Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Eee-4126 04
Загружено:
Isaac CohenОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Eee-4126 04
Загружено:
Isaac CohenАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Objectives:
In this experiment, a simple circuit will be constructed to study the
switching characteristic of TRIode for Alternating Current (TRIAC).
Theory:
The TRIAC is a member of the thyristor family. But unlike a SCR which conducts
only in one
direction (from anode to cathode) a TRIAC can conduct in both directions. Thus
a triac is similar to
two back to back (anti parallel) connected SCR but with only three terminals.
Standard triacs can be triggered by positive or negative current flow between
the gate and MT1
TRIAC I-V characteristic:
Figure 1.1: TRIAC I-V characteristic
First Quadrant Operation of TRIAC :
Voltage at terminal MT2 is positive with respect to terminal MT1 and gate
voltage is also positive with respect to first terminal.
Second Quadrant Operation of TRIAC:
Voltage at terminal 2 is positive with respect to terminal 1 and gate
voltage is negative with respect to terminal 1.
Third Quadrant Operation of TRIAC:
Voltage of terminal 1 is positive with respect to terminal 2 and the gate
voltage is negative.
Fourth Quadrant Operation of TRIAC:
Voltage of terminal 2 is negative with respect to terminal 1 and gate
voltage is positive.
TRIAC Turn-OFF Characteristics:
Since triacs are used in AC circuits, they naturally commutate at the end
of each half cycle of load current unless a gate signal is applied to maintain
conduction from the beginning of the next half cycle.
Equipments:
BT136 TRIAC
Resistors: 220
Potentiometer; Extech Resistance Decade Box
Multimeter
Trainer Board
Bench Power Supply
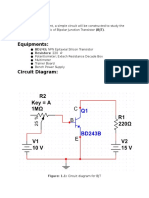
Circuit Diagram:
Figure 1.2: Circuit Diagram using BT136 TRIAC
Figure 1.3: Circuit Diagram using 2 SCR as TRIAC
Procedure:
The value of V1 & V2 was set to +10 VDC & +15 VDC
Voltage reading was taken by Multimeter between MT1 & MT2
Similarly voltage reading was taken by Multimeter between R1 (VR1) & R2 (VG).
The IG current was measured by dividing the voltage drop across the R2 Resistor
(VG) with the current value of R2 resistor. IG=VR2/R2 (IG=VG/RG)
R2 value was changed & VR2 (VG) was measured for different R2 values.
Different values were measured & logged on a Data Table.
This procedure was continued until current through the load resistor R2 reached
almost equal to IL=VR1/220.
Data Collection:
RG
VG
In Volts
VR1
In Volts
IG=VG/RG
IL=VR1/22
0
Voltages
Between MT1
In Amps
& MT2
10 M
9.30
14.21
0.00093
mA
0.06459
0.775 V
2M
9.30
14.24
0.00465
mA
0.06473
0.775 V
1M
9.30
14.25
0.0093
mA
0.06477
0.778 V
900 K
9.30
14.24
0.01033
mA
0.06472
0.777 V
500 K
9.30
14.24
0.0186
mA
0.06472
0.777 V
100 K
9.30
14.24
0.093 mA
0.06472
0.777 V
1K
9.24
14.23
9.24 mA
0.06468
0.782 V
500
9.20
14.22
0.0184 A
0.06463
0.786 V
100
9.02
14.20
0.0902 A
0.0645
0.822 V
Discussion:
triac is used in AC power control.
A triac is functionally equivalent to two antiparallel connected thyristors. It can
block
voltages in both directions and conduct current in both directions.
A triac has three terminals like a thyristor. It can be turned on in either half cycle
by
either a positive on a negative current pulse at the gate terminal.
Triacs are extensively used at power frequency ac load (eg heater, light, motors)
control
Applications.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Qcomm LTE Log Packet Information 80 VP457 5 C LTE LPID PDFДокумент232 страницыQcomm LTE Log Packet Information 80 VP457 5 C LTE LPID PDFMichał Ujma100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Marine PropellersДокумент38 страницMarine PropellersHung Nguyen100% (1)
- Metrology and Measurements - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersДокумент7 страницMetrology and Measurements - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVОценок пока нет
- Eee-4126 03Документ3 страницыEee-4126 03Isaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Geonames Classification For Bengali GeowДокумент35 страницGeonames Classification For Bengali GeowIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Objectives: Theory: EquipmentsДокумент2 страницыObjectives: Theory: EquipmentsIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Eee-4126 02Документ2 страницыEee-4126 02Isaac CohenОценок пока нет
- HL 2130 PDFДокумент22 страницыHL 2130 PDFstevanreljicОценок пока нет
- M Eng 8086Документ148 страницM Eng 8086Suleman Mirza100% (3)
- Traffic 001 Final - With Traffic Light - Modified - 4 Way Super - PDSPRJДокумент1 страницаTraffic 001 Final - With Traffic Light - Modified - 4 Way Super - PDSPRJIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- 2 Weeks in BangkokДокумент54 страницы2 Weeks in BangkokJason LeeОценок пока нет
- 3-1 Basic Principles PDFДокумент26 страниц3-1 Basic Principles PDFmuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Ds 529Документ132 страницыDs 529Sri_CbeОценок пока нет
- Basic HDL Coding Techniques Part1 - 2Документ27 страницBasic HDL Coding Techniques Part1 - 2Isaac CohenОценок пока нет
- A Coding Style Guide For Java WorkShop and Java Studio Programming - Achut ReddyДокумент35 страницA Coding Style Guide For Java WorkShop and Java Studio Programming - Achut ReddyIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle Using MicrocontrollerДокумент0 страницDesign and Implementation of Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle Using MicrocontrollerIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Experiences Designing and Building A Subwoofer AmplifierДокумент6 страницExperiences Designing and Building A Subwoofer AmplifierIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Appearance-Based Statistical Methods For Face RecognitionДокумент8 страницAppearance-Based Statistical Methods For Face RecognitionIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Building A Digital Light Meter With A Calibrated LDRДокумент9 страницBuilding A Digital Light Meter With A Calibrated LDRIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- Guide To Understanding Jtag Fuses and SecurityДокумент7 страницGuide To Understanding Jtag Fuses and SecurityIsaac Cohen100% (1)
- Arduino MotorShield Rev3-SchematicДокумент1 страницаArduino MotorShield Rev3-SchematicgetmicrosОценок пока нет
- A Review of The Current Hypotheses On Inflation in Bangladesh - Selim Raihan, Kaniz FatemaДокумент11 страницA Review of The Current Hypotheses On Inflation in Bangladesh - Selim Raihan, Kaniz FatemaIsaac CohenОценок пока нет
- OOP Java ArraysДокумент60 страницOOP Java ArraysIm Just A SimplexDОценок пока нет
- Big Data Analytics in Supply Chain Management Between 2010 and 2016Документ12 страницBig Data Analytics in Supply Chain Management Between 2010 and 2016Kuldeep LambaОценок пока нет
- Exam Flashcards: by Jonathan DonadoДокумент520 страницExam Flashcards: by Jonathan Donadosolarstuff100% (1)
- CLO 1 Scope and Role of SCM in An OrganizationДокумент28 страницCLO 1 Scope and Role of SCM in An OrganizationMelvinОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Computer Organization and Hardware MaintenanceДокумент28 страницLab Manual Computer Organization and Hardware Maintenanceanshroy7373Оценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Inside The SystemДокумент2 страницыUnit 3 Inside The SystemMartín CrespoОценок пока нет
- DROPS - Reliable Securing Rev 04Документ67 страницDROPS - Reliable Securing Rev 04Chris EasterОценок пока нет
- Interdomain Multicast Soln Guide 1587050838Документ336 страницInterdomain Multicast Soln Guide 1587050838Balaji RajagopalОценок пока нет
- TR 101290v010201pДокумент175 страницTR 101290v010201pAndreas_HBОценок пока нет
- Em 1110 1 1000Документ371 страницаEm 1110 1 1000ingaboОценок пока нет
- Hardware Notes - Creo 1.0 Parametric, Direct and Simulate: Table of ContentДокумент7 страницHardware Notes - Creo 1.0 Parametric, Direct and Simulate: Table of ContentMohankumarОценок пока нет
- User Manual Headset LG HBM-220 EngДокумент9 страницUser Manual Headset LG HBM-220 Engrobnov7529Оценок пока нет
- Design of Five Floors Elevator With SCADA System Based On S7200 PLCДокумент6 страницDesign of Five Floors Elevator With SCADA System Based On S7200 PLCothmanОценок пока нет
- FMEAДокумент3 страницыFMEAyadiОценок пока нет
- ZXWR RNC (V3.07.310) Radio Network Controller Performance Index ReferenceДокумент419 страницZXWR RNC (V3.07.310) Radio Network Controller Performance Index ReferenceWilmer Brito GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Datasheet of DS-KIS204 Video Door Phone V1.1.0 20180502 PDFДокумент3 страницыDatasheet of DS-KIS204 Video Door Phone V1.1.0 20180502 PDFNareshОценок пока нет
- LAB3.2 - Connecting Windows Host Over iSCSI With MPIOДокумент13 страницLAB3.2 - Connecting Windows Host Over iSCSI With MPIOwendy yohanesОценок пока нет
- Aeg DC 2000 enДокумент2 страницыAeg DC 2000 enmauriceauОценок пока нет
- Nissan Tow Hitch InstallationДокумент2 страницыNissan Tow Hitch InstallationalvinОценок пока нет
- Workflow API Reference Guide PDFДокумент340 страницWorkflow API Reference Guide PDFRaghugovindОценок пока нет
- FRIT 7739 - Technology Program Administrator - WeeksДокумент6 страницFRIT 7739 - Technology Program Administrator - WeeksdianambertОценок пока нет
- Presented By:: Kemal Muhammet Akkaya Sr. Instrument Engineer Humod M. Al-Shammari Maintenance SuperintendentДокумент54 страницыPresented By:: Kemal Muhammet Akkaya Sr. Instrument Engineer Humod M. Al-Shammari Maintenance Superintendentmaria neneng bulakОценок пока нет
- Planning of Robots Cooperation Automatic Modelling and ControlДокумент25 страницPlanning of Robots Cooperation Automatic Modelling and ControlMowafak HassanОценок пока нет
- 25 KV Traction SCADA SPECIFICATION No. TISPCRCCSCADA0130 (Rev-1) 1Документ70 страниц25 KV Traction SCADA SPECIFICATION No. TISPCRCCSCADA0130 (Rev-1) 1pradeeepgarg100% (1)
- Phy 104 Lab ReportДокумент6 страницPhy 104 Lab ReportMd. Abdullah ZishanОценок пока нет
- Bs en 12Документ10 страницBs en 12Alvin BadzОценок пока нет
- sm53453 1Документ20 страницsm53453 1zoltanpdcОценок пока нет
- OM Course OutlineДокумент2 страницыOM Course OutlineSeid KassawОценок пока нет