notes - Topic 5 Edexcel (A) Biology A-LevelAhmad MohdОценок пока нет
- IAL/GCE Physics Unit 1 Revision CardДокумент7 страницIAL/GCE Physics Unit 1 Revision CardApollo Wong100% (1)
- As Physics NotesДокумент43 страницыAs Physics Notesleelakdd108100% (1)
- Physics Lab Notes Unit3Документ27 страницPhysics Lab Notes Unit3Natosha Mendoza94% (18)
- AS Units Revision Notes IAL EdexcelДокумент10 страницAS Units Revision Notes IAL EdexcelMahbub KhanОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyДокумент12 страницUnit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyShivani MajithiaОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Physics Nuclear Decay QuestionsДокумент58 страницUnit 5 Physics Nuclear Decay Questionsareyouthere92100% (1)
- IGCSE Equation List PhysicsДокумент5 страницIGCSE Equation List PhysicsJoseLinОценок пока нет
- A2 Physics (Notes)Документ41 страницаA2 Physics (Notes)SamhaMohamed100% (1)
- Student Unit Guide - Unit 4 Physics On The MoveДокумент48 страницStudent Unit Guide - Unit 4 Physics On The MoveYoke Hock Seow100% (10)
- Physical World-Units-Measurements (Physics) Bit BankОт EverandPhysical World-Units-Measurements (Physics) Bit BankРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- A-Level Physics Question and Answers 20 20/2021Документ148 страницA-Level Physics Question and Answers 20 20/2021FireFrostОценок пока нет
- Advanced Level Physics Past Papers Index StudentsДокумент9 страницAdvanced Level Physics Past Papers Index Studentstaryll_01Оценок пока нет
- A2 Physics PracticalДокумент56 страницA2 Physics PracticalFathmath AthfaОценок пока нет
- Physics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Документ4 страницыPhysics Formula List - As at 6 Jul 2011 (Normal)Lim Kew Chong100% (1)
- 4.1 - Further MechanicsДокумент28 страниц4.1 - Further MechanicsEmperor Saladin100% (1)
- Practical 6 Centripetal Force - Whirling BungДокумент1 страницаPractical 6 Centripetal Force - Whirling BungShafkat Sakeebur Rahman100% (3)
- 3 Wave Optics 1Документ16 страниц3 Wave Optics 1sudha24_7Оценок пока нет
- Laws of Motion QuestionsДокумент4 страницыLaws of Motion QuestionsRajesh DeyОценок пока нет
- Forces and Turning EffectsДокумент25 страницForces and Turning EffectsyinkaibironkeОценок пока нет
- Physics As - Unit 2 - Revision NotesДокумент0 страницPhysics As - Unit 2 - Revision NotesRimaz RameezОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Unit 3B NotesДокумент13 страницChemistry Unit 3B NotesShuchi HossainОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент12 страницPhysicscbsegirlsaipmtОценок пока нет
- As and A Level Physics Core Practical 6 SpeeДокумент5 страницAs and A Level Physics Core Practical 6 SpeeHady JawadОценок пока нет
- A-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersДокумент46 страницA-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersAston Hamilton100% (3)
- 3B Revision PDFДокумент21 страница3B Revision PDFpraphul4uОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 6 Source BookДокумент50 страницPhysics Unit 6 Source BookÅzmâñ Khäñ100% (1)
- Mathematics M1 EDEXCELДокумент10 страницMathematics M1 EDEXCELballpoint96Оценок пока нет
- As Physics Practical NotesДокумент6 страницAs Physics Practical NotesUltramix100% (1)
- Chapter 14 OscillationsДокумент54 страницыChapter 14 OscillationsPathmanathan Nadeson100% (1)
- Worksheet 01 MechanicsДокумент10 страницWorksheet 01 MechanicsImran Mirza0% (1)
- Edexcel Biology Unit 3 (Alternative) June 2010 Examiner ReportДокумент22 страницыEdexcel Biology Unit 3 (Alternative) June 2010 Examiner Reportgoharayub3909100% (1)
- Definition of Terms SummaryДокумент3 страницыDefinition of Terms SummaryWenith YapanaОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент4 страницыUntitledJoyce LonzagaОценок пока нет
- ELECTRICITYДокумент33 страницыELECTRICITYSumiОценок пока нет
- Electricity PPT Presentation ModifiedДокумент22 страницыElectricity PPT Presentation ModifiedMark SyОценок пока нет
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionДокумент31 страница5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinОценок пока нет
- ' ElectricityДокумент98 страниц' Electricitya9758127118Оценок пока нет
- Physics Topic 5 Study GuideДокумент8 страницPhysics Topic 5 Study GuideSai 0235Оценок пока нет
- Electricity Review - PhysicsДокумент1 страницаElectricity Review - Physicsellie95Оценок пока нет
- Back To TopДокумент6 страницBack To TopBhanu K PrakashОценок пока нет
- Electricity PP TДокумент18 страницElectricity PP Tahmer100% (3)
- Cse-Lec 01Документ47 страницCse-Lec 01Zain Ul AabidinОценок пока нет
- Electricity: Unit: The Unit of Current Is AmpereДокумент3 страницыElectricity: Unit: The Unit of Current Is Amperejspragati273Оценок пока нет
- As Physics Electricity Chapter 9Документ17 страницAs Physics Electricity Chapter 9LawrenceOnthugaОценок пока нет
- Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orДокумент23 страницыScience Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orAayushiОценок пока нет
- IAL Physics Unit 3 NoteДокумент22 страницыIAL Physics Unit 3 NoteMohamed Al Sharkawy100% (2)
- Physics of Bungee JumpingДокумент1 страницаPhysics of Bungee JumpingMohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Upthrust and DensityДокумент1 страницаUpthrust and DensityMohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- Forces: Newton's Second Law Newton's Third LawДокумент1 страницаForces: Newton's Second Law Newton's Third LawMohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- IAL AS Physics SN 6Документ67 страницIAL AS Physics SN 6Mohamed Al Sharkawy86% (7)
- Core Practical Garlic and MintДокумент4 страницыCore Practical Garlic and MintMohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 0620 s12 Ms 61Документ3 страницы0620 s12 Ms 61Mohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 0620 s11 Ms 61Документ4 страницы0620 s11 Ms 61Mohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 0620 s11 Ms 62Документ3 страницы0620 s11 Ms 62Mohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 0450 s15 in 21Документ4 страницы0450 s15 in 21Mohamed Al SharkawyОценок пока нет
- 2015 Paper 1 Specimen PaperДокумент10 страниц2015 Paper 1 Specimen PaperTan Lee Herng AidanОценок пока нет