Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IPv4 and IPv6 Homework on Addressing, Routing and Headers
Загружено:
Aditya MishraИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IPv4 and IPv6 Homework on Addressing, Routing and Headers
Загружено:
Aditya MishraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EP2120 Internetworking/Internetteknik
IK2218 Internets Protokoll och Principer
Homework Assignment 1
(Solutions due 23:00, Wednesday, 2016. Sept.7)
(Review due 23:00, Friday, 2016. Sept.09)
1. IPv4 Addressing (30/100)
a) What is the best fit netmask (i.e., resulting in as few host addresses as possible) for a
network with 7 hosts in it? (5p)
b) What is the maximum number of hosts can you have in a /24 network? (5p)
c) Split up the network 130.229.134.0/24 into three networks, including one /25 network and
two /26 networks! Provide the results in binary and in dotted decimal notation including
the prefix length. (5p)
d) What is the directed broadcast address of the network 130.229.124.0/27? (5p)
e) What is the limited broadcast address of the network 130.229.124.0/27? (5p)
f) Use the services of IANA and a regional registry to figure out to whom the IP network
130.237.0.0/18 belongs. Provide the name of the organization and the AS number. (5p)
2. Address allocation (30/100)
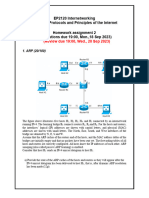
Consider the network above, a routed network in an organizations enterprise network. The
organization built a core network (network F) connected to a central router (R1), and connected a
router (R2) with (long-haul) switched Ethernet (network E). The access routers (R3 to R6) are
connected to a set of local offices (networks A to D). The host H1, connected to network F, performs
various traffic monitoring tasks. All networks use Ethernet on the link layer.
The enterprise allocated prefix 60.88.16.0/21 for its internal addresses.
Make an address allocation using 60.88.16.0/21 in the network by assigning a sub-block to each
network A-F in the following way:
f) The networks A through C require 250 hosts each, while network D requires 450 hosts. Create
a minimal block for each local office A through D. Start with the lowest address for network
A.
g) There are no unnumbered point-to-point links: all Ethernet networks have IP sub-networks and
all nodes (routers and hosts) have an IP address on all their network interfaces. All nodes need
to be reachable from any other host.
h) The address allocation should be such that the sub-networks can be aggregated.
i) Each sub-network should not be larger than necessary in order to accommodate all hosts in the
sub-network.
Based on your address allocation, provide the required entries of the forwarding table of router R1!
Give a sketch of your reasoning to support your solution. (30p)
3. IPv4 forwarding (20/100)
A router has the forwarding table shown below. Determine the next-hop address and the
outgoing interface for the packets arriving to the router with destination addresses as given in
points (a)-(e).
Destination
Next hop
Flags
Interface
157.29.11.0/24
177.121.128.0/18
130.78.0.0/15
73.0.0.0/16
221.182.100.0/25
9.221.80.0/20
198.17.42.160/29
0.0.0.0/0
130.78.11.10
73.0.45.1
221.182.100.28
221.182.100.25
73.0.65.1
UG
G
U
U
U
UG
UG
UG
m1
m0
m1
m0
m2
m2
m2
m0
a) 157.29.11.122
(4p)
b) 177.121.128.2
(4p)
c) 73.16.132.16
(4p)
d) 221.182.100.27
(4p)
e) 21.193.63.142
(4p)
4. IPv4 and IPv6 datagram formats (20/100)
a) What is the function of the header length and time-to-live (TTL) fields in the IPv4 header?
(5p)
b) What is the function of the flow label and of the traffic class fields in the IPv6 header? (5p)
c) Comparing the IPv6 header with the IPv4 header, we notice that the fragmentation related
fields appearing in the IPv4 datagram are not present in the IPv6 header. Give an
explanation why fragmentation related fields are not present in the IPv6 base header? (5p)
d) Comparing the IPv6 header with the IPv4 header, we notice that the header checksum field
appearing in the IPv4 datagram is not present in the IPv6 header. Give an explanation why
the checksum field is not present in the IPv6 header? (5p)
Вам также может понравиться
- Homework 5Документ4 страницыHomework 5constantineОценок пока нет
- Corporate Network Addressing and Routing HomeworkДокумент10 страницCorporate Network Addressing and Routing Homeworkpic616Оценок пока нет
- EP2120 Internetworking Homework ARP and UDP FragmentationДокумент9 страницEP2120 Internetworking Homework ARP and UDP FragmentationRonjaОценок пока нет
- IK2218 Homework 3 Solutions 2019Документ5 страницIK2218 Homework 3 Solutions 2019RonjaОценок пока нет
- Homework1 Solution PDFДокумент7 страницHomework1 Solution PDFTam HoangОценок пока нет
- EP2120 Internetworking/Internetteknik IK2218 Internets Protokoll Och Principer Homework Assignment 4Документ5 страницEP2120 Internetworking/Internetteknik IK2218 Internets Protokoll Och Principer Homework Assignment 4doyaОценок пока нет
- IK2218 Homework 3 Solutions 2020Документ5 страницIK2218 Homework 3 Solutions 2020RonjaОценок пока нет
- EQ2310 Collection of ProblemsДокумент203 страницыEQ2310 Collection of ProblemsESAM980100% (1)
- Wireshark Lab 5Документ17 страницWireshark Lab 5Truonganh BaoОценок пока нет
- Wireshark Lab: DHCP v7.0: 1 ObjectiveДокумент8 страницWireshark Lab: DHCP v7.0: 1 ObjectiveHugo GustavoОценок пока нет
- HCT 207 Final ExamSsolu 2018 NovDecДокумент8 страницHCT 207 Final ExamSsolu 2018 NovDecMarlon TugweteОценок пока нет
- S1 OpenLab Ver16062013Документ2 страницыS1 OpenLab Ver16062013Trương Tùng Dương100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence DD2380 HMM Example: Usain Bolt: Accelerate Prepare Decelerate StopДокумент2 страницыArtificial Intelligence DD2380 HMM Example: Usain Bolt: Accelerate Prepare Decelerate StopAnirudh Seth100% (1)
- University of Zimbabwe Introduction To Data Communications Practice Questions-1Документ3 страницыUniversity of Zimbabwe Introduction To Data Communications Practice Questions-1Gershom MahoriОценок пока нет
- Đề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Документ3 страницыĐề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Ngọc Hiếu100% (1)
- HCT 207 Final ExamS 2019 Revised May-JuneДокумент4 страницыHCT 207 Final ExamS 2019 Revised May-JuneMarlon TugweteОценок пока нет
- 28 Hw5-SolДокумент18 страниц28 Hw5-Solkisibongdem1412Оценок пока нет
- Tổng hợp câu hỏi ôn thi CCNAДокумент15 страницTổng hợp câu hỏi ôn thi CCNAkspark595Оценок пока нет
- Avg Data Rate To Browsers: 1.50 MbpsДокумент2 страницыAvg Data Rate To Browsers: 1.50 MbpsRayhan AhmedОценок пока нет
- Wireshark Lab: TCP v7.0: 1 ObjectiveДокумент6 страницWireshark Lab: TCP v7.0: 1 ObjectiveHugo GustavoОценок пока нет
- Homework 4 Solution GuidelinesДокумент12 страницHomework 4 Solution GuidelinesSurya AhujaОценок пока нет
- CE707 Assignment1 2021-2-7Документ6 страницCE707 Assignment1 2021-2-7saleem razaОценок пока нет
- A Network Ready Device Is Directly Connected To A Mikrotik Routerboard 750 With A Correct U.T.PДокумент6 страницA Network Ready Device Is Directly Connected To A Mikrotik Routerboard 750 With A Correct U.T.Ppomade storeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: Application LayerДокумент19 страницChapter 2: Application LayerAmallul MustaqimОценок пока нет
- OSPF QuestionsДокумент6 страницOSPF Questionsstorm2010Оценок пока нет
- Ccna 1Документ16 страницCcna 1aboubakrysyОценок пока нет
- Routing and Switching Case StudyДокумент12 страницRouting and Switching Case StudyRUKNUDDIN ASRARI100% (1)
- CPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATДокумент11 страницCPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATCharles CarpenterОценок пока нет
- Answer SheetДокумент8 страницAnswer SheetChris McoolОценок пока нет
- Homework3 SolutionsДокумент6 страницHomework3 SolutionsANAMITRA BHAR (RA1811003010684)Оценок пока нет
- Ccna 200-125 MCQДокумент157 страницCcna 200-125 MCQJesus Macias RamirezОценок пока нет
- Sample Problems For Computer ComunicationsДокумент3 страницыSample Problems For Computer ComunicationsFakrul HanifОценок пока нет
- Correct Answer: AДокумент76 страницCorrect Answer: Amark jayОценок пока нет
- Wireshark Lab: 802.11 Wifi: Approach, 8 Ed., J.F. Kurose and K.W. RossДокумент5 страницWireshark Lab: 802.11 Wifi: Approach, 8 Ed., J.F. Kurose and K.W. RossInceptionОценок пока нет
- 9.1.4.9 Lab - Subnetting Network TopologiesДокумент11 страниц9.1.4.9 Lab - Subnetting Network TopologiesEdgar RamirezОценок пока нет
- Subnetting Exercise SolutionsДокумент7 страницSubnetting Exercise SolutionsMalikMohsin0% (1)
- Homework 2 Dijkstra's Algorithm and Network ProblemsДокумент7 страницHomework 2 Dijkstra's Algorithm and Network ProblemsTam HoangОценок пока нет
- ENetwork Final Exam CCNA 1 4Документ22 страницыENetwork Final Exam CCNA 1 4Jay LeeОценок пока нет
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructДокумент4 страницы9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- CCNA 1 Skill Exam AnswerДокумент8 страницCCNA 1 Skill Exam Answerronzp100% (1)
- ВопросыДокумент12 страницВопросыRoman Travin33% (3)
- MX14R1 - Kumpulan Soal MTCNA 2014Документ9 страницMX14R1 - Kumpulan Soal MTCNA 2014believa dyanneОценок пока нет
- Routing Protocols (RIP, OSPF, and BGP) : Mi-Jung Choi Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mjchoi@postech - Ac.krДокумент86 страницRouting Protocols (RIP, OSPF, and BGP) : Mi-Jung Choi Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mjchoi@postech - Ac.krHafeez MohammedОценок пока нет
- HW1Документ9 страницHW1Amitesh SahОценок пока нет
- Transport Layer - MukeshДокумент54 страницыTransport Layer - MukeshMukeshОценок пока нет
- Is IsДокумент46 страницIs IsNdahimana EmmyОценок пока нет
- HCT 207 Final ExamS 2019 May-JuneДокумент6 страницHCT 207 Final ExamS 2019 May-JuneMarlon TugweteОценок пока нет
- H12-221 Exam QuestionsДокумент66 страницH12-221 Exam QuestionsmohammadОценок пока нет
- Network Chapter# 20: Transport Protocols Transport Protocols Transport Protocols Transport ProtocolsДокумент6 страницNetwork Chapter# 20: Transport Protocols Transport Protocols Transport Protocols Transport ProtocolsRevathi RevaОценок пока нет
- Homework4 SolutionsДокумент4 страницыHomework4 SolutionsANAMITRA BHAR (RA1811003010684)Оценок пока нет
- Lab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterДокумент8 страницLab 7 Configure Static Routing Cisco RouterAzrul Ikhwan ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- 15 DHCP Protocol Principles PDFДокумент17 страниц15 DHCP Protocol Principles PDFMuhammadSarmadMahmoodMalikОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 SolutionsДокумент5 страницHomework 1 SolutionsANAMITRA BHAR (RA1811003010684)Оценок пока нет
- Homework_1_solutionsДокумент5 страницHomework_1_solutionsdawliОценок пока нет
- Problem Sheet 4 PDFДокумент2 страницыProblem Sheet 4 PDFBhavya NagОценок пока нет
- IMP CNT5008 Sample FinalДокумент8 страницIMP CNT5008 Sample FinalArun VermaОценок пока нет
- EC 504 End Semester QPДокумент3 страницыEC 504 End Semester QPVinod PrakashОценок пока нет
- Quiz1 w15Документ4 страницыQuiz1 w15Mohamed KhedrОценок пока нет
- Homework_2Документ4 страницыHomework_2dawliОценок пока нет
- Ch2 Static Routing 1. A Static Route That Points To The Next Hop IP Will Have What AdministrativeДокумент10 страницCh2 Static Routing 1. A Static Route That Points To The Next Hop IP Will Have What Administrativeرغد ابراهيمОценок пока нет
- Good Formatted Accounting Finance For Bankers AFB 1 1Документ32 страницыGood Formatted Accounting Finance For Bankers AFB 1 1Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Cisco SubnettingДокумент1 страницаCisco SubnettingAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- RemainderДокумент1 страницаRemainderAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Advt Eng Fraud MGMT Chief Off Security 01122016Документ1 страницаAdvt Eng Fraud MGMT Chief Off Security 01122016Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Cloud Affairs - Time and WorkДокумент22 страницыCloud Affairs - Time and WorkAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Linux Important CommandДокумент1 страницаLinux Important CommandAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Cloud Affairs - ProbabilityДокумент23 страницыCloud Affairs - ProbabilityAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Sixth Question SetДокумент10 страницSixth Question SetAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Project ChemistryДокумент4 страницыProject ChemistryAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Probabilityp PDFДокумент2 страницыProbabilityp PDFKarn KumarОценок пока нет
- Part A Common QuestionsДокумент16 страницPart A Common Questions'Vinay Kumar MachamrajОценок пока нет
- Computer Science Foundation Exam: SolutionsДокумент5 страницComputer Science Foundation Exam: SolutionsAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Cisb 351Документ5 страницCisb 351Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Comptia Cybersecurity Analyst (cs0 001)Документ15 страницComptia Cybersecurity Analyst (cs0 001)Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Bharat Bill Payments SystemДокумент2 страницыBharat Bill Payments SystemAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Logic Problemset PDFДокумент108 страницLogic Problemset PDFAditya Mishra100% (2)
- Gate New Syllabus Computer Science and Information Technology For 2016Документ2 страницыGate New Syllabus Computer Science and Information Technology For 2016ersayantanОценок пока нет
- Exercise Set2 SolutionsДокумент4 страницыExercise Set2 SolutionsAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Boats & Streams Problem Solved in 3 StepsДокумент2 страницыBoats & Streams Problem Solved in 3 StepsVikas BanpurkarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Regular ExpressionsДокумент12 страницChapter 4: Regular ExpressionsAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- 14 1uДокумент3 страницы14 1uAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Solutions To Problem Set 0: Math 149S: Matthew Rognlie September 8, 2009Документ5 страницSolutions To Problem Set 0: Math 149S: Matthew Rognlie September 8, 2009Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- CSC 263 H5S Homework 2 SolutionsДокумент3 страницыCSC 263 H5S Homework 2 SolutionsAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Other Geometry PДокумент2 страницыOther Geometry PAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- 15 1Документ3 страницы15 1Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- E2 AnswersДокумент19 страницE2 AnswersAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Probabilityp PDFДокумент2 страницыProbabilityp PDFKarn KumarОценок пока нет
- cs151 sq07 q4 SolДокумент8 страницcs151 sq07 q4 SolAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Graduate Examination: Department of Computer Science The University of Arizona Spring 2003Документ15 страницGraduate Examination: Department of Computer Science The University of Arizona Spring 2003Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Midterm1 SolutionДокумент7 страницMidterm1 SolutionAditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Am79C970 PCnet PCI Single-Chip Ethernet Controller DatasheetДокумент168 страницAm79C970 PCnet PCI Single-Chip Ethernet Controller DatasheetrkaippullyОценок пока нет
- Handout of Small Net - 220718 - 103003Документ123 страницыHandout of Small Net - 220718 - 103003paxifiq IkОценок пока нет
- Pacis System General PresentationДокумент31 страницаPacis System General PresentationHutch WoОценок пока нет
- Computer Organization & ArchitectureДокумент37 страницComputer Organization & ArchitectureHardik DarjiОценок пока нет
- Spinner ComboBox DropDown List Android Example CodeДокумент6 страницSpinner ComboBox DropDown List Android Example CodeimsukhОценок пока нет
- Binary To BCD C-WPS OfficeДокумент5 страницBinary To BCD C-WPS OfficestephenОценок пока нет
- Commonly Asked Python Telephonic Interview QuestionsДокумент6 страницCommonly Asked Python Telephonic Interview Questionsnagub100% (1)
- .N-Series Intel® Pentium® Processors EDSДокумент316 страниц.N-Series Intel® Pentium® Processors EDSjayixi4827Оценок пока нет
- EM Pro USB Driver Installation Manual - 03Документ10 страницEM Pro USB Driver Installation Manual - 03mac_scribdОценок пока нет
- 305 DocumentДокумент46 страниц305 Documentswathi reddyОценок пока нет
- SSL Protocol AnalysisДокумент8 страницSSL Protocol Analysisbsnl007Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 2.5 Operators in C++Документ14 страницLesson 2.5 Operators in C++Keanu EspinaОценок пока нет
- CrashДокумент3 страницыCrashshotiko mamulashviliОценок пока нет
- WinScope 2 0 Reference Guide r1Документ28 страницWinScope 2 0 Reference Guide r1Waleed LemsilkhiОценок пока нет
- Supporting Cisco Data Center Networking Devices (010-151) : Exam DescriptionДокумент2 страницыSupporting Cisco Data Center Networking Devices (010-151) : Exam DescriptionMeiqi LouverОценок пока нет
- KL 002.104 Eng Student Guide v1.0Документ347 страницKL 002.104 Eng Student Guide v1.0ppicyber100% (1)
- Huawei SmartAX MA5616 Configuration Guide (V800R310C00 - 03)Документ717 страницHuawei SmartAX MA5616 Configuration Guide (V800R310C00 - 03)Philip Evans100% (6)
- Microprocessor Lab ManualДокумент74 страницыMicroprocessor Lab ManualDhiraj IppiliОценок пока нет
- Cisco SD-WAN Template - Configuration & Deployment - IP With EaseДокумент5 страницCisco SD-WAN Template - Configuration & Deployment - IP With EasemvsnkraoОценок пока нет
- A. M. Lister (Auth.) - Fundamentals of Operating Systems-Springer-Verlag New York (1984) PDFДокумент172 страницыA. M. Lister (Auth.) - Fundamentals of Operating Systems-Springer-Verlag New York (1984) PDFSelva100% (2)
- BRKDCT-2049 (2015)Документ90 страницBRKDCT-2049 (2015)Paul ZetoОценок пока нет
- QUOTE21013511 - Dell 3060 MT - CAGДокумент1 страницаQUOTE21013511 - Dell 3060 MT - CAGDavid WebbОценок пока нет
- AUTOSAR 3.2 Based Protocol Data Unit Router ModuleДокумент6 страницAUTOSAR 3.2 Based Protocol Data Unit Router ModuleEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- ATM Security System Using GSM and MEMS ModuleДокумент82 страницыATM Security System Using GSM and MEMS ModuleKrishna Prabhu80% (10)
- Midterm AnswersДокумент9 страницMidterm Answerspocho_gt500Оценок пока нет
- Error Control CodingДокумент13 страницError Control CodingPankaj ToppoОценок пока нет
- LongTermDataArchives en v20-2Документ38 страницLongTermDataArchives en v20-2Sandeep Kumar GudapatiОценок пока нет
- Epking enДокумент6 страницEpking enSandeep DeshpandeОценок пока нет
- Software ListingДокумент5 страницSoftware ListingStefan RadaОценок пока нет
- MATLAB Functions for LabJack U12 CommunicationДокумент18 страницMATLAB Functions for LabJack U12 CommunicationgennarinomingОценок пока нет