Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Access Management
Загружено:
zulkis73Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Access Management
Загружено:
zulkis73Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
11/11/2016
WhatisAccessManagement?
AccessManagement(AM)
TrafficEngineering(SBEP1512)
ManagingAccess
ManagingandPlanningtheSpacing andDesign of:
Driveways
MedianOpenings
TrafficSignals
Interchanges/Intersections
Roundabouts
3
Whathappensifyoudont
manageaccess?
DefinitionofAM
FORMAL: Accessmanagementisthesystematic
controlofthelocation,spacing,design,and
operationofdriveways,medianopenings,
interchanges,andstreetconnectionstoa
roadway.(TRBManual)
Moreover: AMalsoinvolvesroadwaydesign
applications,suchasmediantreatmentsand
auxiliarylanes,andtheappropriatespacingof
trafficsignals.
IntroductiontoAccess
ManagementPrinciples
CumulativeImpactsofroadsidedevelopment
overtime
Slowedthroughtraffic,Excessivecongestion,Morecrashes,
Toomanydrivewaysandintersection,Moretraveltime,
Toomanyconflictpoints
11/11/2016
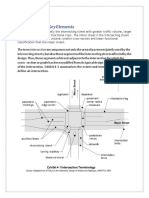
ConflictPoint
TrafficConflicts
Drivers make more mistakes when driving
in complex situations due to the numerous
conflict points.
Conflict Point
Location: Near Mahkota Parade, Bandar Hilir, Melaka, 2004
AccidentsatIntersection
Conflicts,contd
Traffic Conflict
Thinkofasingletrafficconflictasonerockinapond.
Theripplesareeasytoseeandarepredictable.
However,whendozensofrocksarethrowninatonce,
theripplesaredynamic,theycreatechaos,anditis
difficulttoavoidoneatthecostofanother.
Source: Flickr
IntroductiontoAccess
ManagementPrinciples
10
GoalofAM
TypesofConflictPoints
Eachaccesspointcreatespotentialconflicts
betweenthroughtrafficandturningtraffic.
Limit thenumberandimpact ofdriverdecision
andconflictpoints fromimpactingonthrough
traffic
traffic.
Diverge
Merge
Stop/Queue
Cross
Akeygoalofaccessmanagementistomaintain
thefunctionalintegrity oftheroadwaysystem
Weave
11
IntroductiontoAccess
ManagementPrinciples
12
11/11/2016
ConsequencesofPoorAM
Moreaccess=lessmobility
Lessaccess=moremobility
Mobility
Access
Increaseincrashes andcrashrates
Poorcapacitythroughput
Increasecommutingtime,fuelconsumptionand
vehicleemissionsastrafficsignalsintensify
congestionsanddelay
g
y
Reducedroadwayefficiency
Decreasedpropertyvalues
Morecutthroughtrafficinresidentialareas,because
arterialsareoverburdened
Homesandbusinessesareadverselyaffected
14
EffectsofAccessManagement
LandscapedMedian
ImprovedSafety
Roadwayoperations:fluency,lesstraveltime
etc.
Localeconomy
L l
Landuse:Aestheticseffects
Landscapedmedians
Environmentaleffects
savefuelandreducepollution
10PrinciplesofAM
Principle 1
TRBAccessManagementManualpublished
l bl h d
in2003
SPECIALIZEDROADWAYSYSTEM
11/11/2016
RoadwayFunctionalClassification
RoadHierarchy
Increasing Pro
oportion of
Through T
Traffic
Freeway
AccessCategory
Function
1:Freeway
Majorhighways thatprovideaccessviainterchangesonly.Primarilyfor
intercitytravel.Nodirectaccesstolanduses/property.
2:MajorArterial
Ofregionalimportanceandisintendedtoservehightrafficvolumes
travellingrelativelylongdistances.Primarily servingthroughtraffic.
Accessiscontrolled.
3:MinorArterial
SimilarinfunctionasMajorArterialhoweveroperatesunderlowertraffic
volumestravellingovermoderatedistances.Connectsneighborhoods.
4:Major
Collector
Connectsbetweenarterialsandlocalstreets.Serve tripstravellingover
shortdistances.Mayprovidedirectaccesstoabuttingpropertiese.g.
commercial/industrial complexes,butNOTresidential.
5:Minor
Collector
SimilarinfunctionasMajorCollectorbutcarrieslowertraffic volumes
overshortdistances.Provideshigherdegreesofaccesstoproperties
includingresidential.
6:LocalStreet
Intendedtoprovidedirectaccesstoproperties.Connectstocollector
streets. Fortraffictravellingshortertrips.Havelowtrafficvolumes.
7:CuldeSac
ProvidesPRIVATEaccesstoproperties.Does notallowTHROUGHtraffic.
Major Arterial
Minor Arterial
M j C
Major
Collector
ll t
Minor Collector
Local Street
Cul-de-Sac
Increasing Access
TheRoadwaydesignSystem
Principle 2
LIMITDIRECTACCESS
ExampleofPoorAccess
Management
PoorAccessControl
11/11/2016
BetterAccess
Principle 3
PROMOTEINTERSECTION
HIERARCHY
RoadwayHierarchy:Illustration
ExampleofRoadHierarchies:Florida,
USA
Minor Artterial
Minor Arte
erial
Major Arterial
Local Street
FREEWAY
Major Collector
Cul-de-Sac
Roadhierarchy:CloseupView
RoadHierarchies:BiggerPicture(Peoria,Illinois,USA)
Minor Collector
Local Street
Cul-de-Sac
Minor Arterial
Major Collector
11/11/2016
RoadHierarchies:BiggerPicture(Peoria,Illinois,USA)
Principle 4
Freeway
M j Arterial
Major
At i l
Minor Collector
Major Collector
Minor Arterial
Cul-deSac
LOCATESIGNALTOPROMOTE
THROUGHMOVEMENT
Local Street
FacilitateThroughMovements
FacilitateThroughMovements
LimitingDrivewaysintheFunctionalAreaofan
IntersectionImprovesSafety
Principle 5
PRESERVETHEFUNCTIONSOF
INTERSECTIONS
Thefunctionalareaistheaffectedareaupstream
anddownstreamofintersection.
Limitingdriveways
g
y
helpsreducethe
numberofdecisions
motoristsmustmake
nearanintersection,
improvingsafety.
36
11/11/2016
FunctionofIntersection
FunctionofIntersection
Access connections too close to an
intersection can cause serious traffic
conflicts that results in accidents or
congestion!
Intersections are areas where
motorists decelerate, stops or
slows to complete the turn.
Proper spacing of intersection can
reduce the trauma of negotiating
a difficult intersection and reduce
chances of crashes!
Restore the function of intersection as providing access to
land uses NOT a place for accidents to happen!
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
Principle 6
LIMITTHENUMBEROF
CONFLICTPOINTS
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
C
Crossing
i
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
=4
C
Crossing
i
=4
Diverge = 0
Diverge = 0
Merge
=0
Merge
=0
Total
=4
Total
=4
11/11/2016
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
C
Crossing
i
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
=4
C
Crossing
i
= 16
Diverge = 4
Diverge = 4
Merge
=0
Merge
=0
Total
=8
Total
= 20
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
C
Crossing
i
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
= 16
C
Crossing
i
= 16
Diverge = 4
Diverge = 4
Merge
=4
Merge
=4
Total
= 24
Total
= 24
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
C
Crossing
i
ConflictPoints:4wayIntersection
= 16
C
Crossing
i
= 16
Diverge = 8
Diverge = 8
Merge
=4
Merge
=8
Total
= 28
Total
= 32
These conflict points HAVE NOT even
consider the pedestrian and bicyclist
movements!
11/11/2016
Solutions:4wayIntersection
Solutions:4wayIntersection
C
Crossing
i
Median
Median
Median
Median
Or,betterstill
=4
Total
=8
=0
Diverge = 2
Merge
=2
Total
=4
TaxonomyofaRoundabout
Circulatory
roadway
Merge
Roundabout
C
Crossing
i
Median
=1
Diverge = 3
Roundabout:PointsofConflict
Pedestrian crossing
Crossing
=0
Diverge = 4
Central Island
Splitter Island
Merge
=4
Total
=8
Yield line
Apron
11/11/2016
Roundabout:Benefits
Benefits
How?
Feweraccidents
Upto90%reductioninfatalities
30%40%reductioninpedestriancrashes
75%fewerconflictpointsthan4wayintersection
Slowerspeed
Drivershavemoretimetojudgeandreact
Saferforpedestrianesp.olderpeopleandchildren
Reducesseverityofcrashes
Efficient traffic flow
Efficienttrafficflow
30%50%increaseintrafficcapacity
30%50% increase in traffic capacity
Principle 7
Reduction inpollution Improvedtrafficflowforintersectionsthathandleahighnumberof
rightturns
andfueluse
Reducedneedforstoragelanes
Moneysaved
Nosignalequipmenttoinstallandrepair
Savingsestimatedatanaverageof$5,000peryearinelectricityand
maintenancecosts
Servicelifeofaroundaboutis25years(vs.the10yearservicelifeof
signalequipment)
Communitybenefits
Trafficcalming
Aestheticlandscape
HighAccessDensity
SEPARATECONFLICTAREAS
HighAccessDensity
Closely-spaced intersections create overlapping conflict points
SeparatetheConflictAreas
Principle 8
Separate the conflict areas
REMOVETURNINGVEHICLESFROM
THROUGHTRAFFICLANES
10
11/11/2016
ThroughTraffic
TurningTraffic
Turning traffic blocks through vehicles
TurningLanes
Principle 9
USENONTRAVERSABLEMEDIAN
FORRIGHTTURNING
TraversableMedian
NonTraversableMedian
11
11/11/2016
UnplannedCommunities
Principle 10
PROVIDESUPPORTINGSTREETAND
CIRCULATIONSYSTEM
WellplannedCommunities
Communities must be
planned with their
supporting street systems
Whatisacorridorplan
Anearterm(10year)plan.
Analysisoffuturetraveldemandand
performanceinthecorridor.
Evaluation of problems and needs.
Evaluationofproblemsandneeds.
Identificationofcorridorimprovementpriorities.
objectiveistocontinuetoprovidea
roadwaythatisbothsafeandefficient.
DifferentCorridor
Treatments
CorridorManagementAnalysis
` LandUseAnalysis
Medians size&width
Accesscontrol
Superstreets
Intersectioncontrol
Roundabouts
Stopsigns
Signals
Urbandesign(streetscape)
Bikelanes
Trafficcalming
` Existinglanduse
` Propertyownershipandparcelboundaries
` Existingzoning
` Planned,proposedandapproveddevelopments
` TrafficAnalysis
` Accidentdata
` Traffic(includingbike)andpedestrianvolumes
` Trafficgrowthandprojectedtrafficdemand
` Travelspeedandtrafficdelay
` Turningvolumes
` Vehicleclassificationcounts
` Queuing
12
11/11/2016
CorridorManagementAnalysis
RoadwayDesignandAccess
Rightofwaywidthoftheroadway
Numberandwidthoftrafficlanes
Medianwidthanddesign
Locationanddesignofallmedianopenings
widthandcurbtypes
Locationanddesignofallintersections
Locationofallaccessconnections
Locationanddesignofallrightturnandrightturnlanes
Locationandwidthofsidewalksandbikelanes
Typeanddesignoftrafficcontrolatallintersections
MIDTERMTEST
10th December
IndividualAssignment(10%)
Selectanappropriateintersectionoraroad
segmentwithtrafficaccessissuesinJBorin
yourhometown
Draw,identifyanddiscusskeytrafficAccess
Managementissues
Redesigntheselectedintersectionorroad
segmenttoimprovethetrafficsituationas
discussedwithin10principlesofTRB.
SubmissionTime:on/before27th Marchat5PM
THANK YOU..!!!
Questions
Questions..Input??
Input??
TotalMarks:40
TotalMarks:
40%
%
13
Вам также может понравиться
- Conflict Points: Access Management Frequently Asked Questions: 6Документ2 страницыConflict Points: Access Management Frequently Asked Questions: 6Suman MandalОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Design of Road IntersectionДокумент16 страницProject Report On Design of Road IntersectionJohn Malkin100% (2)
- Project Report On Design of Road IntersectionДокумент15 страницProject Report On Design of Road IntersectionJohn MalkinОценок пока нет
- Intersection Design PDFДокумент60 страницIntersection Design PDFprashant100% (1)
- Midterm Exam CoverageДокумент65 страницMidterm Exam CoverageEduard Joseph Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Intersection DesignДокумент60 страницIntersection Designsareenpriya100% (3)
- Sustainable Parking Management: Practices, Policies, and MetricsОт EverandSustainable Parking Management: Practices, Policies, and MetricsОценок пока нет
- 4 Steps To Improve Pedestrian CrossingsДокумент4 страницы4 Steps To Improve Pedestrian CrossingsFrancisco GranadosОценок пока нет
- Traffic QuestionnaireДокумент2 страницыTraffic QuestionnaireMeldred PilongoОценок пока нет
- Test Questions ShafqatДокумент4 страницыTest Questions ShafqatEngr Imtiaz AhmadОценок пока нет
- Round AboutДокумент12 страницRound Aboutziaurahmanali2Оценок пока нет
- Intersections - 4Документ6 страницIntersections - 4Ali AlmusawiОценок пока нет
- A Report On Road IntersectionsДокумент8 страницA Report On Road IntersectionsDheeraj MathurОценок пока нет
- At Grade IntersectionДокумент12 страницAt Grade IntersectionRainnie Casandra100% (1)
- Design of Roadways FinalДокумент11 страницDesign of Roadways FinalJude TicseОценок пока нет
- Bottlenecks On RoadwayДокумент3 страницыBottlenecks On RoadwaymelodyОценок пока нет
- Road Transport BottlenecksДокумент3 страницыRoad Transport BottlenecksmelodyОценок пока нет
- Bottlenecks On RoadwayДокумент3 страницыBottlenecks On RoadwaymelodyОценок пока нет
- SVCP313 Intersection Design and ControlДокумент52 страницыSVCP313 Intersection Design and ControlRalph Denver RomanoОценок пока нет
- LECTURE NO 10 (Intersection)Документ40 страницLECTURE NO 10 (Intersection)Arman AliОценок пока нет
- Traffic Management 2Документ87 страницTraffic Management 2Roldan LumawasОценок пока нет
- Uncontrolled IntersectionДокумент20 страницUncontrolled Intersectionhassan amiriОценок пока нет
- Transportation Engineering: A Report On Road Accident StudiesДокумент14 страницTransportation Engineering: A Report On Road Accident StudiesEng-Mohammed TwiqatОценок пока нет
- VII Intersection DesignДокумент90 страницVII Intersection DesignPamela JezreelОценок пока нет
- Saron EcoДокумент10 страницSaron EcoMahider getachewОценок пока нет
- TD. Kuliah 4 Konflik Lalu LintasДокумент5 страницTD. Kuliah 4 Konflik Lalu LintasRafОценок пока нет
- Intersection Design PDFДокумент73 страницыIntersection Design PDFgiovana blas oceda100% (1)
- Intersection ControlДокумент12 страницIntersection ControlMMAGОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ4 страницыAssignment 4benami manushОценок пока нет
- Chapter FiveДокумент60 страницChapter FiveTemam MohammedОценок пока нет
- R S A F J: Chapter 4: Road Safety Audit For JunctionsДокумент10 страницR S A F J: Chapter 4: Road Safety Audit For JunctionsVandhana Rajasekaran100% (1)
- Mona Part 2 NewwwДокумент46 страницMona Part 2 NewwwKavenОценок пока нет
- PGJ PPT Channelization by AliДокумент25 страницPGJ PPT Channelization by AliAli RizaОценок пока нет
- Chapter OneДокумент19 страницChapter OneMahider getachewОценок пока нет
- Norwalk TMP Chapter 1-4 - Intersection DesignДокумент73 страницыNorwalk TMP Chapter 1-4 - Intersection DesignMarc Mathieu100% (1)
- Introduction To Transport B3: LecturersДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To Transport B3: LecturersSubbaReddyОценок пока нет
- Bike Lane Design Guidelines 09-22-2014Документ17 страницBike Lane Design Guidelines 09-22-2014civilanОценок пока нет
- QuizДокумент2 страницыQuizskill eruelОценок пока нет
- IAT-I Question Paper With Solution of 18CV652 Traffic Engineering May-2021-Dr. Asha M NairДокумент7 страницIAT-I Question Paper With Solution of 18CV652 Traffic Engineering May-2021-Dr. Asha M Nair2bl20me017soumyashiranalОценок пока нет
- 1-Intersection Design PDFДокумент51 страница1-Intersection Design PDFRedline Prenting PressОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes in Traffic Engineering and Management: Grade Separated IntersectionДокумент21 страницаLecture Notes in Traffic Engineering and Management: Grade Separated IntersectionMohamed YoussifОценок пока нет
- Greenport Parking StudyДокумент32 страницыGreenport Parking StudyRiverhead News-ReviewОценок пока нет
- Grade Separated Intersection Lecture NotДокумент15 страницGrade Separated Intersection Lecture NotNick Avis100% (1)
- JUNE, 2000 Road Design Manual (English) 5-0 (1) At-Grade IntersectionsДокумент49 страницJUNE, 2000 Road Design Manual (English) 5-0 (1) At-Grade IntersectionsVladimir MalinaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Junction DesignДокумент49 страницChapter 7 Junction DesignMuhd Fareez100% (6)
- Chapter 3Документ9 страницChapter 3SudipThapa100% (1)
- Transportation Slide PDFДокумент147 страницTransportation Slide PDFMd ZimОценок пока нет
- BFC 32302 Revision FinalДокумент148 страницBFC 32302 Revision Finalأفيق .яIОценок пока нет
- Design Ntersections, Ramps & Exit-Enterance SectionsДокумент31 страницаDesign Ntersections, Ramps & Exit-Enterance Sectionsعصام ايادОценок пока нет
- L EntersДокумент15 страницL Entersebinsams007Оценок пока нет
- Lecturenote - 243765026HW I-Chap-6-HandoutДокумент11 страницLecturenote - 243765026HW I-Chap-6-HandoutMahlet EshetuОценок пока нет
- Subdivision Staging Transportation Recommendations Subdivision Staging Policy Community Meeting II April 12, 2016Документ36 страницSubdivision Staging Transportation Recommendations Subdivision Staging Policy Community Meeting II April 12, 2016M-NCPPCОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент3 страницыNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAhmed GaklОценок пока нет
- Highway Intersection and Its TypesДокумент13 страницHighway Intersection and Its Typessydney augustОценок пока нет
- Lecture Note-Chap-6-Handout AddditionalДокумент11 страницLecture Note-Chap-6-Handout Addditionaltamratdugo9Оценок пока нет
- CP 2Документ44 страницыCP 2MD MREDULОценок пока нет
- Design of Parking Facilities: Dr. Taleb M. Al-RousanДокумент14 страницDesign of Parking Facilities: Dr. Taleb M. Al-RousanPenelope MalilweОценок пока нет
- TM - QBДокумент7 страницTM - QBDipankar NimkarОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Questions Transportation Depth Vf18Документ28 страницQualitative Questions Transportation Depth Vf18Dina ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Review of Budget 2020 Proposals On The Malaysian Real Estate SectorДокумент16 страницReview of Budget 2020 Proposals On The Malaysian Real Estate Sectorzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- AGENDA 5 - ARTA Abattoir PlantДокумент14 страницAGENDA 5 - ARTA Abattoir Plantzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Market Outlook MOR2020Документ96 страницMarket Outlook MOR2020HidayahОценок пока нет
- Klang Valley, Johor Bahru and George Town: Index Point, Average Rent & Yearly Change Q2 2019 and Q2 2020Документ2 страницыKlang Valley, Johor Bahru and George Town: Index Point, Average Rent & Yearly Change Q2 2019 and Q2 2020zulkis73Оценок пока нет
- H1 2018 H2 2018 H1 2019 H2 2019 H1 2020: Unit Launched Sales Performance (%)Документ2 страницыH1 2018 H2 2018 H1 2019 H2 2019 H1 2020: Unit Launched Sales Performance (%)zulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Basics Economics IntroductionДокумент19 страницBasics Economics Introductionzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Residential Property Transactions Data H1 2020Документ4 страницыResidential Property Transactions Data H1 2020zulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Sustainable CityДокумент52 страницыSustainable Cityzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Parking Studies Parking Studies: Outline OutlineДокумент5 страницParking Studies Parking Studies: Outline Outlinezulkis73Оценок пока нет
- GHPO Center MapДокумент2 страницыGHPO Center Mapzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Urban Unfriendliness in StreetscapeДокумент8 страницUrban Unfriendliness in Streetscapezulkis73Оценок пока нет
- People Vs Urban DesignДокумент99 страницPeople Vs Urban Designzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Putrajaya 2012Документ56 страницPutrajaya 2012zulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Contoh ExecsummaryДокумент45 страницContoh Execsummaryzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Q410residential PДокумент142 страницыQ410residential Pzulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Putrajaya 2012Документ56 страницPutrajaya 2012zulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Scale FeesДокумент26 страницScale Feeszulkis73Оценок пока нет
- Attached GrowthДокумент42 страницыAttached GrowthDini AryantiОценок пока нет
- F&P Paul AndersonДокумент41 страницаF&P Paul AndersonMax Calun Rosellon PalmieryОценок пока нет
- Mother Goose Special Science High SchoolДокумент7 страницMother Goose Special Science High Schoolmarie-joseph paul yvech roches marquis de lafayetteОценок пока нет
- Municipal Solid Waste: Public InfrastructureДокумент30 страницMunicipal Solid Waste: Public InfrastructureRonnel MauzarОценок пока нет
- Table 1 Minimum Separation DistancesДокумент123 страницыTable 1 Minimum Separation DistancesjhonОценок пока нет
- Part Four Implementing Business Ethics in A Global Economy: Sustainability: Ethical and Social Responsibility DimensionsДокумент30 страницPart Four Implementing Business Ethics in A Global Economy: Sustainability: Ethical and Social Responsibility DimensionsAthirah Nabilah100% (1)
- Ecological FactorДокумент3 страницыEcological FactorJayron NonguiОценок пока нет
- Development of Emission Factors From API 622 - 624 Test Data - Buzz Harris - Bronson PateДокумент23 страницыDevelopment of Emission Factors From API 622 - 624 Test Data - Buzz Harris - Bronson Pateemperor_vamsiОценок пока нет
- Brochure Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme For International Aviation (CORSIA) - Mar 2019 PDFДокумент2 страницыBrochure Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme For International Aviation (CORSIA) - Mar 2019 PDFjouОценок пока нет
- Solid Mensuration by Kern and Bland Solutions ManualДокумент26 страницSolid Mensuration by Kern and Bland Solutions ManualJem Donan0% (2)
- Helicopter Operations: Oil & Gas Consultancy ServicesДокумент4 страницыHelicopter Operations: Oil & Gas Consultancy ServicesJay JayОценок пока нет
- Ratnagiri Sindhudurg Tour Report Final DraftДокумент15 страницRatnagiri Sindhudurg Tour Report Final DraftWaseem ParkarОценок пока нет
- Environmental Laws in IndiaДокумент7 страницEnvironmental Laws in IndiaPriyanka SharmaОценок пока нет
- Critical Areas and Projects. The President of The PhilippinesДокумент1 страницаCritical Areas and Projects. The President of The PhilippinesMary Licel RegalaОценок пока нет
- What Are You Doing To Help NatureДокумент2 страницыWhat Are You Doing To Help NatureAtzel Didier Antonio SolórzanoОценок пока нет
- Letter To Public Official Genre Paper 2Документ3 страницыLetter To Public Official Genre Paper 2api-242810809Оценок пока нет
- Unep Tech Doc April 2012 - 120608b - WebДокумент76 страницUnep Tech Doc April 2012 - 120608b - WebNgoka EliesikiaОценок пока нет
- Effects of Climate ChangeДокумент3 страницыEffects of Climate Changejiofjij100% (1)
- Chapter5 PDFДокумент50 страницChapter5 PDFtowiwaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Dab 30102Документ75 страницChapter 3 Dab 30102Muhammad Fazlan AliffОценок пока нет
- 2.report On Row WorkshopДокумент4 страницы2.report On Row WorkshopPabhat KumarОценок пока нет
- Technical Design Guide: The Complete G UideДокумент35 страницTechnical Design Guide: The Complete G UideElvi PapajОценок пока нет
- Retrofitting The Existing Flare / Burnery For Smoke Less OperationsДокумент31 страницаRetrofitting The Existing Flare / Burnery For Smoke Less Operationsmehul10941Оценок пока нет
- English & Arab DescriptionДокумент15 страницEnglish & Arab DescriptionRacem LoukilОценок пока нет
- Speech About EnvironmentДокумент1 страницаSpeech About EnvironmentLara Mae MangubatОценок пока нет
- E-Waste Management: Its Effect On Human Health and EnvironmentДокумент19 страницE-Waste Management: Its Effect On Human Health and EnvironmentRana Sandrocottus100% (4)
- Easy99 - What Are The Long-Term SolutionsДокумент2 страницыEasy99 - What Are The Long-Term SolutionsWai Kit NgОценок пока нет
- Sustainability & GBRS Lecture Notes 230221aДокумент8 страницSustainability & GBRS Lecture Notes 230221aAMBROSEОценок пока нет
- Dip PDFДокумент27 страницDip PDFolenin64Оценок пока нет
- Development of Dynamic Head Loss Criteria For Raw Sludge Pumping.Документ12 страницDevelopment of Dynamic Head Loss Criteria For Raw Sludge Pumping.cascadedesigns100% (1)