Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ME 404/504 - Finite Element Applications in Engineering Homework 5. Due: Friday, Nov 14, 2014
Загружено:
SeyfullahYıldızИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ME 404/504 - Finite Element Applications in Engineering Homework 5. Due: Friday, Nov 14, 2014
Загружено:
SeyfullahYıldızАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ME 404/504 Finite element applications in Engineering
Homework 5. Due: Friday, Nov 14, 2014
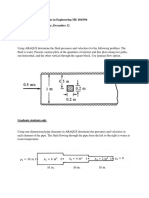
1. A steel sphere impacts an aluminum alloy plate at a velocity v = 150 km/h. The sphere
diameter is d = 1 cm. The plate is 100 x 100 wide and 5 cm thick, and is completely fixed on the
lateral sides. The angle between the direction of motion and the normal to the aluminum plate
is . Consider for the analysis the following angles: (i) = 45 deg, and (ii) = 0.
Use an elastic model for the sphere, and an elastic-plastic-damage (with Johnson-Cook
plasticity damage) for the plate. For the elastic constants of each material use a database to
find relevant material properties for this simulation. For the Johnson Cook plasticity-damage
model for aluminum, use the following constants:
Johnson-Cook
Plasticity
A
[MPa]
B
[MPa]
0
[1/s]
Aluminum Plate
262
162.1
0.2783
1.34
Johnson-Cook
dynamic
damage
d1
d2
d3
d4
d5
Melting
temperature
(C)
Transition
Temperature
(C)
Reference
Strain Rate
1/s
Aluminum Plate
-0.77
1.45
0.47
1.6
651.85
20.05
Perform a finite element simulation of the impact process for each impact angle and analyze
the following data:
a) Does rebound or penetration of the plate occur?
b) Plot velocity of the sphere before and after impact.
c) Show contour the von Mises stresses and the damage in the plate after impact.
Analyze the damage in the plate.
2. A middle-tension specimen (MT) is loaded with a stress = 5 ksi. The dimensions of the
cracked plate are b = 4 in, h = 6 in, thickness t = 0.25 in and crack half-length is a = 0.8 in. The
plate material is a steel alloy with E = 30,000 ksi and v = 0.25. Considering an elastic behavior
only for the plate and using finite element simulations of a 2D model of the plate, determine:
a) The variation of the normal stress in the vertical direction from the crack tip to the
plate edge and compare this variation with the analytical solution. Create a line plot
for the two solutions and discuss your results.
b) Determine the stress intensity factor using the analytical and FE methods and
compare your results. If the fracture toughness of the material is KIc = 3 Ksiin1/2,
determine if failure by crack extension occurs or not.
Вам также может понравиться
- Exercises On Fracture MechanicsДокумент33 страницыExercises On Fracture Mechanicsyaswanth199260% (5)
- Static Analysis of Isotropic & Orthotropic Plates With Central CutoutДокумент7 страницStatic Analysis of Isotropic & Orthotropic Plates With Central CutoutKanak_KalitaОценок пока нет
- Theories of Failure FinalДокумент47 страницTheories of Failure FinalAshutosh JadhavОценок пока нет
- Fracture Mechanics ExercisesДокумент33 страницыFracture Mechanics Exercises2luckystar100% (1)
- Problems 4012 PDFДокумент8 страницProblems 4012 PDFjonthemesОценок пока нет
- M 004 ExercisesДокумент33 страницыM 004 ExercisesKannan MuthusamyОценок пока нет
- Me331 2008Документ451 страницаMe331 2008akshaygiitmОценок пока нет
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IДокумент8 страниц9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- A Simple Method To Determine Ductile Fracture Strain in A Tensile Test of Plane Specimen'SДокумент5 страницA Simple Method To Determine Ductile Fracture Strain in A Tensile Test of Plane Specimen'SksОценок пока нет
- Reg No.: - NameДокумент3 страницыReg No.: - NameSijuKalladaОценок пока нет
- Mechanics of Solids Question PapersДокумент10 страницMechanics of Solids Question PapersNandu Sreekumar SОценок пока нет
- Ass 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsДокумент2 страницыAss 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsVarinder ThandiОценок пока нет
- Assigment 3Документ8 страницAssigment 3Zoheb ShaikhОценок пока нет
- ME302: Materials Mechanics: Chap. 1 Stress (3) Chap. 2 StrainДокумент24 страницыME302: Materials Mechanics: Chap. 1 Stress (3) Chap. 2 StrainMat MatttОценок пока нет
- 2002 Int Ansys Conf 57Документ7 страниц2002 Int Ansys Conf 57Halyna HafiychukОценок пока нет
- Artigo 2Документ6 страницArtigo 2Edmilson LimaОценок пока нет
- Effect of Heat Exchange During Vulcanization On Possible Fabrication of Rubberized Entities by Methods of Plastic DeformationДокумент8 страницEffect of Heat Exchange During Vulcanization On Possible Fabrication of Rubberized Entities by Methods of Plastic DeformationAldi IgnielОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Simple StressesДокумент39 страницAnalysis of Simple StressesEduCartОценок пока нет
- Metal Forming LaboratoryДокумент11 страницMetal Forming Laboratory19Y210 - JEEVA EОценок пока нет
- Question B.Tech (CE) PDFДокумент148 страницQuestion B.Tech (CE) PDFLawrence NgariОценок пока нет
- Photoelastic and Numerical Analysis of A Sphere/plan Contact ProblemДокумент7 страницPhotoelastic and Numerical Analysis of A Sphere/plan Contact ProblemfjОценок пока нет
- AMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23Документ6 страницAMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23rip111176Оценок пока нет
- Examination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2011Документ6 страницExamination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2011BijoyBanikОценок пока нет
- Assignment3forming Solutions 121213110849 Phpapp02Документ4 страницыAssignment3forming Solutions 121213110849 Phpapp02Renaldi Khaesar KumaraОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009Документ2 страницыAssignment 1 Mech 321 Properties and Failure of Materials Jan 2009DSGОценок пока нет
- Performance Criteria For Dissipative Steel Plate Shear Walls StructuresДокумент8 страницPerformance Criteria For Dissipative Steel Plate Shear Walls StructuresgiorgosantzelidisОценок пока нет
- Local Buckling of Cold Formed Stainless Steel SectionsДокумент20 страницLocal Buckling of Cold Formed Stainless Steel Sectionss_bharathkumarОценок пока нет
- 3.9. Self-Study ProblemsДокумент9 страниц3.9. Self-Study Problemsfahmiamri93Оценок пока нет
- Metastable AusteniticsДокумент6 страницMetastable AusteniticsSteveyОценок пока нет
- Lab Sheet For Ultimate Strength of Reinforced Concrete BeamsДокумент6 страницLab Sheet For Ultimate Strength of Reinforced Concrete BeamsAbdirahman RobaОценок пока нет
- Mainadmin Ite Element Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Strengthened With CFRP in FleДокумент16 страницMainadmin Ite Element Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Strengthened With CFRP in FleMalak ShatiОценок пока нет
- Bacha 2006Документ7 страницBacha 2006KlockerОценок пока нет
- Structural Mechanics 2015 PaperДокумент6 страницStructural Mechanics 2015 PaperAlexОценок пока нет
- 2004-Deng-Finite Element Analysis of Effects of Ball Burnishing Parameters OnДокумент6 страниц2004-Deng-Finite Element Analysis of Effects of Ball Burnishing Parameters OnJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaОценок пока нет
- Material ScienceДокумент4 страницыMaterial Sciencediyana8894Оценок пока нет
- Finite Element Simulation of Residual Stresses in Cryogenic Machining of AZ31B MG AlloyДокумент6 страницFinite Element Simulation of Residual Stresses in Cryogenic Machining of AZ31B MG AlloyMekaTronОценок пока нет
- HW #7Документ4 страницыHW #7c_sierra34Оценок пока нет
- E03ST29Документ21 страницаE03ST29José Luis PárragaОценок пока нет
- Amd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017Документ5 страницAmd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017rip111176Оценок пока нет
- Lee2008 Elbow LWTДокумент5 страницLee2008 Elbow LWTKurra SrikanthОценок пока нет
- E Ect of Pre-Straining and Grain Size On The Limit Strains in Sheet Metal FormingДокумент7 страницE Ect of Pre-Straining and Grain Size On The Limit Strains in Sheet Metal Formingmwaseem2011Оценок пока нет
- Ib Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2Документ5 страницIb Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2omarnasriОценок пока нет
- Som Strength of Material Question BankДокумент16 страницSom Strength of Material Question BankarindamckbtОценок пока нет
- A Study Into Optimization of Stiffeners in Plates PDFДокумент16 страницA Study Into Optimization of Stiffeners in Plates PDFJohn PetterОценок пока нет
- Aluru Wen Shen J Mech 2010Документ6 страницAluru Wen Shen J Mech 2010abraham silva hernandezОценок пока нет
- Study On The Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Angle Tension MembersДокумент17 страницStudy On The Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Angle Tension MembersrudynyambiОценок пока нет
- A New Slip Line Theory For Orthogonal CuttingДокумент13 страницA New Slip Line Theory For Orthogonal CuttingRaghu ChowdaryОценок пока нет
- Analysis of PC Beam With Corrugated Steel Web Using Accordion Link ElementДокумент2 страницыAnalysis of PC Beam With Corrugated Steel Web Using Accordion Link ElementNegin MalekiОценок пока нет
- CE470 F07 Beam DesignДокумент27 страницCE470 F07 Beam DesignMoisés Vázquez ToledoОценок пока нет
- Code: 9A01302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations June 2015Документ1 страницаCode: 9A01302 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations June 2015YohannesОценок пока нет
- Wxample - Solution Final Exam Question SKMM3623 1 - UpdatedДокумент16 страницWxample - Solution Final Exam Question SKMM3623 1 - Updatedkarimov1924Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ17 страницLecture 3aqsa zahidОценок пока нет
- A Procedure For The Evaluation of Coupling Beam Characteristics of Coupled Shear WallsДокумент14 страницA Procedure For The Evaluation of Coupling Beam Characteristics of Coupled Shear WallskibzeamОценок пока нет
- Addis Ababa University Lecture NoteДокумент65 страницAddis Ababa University Lecture NoteTADY TUBE OWNER100% (9)
- Examination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2013Документ4 страницыExamination: Testing of Metallic Materials / SS 2013Jaymin PatelОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationОт EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertОценок пока нет
- American Sniper WordsДокумент5 страницAmerican Sniper WordsSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Hector and The Search For Happiness Words: InformalДокумент9 страницHector and The Search For Happiness Words: InformalSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Ux-90 & SX-80: 14'' SeriesДокумент2 страницыUx-90 & SX-80: 14'' SeriesSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Deal Breaker WordsДокумент1 страницаDeal Breaker WordsSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Applications - Heat Sink With FinsДокумент5 страницApplications - Heat Sink With FinsSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Models - Cfd.heat SinkДокумент16 страницModels - Cfd.heat SinkSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- NPL 100A Parent Model1Документ803 страницыNPL 100A Parent Model1SeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Use of CFD in Design: A Tutorial: Sean M. Mcguffie, P.E. Michael A. Porter, P.E. Thomas T. HirstДокумент110 страницUse of CFD in Design: A Tutorial: Sean M. Mcguffie, P.E. Michael A. Porter, P.E. Thomas T. HirstSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Rigid Self Contact Tutorial Win14Документ24 страницыRigid Self Contact Tutorial Win14SeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Project 3 - Plate With Hole (Elastic-Plastic)Документ7 страницProject 3 - Plate With Hole (Elastic-Plastic)SeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Examples For Application of Burrill's and Keller's CriteriaДокумент3 страницыExamples For Application of Burrill's and Keller's CriteriaSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- 21feb14we The UnwantedДокумент20 страниц21feb14we The UnwantedSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Applications in Engineering ME 404/504 Homework 7 - Due: Friday, December 12Документ1 страницаFinite Element Applications in Engineering ME 404/504 Homework 7 - Due: Friday, December 12SeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Problems 1 and 2 Are For All Students. in Addition, Problem 3 Is Required Only For Graduate StudentsДокумент2 страницыProblems 1 and 2 Are For All Students. in Addition, Problem 3 Is Required Only For Graduate StudentsSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- ME 404/504 Finite Element Applications in Engineering Due: Friday, Nov. 21, 2014Документ1 страницаME 404/504 Finite Element Applications in Engineering Due: Friday, Nov. 21, 2014SeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Direct Iteration Method: X F (X) F (X) XДокумент6 страницDirect Iteration Method: X F (X) F (X) XSeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет
- Physics ChemistryДокумент7 страницPhysics ChemistrySeyfullahYıldızОценок пока нет