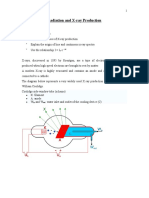
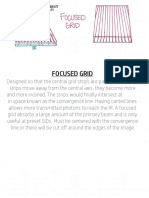
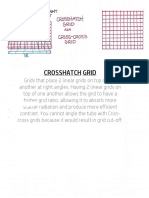
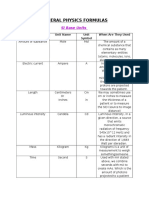
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Notebook 3
Загружено:
api-335583967Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Notebook 3
Загружено:
api-335583967Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Notebook 3
Particulate
Radiation
Electromag
netic
Radiation
Definition
high-energy
electrons,
neutrons, and
protons that
produce
ionization in
matter by direct
atomic collisions
Properties
two principle types associated with
radioactive decay, alpha and beta
particles. Alpha particle contains 2
protons and 2 neutrons, a positive
charge and transferred over a short
range in matter (about 5cm). Beta
particles are identical to electrons,
negatively charged, very light, and
travel farther in matter than alpha
particles (10-100cm) in air.
Origin
alpha particles are
emitted from the nuclei
of very heavy elements
as they undergo
radioactive decay, beta
particles are emitted
from the nuclei of
radioactive material
a form of energy
that is the result
of electric and
magnetic
disturbances in
space
includes x rays (this <200keV
range results in ionization through
photoelectric absorption and
Compton scattering) and gamma
rays. Photon energy transfer starts
when a photo interacts with an
atom causing an electron to be set
in motion resulting in a release of
kinetic energy, which is then
absorbed, by the electron via
excitation or ionization; this gives
rise to biological damage in tissue.
gamma rays are emitted
by the nuclei of
radioactive materials
whereas x-ray are manmade in an x-ray tube
Notebook 3
The Wave Theory
Electromagnetic energy travels through space in the form of waves which is defined itself as
disturbances through medium
Such as through the ocean or sound waves
Electromagnetic waves are unique in that no medium is required
they can travel through a vacuum which is what is used in the radiology field.
Waves are measured by wavelength
the distance between any two successive points on a wave measured crest to crest/trough to
trough varying from kilometers to angstroms), frequency (number of waves that passes in a
particular point in a given time frame, or numbers of cycles per second, hertz Hz), amplitude
(intensity of the wave defined by its maximal height), and period (time required to complete
one cycle of the wave)
Lower energy photons act as waves
Fundamental Properties of X-Rays (identified by Rontgen)
travel at the speed of light (3 x 108 meters per second in a vacuum)
are highly penetrating, invisible x-rays that are a form of electromagnetic radiation
travel in straight lines
produce secondary and scatter radiation
are electrically neutral and therefore not affected by either electric or magnetic fields
can be produced over a wide variety of energies and wavelengths (polyenergetic and
heterogeneous)
release very small amounts of heat upon passing through matter
can ionize matter
can fluorescence (the emission of light) of certain crystals
affect photographic film
Notebook 3
produce chemical and biological changes in matter through ionization and excitation
Вам также может понравиться
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itОт EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itОценок пока нет
- Notebook 3Документ2 страницыNotebook 3api-340425056Оценок пока нет
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsОт EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields On Human's HealthДокумент18 страницBiological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields On Human's HealthMarina ZaraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Introduction To RadiationДокумент36 страницChapter 3 Introduction To Radiationhailemicael mesfinОценок пока нет
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearДокумент52 страницыPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaОценок пока нет
- Fizika RadiologijaДокумент9 страницFizika RadiologijaBorislav TapavičkiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic WavesДокумент10 страницElectromagnetic WavesJahleel TroupeОценок пока нет
- Regions: The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент7 страницRegions: The Electromagnetic SpectrumIrene PontillasОценок пока нет
- Ionizing RadiationДокумент5 страницIonizing RadiationCristinaОценок пока нет
- Notebook 3 FinalДокумент6 страницNotebook 3 Finalapi-339050167Оценок пока нет
- Waves Packet KEYДокумент44 страницыWaves Packet KEYlauraОценок пока нет
- EMFT Assignment 5Документ48 страницEMFT Assignment 5M. HamzaОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Radiation Particle Radiation Acoustic Gravitational Radiation Ionizing Non-IonizingДокумент1 страницаElectromagnetic Radiation Particle Radiation Acoustic Gravitational Radiation Ionizing Non-IonizingtestaksdfОценок пока нет
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент41 страницаThe Electromagnetic SpectrumNoel John UmallaОценок пока нет
- حوراء نظري كاملДокумент78 страницحوراء نظري كاملbbnnnОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Energy Sources of RsДокумент10 страниц2.1 Energy Sources of RsrowlinОценок пока нет
- RT BasicsДокумент27 страницRT BasicsAwais JamilОценок пока нет
- Laser Scanner TechnologyДокумент22 страницыLaser Scanner TechnologyEng M G ElkhateebОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент17 страниц1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumShreyas SvОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterДокумент49 страниц1.1 Radiation: Interaction of Radiation With MatterShiva KumarОценок пока нет
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент34 страницыThe Electromagnetic Spectrumsoha baigОценок пока нет
- Principles and Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy: Pranjal Verma Sem - 3 BSC Physics Honors A8955718005Документ33 страницыPrinciples and Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy: Pranjal Verma Sem - 3 BSC Physics Honors A8955718005pranjalОценок пока нет
- What Is Electro MegnaticДокумент1 страницаWhat Is Electro Megnaticzhungjian586Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3. Electronic Spectros PDFДокумент38 страницChapter 3. Electronic Spectros PDFPoorvansh MahajanОценок пока нет
- Rad PhysicsДокумент109 страницRad PhysicsRicardo EdanoОценок пока нет
- Lct-1 General Introduction - 2019Документ38 страницLct-1 General Introduction - 2019Abdelfattah Mohamed OufОценок пока нет
- History: Spectrum IsДокумент23 страницыHistory: Spectrum IsMuhamad NurhudayahОценок пока нет
- Radiography l2 NotesДокумент63 страницыRadiography l2 NotesaasattiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chapter 7Документ12 страницChemistry Chapter 7Heather KieferОценок пока нет
- Module-1Principles of SpectrosДокумент9 страницModule-1Principles of SpectrosveronislisteningОценок пока нет
- Notebook 3Документ2 страницыNotebook 3api-340731900Оценок пока нет
- Physics of RadiationДокумент8 страницPhysics of Radiationalialahmedy24Оценок пока нет
- Interaction of Radiation With MatterДокумент16 страницInteraction of Radiation With MatterRachit KanchanОценок пока нет
- SBC 470 Principles of Organic SpectroscoДокумент107 страницSBC 470 Principles of Organic SpectroscoVaittianathan MahavapillaiОценок пока нет
- Notebook 3Документ2 страницыNotebook 3api-338661748Оценок пока нет
- Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumДокумент6 страницForms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumMicah TormonОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic RadiationДокумент6 страницElectromagnetic Radiation09ANKIT MISHRAОценок пока нет
- Ijiset - V5 - I12 - 01 (Mri)Документ20 страницIjiset - V5 - I12 - 01 (Mri)Ivan CheahОценок пока нет
- Fundamental To Electromagnetic WavesДокумент9 страницFundamental To Electromagnetic WavesResearch ParkОценок пока нет
- Radiation and X-Ray ProductionДокумент6 страницRadiation and X-Ray ProductionStephon RaghunananОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of RediationДокумент7 страницFundamental of RediationTejinder SinghОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: I Spectroscopy and The Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент5 страницIntroduction To Spectroscopy: I Spectroscopy and The Electromagnetic Spectrumbinfa kashafОценок пока нет
- Ec Seminar ReportДокумент20 страницEc Seminar ReportDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент12 страницElectromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic SpectrumAsim ZargarОценок пока нет
- Phy 104 Atomic SpectraДокумент24 страницыPhy 104 Atomic SpectraAisha abba HabibОценок пока нет
- Useful Tips On How To Properly Study Chapter 32Документ8 страницUseful Tips On How To Properly Study Chapter 32pauljkt1Оценок пока нет
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLДокумент42 страницыSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiОценок пока нет
- Untitled 2Документ6 страницUntitled 2Faizal DinjoeОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 ReviewerДокумент6 страницGrade 10 ReviewerDino M PangilinanОценок пока нет
- Chap 2 - Principles of SpectrosДокумент59 страницChap 2 - Principles of SpectrosRezaul Karim100% (3)
- OCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.5: Medical ImagingДокумент12 страницOCR A Physics A Level: Topic 6.5: Medical Imagingsohaib389892Оценок пока нет
- Source of ColorДокумент6 страницSource of ColoryemiОценок пока нет
- Advanced Physics Laboratory XRF X-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Analysis (EDXRF)Документ14 страницAdvanced Physics Laboratory XRF X-Ray Fluorescence: Energy-Dispersive Analysis (EDXRF)Gandis YulianaОценок пока нет
- Omr Aparna S BДокумент15 страницOmr Aparna S BSûr Å BhíñОценок пока нет
- Wireless Charging of Mobile PhonesДокумент18 страницWireless Charging of Mobile PhonesChakraPaniОценок пока нет
- Wireless Charging of Mobile PhonesДокумент18 страницWireless Charging of Mobile PhonesChakraPaniОценок пока нет
- 12 UvДокумент24 страницы12 UvMohit KambojОценок пока нет
- X RayДокумент127 страницX RayDhruv DesaiОценок пока нет
- Investigation Project PhysicsДокумент16 страницInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08Оценок пока нет
- Final Notebook 10 2Документ3 страницыFinal Notebook 10 2api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 5Документ2 страницыNotebook 5api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 11Документ4 страницыNotebook 11api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 12Документ6 страницNotebook 12api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Final Notebook 10 3Документ2 страницыFinal Notebook 10 3api-335583967100% (1)
- Digital vs. Film-Screen Radiography: Notebook 7Документ5 страницDigital vs. Film-Screen Radiography: Notebook 7api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Parallel Grid Notebook 2Документ1 страницаParallel Grid Notebook 2api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Sensitivity SpeckДокумент2 страницыSensitivity Speckapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Final Notebook 10Документ2 страницыFinal Notebook 10api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Double Emulsion Notebook 3Документ1 страницаDouble Emulsion Notebook 3api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Intensifying Screen Notebook 3Документ1 страницаIntensifying Screen Notebook 3api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 9 GeneratorsДокумент2 страницыNotebook 9 Generatorsapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 8Документ2 страницыNotebook 8api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Single Emulsion Notebook 3Документ1 страницаSingle Emulsion Notebook 3api-335583967100% (1)
- Notebook 6 X Ray CircuitДокумент1 страницаNotebook 6 X Ray Circuitapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Focused Grids Notebook 2Документ1 страницаFocused Grids Notebook 2api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Crosshatch Grid Notebook 2Документ1 страницаCrosshatch Grid Notebook 2api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 15 All The StepsДокумент2 страницыNotebook 15 All The Stepsapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 4Документ1 страницаNotebook 4api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 9Документ7 страницNotebook 9api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 12Документ1 страницаNotebook 12api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 10 Anode Cooling ChartДокумент1 страницаNotebook 10 Anode Cooling Chartapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 9 GeneratorsДокумент2 страницыNotebook 9 Generatorsapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 2Документ4 страницыNotebook 2api-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 5 - Fleming Hand RuleДокумент3 страницыNotebook 5 - Fleming Hand Ruleapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 4 Electrical CircuitДокумент4 страницыNotebook 4 Electrical Circuitapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 2 Atomic StructureДокумент3 страницыNotebook 2 Atomic Structureapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Home PageДокумент1 страницаHome Pageapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- Notebook 1 Genral Physics VocabДокумент3 страницыNotebook 1 Genral Physics Vocabapi-335583967Оценок пока нет
- A Theory of Latticed Plates and Shells PDFДокумент320 страницA Theory of Latticed Plates and Shells PDFAnonymous 9IbJK5jhVNОценок пока нет
- Notes On Q M C Delta TДокумент2 страницыNotes On Q M C Delta TDing30180Оценок пока нет
- Control Valve Failure Relief Rate - Liquid ServiceДокумент2 страницыControl Valve Failure Relief Rate - Liquid ServiceSaeid Rahimi MofradОценок пока нет
- Forces BookletДокумент14 страницForces BookletDiana ArnoldОценок пока нет
- Properties of GasesДокумент20 страницProperties of Gasescale suarezОценок пока нет
- Failure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Документ6 страницFailure Analysis of High-Performance Surfaces Used For Transversal Stability of Ships (Bilge Keels)Brizamar AguiarОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics d203 ReseniДокумент90 страницFluid Mechanics d203 ReseniDennys Fabricio Ramirez100% (1)
- Physics Project Final1Документ15 страницPhysics Project Final1sohamОценок пока нет
- Similarity and Modelling - 2Документ7 страницSimilarity and Modelling - 2Alexander MugabeОценок пока нет
- Lehtovaara CSC GPAW TDDFT Course v3Документ28 страницLehtovaara CSC GPAW TDDFT Course v3Kalakkan KollamОценок пока нет
- Full Seismic Waveform Inversion For Structural andДокумент266 страницFull Seismic Waveform Inversion For Structural andGadhoumiWalidОценок пока нет
- Computer Simulation of The Packing of Fine ParticlesДокумент9 страницComputer Simulation of The Packing of Fine ParticlesahmedsidalaОценок пока нет
- MC MomentumДокумент33 страницыMC MomentumPuntos de periciaОценок пока нет
- PID Controller - WikipediaДокумент41 страницаPID Controller - WikipediaHaroon Mohamed MorshedОценок пока нет
- Design of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDДокумент32 страницыDesign of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDkevin_au18Оценок пока нет
- WS - Igcse 9 - (Physics 9) - 2021 - 22Документ9 страницWS - Igcse 9 - (Physics 9) - 2021 - 22Karan PuriОценок пока нет
- STRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFДокумент99 страницSTRC201 Sdof JMWB PDFAkash ChandraОценок пока нет
- 2d Plaxis Finite Element Modeling of Ashhalt ConcreteДокумент13 страниц2d Plaxis Finite Element Modeling of Ashhalt ConcreteAnonymous 5exSer100% (1)
- Lecture 03Документ27 страницLecture 03nghaОценок пока нет
- XII - Physics - Frequently Asked Question BankДокумент200 страницXII - Physics - Frequently Asked Question BankPiyush SuryawanshiОценок пока нет
- 6.lec2 2Документ11 страниц6.lec2 2Shahzaib Anwar OffОценок пока нет
- Motion 3Документ9 страницMotion 3gobinda prasad barmanОценок пока нет
- Planck's Quantum Theory: Quantization of EnergyДокумент3 страницыPlanck's Quantum Theory: Quantization of EnergyTowfiqabdullahОценок пока нет
- Physics Paper 1 SECTION B: Question Book B: This Paper Must Be Answered in EnglishДокумент6 страницPhysics Paper 1 SECTION B: Question Book B: This Paper Must Be Answered in EnglishporterОценок пока нет
- Crossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)Документ1 страницаCrossing Calculation API RP1102 (TEMPLATE)Hendra Yudistira100% (1)
- Thermal Modelling of Electric MachinesДокумент56 страницThermal Modelling of Electric MachinesDhanrajОценок пока нет
- Commensurability, Comparability, Communicability Thomas KuhnДокумент21 страницаCommensurability, Comparability, Communicability Thomas KuhnPablo MelognoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 Airy Stress FunctionДокумент20 страницTopic 2 Airy Stress FunctionAnonymous ohCM2ktv100% (1)
- Cable and ArchesДокумент15 страницCable and Archess k sharmaОценок пока нет
- Photon Interaction With MatterДокумент16 страницPhoton Interaction With MatterShafuan WanОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceОт EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectОт EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (20)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОт EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОценок пока нет
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceОт EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseОт EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsОт EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (94)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionОт EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldОт EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterОт EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (264)